在windows系统中,注册表 是系统定义的数据库,应用程序和系统组件在其中存储和检索配置数据。
注册表是一个分层数据库,其中包含对 windows本身以及windows上运行的应用程序和服务至关重要的数据。 因此我们还是不好进行随意操作,但是查看注册表的信息可以让我们更加了解系统的运行情况。
数据以树格式进行结构化。树中的每个节点称为键。每个键可以同时包含子项和数据条目,称为值。
通过查看注册表的数据我们可以发现一些比较有趣的系统信息。比如我们可以通过注册表看到用户定义的环境变量
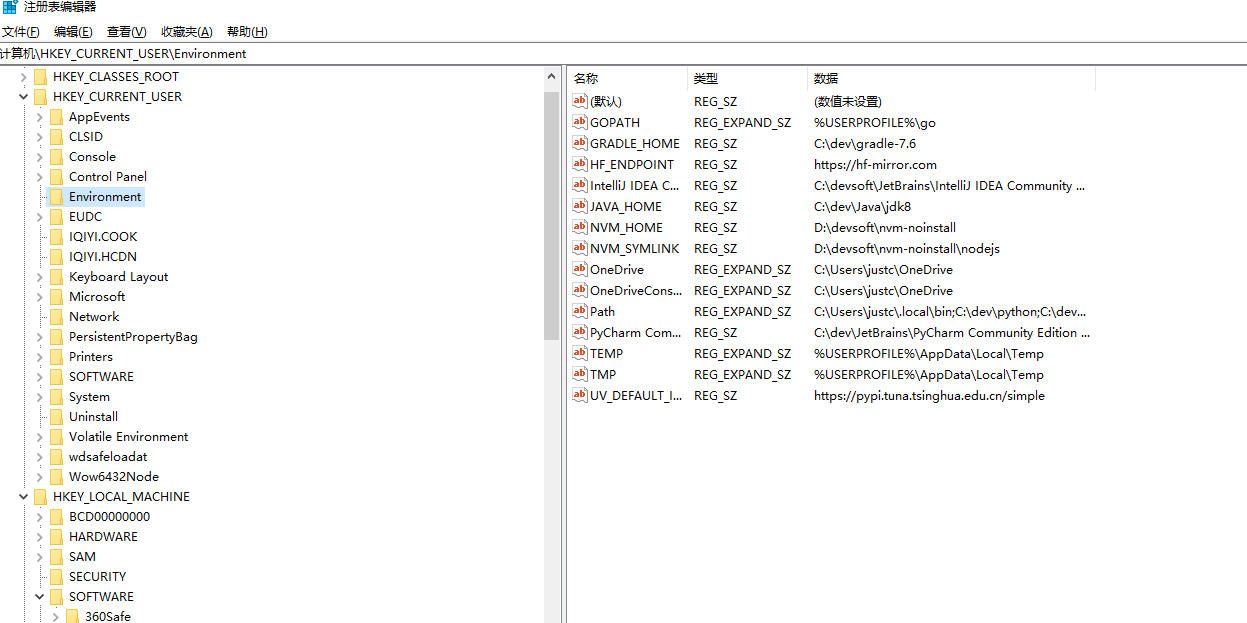
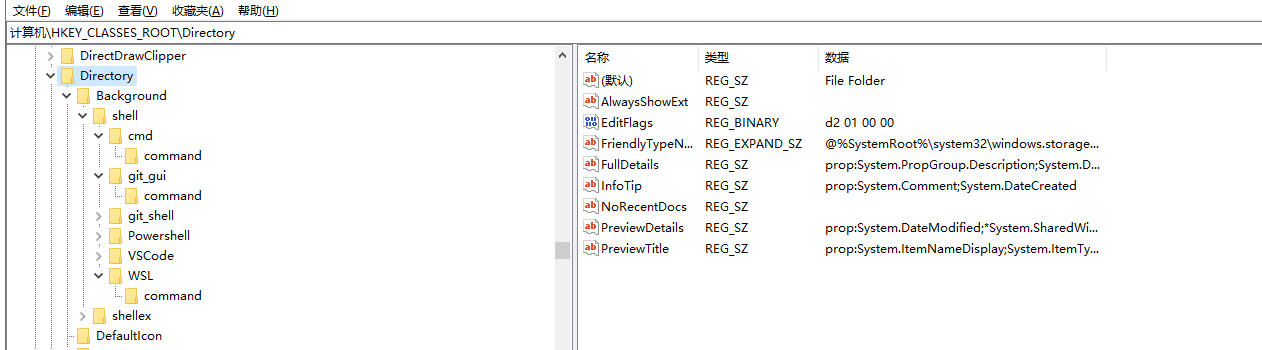
也可以查看菜单在文件夹空白处右键的菜单操作。
以下是使用python3对注册表进行读取的代码。
import winreg
def enumerate_registry_values(key, sub_key):
"""
枚举注册表键中的所有值
:param key_path: 注册表键路径
"""
# key 可以是一个打开的key,或者winreg预定义的值hkey_* constants
try:
reg_key = winreg.openkey(key, sub_key, 0, winreg.key_read)
except oserror:
print(f"can't open key {key}/{sub_key}")
return
values = []
index = 0
while true:
try:
# 枚举值
value_name, value_data, value_type = winreg.enumvalue(reg_key, index)
values.append((value_name, value_data, value_type))
index += 1
except oserror:
# 当没有更多值时跳出循环
break
winreg.closekey(key)
print(f"枚举值成功 - 路径: {key}{sub_key}, 值数量: {len(values)}")
for name, data, type_ in values:
print(f" 名称: {name}, 值: {data}, 类型: {type_}")
print("基于注册表查看用户环境变量")
# 查看用户定义的环境变量路径是:hkey_current_user\environment
enumerate_registry_values(winreg.hkey_current_user,"environment")
def get_children_key_names(key, sub_key):
"""
获取key的子节点的key
并且以数组返回
"""
# key 可以是一个打开的key,或者winreg预定义的值hkey_* constants
reg_key = winreg.openkey(key, sub_key, 0, winreg.key_read)
sub_key_names = []
index = 0
while true:
try:
# 枚举值
sub_key_name = winreg.enumkey(reg_key, index)
sub_key_names.append(sub_key_name)
index += 1
except oserror:
# 当没有更多值时跳出循环
break
winreg.closekey(key)
return sub_key_names
print("基于注册表查看对文件夹右键菜单的操作")
# 遍历路径:\hkey_classes_root\directory\background\shell,查看针对文件夹中空白处右键菜单的操作
sub_key_names=get_children_key_names(winreg.hkey_classes_root,r"directory\background\shell")
for sub_key_name in sub_key_names:
# 菜单的操作在command的值中
enumerate_registry_values(winreg.hkey_classes_root,r'directory\background\shell\\'+""+sub_key_name+r"\command")
输出如下:
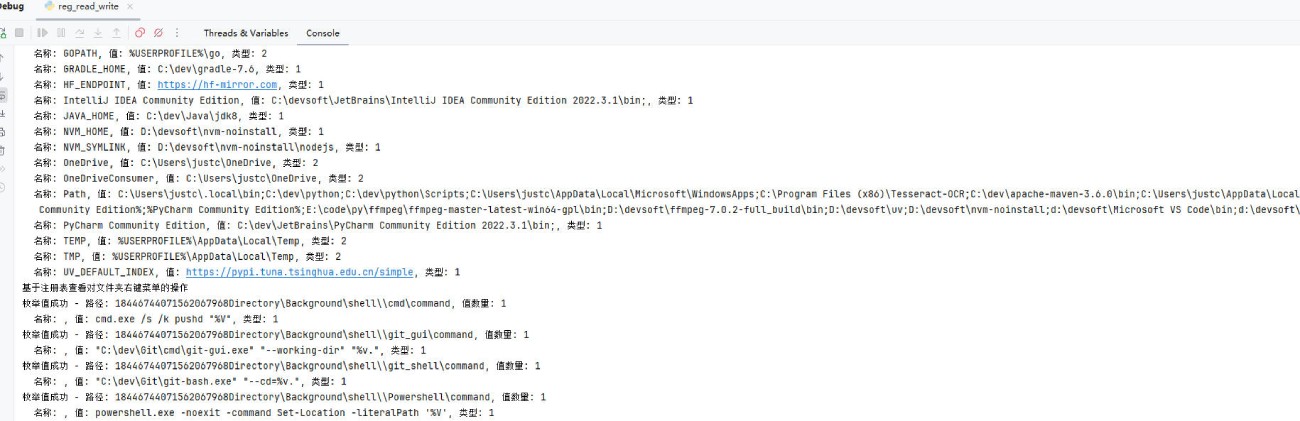
方法补充
python操作注册表的方法及应用
1.打开注册表
可以使用winreg模块的openkey()方法打开注册表。该方法的参数是一个表示注册表项的句柄和一个表示要打开的子项的名称的字符串。如果要打开的子项不存在,将会抛出一个windowserror异常。
下面是打开注册表的示例代码:
import winreg # 打开hkey_current_user\software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\explorer键 key = winreg.openkey(winreg.hkey_current_user, r'software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\explorer')
在上面的代码中,我们首先使用winreg.hkey_current_user常量表示hkey_current_user根键。然后使用winreg.openkey()方法打开注册表项software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\explorer,并将结果保存在变量key中。
2.读取注册表值
可以使用winreg模块的queryvalue()方法读取注册表值。该方法的参数是一个表示注册表项的句柄和一个表示要读取的值的名称的字符串。如果要读取的值不存在,将会抛出一个windowserror异常。
下面是读取注册表值的示例代码:
import winreg # 打开hkey_current_user\software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\explorer键 key = winreg.openkey(winreg.hkey_current_user, r'software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\explorer') # 读取startpage键的值 value = winreg.queryvalue(key, 'startpage') print(value)
在上面的代码中,我们首先使用winreg.openkey()方法打开注册表项software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\explorer,并将结果保存在变量key中。然后使用winreg.queryvalue()方法读取startpage键的值,并将结果保存在变量value中。最后打印value的值。
3.写入注册表值
可以使用winreg模块的setvalue()方法写入注册表值。该方法的参数是一个表示注册表项的句柄、一个表示要写入的值的名称的字符串和一个表示要写入的值的类型的常量。如果要写入的值已存在,将会覆盖原有的值。
下面是写入注册表值的示例代码:
import winreg # 打开hkey_current_user\software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\explorer键 key = winreg.openkey(winreg.hkey_current_user, r'software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\explorer', 0, winreg.key_write) # 写入testvalue键的值 winreg.setvalue(key, 'testvalue', winreg.reg_sz, 'hello, world!')
在上面的代码中,我们首先使用winreg.openkey()方法打开注册表项software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\explorer,并将结果保存在变量key中。然后使用winreg.setvalue()方法写入testvalue键的值。需要注意的是,我们需要将要写入的值的类型作为winreg.setvalue()方法的第三个参数传入,并使用常量表示类型。
4. 关闭注册表
在操作注册表之后,我们需要关闭注册表。可以使用winreg模块的closekey()方法关闭注册表。该方法的参数是一个表示注册表项的句柄。
下面是关闭注册表的示例代码:
import winreg # 打开hkey_current_user\software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\explorer键 key = winreg.openkey(winreg.hkey_current_user, r'software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\explorer') # 关闭注册表 winreg.closekey(key)
在上面的代码中,我们首先使用winreg.openkey()方法打开注册表项software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\explorer,并将结果保存在变量key中。然后使用winreg.closekey()方法关闭注册表。
5.python 读取注册表项值
import winreg # 导入winreg库
reg_path = r"software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\explorer" # 注册表路径
reg_key_name = "shell folders" # 要读取的具体项名
try:
reg_key = winreg.openkey(winreg.hkey_current_user, reg_path) # 打开注册表项
value, regtype = winreg.queryvalueex(reg_key, reg_key_name) # 读取注册表项的值
except windowserror as e: # 捕捉 windows 错误
print(f"发生错误: {e}") # 输出错误信息
else:
print(f"读取到的值: {value}") # 输出注册表项的值
finally:
winreg.closekey(reg_key) # 关闭注册表项到此这篇关于利用python读取windows注册表的方法详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python读取windows注册表内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论