一、caffeine 简介
1. 框架概述
caffeine是由google工程师ben manes开发的一款java本地缓存框架,其初始版本发布于2014年。该框架的设计灵感来源于guava cache,但在性能和功能方面进行了革命性的优化。caffeine基于"w-tinylfu"(window-tiny least frequently used)算法实现,这是一种改进的lfu缓存淘汰算法,结合了lfu的高命中率优势和lru的时效性特点。
1.1 caffeine的核心优势
1.1.1 超高性能
caffeine在性能方面实现了质的飞跃:
- 基准测试显示,相比guava cache,caffeine的读性能提升约8-12倍,写性能提升约5-10倍
- 支持每秒数百万次(典型值300-500万qps)的缓存操作
- 采用无锁并发设计,大幅减少线程竞争(如使用并发哈希表和非阻塞队列)
- 对jvm的内存模型进行了深度优化,减少缓存行伪共享问题
1.1.2 灵活的过期策略
caffeine提供三种核心过期策略:
- 写入后过期:通过
expireafterwrite设置,例如:caffeine.newbuilder().expireafterwrite(10, timeunit.minutes).build();
- 访问后过期:通过
expireafteraccess设置,适合热点数据场景 - 自定义过期:通过
expireafter方法实现基于业务逻辑的复杂过期判断
1.1.3 异步支持
caffeine提供完整的异步缓存(asynccache)支持:
- 异步加载机制:通过
asyncloadingcache实现非阻塞式数据加载 - 支持completablefuture:可与java8的异步编程模型完美结合
- 典型应用场景:高并发环境下的微服务接口缓存
1.1.4 丰富的监听器
caffeine提供完善的监控支持:
- 移除监听器(
removallistener):可监听缓存项的驱逐、失效或手动移除 - 统计功能:通过
recordstats()开启命中率统计 - 典型配置:
cache.recordstats(); cachestats stats = cache.stats(); double hitrate = stats.hitrate();
1.1.5 内存安全
caffeine提供多种内存保护机制:
- 基于容量:通过
maximumsize限制缓存项数量 - 基于时间:通过上述过期策略控制
- 基于引用:支持弱引用键/值(
weakkeys/weakvalues)和软引用值(softvalues) - 权重控制:通过
weigher和maximumweight实现基于对象大小的精确控制
典型内存安全配置示例:
caffeine.newbuilder()
.maximumsize(10_000)
.weigher((string key, string value) -> value.length())
.maximumweight(50_000_000) // ~50mb
.build();二、caffeine 基础
在使用 caffeine 前,需先引入依赖,并了解其核心组件的作用。
2.1 依赖引入(maven/gradle)
caffeine 的最新版本可在 maven 中央仓库查询(https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.github.ben-manes.caffeine/caffeine)
maven 配置示例(含注释说明)
<!-- caffeine核心依赖(必选) -->
<dependency>
<groupid>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupid>
<artifactid>caffeine</artifactid>
<version>3.2.7</version> <!-- 截至2024年1月最新稳定版 -->
<!-- 建议通过dependencymanagement统一管理版本 -->
</dependency>
<!-- 异步支持依赖(可选) -->
<!-- 当需要配合java11+的httpclient实现异步缓存加载时添加 -->
<dependency>
<groupid>java.net.http</groupid>
<artifactid>http-client</artifactid>
<version>11.0.1</version> <!-- 最低要求jdk11 -->
<scope>runtime</scope> <!-- 通常只需运行时依赖 -->
</dependency>gradle 配置示例(kotlin dsl)
dependencies {
// 核心实现(必选)
implementation("com.github.ben-manes.caffeine:caffeine:3.2.7")
// 异步支持(可选)
runtimeonly("java.net.http:http-client:11.0.1") {
because("for async cache loading with http requests")
}
}2.2 核心组件解析
caffeine 的核心组件采用分层设计,主要分为基础缓存接口和功能扩展接口两大类:
1.基础缓存接口层次结构
cache (基本功能)
├── loadingcache (同步加载)
└── asynccache (异步基础)
└── asyncloadingcache (异步加载)2.关键组件详细说明(含典型应用场景)
| 组件 | 作用说明 | 典型使用场景 | 示例代码片段 |
|---|---|---|---|
cache<k,v> | 手动管理缓存,需显式处理缓存未命中 | 简单缓存场景,数据源访问成本较低 | cache.get(key, k -> fetchfromdb(k)) |
loadingcache<k,v> | 自动加载缓存,内置cacheloader | 高频访问且加载逻辑固定的场景 | loadingcache.from(this::loadfromapi) |
asynccache<k,v> | 返回completablefuture的异步接口 | 配合非阻塞io或远程调用 | cache.get(key).thenaccept(value -> ...) |
asyncloadingcache<k,v> | 异步自动加载缓存 | 微服务间数据缓存 | asyncloadingcache.from(this::asyncload) |
cacheloader<k,v> | 定义加载逻辑的函数式接口 | 统一数据加载策略 | new cacheloader<>() { @override public v load(k key)... } |
removallistener<k,v> | 移除事件监听器 | 缓存一致性维护、监控统计 | listener((key,value,reason) -> logremoval()) |
expiry<k,v> | 细粒度过期控制 | 动态ttl场景(如会话缓存) | expireafter((key,value,currenttime) -> customttl) |
3.高级特性支持
- 权重计算:通过
weigher接口实现基于缓存对象大小的淘汰策略 - 刷新机制:
refreshafterwrite配合cacheloader.reload实现后台刷新 - 统计监控:
recordstats()启用命中率等统计指标 - 线程模型:默认使用forkjoinpool.commonpool(),可通过
executor自定义
4.最佳实践提示:
- 对于长时间加载操作,优先选择asyncloadingcache避免阻塞
- 移除监听器不要执行耗时操作,否则会影响缓存性能
- 在spring环境中建议通过@bean配置全局缓存管理器
- 生产环境务必启用统计功能(recordstats)进行监控
三、caffeine 核心用法
caffeine 的使用流程遵循 "构建器模式配置 → 创建缓存实例 → 读写缓存" 的逻辑,下面分场景讲解具体用法。
3.1 基础缓存(cache):手动控制读写
cache 是最基础的缓存类型,需手动处理缓存未命中(未命中时返回 null),适合缓存逻辑简单的场景。
3.1.1 创建 cache 实例
通过 caffeine.newbuilder() 配置缓存规则,常见配置包括:
- 容量控制:
maximumsize(long):设置缓存最大容量(条目数),超过后按 w-tinylfu 算法淘汰。maximumweight(long)+weigher(weigher):基于权重控制缓存大小,适合不同条目占用不同内存的场景。
- 过期策略:
expireafterwrite(duration):写入后过期(如 10 分钟未更新则过期),适合数据变更频繁的场景。expireafteraccess(duration):访问后过期(如 5 分钟未访问则过期),适合热点数据缓存。expireafter(expiry):自定义过期时间计算逻辑,可实现基于业务规则的过期。
- 监听器:
removallistener(removallistener):设置缓存移除监听器,可记录日志或触发后续操作。
- 其他特性:
weakkeys()/weakvalues():使用弱引用,允许被垃圾回收。softvalues():使用软引用,在内存不足时被回收。recordstats():启用统计信息收集。
import com.github.ben-manes.caffeine.cache.caffeine;
import com.github.ben-manes.caffeine.cache.cache;
import java.util.concurrent.timeunit;
public class caffeinebasicdemo {
public static void main(string[] args) {
// 1. 配置并创建cache实例(带详细注释)
cache<string, string> usercache = caffeine.newbuilder()
.maximumsize(1000) // 最大容量1000条
.expireafterwrite(10, timeunit.minutes) // 写入后10分钟过期
.expireafteraccess(5, timeunit.minutes) // 访问后5分钟过期(优先级低于expireafterwrite)
.removallistener((key, value, cause) -> { // 缓存移除监听器
system.out.printf("缓存移除:key=%s, value=%s, 原因=%s%n",
key, value, cause.tostring());
// 原因可能是:explicit(手动删除)、replaced(值被替换)、
// collected(垃圾回收)、expired(过期)、size(超过容量限制)
})
.recordstats() // 启用统计
.build(); // 构建cache实例
// 2. 写入缓存(多种方式)
usercache.put("user:1001", "张三"); // 常规put
usercache.asmap().putifabsent("user:1002", "李四"); // 线程安全写入
// 3. 读取缓存(未命中返回null)
string user1 = usercache.getifpresent("user:1001");
system.out.println("读取user:1001:" + user1); // 输出:张三
// 4. 读取并计算(未命中时执行函数逻辑,但不自动存入缓存)
string user3 = usercache.get("user:1003", key -> {
// 模拟从数据库查询数据(仅当缓存未命中时执行)
system.out.println("缓存未命中,查询db:" + key);
return "王五"; // 此结果不会自动存入缓存
});
system.out.println("读取user:1003:" + user3); // 输出:王五
// 5. 缓存维护操作
usercache.invalidate("user:1002"); // 单个删除
usercache.invalidateall(list.of("user:1001", "user:1003")); // 批量删除
usercache.cleanup(); // 手动触发清理过期条目
usercache.invalidateall(); // 清空所有缓存
// 6. 查看统计信息(需先启用recordstats)
system.out.println("命中率:" + usercache.stats().hitrate());
}
}3.1.2 应用场景示例
- 简单kv缓存:
- 缓存用户session信息
- 缓存系统配置项
- 临时数据存储(如验证码)
- 配合spring cache:
@configuration
@enablecaching
public class cacheconfig {
@bean
public cachemanager cachemanager() {
caffeinecachemanager manager = new caffeinecachemanager();
manager.setcaffeine(caffeine.newbuilder()
.maximumsize(1000)
.expireafterwrite(10, timeunit.minutes));
return manager;
}
}多级缓存:
// 作为本地缓存与redis组成二级缓存
public class multilevelcache {
private final cache<string, object> localcache;
private final redistemplate<string, object> redistemplate;
public object get(string key) {
object value = localcache.getifpresent(key);
if (value == null) {
value = redistemplate.opsforvalue().get(key);
if (value != null) {
localcache.put(key, value);
}
}
return value;
}
}3.2 加载缓存(loadingcache):自动加载未命中数据
loadingcache 是 cache 的子类,通过实现 cacheloader 接口,实现 "缓存未命中时自动加载数据并存入缓存",适合缓存数据需从数据源(如 db、redis)加载的场景。
3.2.1 创建 loadingcache 实例
import com.github.ben-manes.caffeine.cache.caffeine;
import com.github.ben-manes.caffeine.cache.loadingcache;
import java.util.concurrent.executionexception;
import java.util.concurrent.timeunit;
import java.util.list;
public class caffeineloadingdemo {
public static void main(string[] args) throws executionexception {
// 1. 实现cacheloader:定义缓存未命中时的加载逻辑
loadingcache<string, string> productcache = caffeine.newbuilder()
.maximumsize(500)
.expireafterwrite(30, timeunit.minutes)
.refreshafterwrite(10, timeunit.minutes) // 10分钟后刷新(不阻塞读取)
.recordstats()
.build(new cacheloader<string, string>() {
@override
public string load(string key) throws exception {
// 模拟从数据库加载数据(缓存未命中时自动执行)
system.out.println("缓存未命中,从db加载:" + key);
if (key.startswith("prod:")) {
return "商品-" + key.substring(5); // 如key=prod:101 → 商品-101
}
throw new illegalargumentexception("invalid key format");
}
// 可选:实现批量加载(提升getall性能)
@override
public map<string, string> loadall(iterable<? extends string> keys) {
system.out.println("批量加载keys:" + keys);
// 实际应从db批量查询
map<string, string> result = new hashmap<>();
for (string key : keys) {
result.put(key, "商品-" + key.substring(5));
}
return result;
}
});
// 2. 读取缓存(未命中时自动调用load()加载并存入缓存)
string product1 = productcache.get("prod:101"); // 首次:加载并返回
system.out.println("读取prod:101:" + product1); // 输出:商品-101
// 3. 批量读取(getall())
map<string, string> products = productcache.getall(list.of("prod:102", "prod:103"));
system.out.println("批量读取结果:" + products);
// 4. 主动刷新(异步)
productcache.refresh("prod:101"); // 后台刷新,旧值仍可用
// 5. 统计信息
system.out.println("加载次数:" + productcache.stats().loadcount());
}
}3.2.2 关键特性:刷新(refresh)与过期(expire)的区别
| 特性 | 刷新(refresh) | 过期(expire) |
|---|---|---|
| 触发时机 | 刷新时间到后 | 过期时间到后 |
| 读取行为 | 异步刷新,立即返回旧值 | 同步重新加载,可能阻塞请求 |
| 适用场景 | 数据允许短暂不一致(如商品详情) | 数据强一致要求(如订单状态) |
| 实现方式 | 需配置refreshafterwrite | 配置expireafterwrite/afteraccess |
典型使用模式:
// 商品详情缓存:10分钟强制过期,5分钟自动刷新
loadingcache<string, product> productcache = caffeine.newbuilder()
.maximumsize(10000)
.expireafterwrite(10, timeunit.minutes) // 强制过期时间
.refreshafterwrite(5, timeunit.minutes) // 自动刷新时间
.build(this::loadproductfromdb);
3.3 异步缓存(asynccache/asyncloadingcache):非阻塞读写
在高并发场景下,同步缓存的 load() 可能会阻塞线程,而 asynccache 通过返回 completablefuture 实现非阻塞操作,所有 io 操作均在异步线程池中执行。
3.3.1 创建 asyncloadingcache 实例
import com.github.ben-manes.caffeine.cache.asyncloadingcache;
import com.github.ben-manes.caffeine.cache.caffeine;
import java.util.concurrent.completablefuture;
import java.util.concurrent.executor;
import java.util.concurrent.executors;
import java.util.concurrent.timeunit;
public class caffeineasyncdemo {
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
// 1. 自定义线程池(生产环境建议使用有界队列和拒绝策略)
executor executor = executors.newfixedthreadpool(5, r -> {
thread thread = new thread(r);
thread.setname("caffeine-async-" + thread.getid());
return thread;
});
// 2. 创建asyncloadingcache实例
asyncloadingcache<string, string> ordercache = caffeine.newbuilder()
.maximumsize(1000)
.expireafterwrite(15, timeunit.minutes)
.executor(executor) // 指定异步线程池
.buildasync(key -> {
// 模拟耗时操作(如rpc调用,耗时200ms)
timeunit.milliseconds.sleep(200);
system.out.println(thread.currentthread().getname() + " 加载订单:" + key);
return "订单-" + key.substring(6); // 如key=order:2024 → 订单-2024
});
// 3. 异步读取(推荐方式)
completablefuture<string> future = ordercache.get("order:2024");
future.thenapplyasync(order -> {
system.out.println("处理订单数据:" + order);
return order.touppercase();
}, executor); // 使用相同线程池处理结果
// 4. 批量读取(返回map<key, completablefuture>)
map<string, completablefuture<string>> futures =
ordercache.getall(list.of("order:2025", "order:2026"));
// 5. 同步获取(仅测试用,实际应避免)
string order = ordercache.get("order:2027").get();
system.out.println("同步获取结果:" + order);
}
}3.3.2 最佳实践
线程池配置:
// 更完善的线程池配置
threadpoolexecutor executor = new threadpoolexecutor(
5, // 核心线程数
10, // 最大线程数
60, timeunit.seconds, // 空闲线程存活时间
new linkedblockingqueue<>(1000), // 有界队列
new threadfactorybuilder().setnameformat("cache-loader-%d").build(),
new threadpoolexecutor.callerrunspolicy() // 拒绝策略
);
异常处理:
ordercache.get("badkey").exceptionally(ex -> {
system.err.println("加载失败: " + ex.getmessage());
return "defaultvalue";
});
结合spring使用:
@cacheable(value = "orders", cachemanager = "asynccachemanager")
public completablefuture<order> getorderasync(string orderid) {
return completablefuture.supplyasync(() -> orderservice.loadorder(orderid));
}
性能监控:
cachestats stats = ordercache.synchronous().stats();
system.out.println("平均加载时间:" + stats.averageloadpenalty() + "ns");
四、caffeine 高级特性
4.1 缓存统计(cache statistics)
缓存统计功能是优化缓存性能的重要工具。通过开启缓存统计,可以实时监控以下关键指标:
- 命中率(hit rate):反映缓存有效性,计算公式为:
命中次数/(命中次数+未命中次数) - 加载耗时(load penalty):统计从数据源加载数据的平均耗时
- 移除次数(eviction count):因容量或过期策略导致的缓存移除次数
- 加载失败率(load failure rate):数据源加载失败的比例
典型应用场景:
- 评估缓存配置是否合理
- 识别热点数据
- 监控缓存性能瓶颈
import com.github.ben-manes.caffeine.cache.cachestats;
public class caffeinestatsdemo {
public static void main(string[] args) {
loadingcache<string, string> statscache = caffeine.newbuilder()
.maximumsize(100)
.recordstats() // 必须显式开启统计功能
.build(key -> {
// 模拟耗时加载
try {
thread.sleep(100);
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
thread.currentthread().interrupt();
}
return "统计测试:" + key;
});
// 模拟读写操作
statscache.get("key1"); // 第一次加载(未命中)
statscache.get("key1"); // 命中已有缓存
statscache.get("key2"); // 新键加载
statscache.invalidate("key1"); // 手动失效
// 获取统计结果
cachestats stats = statscache.stats();
system.out.println("缓存命中率:" + stats.hitrate()); // 50%(1次命中/2次查询)
system.out.println("加载成功次数:" + stats.loadsuccesscount()); // 2次加载
system.out.println("移除次数:" + stats.evictioncount()); // 0(未达到容量上限)
system.out.println("平均加载耗时(ns):" + stats.averageloadpenalty()); // 约100ms
system.out.println("加载失败率:" + stats.loadfailurerate()); // 0.0
}
}4.2 自定义过期策略(expiry)
标准的ttl(time-to-live)过期策略对所有缓存条目采用统一设置,而自定义过期策略允许基于业务特性实现精细化控制。
常见应用场景:
- 不同优先级数据设置不同有效期(如热点数据短时效,冷数据长时效)
- 读写操作影响过期时间(如读操作续期)
- 动态调整过期时间(如根据数据价值计算)
import com.github.ben-manes.caffeine.cache.caffeine;
import com.github.ben-manes.caffeine.cache.expiry;
import com.github.ben-manes.caffeine.cache.loadingcache;
import java.util.concurrent.timeunit;
class customexpiry implements expiry<string, string> {
@override
public long expireaftercreate(string key, string value, long currenttime) {
// 创建时过期策略
if (key.startswith("flash:")) { // 闪存数据:30秒过期
return timeunit.seconds.tonanos(30);
} else if (key.startswith("hot:")) { // 热门数据:5分钟
return timeunit.minutes.tonanos(5);
} else { // 普通数据:30分钟
return timeunit.minutes.tonanos(30);
}
}
@override
public long expireafterupdate(string key, string value,
long currenttime, long currentduration) {
// 更新策略:保持原有过期时间(默认)
return currentduration;
// 或者重置为创建时间:return expireaftercreate(key, value, currenttime);
}
@override
public long expireafterread(string key, string value,
long currenttime, long currentduration) {
// 读取时策略:热门数据读取后续期5分钟
if (key.startswith("hot:")) {
return timeunit.minutes.tonanos(5);
}
return currentduration;
}
}
public class caffeinecustomexpirydemo {
public static void main(string[] args) {
loadingcache<string, string> customexpirycache = caffeine.newbuilder()
.expireafter(new customexpiry())
.build(key -> "自定义过期:" + key);
customexpirycache.get("flash:news:2023"); // 30秒过期
customexpirycache.get("hot:product:101"); // 5分钟且读取续期
customexpirycache.get("normal:user:201"); // 30分钟过期
}
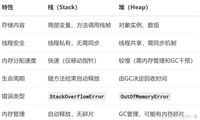
}4.3 弱引用与软引用:避免内存溢出
java引用类型与缓存回收策略:
| 引用类型 | gc行为 | 适用场景 | caffeine配置 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 强引用 | 永不回收 | 默认方式 | - |
| 软引用 | 内存不足时回收 | 缓存大对象 | .softvalues() |
| 弱引用 | 下次gc时回收 | 临时性缓存 | .weakkeys()/.weakvalues() |
注意事项:
- 使用
weakkeys()时,key比较基于==而非equals() softvalues()可能导致gc压力增大- 引用回收与显式失效策略共同作用
// 弱引用key+value的缓存(适合临时性数据)
cache<string, byte[]> weakcache = caffeine.newbuilder()
.weakkeys() // key无强引用时回收
.weakvalues() // value无强引用时回收
.maximumsize(10_000) // 仍保持容量限制
.build();
// 软引用value的缓存(适合大对象)
cache<string, byte[]> softcache = caffeine.newbuilder()
.softvalues() // 内存不足时回收value
.expireafterwrite(1, timeunit.hours) // 配合显式过期
.build();
// 典型使用场景
void processlargedata(string dataid) {
byte[] data = softcache.get(dataid, id -> {
// 从数据库加载大对象(如图片、文件等)
return loadlargedatafromdb(id);
});
// 使用数据...
}五、caffeine 注意事项
在实际开发中,若使用不当,caffeine 可能出现缓存穿透、内存溢出、线程阻塞等问题,以下是核心注意事项:
5.1 区分 "刷新(refresh)" 与 "过期(expire)"
刷新(refreshafterwrite):
- 工作机制:当缓存条目超过指定时间未被写入时,下次读取会触发异步刷新,但在此期间仍会返回旧值
- 适用场景:对数据一致性要求不高,可接受短暂延迟的场景
- 商品详情页的评论数统计
- 新闻资讯的阅读量统计
- 排行榜数据的更新
过期(expireafterwrite/expireafteraccess):
- expireafterwrite:从写入开始计时
- expireafteraccess:从最后一次访问开始计时
- 工作机制:过期后缓存条目立即失效,读取时会同步阻塞直到重新加载完成
- 适用场景:对数据一致性要求高的核心业务
- 用户账户余额
- 订单支付状态
- 库存数量
⚠️ 典型误用场景:
将用户余额这类强一致性数据配置为refreshafterwrite(5s).可能导致:
- 用户a看到余额100元
- 用户b完成扣款50元
- 5秒内用户a仍看到100元(旧值)
- 直到下次读取才刷新为50元
5.2 避免缓存穿透:空值缓存与布隆过滤器
缓存穿透的典型特征:
- 查询一个必然不存在的数据(如不存在的用户id)
- 每次请求都穿透到数据库
- 可能被恶意攻击者利用,造成数据库压力
解决方案1:空值缓存
loadingcache<string, string> cache = caffeine.newbuilder()
.expireafterwrite(1, timeunit.minutes) // 空值缓存1分钟
.build(key -> {
string value = queryfromdb(key);
// 特殊空值标记,避免与真实空值混淆
return value != null ? value : "null_value";
});
解决方案2:布隆过滤器(适合千万级key场景)
// 初始化布隆过滤器
bloomfilter<string> bloomfilter = bloomfilter.create(
funnels.stringfunnel(charset.defaultcharset()),
1000000, // 预期元素数量
0.01 // 误判率
);
// 查询流程
if (!bloomfilter.mightcontain(key)) {
return null; // 肯定不存在
} else {
return cache.get(key); // 可能存在
}5.3 缓存键(key)必须重写 hashcode() 和 equals()
常见错误案例:
class compositekey {
private long id;
private string category;
// 缺少hashcode/equals实现
}
// 实际使用中
compositekey key1 = new compositekey(1l, "a");
compositekey key2 = new compositekey(1l, "a");
cache.put(key1, "value");
// 将返回null,因为key2被视为不同key
cache.getifpresent(key2); 正确实现要点:
- 使用objects工具类自动生成
- 保证不可变(final字段)
- 实现serializable接口(分布式缓存需要)
class compositekey implements serializable {
private final long id;
private final string category;
@override
public boolean equals(object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof compositekey)) return false;
compositekey that = (compositekey) o;
return objects.equals(id, that.id) &&
objects.equals(category, that.category);
}
@override
public int hashcode() {
return objects.hash(id, category);
}
}5.4 异步缓存(asynccache)的线程池选择
默认线程池的问题:
- forkjoinpool.commonpool()是jvm全局共享的
- 可能被completablefuture等其他组件占用
- 在容器环境中可能线程数不足
推荐配置:
executorservice executor = executors.newfixedthreadpool(
runtime.getruntime().availableprocessors() * 2,
new threadfactorybuilder()
.setnameformat("caffeine-loader-%d")
.setdaemon(true)
.build()
);
asyncloadingcache<string, string> cache = caffeine.newbuilder()
.executor(executor) // 指定专属线程池
.buildasync(key -> loadexpensivevalue(key));5.5 避免内存溢出:合理配置容量与过期时间
典型配置示例:
caffeine.newbuilder()
.maximumsize(10_000) // 基于条目数限制
.expireafterwrite(30, timeunit.minutes) // 写入后30分钟过期
.expireafteraccess(10, timeunit.minutes) // 10分钟无访问过期
.weigher((string key, string value) -> value.length()) // 按value大小计算权重
.maximumweight(50_000_000) // 约50mb内存限制
监控建议:
- 通过cache.stats()获取命中率
- 使用jmx监控缓存大小
- 设置告警阈值(如内存使用>80%)
5.6 cacheloader 的异常处理
完整异常处理方案:
loadingcache<string, string> cache = caffeine.newbuilder()
.build(new cacheloader<string, string>() {
@override
public string load(string key) {
try {
return querydb(key);
} catch (sqlexception e) {
// 记录详细日志
log.error("db查询失败, key: {}", key, e);
// 返回降级值
return "default_value";
// 或者抛出特定异常
// throw new cacheloadexception(e);
}
}
});
// 使用时的异常处理
try {
return cache.get(key);
} catch (cacheloaderexception e) {
// 处理加载失败
return processfallback(key);
} catch (exception e) {
// 兜底处理
return "system_error";
}六、常见问题
q1:caffeine 与 guava cache 的详细区别
性能比较
caffeine 采用了创新的 w-tinylfu 缓存淘汰算法,该算法结合了 tinylfu 和 lru 的优势:
- 使用 count-min sketch 数据结构高效统计访问频率
- 适应不同工作负载模式(突发性和长期性访问)
- 在基准测试中,caffeine 的读写性能比 guava cache 高出 10-20 倍
功能特性对比
| 特性 | caffeine | guava cache |
|---|---|---|
| 异步加载 | 支持 asyncloadingcache | 仅同步加载 |
| 过期策略 | 支持基于大小、时间、引用等多种策略 | 仅基本过期策略 |
| 自动刷新 | 支持 refreshafterwrite | 不支持 |
| 权重计算 | 支持自定义权重 | 支持但性能较差 |
| 监听器 | 支持移除监听器 | 支持移除监听器 |
| 统计 | 提供命中率等详细统计 | 提供基本统计 |
兼容性与迁移
caffeine 在设计时特别考虑了与 guava cache 的兼容性:
- 90%以上的 api 可以直接替换
- 主要差异在于构建方式(caffeine.newbuilder() vs cachebuilder.newbuilder())
- 迁移示例:
// guava cache
loadingcache<key, value> cache = cachebuilder.newbuilder()
.maximumsize(1000)
.build(new cacheloader<key, value>() {
public value load(key key) {
return createvalue(key);
}
});
// 迁移到 caffeine
loadingcache<key, value> cache = caffeine.newbuilder()
.maximumsize(1000)
.build(key -> createvalue(key));q2:caffeine 的分布式缓存支持与多级缓存架构
本地缓存特性
caffeine 作为本地缓存的核心特点:
- 仅作用于单个 jvm 进程内
- 不同服务器节点间的缓存数据不共享
- 适用于高频访问、低变化率的数据
二级缓存架构实现
典型的生产级缓存架构组合:
- 第一层:caffeine 本地缓存(纳秒级响应)
- 设置合理的过期时间(如30秒)
- 适合极端热点数据
- 第二层:redis 分布式缓存(毫秒级响应)
- 设置较长的过期时间(如5分钟)
- 使用redis集群保证高可用
- 数据源:数据库/服务(秒级响应)
- 最终数据一致性保障
实现示例
public class twolevelcacheservice {
private final cache<string, object> localcache = caffeine.newbuilder()
.maximumsize(10_000)
.expireafterwrite(30, timeunit.seconds)
.build();
private final redistemplate<string, object> redistemplate;
public object getdata(string key) {
// 1. 尝试从本地缓存获取
object value = localcache.getifpresent(key);
if (value != null) {
return value;
}
// 2. 尝试从redis获取
value = redistemplate.opsforvalue().get(key);
if (value != null) {
localcache.put(key, value);
return value;
}
// 3. 回源查询
value = querydatabase(key);
redistemplate.opsforvalue().set(key, value, 5, timeunit.minutes);
localcache.put(key, value);
return value;
}
}q3:缓存击穿解决方案的深入分析
互斥锁方案详解
实现要点:
- 使用
key.intern()获取字符串规范表示,确保相同key锁定同一对象 - 采用双重检查锁定模式减少锁竞争
- 设置合理的锁等待超时时间
增强版实现:
public object getdatawithlock(string key) {
object value = cache.getifpresent(key);
if (value != null) {
return value;
}
synchronized (key.intern()) {
// 双重检查
value = cache.getifpresent(key);
if (value != null) {
return value;
}
try {
value = querydatasource(key);
cache.put(key, value);
} finally {
// 释放资源
}
}
return value;
}热点key永不过期方案
实现模式:
主动更新:后台线程定期(如每分钟)刷新热点数据
scheduledexecutorservice scheduler = executors.newscheduledthreadpool(1);
scheduler.scheduleatfixedrate(() -> {
list<string> hotkeys = gethotkeylist();
hotkeys.foreach(key -> {
object value = querydatasource(key);
cache.put(key, value);
});
}, 0, 1, timeunit.minutes);
被动更新:获取数据时异步刷新
loadingcache<string, object> cache = caffeine.newbuilder()
.maximumsize(10_000)
.refreshafterwrite(1, timeunit.minutes)
.build(key -> querydatasource(key));
其他防护策略
- 布隆过滤器:前置过滤不存在的key请求
- 缓存预热:系统启动时加载热点数据
- 随机过期时间:对相同类型key设置不同的过期时间偏移量
int baseexpire = 3600; // 基础1小时 int randomoffset = threadlocalrandom.current().nextint(600); // 0-10分钟随机 cache.put(key, value, baseexpire + randomoffset, timeunit.seconds);





发表评论