mysql 索引深度解析:从原理到实践

1. 索引基础概念
1.1 什么是索引
索引(index)是数据库管理系统中一种重要的数据结构,它为表中的数据创建了一个有序的引用结构,类似于书籍的目录。通过索引,数据库可以快速定位到特定的数据行,而不需要扫描整个表。
-- 创建一个示例表
create table users (
id int primary key auto_increment,
username varchar(50) not null,
email varchar(100) unique,
age int,
created_at timestamp default current_timestamp,
index idx_username (username),
index idx_age_created (age, created_at)
);
1.2 索引的作用和重要性
索引在数据库性能优化中扮演着至关重要的角色:
- 加速查询:将 o(n) 的线性查找优化为 o(log n) 的树形查找
- 排序优化:利用索引的有序性避免额外的排序操作
- 分组优化:提高 group by 操作的效率
- 连接优化:加速表之间的 join 操作
-- 没有索引的查询(全表扫描) select * from users where username = 'john_doe'; -- 有索引的查询(索引查找) -- 执行计划会显示使用 idx_username 索引 explain select * from users where username = 'john_doe';
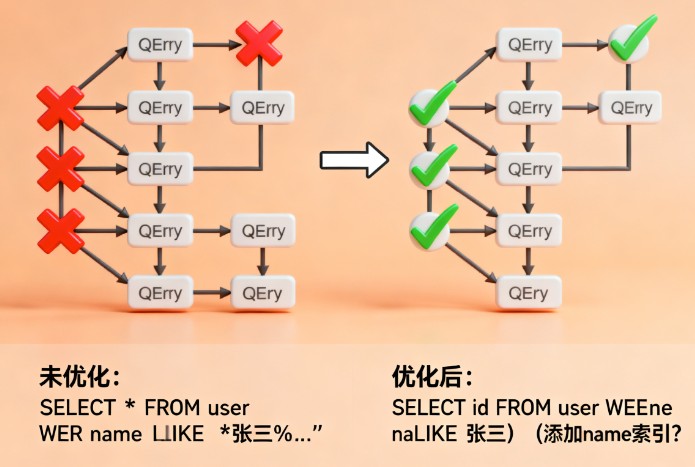
1.3 索引的优缺点
优点:
- 大幅提升查询速度
- 加速排序和分组操作
- 提高多表连接效率
- 保证数据唯一性(唯一索引)
缺点:
- 占用额外存储空间
- 降低写操作性能(insert、update、delete)
- 维护成本增加
2. mysql 索引类型详解
2.1 主键索引(primary key index)
主键索引是表中最重要的索引,每个表只能有一个主键索引,它具有唯一性且不能为空。
-- 创建表时定义主键
create table products (
product_id int primary key auto_increment,
product_name varchar(100) not null,
price decimal(10,2)
);
-- 为已存在的表添加主键
alter table products add primary key (product_id);2.2 唯一索引(unique index)
唯一索引确保索引列的值在表中是唯一的,但允许 null 值。
-- 创建唯一索引
create unique index idx_email on users (email);
-- 或者在创建表时定义
create table users (
id int primary key,
email varchar(100) unique
);2.3 普通索引(normal index)
普通索引是最基本的索引类型,没有唯一性限制。
-- 创建普通索引 create index idx_username on users (username); create index idx_age on users (age); -- 查看索引使用情况 explain select * from users where username = 'alice' and age > 25;
2.4 复合索引(composite index)
复合索引包含多个列,遵循最左前缀原则。
-- 创建复合索引 create index idx_name_age_city on users (username, age, city); -- 以下查询可以使用该索引 select * from users where username = 'bob'; select * from users where username = 'bob' and age = 30; select * from users where username = 'bob' and age = 30 and city = 'beijing'; -- 以下查询无法使用该索引 select * from users where age = 30; -- 跳过了最左列 select * from users where city = 'beijing'; -- 跳过了最左列
2.5 全文索引(full-text index)
全文索引用于文本搜索,支持自然语言搜索和布尔搜索。
-- 创建全文索引
create table articles (
id int primary key auto_increment,
title varchar(200),
content text,
fulltext(title, content)
);
-- 使用全文搜索
select * from articles
where match(title, content) against('mysql 索引优化' in natural language mode);3. 索引底层原理
3.1 b+ 树数据结构
mysql 的 innodb 存储引擎使用 b+ 树作为索引的数据结构。b+ 树具有以下特点:
- 所有叶子节点在同一层
- 非叶子节点只存储键值,不存储数据
- 叶子节点存储完整的数据记录
- 叶子节点之间通过指针连接,支持范围查询
-- 演示 b+ 树索引的范围查询优势 select * from users where age between 25 and 35 order by age; -- 由于 b+ 树的有序性,这个查询非常高效
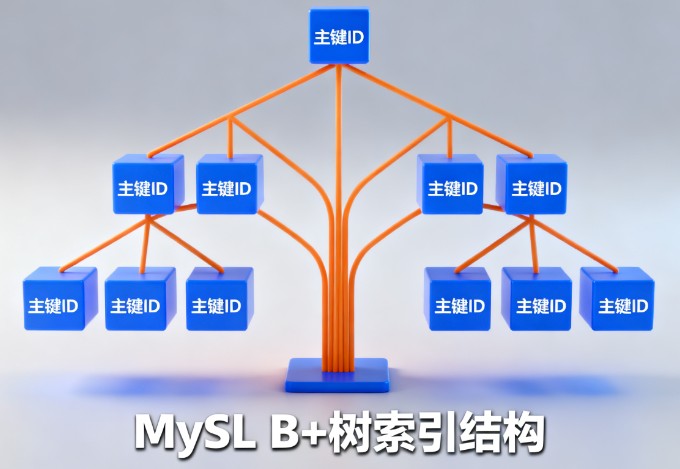
3.2 聚簇索引与非聚簇索引
聚簇索引(clustered index):
- innodb 表的主键索引就是聚簇索引
- 数据行按照主键顺序物理存储
- 每个表只能有一个聚簇索引
非聚簇索引(non-clustered index):
- 除主键外的其他索引都是非聚簇索引
- 叶子节点存储主键值,需要回表查询完整数据
-- 创建测试表演示聚簇索引和非聚簇索引
create table orders (
order_id int primary key, -- 聚簇索引
customer_id int,
order_date date,
total_amount decimal(10,2),
index idx_customer (customer_id), -- 非聚簇索引
index idx_date (order_date) -- 非聚簇索引
);
-- 通过主键查询(使用聚簇索引)
select * from orders where order_id = 1001;
-- 通过非聚簇索引查询(需要回表)
select * from orders where customer_id = 123;3.3 索引存储机制
-- 查看表的索引信息
show index from users;
-- 查看索引的存储统计信息
select
table_name,
index_name,
stat_name,
stat_value
from mysql.innodb_index_stats
where table_name = 'users';4. 索引的创建与管理
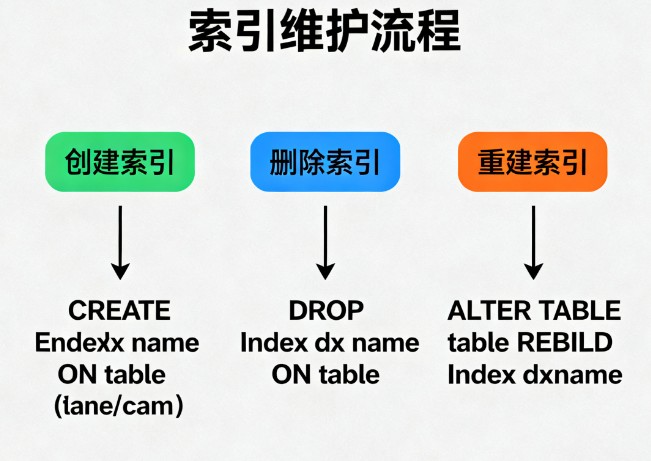
4.1 创建索引的语法
-- 基本语法 create [unique|fulltext] index index_name on table_name (column1, column2, ...); -- 实际示例 create index idx_user_status on users (status); create unique index idx_user_phone on users (phone_number); create index idx_order_date_status on orders (order_date, status); -- 使用 alter table 创建索引 alter table users add index idx_created_at (created_at); alter table users add unique index idx_username_email (username, email);
4.2 查看索引信息
-- 查看表的所有索引
show index from users;
-- 查看索引使用统计
select
object_schema,
object_name,
index_name,
count_read,
count_write,
count_fetch,
count_insert,
count_update,
count_delete
from performance_schema.table_io_waits_summary_by_index_usage
where object_schema = 'your_database' and object_name = 'users';4.3 删除索引
-- 删除索引 drop index idx_username on users; -- 使用 alter table 删除索引 alter table users drop index idx_age; -- 删除主键(需要先删除 auto_increment 属性) alter table users modify id int; alter table users drop primary key;
4.4 修改索引
-- mysql 不支持直接修改索引,需要先删除再创建 drop index idx_old_name on users; create index idx_new_name on users (username, email); -- 或者使用 alter table alter table users drop index idx_old_name, add index idx_new_name (username, email);
5. 索引性能优化策略
5.1 索引选择性分析
索引选择性是指索引列中不同值的数量与表中记录总数的比值。选择性越高,索引效果越好。
-- 计算列的选择性
select
count(distinct username) / count(*) as username_selectivity,
count(distinct email) / count(*) as email_selectivity,
count(distinct age) / count(*) as age_selectivity
from users;
-- 分析最适合创建索引的列
select
column_name,
cardinality,
cardinality / table_rows as selectivity
from information_schema.statistics s
join information_schema.tables t on s.table_name = t.table_name
where s.table_schema = 'your_database' and s.table_name = 'users';5.2 查询执行计划分析
使用 explain 分析查询的执行计划,优化索引使用。
-- 分析查询执行计划 explain select * from users where username = 'john' and age > 25; -- 详细的执行计划分析 explain format=json select * from users where username = 'john' and age > 25; -- 实际执行统计 explain analyze select * from users where username = 'john' and age > 25;
5.3 索引覆盖优化
索引覆盖是指查询所需的所有列都包含在索引中,避免回表操作。
-- 创建覆盖索引 create index idx_user_cover on users (username, email, age); -- 以下查询可以使用覆盖索引,避免回表 select username, email, age from users where username = 'alice'; -- 查看是否使用了覆盖索引 explain select username, email, age from users where username = 'alice'; -- extra 列会显示 "using index"
5.4 避免索引失效
-- 索引失效的常见情况 -- 1. 使用函数或表达式 -- 错误:索引失效 select * from users where upper(username) = 'john'; -- 正确:使用索引 select * from users where username = 'john'; -- 2. 使用 like 以通配符开头 -- 错误:索引失效 select * from users where username like '%john%'; -- 正确:使用索引 select * from users where username like 'john%'; -- 3. 使用 or 连接不同列 -- 错误:可能索引失效 select * from users where username = 'john' or age = 25; -- 正确:使用 union select * from users where username = 'john' union select * from users where age = 25; -- 4. 数据类型不匹配 -- 错误:索引失效 select * from users where age = '25'; -- age 是 int 类型 -- 正确:使用索引 select * from users where age = 25;
6. 索引最佳实践
6.1 索引设计原则
- 选择性原则:为选择性高的列创建索引
- 最左前缀原则:复合索引要考虑查询模式
- 覆盖索引原则:尽量使用覆盖索引避免回表
- 适度原则:避免过多索引影响写性能
-- 好的索引设计示例
create table user_orders (
id int primary key auto_increment,
user_id int not null,
order_status enum('pending', 'paid', 'shipped', 'delivered', 'cancelled'),
order_date date not null,
total_amount decimal(10,2),
-- 基于查询模式设计的复合索引
index idx_user_status_date (user_id, order_status, order_date),
-- 覆盖索引,避免回表
index idx_status_date_amount (order_status, order_date, total_amount)
);6.2 常见索引陷阱
-- 陷阱1:过多的单列索引
-- 错误做法
create index idx_user_id on orders (user_id);
create index idx_status on orders (order_status);
create index idx_date on orders (order_date);
-- 正确做法:根据查询模式创建复合索引
create index idx_user_status_date on orders (user_id, order_status, order_date);
-- 陷阱2:重复索引
-- 错误:创建了重复的索引
create index idx_username on users (username);
create index idx_username_duplicate on users (username); -- 重复索引
-- 陷阱3:无用的索引
-- 检查从未使用的索引
select
object_schema,
object_name,
index_name
from performance_schema.table_io_waits_summary_by_index_usage
where count_read = 0 and count_write = 0 and count_fetch = 0;6.3 索引维护策略
-- 定期分析表和索引统计信息
analyze table users;
-- 检查索引碎片
select
table_schema,
table_name,
data_length,
index_length,
data_free,
(data_free / (data_length + index_length)) * 100 as fragmentation_pct
from information_schema.tables
where table_schema = 'your_database';
-- 重建索引(减少碎片)
alter table users engine=innodb;
-- 监控索引使用情况
select
object_name,
index_name,
count_read,
count_write,
count_fetch / count_read as fetch_ratio
from performance_schema.table_io_waits_summary_by_index_usage
where object_schema = 'your_database'
order by count_read desc;7. 总结与展望
7.1 核心要点总结
通过本文的深入分析,我们可以总结出 mysql 索引优化的核心要点:
- 理解索引本质:索引是以空间换时间的数据结构,基于 b+ 树实现高效的数据检索
- 合理选择索引类型:根据业务需求选择主键索引、唯一索引、普通索引或复合索引
- 遵循设计原则:考虑选择性、最左前缀、覆盖索引等原则
- 持续监控优化:通过执行计划分析、性能监控等手段持续优化索引策略
7.2 性能提升效果
正确使用索引可以带来显著的性能提升:
- 查询速度提升:从秒级优化到毫秒级
- 系统吞吐量:提升 10-100 倍不等
- 资源利用率:减少 cpu 和 i/o 消耗
7.3 未来发展趋势
随着数据库技术的不断发展,索引技术也在持续演进:
- 智能索引推荐:基于机器学习的自动索引优化
- 列式存储索引:适应大数据分析场景的新型索引结构
- 内存索引优化:针对内存数据库的索引算法优化
- 分布式索引:支持分布式数据库的全局索引管理
7.4 实践建议
在实际项目中应用索引优化时,建议:
- 渐进式优化:从最频繁的查询开始,逐步优化索引策略
- 测试驱动:在生产环境应用前,充分测试索引的性能影响
- 监控为先:建立完善的性能监控体系,及时发现和解决问题
- 团队协作:建立索引设计规范,确保团队成员遵循最佳实践
索引优化是一个持续的过程,需要结合具体的业务场景和数据特点,通过不断的分析、测试和调优,才能发挥索引的最大价值。掌握了这些核心概念和实践技巧,相信你能够在实际项目中有效地运用 mysql 索引,显著提升数据库的查询性能。
到此这篇关于mysql 索引从入门到精通(从原理到实践)的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关mysql索引从入门到精通内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!




发表评论