引言
文件读写是编程中的常见操作,python提供了简洁且强大的文件操作接口。本文将详细介绍python中文本文件和二进制文件的读写操作,包括文件打开、读取、写入、关闭及异常处理等内容,并通过具体示例代码展示如何高效地处理文件。
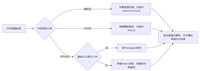
文件的基本操作
打开文件
在python中,使用open函数打开文件。open函数的基本语法如下:
open(filename, mode, encoding=none)
filename:要打开的文件名。mode:文件打开模式,如'r'(读取)、'w'(写入)、'a'(追加)等。encoding:文本文件的编码方式,通常使用'utf-8'。
文件模式
常见的文件打开模式包括:
'r':只读模式(默认)。'w':写入模式,会覆盖文件内容。'a':追加模式,在文件末尾添加内容。'b':二进制模式。'+':读写模式。
文本文件处理
读取文本文件
逐行读取
使用readline方法逐行读取文件内容:
with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
line = file.readline()
while line:
print(line.strip())
line = file.readline()
读取整个文件
使用read方法一次性读取整个文件内容:
with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
content = file.read()
print(content)
读取文件的所有行
使用readlines方法读取文件的所有行,并返回一个列表:
with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
lines = file.readlines()
for line in lines:
print(line.strip())
写入文本文件
使用write方法写入文本文件:
with open('output.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write('这是第一行文本。\n')
file.write('这是第二行文本。')
追加文本文件
使用append模式在文件末尾追加内容:
with open('output.txt', 'a', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write('\n这是追加的一行文本。')
二进制文件处理
读取二进制文件
使用rb模式读取二进制文件:
with open('example.bin', 'rb') as file:
content = file.read()
print(content)
写入二进制文件
使用wb模式写入二进制文件:
with open('output.bin', 'wb') as file:
file.write(b'this is a binary file.')
异常处理
在文件操作过程中,可能会遇到一些异常情况,如文件不存在、没有权限等。可以使用try-except语句进行异常处理:
try:
with open('nonexistent.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
content = file.read()
except filenotfounderror:
print('文件未找到。')
except permissionerror:
print('没有权限读取文件。')
实际应用示例
复制文本文件
def copy_text_file(source, destination):
try:
with open(source, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as src_file:
content = src_file.read()
with open(destination, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as dest_file:
dest_file.write(content)
print(f'文件已成功复制到 {destination}')
except exception as e:
print(f'复制文件时出错: {e}')
copy_text_file('example.txt', 'example_copy.txt')
复制二进制文件
def copy_binary_file(source, destination):
try:
with open(source, 'rb') as src_file:
content = src_file.read()
with open(destination, 'wb') as dest_file:
dest_file.write(content)
print(f'文件已成功复制到 {destination}')
except exception as e:
print(f'复制文件时出错: {e}')
copy_binary_file('example.bin', 'example_copy.bin')
统计文本文件的行数、单词数和字符数
def file_statistics(filename):
try:
with open(filename, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
lines = file.readlines()
line_count = len(lines)
word_count = sum(len(line.split()) for line in lines)
char_count = sum(len(line) for line in lines)
print(f'行数: {line_count}, 单词数: {word_count}, 字符数: {char_count}')
except exception as e:
print(f'统计文件时出错: {e}')
file_statistics('example.txt')
使用json文件
json是一种常用的轻量级数据交换格式。在python中,可以使用json模块读写json文件。
读取json文件
import json
def read_json(filename):
try:
with open(filename, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
data = json.load(file)
return data
except exception as e:
print(f'读取json文件时出错: {e}')
return none
data = read_json('data.json')
print(data)
写入json文件
import json
def write_json(data, filename):
try:
with open(filename, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
json.dump(data, file, ensure_ascii=false, indent=4)
print(f'数据已写入到 {filename}')
except exception as e:
print(f'写入json文件时出错: {e}')
data = {'name': 'alice', 'age': 25, 'city': 'new york'}
write_json(data, 'data.json')
总结
本文详细介绍了python中文本文件和二进制文件的读写操作,包括文件的打开、读取、写入、追加和关闭等基本操作,同时讲解了如何进行异常处理。通过具体的示例代码,展示了如何高效地处理文件,例如逐行读取文件、写入文件、复制文件、统计文件信息以及处理json文件等实际应用场景。掌握这些文件操作技巧,能够帮助大家在python编程中更加灵活地处理各种文件,提高代码的可读性和可维护性。
以上就是python文本与二进制文件读写操作指南的详细内容,更多关于python文本与二进制文件读写的资料请关注代码网其它相关文章!





发表评论