介绍
spring cache 是 spring 框架提供的缓存抽象层,它简化了在应用中添加缓存功能的过程,允许开发者通过注解方式轻松实现缓存逻辑,而无需关注具体的缓存实现细节。
- 缓存抽象:spring cache 不直接提供缓存实现,而是定义了一套接口(如
cache、cachemanager),支持多种缓存实现(如 caffeine、ehcache、redis 等)。 - 注解驱动:通过注解(如
@cacheable、@cacheput、@cacheevict)声明缓存规则,无需手动编写缓存逻辑。 - 透明集成:缓存操作与业务逻辑解耦,开发者只需关注业务代码。
常用注解
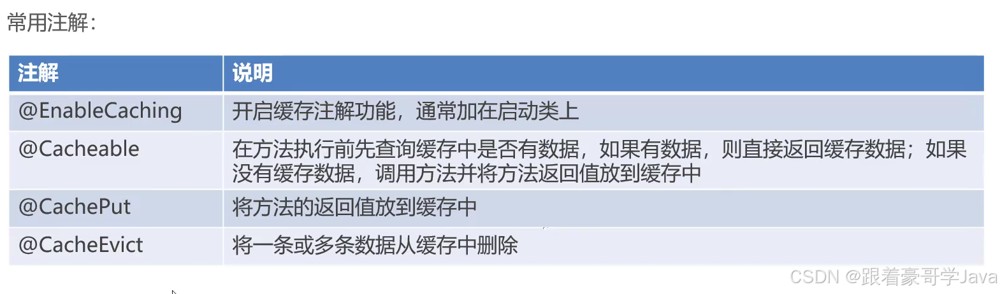
@cacheable
标记方法结果可被缓存。调用方法时,先检查缓存:
@cacheable(value = "users", key = "#id")
public user getuserbyid(long id) {
// 从数据库查询用户
return userrepository.findbyid(id);
}若缓存存在,直接返回缓存值,不执行方法。
若缓存不存在,执行方法并将结果存入缓存。
@cacheput
保证方法执行,并将结果更新到缓存(常用于更新操作)。
@cacheput(value = "users", key = "#user.id")
public user updateuser(user user) {
return userrepository.save(user);
}
@cacheevict
移除缓存条目(常用于删除操作)。
@cacheevict(value = "users", key = "#id")
public void deleteuser(long id) {
userrepository.deletebyid(id);
}
@caching
组合多个缓存注解(如同时更新和删除缓存)。
@caching(
put = @cacheput(value = "users", key = "#user.id"),
evict = @cacheevict(value = "userlist", allentries = true)
)
public user saveuser(user user) {
return userrepository.save(user);
}
@cacheconfig
在类级别统一配置缓存属性(如 value、keygenerator),简化方法上的注解。
案例
- 添加依赖(maven):
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactid>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactid>
</dependency>- 启用缓存:
在启动类添加@enablecaching注解。
@springbootapplication
@enabletransactionmanagement //开启注解方式的事务管理
@slf4j
@enablecaching//开启缓存功能
public class skyapplication {
public static void main(string[] args) {
springapplication.run(skyapplication.class, args);
log.info("server started");
}
}
- c端
/**
* 条件查询
*
* @param categoryid
* @return
*/
@getmapping("/list")
@apioperation("根据分类id查询套餐")
@cacheable(cachenames = "setmealcache",key = "#categoryid")//key: setmealcache::categoryid
public result<list<setmeal>> list(long categoryid) {
setmeal setmeal = new setmeal();
setmeal.setcategoryid(categoryid);
setmeal.setstatus(statusconstant.enable);
list<setmeal> list = setmealservice.list(setmeal);
return result.success(list);
}
- 管理端
/**
* 新增套餐
* @param setmealdto
* @return
*/
@postmapping
@apioperation("新增套餐")
@cacheevict(cachenames = "setmealcache",key = "#setmealdto.categoryid")
public result save(@requestbody setmealdto setmealdto){
log.info("新增套餐:{}",setmealdto);
setmealservice.savewithdish(setmealdto);
return result.success();
}
/**
* 删除套餐
* @param ids
* @return
*/
@deletemapping
@apioperation("批量删除套餐")
@cacheevict(cachenames = "setmealcache",allentries = true)
public result delete(@requestparam list<long> ids){
log.info("批量删除套餐:{}",ids);
setmealservice.deletebatch(ids);
return result.success();
}
/**
* 修改套餐起售停售状态
* @param status
* @param id
* @return
*/
@postmapping("/status/{status}")
@apioperation("修改套餐起售停售状态")
@cacheevict(cachenames = "setmealcache",allentries = true)
public result startorstop(@pathvariable("status") integer status, long id){
log.info("套餐起售或停售:{}",id);
setmealservice.startorstop(status,id);
return result.success();
}注意事项
- 缓存键生成:默认使用方法参数生成键,可通过
key属性自定义(spel 表达式),或配置keygenerator。 - 缓存穿透:可通过空值缓存(
@cacheable(unless = "#result == null"))避免。 - 缓存更新:使用
@cacheput确保缓存与数据源一致性,避免直接修改缓存。 - 分布式缓存:在分布式系统中,推荐使用 redis 等集中式缓存,避免本地缓存(如 caffeine)的一致性问题。
通过 spring cache,开发者可以快速为应用添加缓存能力,提升系统性能,同时保持代码简洁易维护。
到此这篇关于spring cache 整合 redis 实现高效缓存的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关spring cache redis 高效缓存内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!







发表评论