本文介绍了使用python处理json及csv文件的方法。首先展示了如何从json文件中提取2010年的各国人口数据并利用国别码进行展示;其次通过一个csv文件案例,演示了如何读取气象数据并绘制成易于理解的图表。
1、python3处理json文件
'''
the i18n module was removed in pygal-2.0.0.
however, it can now be found in the pygal_maps_world plugin.
you can install that with pip install pygal_maps_world.
then you can access countries as pygal.maps.world.countries:
from pygal.maps.world import countries
whats left of the i18n module can be imported with:
from pygal_maps_world import i18n
'''
#获取两个字母的国别码
from pygal_maps_world.i18n import countries
def get_country_code(country_name):
for code,name in countries.items():
if name==country_name:
return code
return noneimport json
from country_codes import get_country_code
#提取相关数据
filename='population_data.json'
with open(filename) as f:
pop_data=json.load(f) #json.load()将数据转换为python能够处理的格式并存储在pop_data中
for pop_dict in pop_data:
#获得每个国家2010年的人口数量
if pop_dict['year']=='2010':
country_name=pop_dict['country name']
population=int(float(pop_dict['value']))#先将字符串转换为浮点数,再将浮点数转换为整数
code=get_country_code(country_name) #获得国家的国别码
if code:
print(code+':'+str(population))
else:
print('error-'+country_name)2、python3处理csv文件
import csv
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from datetime import datetime
#读取csv文件数据
filename='sitka_weather_2014.csv'
with open(filename) as f: #打开这个文件,并将结果文件对象存储在f中
reader=csv.reader(f) #创建一个阅读器reader
header_row=next(reader) #返回文件中的下一行
dates,highs,lows=[],[],[] #声明存储日期,最值的列表
for row in reader:
current_date=datetime.strptime(row[0],'%y-%m-%d') #将日期数据转换为datetime对象
dates.append(current_date) #存储日期
high=int(row[1]) #将字符串转换为数字
highs.append(high) #存储温度最大值
low=int(row[3])
lows.append(low) #存储温度最小值
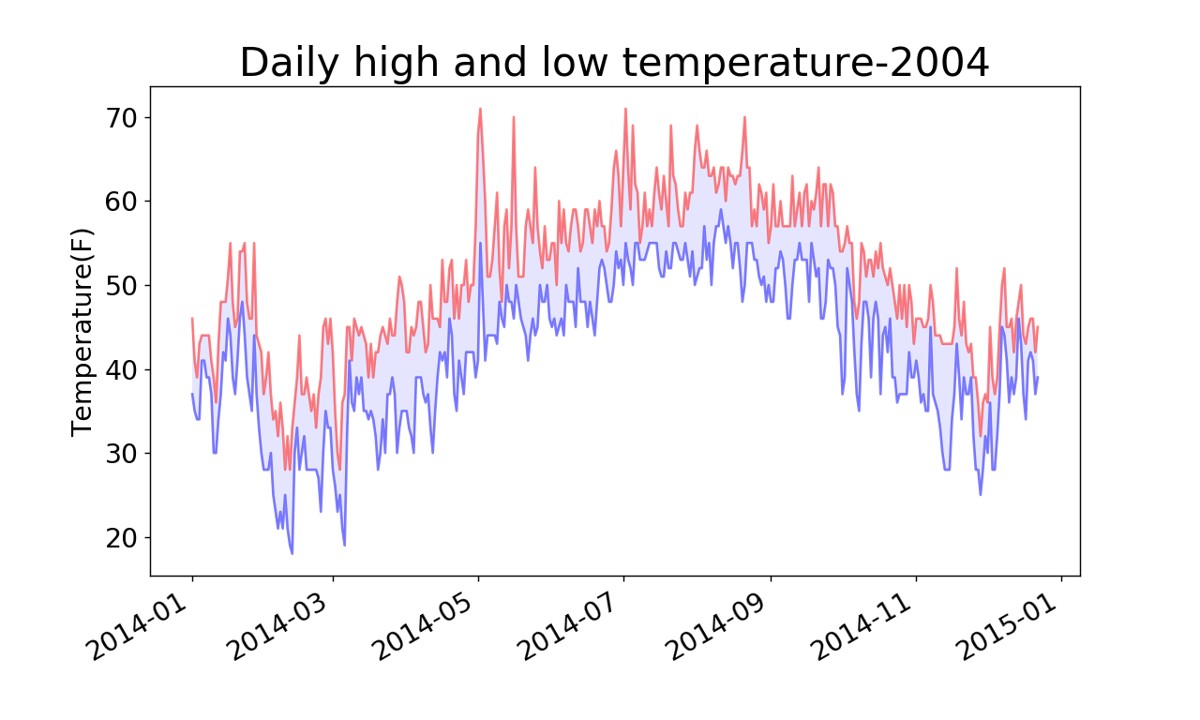
#根据数据绘制图形
fig=plt.figure(dpi=128,figsize=(10,6))
plt.plot(dates,highs,c='red',alpha=0.5)#实参alpha指定颜色的透明度,0表示完全透明,1(默认值)完全不透明
plt.plot(dates,lows,c='blue',alpha=0.5)
plt.fill_between(dates,highs,lows,facecolor='blue',alpha=0.1) #给图表区域填充颜色
plt.title('daily high and low temperature-2004',fontsize=24)
plt.xlabel('',fontsize=16)
plt.ylabel('temperature(f)',fontsize=16)
plt.tick_params(axis='both',which='major',labelsize=16)
fig.autofmt_xdate() #绘制斜的日期标签
plt.show()结果如下:
3、方法补充
python3处理json格式的文件数据
下面介绍了一种从世界地图插件中获取国别码的方法,并演示了如何使用python从json文件中提取指定年份的各国人口数据。通过安装pygal_maps_world插件并利用其i18n模块中的countries字典来匹配国家名称与其对应的两字母国别码。
country_code.py
'''
the i18n module was removed in pygal-2.0.0.
however, it can now be found in the pygal_maps_world plugin.
you can install that with pip install pygal_maps_world.
then you can access countries as pygal.maps.world.countries:
from pygal.maps.world import countries
whats left of the i18n module can be imported with:
from pygal_maps_world import i18n
'''
#获取两个字母的国别码
from pygal_maps_world.i18n import countries
def get_country_code(country_name):
for code,name in countries.items():
if name==country_name:
return code
return nonepopulation.py
import json
from country_codes import get_country_code
#提取相关数据
filename='population_data.json'
with open(filename) as f:
pop_data=json.load(f) #json.load()将数据转换为python能够处理的格式并存储在pop_data中
for pop_dict in pop_data:
#获得每个国家2010年的人口数量
if pop_dict['year']=='2010':
country_name=pop_dict['country name']
population=int(float(pop_dict['value']))#先将字符串转换为浮点数,再将浮点数转换为整数
code=get_country_code(country_name) #获得国家的国别码
if code:
print(code+':'+str(population))
else:
print('error-'+country_name)python将csv文件如何转json文件
csv文件:csv(comma-separated values,逗号分隔的值)是一种简单、实用的文件格式,用于存储和表示包括文本、数值等各种类型的数据。csv 文件通常以 .csv 作为文件扩展名。这种文件格式的一个显著特点是:文件内的数据以逗号 , 分隔,呈现一个表格形式。csv 文件已广泛应用于存储、传输和编辑数据。
json文件:json 指的是 javascript 对象表示法(javascript object notation),json是轻量级的文本数据交换格式 json 独立于语言:json 使用 javascript语法来描述数据对象,但是 json 仍然独立于语言和平台。json 解析器和 json 库支持许多不同的编程语言。 目前非常多的动态(php,jsp,.net)编程语言都支持json。
实现方法
import json
f = open("d:/文件/资料/gt.csv", "r", encoding='gb2312') # csv文件的路径
data_lines = f.readlines()
f.close()
data_lines.pop(0)
values = []
for line in data_lines:
line = line.replace("\n", "")
values.append(line.split(","))
# print(ls)
# json文件为键值对,keys为左侧键
keys = ["stamp_sec", "obj_stamp_sec", "frame_num", "source", "id", "track_id", "lane_id", "center_x", "center_y", "center_z", "closest_point_x",
"closest_point_y", "closest_point_z", "closest_box_x", "closest_box_y", "closest_box_z", "front_bumper_x",
"front_bumper_y", "front_bumper_z", "rear_bumper_x", "rear_bumper_y", "rear_bumper_z", "move_status", "cut_in", "cut_out",
"cipv", "velocity_x", "velocity_y", "velocity_z", "project_velocity_x", "project_velocity_y", "project_velocity_z",
"acceleration_x", "acceleration_y", "acceleration_z", "project_acceleration_x", "project_acceleration_y",
"project_acceleration_z", "angular_velocity", "obj_yaw", "direction_x", "direction_y", "direction_z", "height", "length",
"width", "is_radar_matching", "is_tracked", "radar_velocity_x", "radar_velocity_y", "radar_velocity_z", "type",
"type_confidence", "pose_pos_x", "pose_pos_y", "pose_pos_z", "roll", "pitch", "yaw", "car_twist", "car_acceleration",
"reserve_score", "reserve_info", "anchor_x", "anchor_y", "anchor_z", "lidar_name"]
fw = open("d:/文件/资料/a.json", "w", encoding='utf-8') # 创建json文件的路径
# 利用for循环遍历,形成键值对
dict_re = [dict(zip(keys, row)) for row in values] if values else none
# print(dict_re)
a = json.dumps(dict_re, indent=4, ensure_ascii=false)
print(a)
fw.write(a)
fw.close()到此这篇关于python3处理json文件和csv文件的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python处理json和csv内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论