提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
前言
3. spring boot⾃动配置
自动装配是属性的自动装配,比如刚刚说的,set注入ben,构造方法注入bean
自动配置呢
springboot的⾃动配置就是当spring容器启动后, ⼀些配置类, bean对象等就自动存入到了ioc容器中,不需要我们手动去声明, 从而简化了开发, 省去了繁琐的配置操作.
springboot⾃动配置, 就是指springboot是如何将依赖jar包中的配置类以及bean加载到spring ioc容
器中的.
主要分以下两个⽅⾯:
- spring 是如何把对象加载到springioc容器中的
- springboot 是如何实现的
3.1 spring 加载bean
为什么加入依赖,一些bean,注解(@mapper),就自动配置了
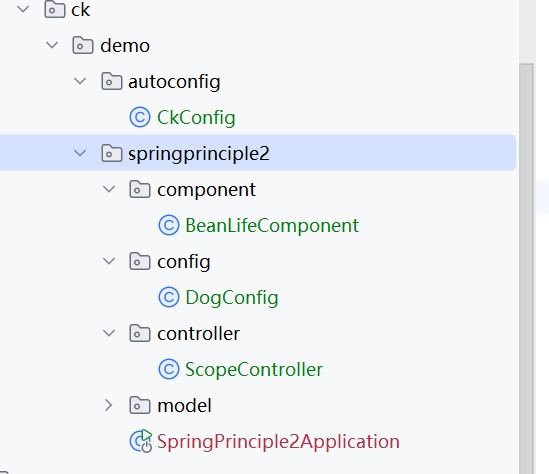
比如我们现在加入了一个包autoconfig,假设它是第三方的包
如果对这个打包,通过pom引入,那么就会出现在外部库中
所以这个我们自定义的第三方的包,放在这里和放在外部库是一样的效果
为什么放在这里效果和打包加依赖放在外部库是一样的效果呢
因为启动类只能加载它所在目录下的所有bean,不能加载它所在目录下的其他包下的bean的
我们的包autoconfig就是放在外面的
@component
public class ckconfig {
public void use(){
system.out.println("ckconfig");
}
}
然后我们在项目中就想使用这个包
@springbootapplication
public class springprinciple2application {
public static void main(string[] args) {
applicationcontext context = springapplication.run(springprinciple2application.class, args);
ckconfig bean = context.getbean(ckconfig.class);
bean.use();
}
}执行
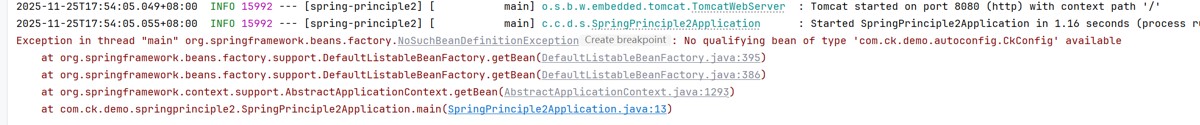
直接报错了,说找不到这个bean
因为spring扫描的路径,默认是启动类所在的目录
但是这个包在外面,所有加了注解component也没有用
第一种方式是使用注解componentscan,这个就是指定要扫描的路径了
@springbootapplication
@componentscan("com.ck.demo.autoconfig")
public class springprinciple2application {
public static void main(string[] args) {
applicationcontext context = springapplication.run(springprinciple2application.class, args);
ckconfig bean = context.getbean(ckconfig.class);
bean.use();
}
}
这样就成功了
就是手动指定spring的扫描路径,但是缺点就是所有的外部的bean都要手动指定,比如redis的,mybatis的包都要手动加入
而且加了componentscan的话,原来的启动类下的路径就不会再扫描了,意思就是原来的config下的bean,就是package com.ck.demo.springprinciple2;包下的都不会再扫描了
componentscan下可以写数组的
@springbootapplication
@componentscan({"com.ck.demo.autoconfig","com.ck.demo.springprinciple2"})
public class springprinciple2application {
public static void main(string[] args) {
applicationcontext context = springapplication.run(springprinciple2application.class, args);
ckconfig bean = context.getbean(ckconfig.class);
bean.use();
}
}所以这样之前的,和新加入的都可以生效了
@import(ckconfig.class)
@springbootapplication
public class springprinciple2application {
public static void main(string[] args) {
applicationcontext context = springapplication.run(springprinciple2application.class, args);
ckconfig bean = context.getbean(ckconfig.class);
bean.use();
}
}还可以通过这个方式,使用注解import,来导入class
但是spring的话,这两种方式都没有采用
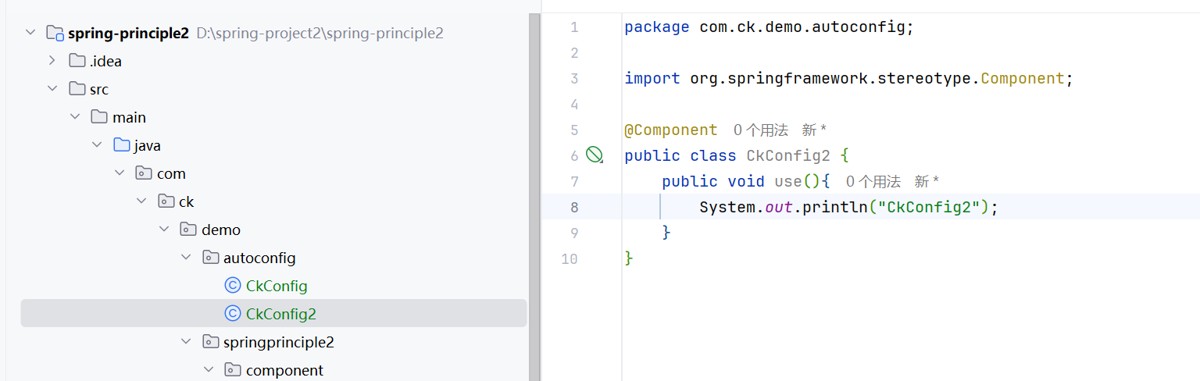
@import({ckconfig.class, ckconfig2.class})
也是可以添加多个的
public class myimport implements importselector {
@override
public string[] selectimports(annotationmetadata importingclassmetadata) {
return new string[]{"com.ck.demo.autoconfig.ckconfig","com.ck.demo.autoconfig.ckconfig2"};
}
}
我们在第三方autoconfig下写一个这个类,表示import要扫描的路径
@import(myimport.class)
@springbootapplication
public class springprinciple2application {
public static void main(string[] args) {
applicationcontext context = springapplication.run(springprinciple2application.class, args);
ckconfig bean = context.getbean(ckconfig.class);
bean.use();
}
}这样就可以了,这个就是第三方提供给你bean的路径
但是还是麻烦,继续升级,第三方提供注解就好了
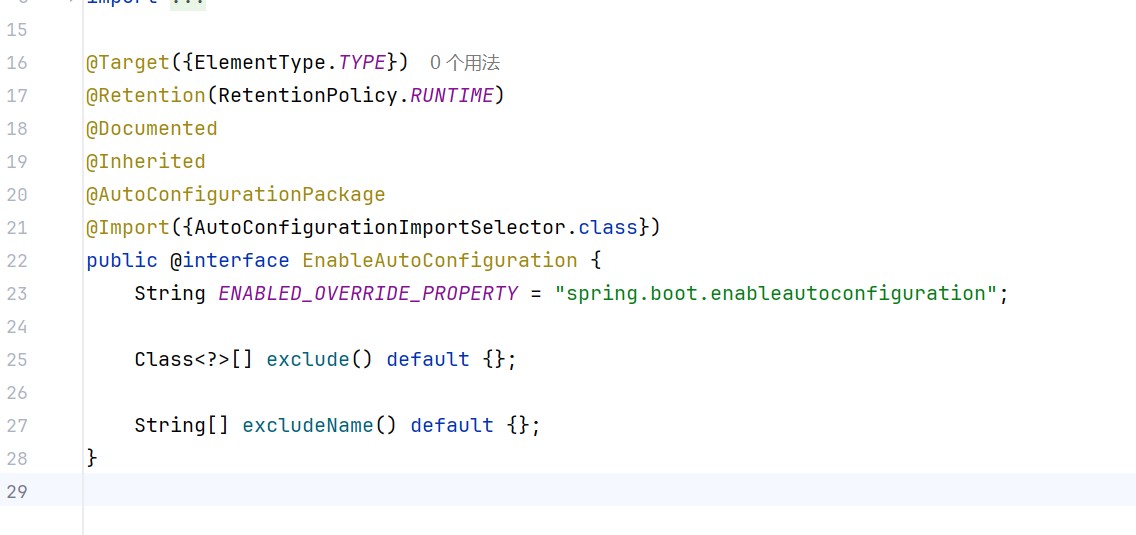
@target(elementtype.type)//这个注解可以加在什么地方上
@retention(retentionpolicy.runtime)//生命周期
@import(myimport.class)//注解的作用
public @interface enableckconfig {
}
这个注解定义在autoconfig下,也是第三方提供的
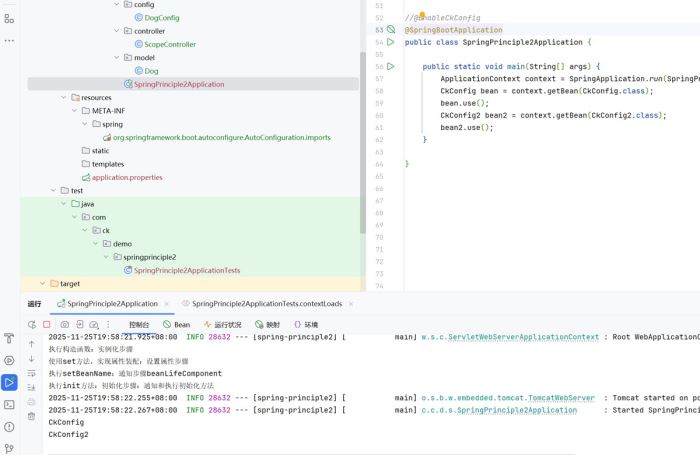
@enableckconfig
@springbootapplication
public class springprinciple2application {
public static void main(string[] args) {
applicationcontext context = springapplication.run(springprinciple2application.class, args);
ckconfig bean = context.getbean(ckconfig.class);
bean.use();
ckconfig2 bean2 = context.getbean(ckconfig2.class);
bean2.use();
}
}这样就可以了
所以第三方只需要提供注解就可以了
但是导入mybatis的依赖的时候,就那些bean也不用在启动类上加入注解啊
所以还有其他方式,连注解也不需要加
就是在resource目录下创建一个文件,放入"com.ck.demo.autoconfig.ckconfig","com.ck.demo.autoconfig.ckconfig2"这些东西,就会自动创建和管理了
这个文件就是meta-inf/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.autoconfiguration.imports
放入
com.ck.demo.autoconfig.ckconfig com.ck.demo.autoconfig.ckconfig2
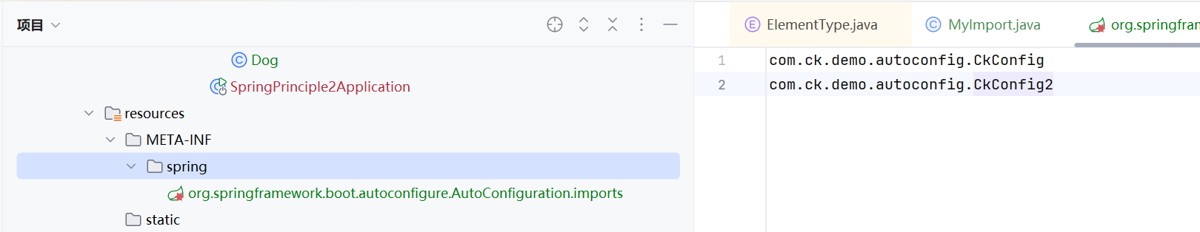
这个就是告诉spring,我要管理哪些对象
这样的话,自定义注解enableckconfig也不需要了,也可以获取第三方的bean了
3.2 源码分析
但是spring用的是什么方式呢
我们去看启动类@springbootapplication
因为这个注解,所以它是启动类
还有applicationcontext context = springapplication.run(springprinciple2application.class, args);这个来启动
点进去注解springbootapplication

@target({elementtype.type})表示主要要加在什么上
@retention(retentionpolicy.runtime)生命周期
@documented文档相关
@inherited继承相关,是源注解,不看了
@springbootconfiguration
@enableautoconfiguration
@componentscan
这三个最重要
@componentscan(
excludefilters = {@filter(
type = filtertype.custom,
classes = {typeexcludefilter.class}
), @filter(
type = filtertype.custom,
classes = {autoconfigurationexcludefilter.class}
)}
)因为这个,所以会扫码启动类下的路径
加了这个,默认扫描componentscan注解所在的路径,也就是springbootapplication注解所在的路径
springbootconfiguration注解点进去
indexed注解是一个优化的注解,不重要
重点是configuration,五大注解之一,所以springbootconfiguration注解就是configuration分装了一下
所以注解springbootconfiguration表示这是一个配置类,这个会被spring给识别到
所以重点就是注解enableautoconfiguration了
3.3 注解@enableautoconfiguration
@import({autoconfigurationimportselector.class})
autoconfigurationimportselector这个实现了deferredimportselector,deferredimportselector实现了importselector
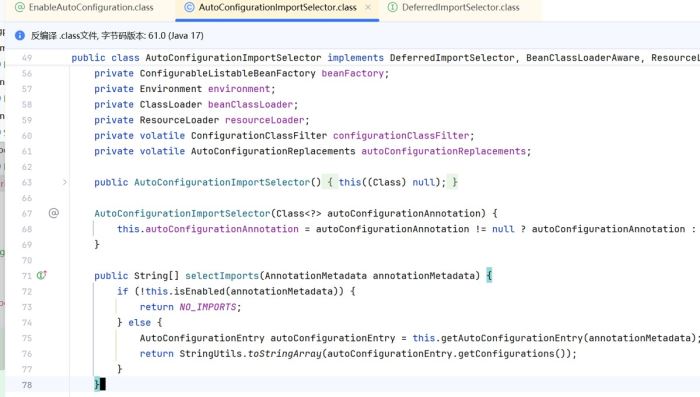
实现了方法selectimports
返回了要管理的bean
autoconfigurationentry autoconfigurationentry = this.getautoconfigurationentry(annotationmetadata);
return stringutils.tostringarray(autoconfigurationentry.getconfigurations());
主要是从这个getautoconfigurationentry来的
点进去

annotationmetadata是注解的原信息
list<string> configurations = this.getcandidateconfigurations(annotationmetadata, attributes);
这个方法点进去

这个就是加载配置了
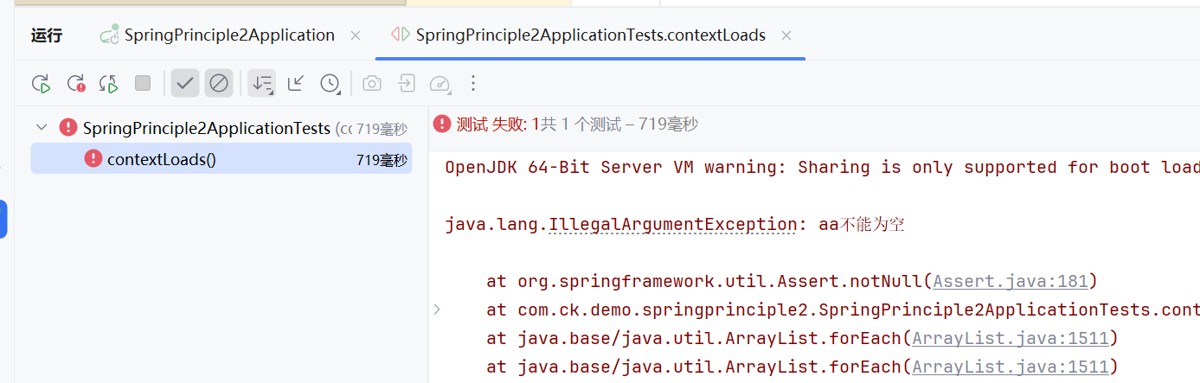
assert是断言
string aa=null;
assert.notnull(aa,"aa不能为空");
比如这个意思就是断言aa不能为空
为空的话,就报"aa不能为空"的错误

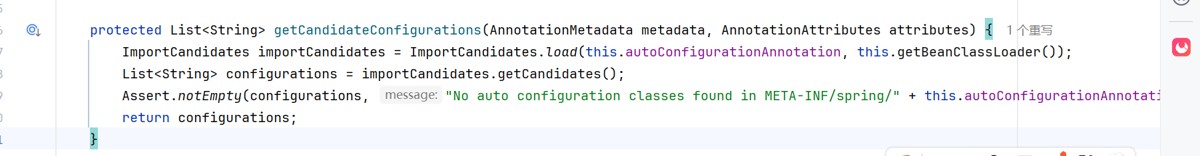
这个断言的就是没有配置信息在meta-inf/spring/。。。。。
所以
importcandidates importcandidates = importcandidates.load(this.autoconfigurationannotation, this.getbeanclassloader());
这个就是读取meta-inf/spring/这个文件的配置信息的,没有的话,就会包一个异常
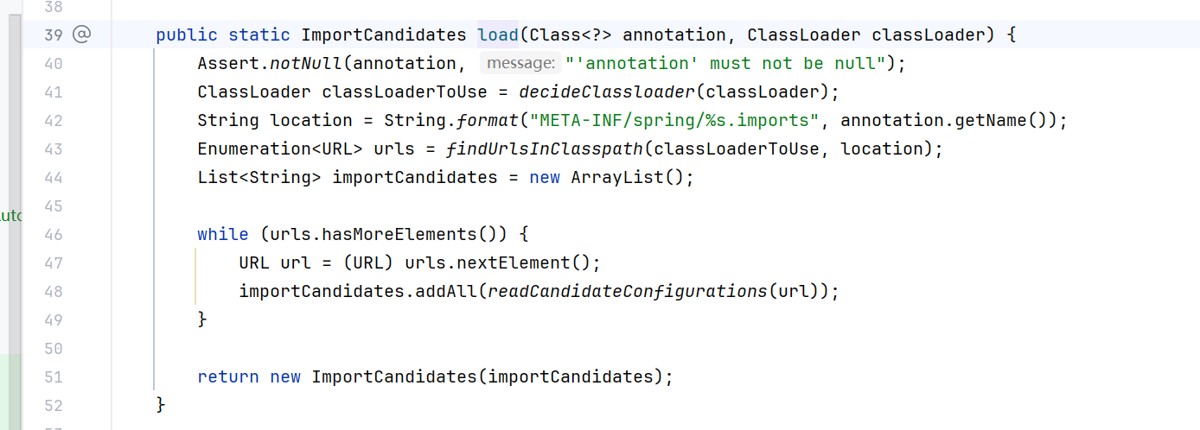
但是我们平时并没有这个文件啊,为什么没有报错
ctrl+n搜索org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.autoconfiguration.imports
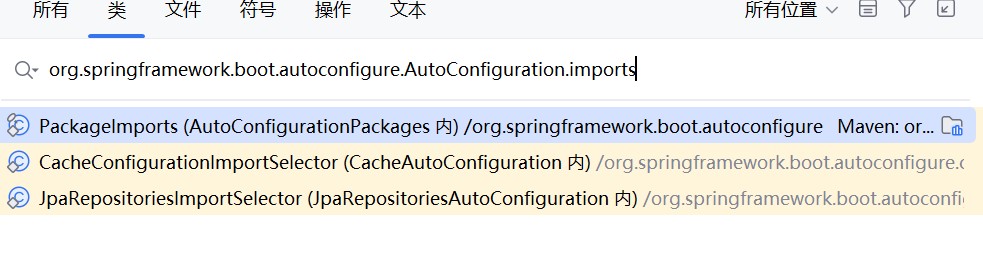
点击第一个

找到这里,发现这里就有那个meta-inf/spring/的文件
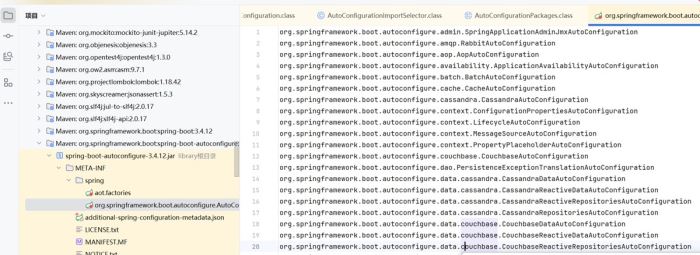
这里面放的就是spring要加载的bean
说明spring它自己就写了一个这种文件了
所以要管理我们第三方的bean的话,也是写一个这个路径就可以了,spring就会认识了,spring是根据路径来扫描的,都是这个路径的就都可以扫描到了
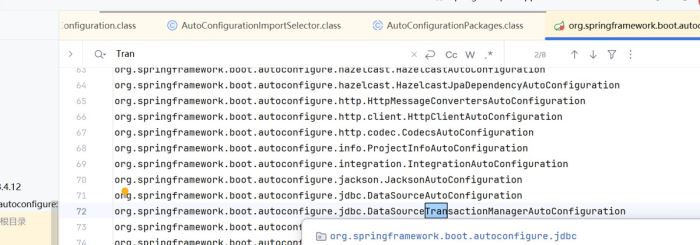
比如这个里面就有事务
spring就会管理datasourcetransactionmanagerautoconfiguration这个bean了
ctrl+n搜索

然后datasourcetransactionmanagerautoconfiguration这个里面还有bean
这样就都生效了

比如redis的,搜索redisautoconfiguration这个bean
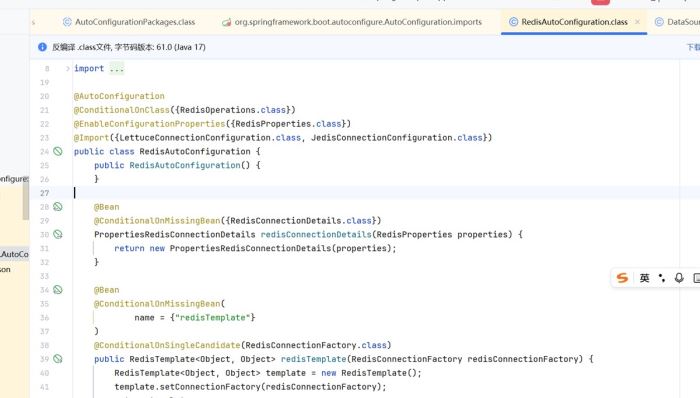
然后redisautoconfiguration这个bean里面就有redistemplate这个bean,所以redistemplate这个bean也是自动注入的

除了@bean之外,还有其他注解
比如注解conditionalonmissingbean
表示在不同的条件下才注入这个bean
@bean
@conditionalonmissingbean
public stringredistemplate stringredistemplate(redisconnectionfactory redisconnectionfactory) {
return new stringredistemplate(redisconnectionfactory);
}
这个意思就是,如果你没有声明stringredistemplate这个bean,我就声明stringredistemplate这个bean
@conditionalonmissingbean(
name = {"redistemplate"}
)
意思就是你要是声明了redistemplate这个bean,我就不声明了,你没有声明,我就声明
@conditionalonclass({redisoperations.class})
看有没有redisoperations这个类,没有的话,这个类下的所有bean都不,包括自己这个类的bean都不生效

这个redisoperations就在import org.springframework.data.redis.core.redisoperations;上面摆着
这个redisoperations类就是我们要引入的依赖里面的,换个意思就是没有引入依赖,就没有redisoperations这个类,就不能加载bean了
所以加了依赖,外部库就有org.springframework.data.redis.core,这个类redisoperations就有了,对应的redisautoconfiguration和它下面的方法这些bean就有了

不加依赖所以就不行了
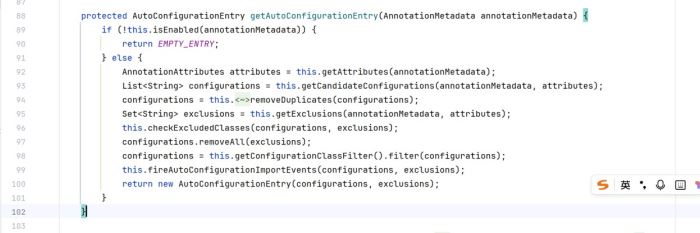
继续回到这里,就是获取meta-inf/spring/配置的这里
就是
list<string> configurations = this.getcandidateconfigurations(annotationmetadata, attributes);
这里configurations就是meta-inf/spring/文件里面的配置,包括我们自己写在meta-inf/spring/里面的
this.checkexcludedclasses(configurations, exclusions);
这个是检查排除,根据依赖信息来检查排除
configurations.removeall(exclusions);
这个就是删除没有引入依赖的配置
最后返回
所以getautoconfigurationentry返回的就是要求spring给我们管理的配置,对象,bean
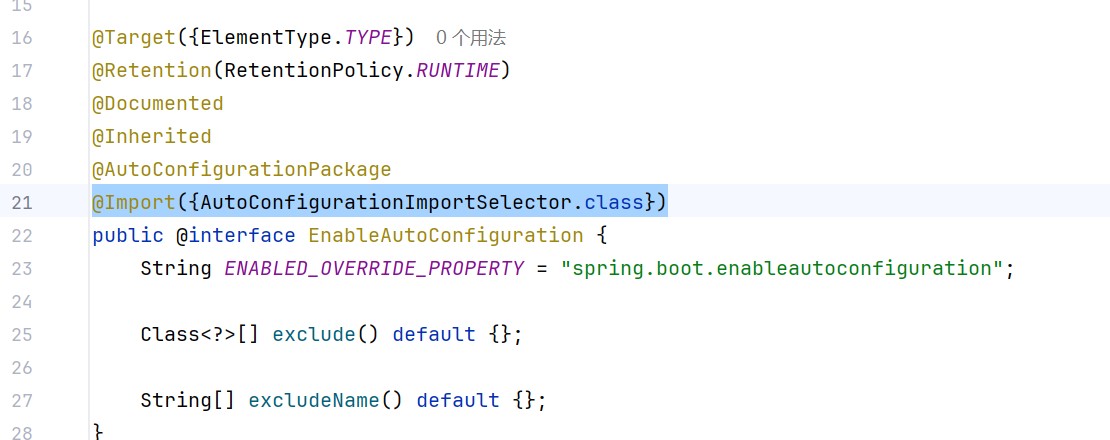
所以注解@import({autoconfigurationimportselector.class}),返回的就是要求spring给我们管理的配置,对象,bean
现在我们看autoconfigurationpackage这个注解

它又import了

import了register,这又是一个我们注入包的方式
register加载bean
public class myregister implements importbeandefinitionregistrar {
@override
public void registerbeandefinitions(annotationmetadata importingclassmetadata, beandefinitionregistry registry) {
genericbeandefinition beandefinition = new genericbeandefinition();
beandefinition.setbeanclass(ckconfig.class);
// beandefinition.setscope("xxxx");//表示这个bean是单例的还是多例的
registry.registerbeandefinition("ckconfig",beandefinition);//注入bean,第一个参数是bean的名称
}
}
我们在autoconfig下定义myregister
@springbootapplication
@import(myregister.class)
public class springprinciple2application {
public static void main(string[] args) {
applicationcontext context = springapplication.run(springprinciple2application.class, args);
ckconfig bean = context.getbean(ckconfig.class);
bean.use();
// ckconfig2 bean2 = context.getbean(ckconfig2.class);
// bean2.use();
}
}
这又是一种方式导入在这里插入代码片
继续分析
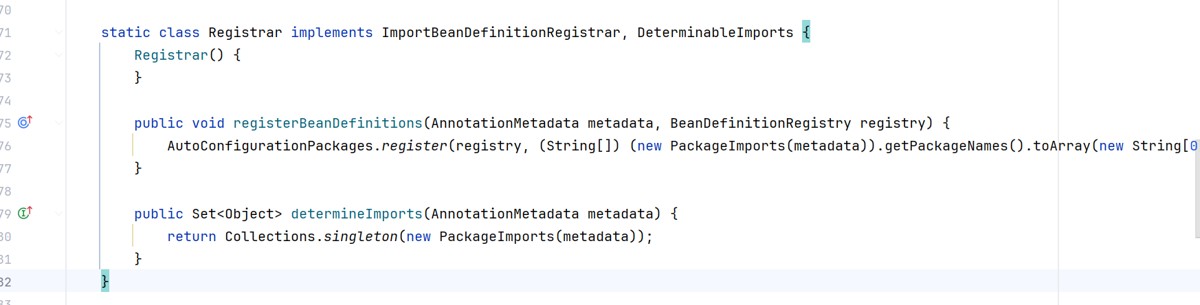
这里定义了一个register的类
定义了registerbeandefinitions这个方法
public void registerbeandefinitions(annotationmetadata metadata, beandefinitionregistry registry) {
autoconfigurationpackages.register(registry, (string[])(new packageimports(metadata)).getpackagenames().toarray(new string[0]));
}
(string[])(new packageimports(metadata)).getpackagenames().toarray(new string[0])这个得到的就是我们启动类所在路径com.ck.demo.springprinciple2
autoconfigurationpackages.register这个就是注入第三方的注解,比如@mapper
为什么spring能够管理第三方的注解

第三方就会写那些register
然后给我们注入
然后bloginfomapper使用了注解mapper
然后注解mapper就会拿到bloginfomapper的路径
比如我们搜索这个mybatisplus的这个类
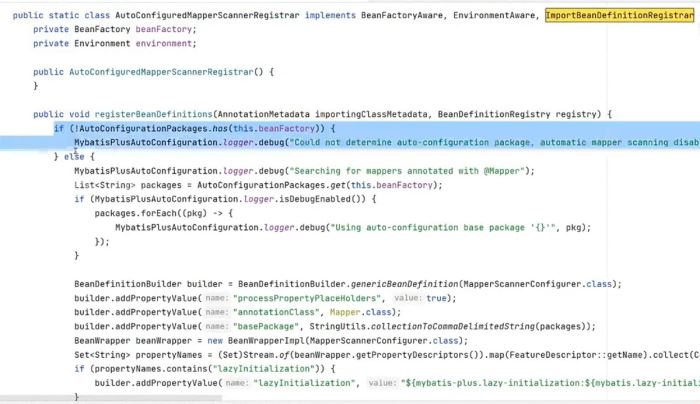
找到这里,这里实现了register

这里调用的registerbeandefinitions,就是我们刚刚看到的启动类原码里面定义的方法
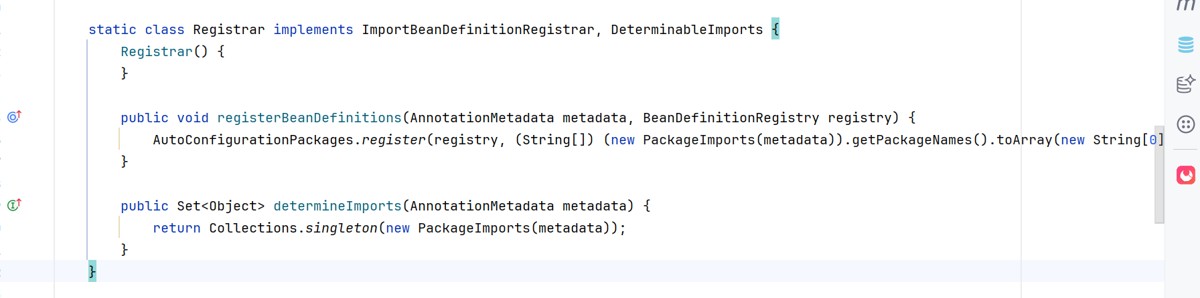
就是这个方法
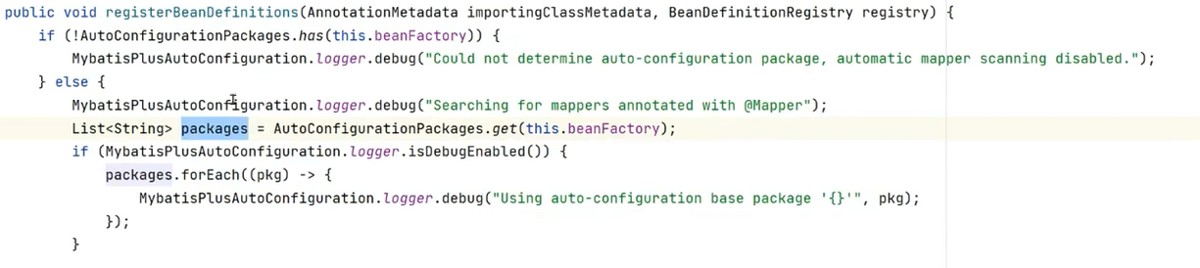
这里会得到启动类的路径
然后在这个启动类里面扫描得到mapper注解,扫描谁加了mapper注解
然后调用方法registerbeandefinitions加到spring就可以管理了
这个就是mybatisplus第三方注解加入bean的方式
就是调用第三方的注解,但是第三方的注解不是立马加入bean,而是,先获取启动类路径,根据启动类路径扫描谁
调用了mapper注解,谁调用个,就调用方法registerbeandefinitions加到spring就可以管理了
public class myregister implements importbeandefinitionregistrar {
@override
public void registerbeandefinitions(annotationmetadata importingclassmetadata, beandefinitionregistry registry) {
genericbeandefinition beandefinition = new genericbeandefinition();
beandefinition.setbeanclass(ckconfig.class);
// beandefinition.setscope("xxxx");//表示这个bean是单例的还是多例的
registry.registerbeandefinition("ckconfig",beandefinition);//注入bean,第一个参数是bean的名称
}
}
比如这个,xx使用了注解mapper(会自动调用相应方法),—》把xx给registry.registerbeandefinition,然后myregister 由于引入了依赖,而且implements importbeandefinitionregistrar,就自动会被spring给@import(myregister.class)
3.4 总结
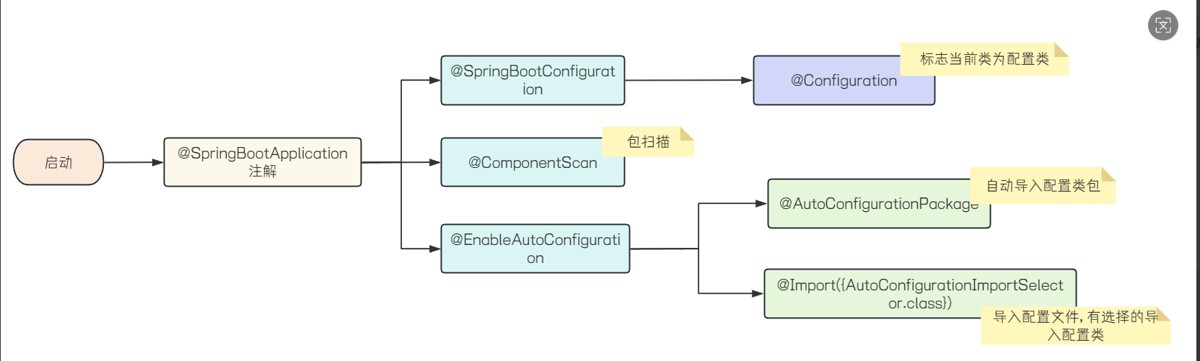
autoconfigurationpackage用的是register的方式来注入bean,主要是用来扫描第三方注解,比如@mapper,
第三方实现importbeandefinitionregistrar,然后就可以注入了
当springboot程序启动时, 会加载配置⽂件当中所定义的配置类, 通过 @import 注解将这些配置类全
部加载到spring的ioc容器中, 交给ioc容器管理.
- bean的作⽤域共分为6种: singleton, prototype, request, session, application和websocket.
- bean的⽣命周期共分为5⼤部分: 实例化, 属性复制, 初始化, 使⽤和销毁
- springboot的⾃动配置原理源码⼝是 @springbootapplication 注解, 这个注解封装了3个注解◦@springbootconfiguration 标志当前类为配置类
◦ @componentscan 进⾏包扫描(默认扫描的是启动类所在的当前包及其⼦包)
◦ @enableautoconfiguration
▪ @import 注解 : 读取当前项⽬下所有依赖jar包中 meta-inf/spring.factories ,
metainf/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.autoconfiguration.imports 两个⽂件⾥⾯定义的配置类(配置类中定义了 @bean 注解标识的⽅法)
▪ @autoconfigurationpackage : 把启动类所在的包下⾯所有的组件都注⼊到 spring容器中
总结
到此这篇关于springboot spring原理2的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关springboot spring原理内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论