一、ip白名单控制概述
1.1 什么是ip白名单
ip白名单(ip whitelist)是一种网络安全机制,它通过预先定义一组被允许访问系统资源的ip地址列表,实现对网络请求来源的精确控制。只有来自白名单中ip地址的请求才会被系统接受和处理,其他所有来源的请求都将被拒绝。
在spring boot应用中实现ip白名单控制具有以下核心价值:
- 增强安全性:有效防止未授权访问,降低恶意攻击风险
- 访问控制:精确管理可访问系统的客户端范围
- 资源保护:避免非预期流量消耗服务器资源
- 合规要求:满足某些行业对访问控制的监管要求
1.2 ip白名单 vs 黑名单
| 特性 | ip白名单 | ip黑名单 |
|---|---|---|
| 控制逻辑 | 默认拒绝,明确允许 | 默认允许,明确拒绝 |
| 安全性 | 更高,仅已知安全ip可访问 | 较低,新型攻击源可能不在名单中 |
| 维护成本 | 较高,需要持续更新合法ip | 较低,只需添加已知恶意ip |
| 适用场景 | 内部系统、高安全要求接口 | 公开服务、需要阻止特定恶意源 |
| 误杀可能性 | 可能误拒绝合法但未登记的ip | 可能漏过未登记的恶意ip |
1.3 ip白名单的应用场景
- 内部管理系统:限制只有公司内网或vpn ip可以访问
- 支付接口:确保只有支付网关的服务器ip可以调用
- 数据同步接口:仅允许合作伙伴的指定服务器ip访问
- 管理后台:防止未授权的管理员访问
- 第三方服务集成:限定合作方的调用来源
二、spring boot中实现ip白名单的技术选型
2.1 实现方案对比
在 spring boot 中实现 ip 白名单功能时,可以选择多种技术方案。以下是常见的 技术选型 及其适用场景、优缺点分析:
1. 自定义 filter 实现
实现方式
- 通过实现
javax.servlet.filter接口,在dofilter方法中检查请求的 ip 是否在白名单中。 - 配合
@component注解注册为 spring bean,并配置拦截路径。
优点
- 简单直接:无需依赖额外框架,代码实现灵活。
- 低耦合:与 spring security 无关,适合轻量级需求。
- 可扩展性强:支持动态更新白名单(如从数据库加载)。
缺点
- 需要手动处理 ip 获取逻辑:需注意代理服务器(如 nginx)后的真实 ip 获取。
- 缺乏安全框架集成:无法与 spring security 的权限控制无缝结合。
适用场景
- 简单项目或对安全要求不高的场景。
- 需要完全自定义逻辑(如动态加载白名单)。
2. spring security 集成
实现方式
- 使用 spring security 提供的
hasipaddress方法,配置白名单。 - 对于多 ip 白名单,需结合自定义表达式或策略。
优点
- 与安全框架无缝集成:可与其他安全规则(如角色权限)结合。
- 配置灵活:支持基于路径的细粒度控制。
缺点
- 配置复杂度较高:需要编写自定义表达式或策略类。
- 不支持通配符:直接配置时仅支持精确匹配。
适用场景
- 已使用 spring security 的项目。
- 需要将 ip 白名单与其他安全规则(如 jwt、oauth)结合。
3. aop(面向切面编程)
实现方式
- 使用
@aspect定义切面,在方法执行前检查 ip 是否在白名单中。 - 适用于对特定方法或类的访问控制。
优点
- 细粒度控制:可针对具体方法或类实现 ip 拦截。
- 解耦业务逻辑:安全逻辑与业务代码分离。
缺点
- 性能开销:aop 会增加方法调用的额外开销。
- ip 获取复杂:需在切面中获取
httpservletrequest对象。
适用场景
- 需要对特定方法(如敏感接口)进行 ip 校验。
- 与业务逻辑解耦需求较高的场景。
4. 动态白名单(结合数据库)
实现方式
- 将白名单存储在数据库中,通过定时任务或缓存刷新机制动态加载。
- 可结合 redis 缓存提高性能。
优点
- 灵活性高:无需重启服务即可更新白名单。
- 适合生产环境:支持动态管理 ip 列表。
缺点
- 实现复杂度较高:需处理数据库连接、缓存更新等逻辑。
- 性能依赖数据库:频繁查询数据库可能影响性能。
适用场景
- 白名单需要频繁更新的场景。
- 多租户系统或需要动态权限管理的系统。
5. 使用 linux 防火墙(iptables/nftables)
实现方式
- 通过 linux 命令行配置防火墙规则,限制访问 ip。
- 与 spring boot 无关,属于操作系统层面的控制。
优点
- 高性能:由操作系统直接处理,无需应用层逻辑。
- 简单高效:适合服务器级别的全局控制。
缺点
- 不可动态更新:需手动执行命令或脚本。
- 缺乏灵活性:无法针对具体接口或方法控制。
适用场景
- 服务器级别的全局访问控制。
- 与 spring boot 应用无关的基础设施防护。
6. 基于interceptor的ip白名单
优点
- 与 spring mvc 集成良好:由于拦截器是 spring mvc 的一部分,因此它能够很好地集成到现有的 spring boot 应用程序中。
- 适用于控制器级别的过滤:对于那些希望基于控制器或 api 级别进行 ip 访问控制的应用来说,这是一个理想的选择。
- 灵活性高:可以根据不同的 url 模式应用不同的拦截规则,使得可以在不同的场景下灵活运用。
缺点
- 不适合全局过滤:对于不在控制器中的资源(例如静态资源),可能无法有效拦截。如果需要对整个应用程序实施 ip 白名单策略,则可能不是最佳选择。
- 性能开销:虽然拦截器的性能开销相对较小,但在高并发情况下,仍然需要注意其对系统性能的影响。
适用场景
- 需要对特定控制器或 api 进行 ip 访问控制的应用:比如某些敏感的操作只能由特定的 ip 地址执行,这时可以使用拦截器来限制访问。
- 已构建了复杂的 spring mvc 应用程序的项目:如果您的应用程序已经大量使用了 spring mvc 的特性,那么使用拦截器将是一个自然且易于维护的选择。
- 轻量级的 ip 白名单需求:当您只需要简单的 ip 白名单功能而不希望引入如 spring security 等较重的安全框架时,拦截器提供了一个轻便的解决方案。
6. 技术选型对比表
| 技术方案 | 优点 | 缺点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 自定义 filter | 简单直接,灵活性高 | 需手动处理 ip 获取逻辑 | 轻量级项目或动态白名单需求 |
| spring security | 与安全框架集成,配置灵活 | 配置复杂,不支持通配符 | 已使用 spring security 的项目 |
| aop | 细粒度控制,解耦业务逻辑 | 性能开销,ip 获取复杂 | 特定方法或类的访问控制 |
| 动态白名单 | 灵活,适合生产环境 | 实现复杂,依赖数据库性能 | 多租户系统或动态管理需求 |
| 基于 interceptor | 与 spring mvc 集成良好,适用于控制器层面的过滤 | 不适合全局过滤,如静态资源等 | 控制器级别的 ip 访问控制 |
| linux 防火墙 | 高性能,简单高效 | 不可动态更新,缺乏灵活性 | 服务器级别全局控制 |
三、完整实现方案
3.1 自定义 filter 实现 ip 白名单
1.1 添加依赖
spring boot 默认支持 servlet api,无需额外依赖。
1.2 创建配置文件
在 application.yml 中配置白名单:
ip: whitelist: "192.168.1.1, 192.168.1.2"
1.3 创建 filter 类
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.component;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.httpservletrequest;
import javax.servlet.http.httpservletresponse;
import java.io.ioexception;
import java.util.arrays;
import java.util.list;
/**
* 自定义 ip 白名单 filter
* 作用:拦截请求,检查客户端 ip 是否在白名单中
*/
@component
public class ipwhitelistfilter implements filter {
@value("${ip.whitelist}")
private string whiteliststr;
// 用于存储白名单的 list
private list<string> whitelist;
/**
* 初始化白名单
*/
@override
public void init(filterconfig filterconfig) {
whitelist = arrays.stream(whiteliststr.split(","))
.map(string::trim)
.collect(java.util.stream.collectors.tolist());
}
/**
* 处理请求
*/
@override
public void dofilter(servletrequest request, servletresponse response, filterchain chain)
throws ioexception, servletexception {
httpservletrequest httprequest = (httpservletrequest) request;
httpservletresponse httpresponse = (httpservletresponse) response;
string clientip = getclientip(httprequest); // 获取真实 ip
if (whitelist.contains(clientip)) {
chain.dofilter(request, response); // ip 在白名单中,放行
} else {
httpresponse.senderror(httpservletresponse.sc_forbidden, "ip 未授权访问");
}
}
/**
* 获取客户端真实 ip(支持代理服务器)
*/
private string getclientip(httpservletrequest request) {
// 从 x-forwarded-for 头获取真实 ip
string ip = request.getheader("x-forwarded-for");
if (ip == null || ip.isempty() || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ip)) {
ip = request.getremoteaddr(); // 如果没有代理,直接获取远程地址
}
return ip;
}
@override
public void destroy() {
// 清理资源
}
}
1.4 注册 filter(可选)
如果未使用 @component 注解,可通过配置类注册:
@configuration
public class filterconfig {
@bean
public filterregistrationbean<ipwhitelistfilter> ipwhitelistfilter(ipwhitelistfilter filter) {
filterregistrationbean<ipwhitelistfilter> registration = new filterregistrationbean<>(filter);
registration.addurlpatterns("/*"); // 拦截所有请求
return registration;
}
}
3.2 spring security 实现 ip 白名单
2.1 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactid>
</dependency>
2.2 配置白名单
在 application.yml 中配置白名单:
ip: whitelist: "192.168.1.1, 192.168.1.2"
2.3 创建 security 配置类
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.httpsecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.websecurityconfigureradapter;
import java.util.arrays;
@configuration
public class securityconfig extends websecurityconfigureradapter {
@value("${ip.whitelist}")
private string[] whitelist;
@override
protected void configure(httpsecurity http) throws exception {
http
.authorizerequests()
.antmatchers("/**")
.access("hasipaddress('192.168.1.1') or hasipaddress('192.168.1.2')") // 支持多个 ip
.and()
.csrf().disable(); // 关闭 csrf 保护
}
}
3.3 aop 实现 ip 白名单
3.1 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactid>
</dependency>
3.2 创建自定义注解
import java.lang.annotation.elementtype;
import java.lang.annotation.retention;
import java.lang.annotation.retentionpolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.target;
/**
* 自定义注解,标记需要 ip 白名单保护的方法
*/
@target(elementtype.method)
@retention(retentionpolicy.runtime)
public @interface ipwhitelist {
}
3.3 创建 aop 切面类
import org.aspectj.lang.proceedingjoinpoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.aspect;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.requestcontextholder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.servletrequestattributes;
import javax.servlet.http.httpservletrequest;
import java.io.ioexception;
import java.util.arrays;
import java.util.list;
/**
* aop 切面类:检查 ip 是否在白名单中
*/
@aspect
@component
public class ipwhitelistaspect {
@value("${ip.whitelist}")
private string whiteliststr;
private list<string> whitelist;
public ipwhitelistaspect() {
// 初始化白名单
whitelist = arrays.stream(whiteliststr.split(","))
.map(string::trim)
.collect(java.util.stream.collectors.tolist());
}
/**
* 切面逻辑:在方法执行前检查 ip
*/
@around("@annotation(ipwhitelist)")
public object checkip(proceedingjoinpoint joinpoint) throws throwable {
httpservletrequest request = ((servletrequestattributes) requestcontextholder.currentrequestattributes()).getrequest();
string clientip = getclientip(request);
if (whitelist.contains(clientip)) {
return joinpoint.proceed(); // ip 在白名单中,继续执行方法
} else {
throw new accessdeniedexception("ip 未授权访问");
}
}
/**
* 获取客户端真实 ip(支持代理服务器)
*/
private string getclientip(httpservletrequest request) {
string ip = request.getheader("x-forwarded-for");
if (ip == null || ip.isempty() || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ip)) {
ip = request.getremoteaddr();
}
return ip;
}
}
3.4 在方法上使用注解
@restcontroller
public class democontroller {
@ipwhitelist
@getmapping("/api/test")
public string test() {
return "access granted";
}
}
3.4 动态白名单(数据库 + 缓存)
4.1 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactid>
</dependency>
4.2 创建数据库表
create table sys_ip_whitelist (
id int primary key auto_increment,
ip varchar(45) not null
);
4.3 创建实体类
import jakarta.persistence.*;
@entity
@table(name = "sys_ip_whitelist")
public class sysipwhitelist {
@id
@generatedvalue(strategy = generationtype.identity)
private long id;
private string ip;
// getters and setters
}
4.4 创建 mapper 接口
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.jparepository;
public interface sysipwhitelistrepository extends jparepository<sysipwhitelist, long> {
sysipwhitelist findbyip(string ip);
}
4.5 创建 service 类
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.service;
import java.util.list;
import java.util.concurrent.timeunit;
@service
public class whitelistservice {
@autowired
private sysipwhitelistrepository repository;
// 使用 redis 缓存白名单(示例代码)
@autowired
private redistemplate<string, object> redistemplate;
private static final string white_list_key = "ip:white_list";
/**
* 检查 ip 是否在白名单中(支持缓存)
*/
public boolean iswhitelisted(string ip) {
// 先查缓存
list<string> cachedlist = (list<string>) redistemplate.opsforvalue().get(white_list_key);
if (cachedlist != null && cachedlist.contains(ip)) {
return true;
}
// 再查数据库
sysipwhitelist entity = repository.findbyip(ip);
if (entity != null) {
// 更新缓存
list<string> list = repository.findall().stream().map(sysipwhitelist::getip).collect(collectors.tolist());
redistemplate.opsforvalue().set(white_list_key, list, 1, timeunit.minutes);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
4.6 在 filter 或 aop 中调用 service
@autowired
private whitelistservice whitelistservice;
// 在 dofilter 或 checkip 方法中调用
if (!whitelistservice.iswhitelisted(clientip)) {
response.senderror(httpservletresponse.sc_forbidden, "ip 未授权访问");
}
3.5 linux 防火墙实现 ip 白名单
5.1 安装 iptables
sudo apt update sudo apt install iptables
5.2 配置白名单规则
# 允许白名单 ip sudo iptables -a input -s 192.168.1.1 -j accept sudo iptables -a input -s 192.168.1.2 -j accept # 拒绝其他所有 ip sudo iptables -a input -j drop
5.3 保存规则(可选)
# 安装保存工具 sudo apt install iptables-persistent # 保存规则 sudo netfilter-persistent save
3.6 基于interceptor的ip白名单
1. 项目初始化与依赖配置
首先创建一个标准的spring boot项目,添加必要依赖:
<dependencies>
<!-- spring boot starter web -->
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactid>
</dependency>
<!-- lombok简化代码 -->
<dependency>
<groupid>org.projectlombok</groupid>
<artifactid>lombok</artifactid>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<!-- 配置处理 -->
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactid>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2. ip白名单配置设计
创建配置类ipwhitelistproperties:
@configurationproperties(prefix = "security.ip.whitelist")
@data
public class ipwhitelistproperties {
/**
* 是否启用ip白名单功能
*/
private boolean enabled = false;
/**
* 全局ip白名单列表
*/
private list<string> globalallowedips = new arraylist<>();
/**
* 监控模式:true-只记录不拦截,false-实际拦截
*/
private boolean monitormode = false;
/**
* 允许的ip段,支持cidr表示法
*/
private list<string> allowedipranges = new arraylist<>();
}
对应的application.yml配置示例:
security:
ip:
whitelist:
enabled: true
global-allowed-ips:
- 192.168.1.100
- 172.16.0.50
allowed-ip-ranges:
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 192.168.0.0/16
monitor-mode: false
3. ip工具类实现
创建iputils工具类处理ip相关逻辑:
public class iputils {
private static final string unknown = "unknown";
private static final string localhost_ipv4 = "127.0.0.1";
private static final string localhost_ipv6 = "0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1";
/**
* 获取客户端真实ip地址
*/
public static string getclientip(httpservletrequest request) {
string ip = request.getheader("x-forwarded-for");
if (stringutils.isempty(ip) || unknown.equalsignorecase(ip)) {
ip = request.getheader("proxy-client-ip");
}
if (stringutils.isempty(ip) || unknown.equalsignorecase(ip)) {
ip = request.getheader("wl-proxy-client-ip");
}
if (stringutils.isempty(ip) || unknown.equalsignorecase(ip)) {
ip = request.getremoteaddr();
}
// 处理多级代理情况
if (ip != null && ip.contains(",")) {
ip = ip.substring(0, ip.indexof(",")).trim();
}
return localhost_ipv6.equals(ip) ? localhost_ipv4 : ip;
}
/**
* 检查ip是否匹配cidr表示法的ip段
*/
public static boolean isipinrange(string ip, string cidr) {
// 实现细节...
}
/**
* 验证ip地址格式
*/
public static boolean isvalidip(string ip) {
// 实现细节...
}
}
4. 自定义注解设计
创建@ipwhitelist注解支持方法级别的控制:
@target({elementtype.method, elementtype.type})
@retention(retentionpolicy.runtime)
@documented
public @interface ipwhitelist {
/**
* 是否启用ip白名单检查
*/
boolean enabled() default true;
/**
* 特定于该接口的允许ip列表
*/
string[] allowedips() default {};
/**
* 特定于该接口的允许ip段(cidr)
*/
string[] allowedipranges() default {};
/**
* 拒绝时的错误消息
*/
string message() default "access denied by ip whitelist";
}
5. 拦截器核心实现
创建ipwhitelistinterceptor拦截器:
@requiredargsconstructor
public class ipwhitelistinterceptor implements handlerinterceptor {
private final ipwhitelistproperties properties;
private final objectmapper objectmapper;
@override
public boolean prehandle(httpservletrequest request, httpservletresponse response, object handler) throws exception {
if (!properties.isenabled()) {
return true;
}
// 处理handlermethod情况
if (!(handler instanceof handlermethod)) {
return true;
}
handlermethod handlermethod = (handlermethod) handler;
method method = handlermethod.getmethod();
// 检查类和方法上的注解
ipwhitelist classannotation = handlermethod.getbeantype().getannotation(ipwhitelist.class);
ipwhitelist methodannotation = method.getannotation(ipwhitelist.class);
// 如果都没有注解,则跳过检查
if (classannotation == null && methodannotation == null) {
return true;
}
// 合并注解配置
boolean enabled = methodannotation != null ? methodannotation.enabled() :
classannotation.enabled();
string[] allowedips = methodannotation != null && methodannotation.allowedips().length > 0 ?
methodannotation.allowedips() :
classannotation != null ? classannotation.allowedips() : new string[0];
string[] allowedipranges = methodannotation != null && methodannotation.allowedipranges().length > 0 ?
methodannotation.allowedipranges() :
classannotation != null ? classannotation.allowedipranges() : new string[0];
string message = methodannotation != null ? methodannotation.message() :
classannotation != null ? classannotation.message() : "access denied by ip whitelist";
if (!enabled) {
return true;
}
string clientip = iputils.getclientip(request);
// 检查全局白名单
boolean isallowed = properties.getglobalallowedips().contains(clientip) ||
properties.getallowedipranges().stream()
.anymatch(range -> iputils.isipinrange(clientip, range));
// 检查注解指定的白名单
if (!isallowed) {
isallowed = arrays.stream(allowedips).anymatch(ip -> ip.equals(clientip)) ||
arrays.stream(allowedipranges)
.anymatch(range -> iputils.isipinrange(clientip, range));
}
if (!isallowed) {
if (properties.ismonitormode()) {
log.warn("ip whitelist monitor mode triggered. denied ip: {}", clientip);
return true;
}
response.setcontenttype(mediatype.application_json_value);
response.setstatus(httpstatus.forbidden.value());
response.getwriter().write(objectmapper.writevalueasstring(
map.of(
"code", 403,
"message", message,
"data", null
)
));
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
6. 拦截器注册配置
创建web配置类注册拦截器:
@configuration
@requiredargsconstructor
public class webconfig implements webmvcconfigurer {
private final ipwhitelistproperties ipwhitelistproperties;
private final objectmapper objectmapper;
@override
public void addinterceptors(interceptorregistry registry) {
if (ipwhitelistproperties.isenabled()) {
registry.addinterceptor(new ipwhitelistinterceptor(ipwhitelistproperties, objectmapper))
.addpathpatterns("/**")
.order(ordered.highest_precedence); // 设置最高优先级
}
}
}
7. 控制器示例
创建测试控制器验证功能:
@restcontroller
@requestmapping("/api")
public class testcontroller {
@getmapping("/public")
public string publicapi() {
return "this is a public api";
}
@ipwhitelist
@getmapping("/secure")
public string secureapi() {
return "this is a secure api with ip whitelist";
}
@ipwhitelist(
allowedips = {"192.168.1.100", "172.16.0.50"},
allowedipranges = {"10.0.0.0/8"},
message = "custom ip restriction"
)
@getmapping("/custom")
public string customapi() {
return "this api has custom ip whitelist rules";
}
}
3.7 注意事项
ip 获取问题:
- 如果使用 nginx 等反向代理,需从
x-forwarded-for头获取真实 ip。 - 示例代码已处理代理逻辑。
- 如果使用 nginx 等反向代理,需从
通配符支持:
- 如果需要支持 cidr 格式(如
192.168.1.0/24),需自行实现 cidr 匹配逻辑。
- 如果需要支持 cidr 格式(如
性能优化:
- 动态白名单建议使用缓存(如 redis)减少数据库查询。
- 高并发场景下,filter 或 aop 的性能开销需评估。
安全性:
- 确保白名单逻辑不被绕过(如伪造
x-forwarded-for头)。 - 结合其他安全措施(如 https、jwt)增强防护。
- 确保白名单逻辑不被绕过(如伪造
四、进阶实现:基于spring security的专业方案
4.1 spring security集成概述
对于企业级应用,使用spring security可以提供更专业的安全控制。我们将基于前面的基础实现,重构为spring security方案。
添加spring security依赖:
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactid>
</dependency>
4.2 自定义authenticationfilter
创建ipauthenticationfilter:
public class ipauthenticationfilter extends onceperrequestfilter {
private final ipwhitelistproperties properties;
private final objectmapper objectmapper;
@override
protected void dofilterinternal(httpservletrequest request, httpservletresponse response, filterchain filterchain)
throws servletexception, ioexception {
// 获取请求路径对应的handlermethod
handlerexecutionchain handlerexecutionchain = null;
try {
handlerexecutionchain = ((dispatcherservlet) request.getattribute(dispatcherservlet.class.getname() + ".context"))
.gethandler(request);
} catch (exception e) {
filterchain.dofilter(request, response);
return;
}
if (handlerexecutionchain == null || !(handlerexecutionchain.gethandler() instanceof handlermethod)) {
filterchain.dofilter(request, response);
return;
}
handlermethod handlermethod = (handlermethod) handlerexecutionchain.gethandler();
// 后续逻辑与interceptor类似...
}
}
4.3 安全配置类
创建安全配置类:
@configuration
@enablewebsecurity
@requiredargsconstructor
public class securityconfig extends websecurityconfigureradapter {
private final ipwhitelistproperties ipwhitelistproperties;
private final objectmapper objectmapper;
@override
protected void configure(httpsecurity http) throws exception {
http
.csrf().disable()
.addfilterbefore(new ipauthenticationfilter(ipwhitelistproperties, objectmapper),
usernamepasswordauthenticationfilter.class)
.authorizerequests()
.antmatchers("/api/public").permitall()
.anyrequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formlogin().disable()
.httpbasic().disable();
}
}
4.4 基于表达式的安全控制
spring security支持使用@preauthorize注解实现更灵活的控制:
@restcontroller
@requestmapping("/api/v2")
public class securecontroller {
@preauthorize("@ipsecurityservice.isallowed(#request)")
@getmapping("/expression")
public string expressionbasedapi(httpservletrequest request) {
return "this api uses expression-based ip control";
}
}
@service
public class ipsecurityservice {
public boolean isallowed(httpservletrequest request) {
// 实现ip检查逻辑
return true;
}
}
五、生产级增强功能
5.1 动态ip白名单管理
实现动态更新白名单而不重启应用:
@service
public class dynamicipwhitelistservice {
private final list<string> dynamicallowedips = new copyonwritearraylist<>();
private final list<string> dynamicallowedipranges = new copyonwritearraylist<>();
public synchronized void addallowedip(string ip) {
if (iputils.isvalidip(ip) && !dynamicallowedips.contains(ip)) {
dynamicallowedips.add(ip);
}
}
public synchronized void removeallowedip(string ip) {
dynamicallowedips.remove(ip);
}
public synchronized void reloadips(list<string> ips) {
dynamicallowedips.clear();
dynamicallowedips.addall(ips.stream()
.filter(iputils::isvalidip)
.collect(collectors.tolist()));
}
// 类似方法实现ip段管理...
}
5.2 结合redis的分布式ip白名单
对于分布式系统,白名单需要集中存储:
@configuration
public class redisipwhitelistconfig {
@bean
public redistemplate<string, string> ipwhitelistredistemplate(redisconnectionfactory factory) {
redistemplate<string, string> template = new redistemplate<>();
template.setconnectionfactory(factory);
template.setkeyserializer(new stringredisserializer());
template.setvalueserializer(new stringredisserializer());
return template;
}
}
@service
@requiredargsconstructor
public class redisipwhitelistservice {
private static final string whitelist_key = "ip:whitelist";
private static final string whitelist_ranges_key = "ip:whitelist:ranges";
private final redistemplate<string, string> redistemplate;
public boolean isallowed(string ip) {
// 检查精确ip
boolean ismember = redistemplate.opsforset().ismember(whitelist_key, ip);
if (boolean.true.equals(ismember)) {
return true;
}
// 检查ip段
set<string> ranges = redistemplate.opsforset().members(whitelist_ranges_key);
if (ranges != null) {
return ranges.stream().anymatch(range -> iputils.isipinrange(ip, range));
}
return false;
}
// 其他管理方法...
}
5.3 性能优化与缓存
实现本地缓存减少远程调用:
@service
public class cachedipwhitelistservice {
private final loadingcache<string, boolean> ipcheckcache;
public cachedipwhitelistservice(redisipwhitelistservice redisservice) {
this.ipcheckcache = caffeine.newbuilder()
.maximumsize(10_000)
.expireafterwrite(5, timeunit.minutes)
.build(redisservice::isallowed);
}
public boolean isallowed(string ip) {
return boolean.true.equals(ipcheckcache.get(ip));
}
}
六、测试策略与验证
6.1 单元测试
针对核心工具类编写单元测试:
class iputilstest {
@test
void testisipinrange() {
asserttrue(iputils.isipinrange("192.168.1.100", "192.168.1.0/24"));
assertfalse(iputils.isipinrange("10.0.0.5", "192.168.1.0/24"));
}
@test
void testgetclientip() {
// 模拟httpservletrequest测试各种头部情况
}
}
6.2 集成测试
使用mockmvc测试完整流程:
@springboottest
@autoconfiguremockmvc
class ipwhitelistintegrationtest {
@autowired
private mockmvc mockmvc;
@test
@withmockuser
void testpublicapi() throws exception {
mockmvc.perform(get("/api/public"))
.andexpect(status().isok());
}
@test
@withmockuser
void testsecureapiwithallowedip() throws exception {
mockmvc.perform(get("/api/secure").with(request -> {
request.setremoteaddr("192.168.1.100");
return request;
}))
.andexpect(status().isok());
}
@test
@withmockuser
void testsecureapiwithdeniedip() throws exception {
mockmvc.perform(get("/api/secure").with(request -> {
request.setremoteaddr("10.1.2.3");
return request;
}))
.andexpect(status().isforbidden());
}
}
6.3 性能测试
使用jmeter模拟不同负载下的表现:
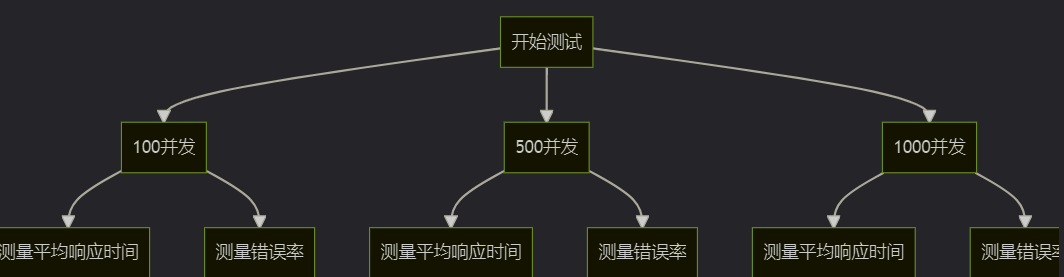
七、生产环境最佳实践
7.1 安全建议
- 最小权限原则:只添加必要的ip到白名单
- 定期审计:每月审查白名单,移除不再需要的ip
- 日志记录:详细记录所有被拒绝的访问尝试
- 监控告警:对异常访问模式设置告警
- 备份机制:定期备份白名单配置
7.2 性能调优
- 缓存策略:对ip检查结果进行适当缓存
- 异步检查:对于非关键路径可以考虑异步验证
- cidr优化:将ip段检查算法优化为o(1)复杂度
- 并发控制:使用线程安全的数据结构
- 预热机制:应用启动时预加载常用ip
7.3 故障排查指南
常见问题及解决方案:
| 问题现象 | 可能原因 | 解决方案 |
|---|---|---|
| 合法ip被拒绝 | ip获取不正确 | 检查x-forwarded-for等头部配置 |
| 白名单修改后不生效 | 缓存未刷新 | 实现配置变更通知机制 |
| 性能下降 | ip检查成为瓶颈 | 引入缓存、优化算法或水平扩展 |
| 分布式环境不一致 | 各节点白名单不同步 | 使用集中式存储如redis |
| ipv6支持问题 | 只配置了ipv4 | 确保同时支持ipv4和ipv6格式 |
八、扩展与演进
8.1 结合微服务架构
在spring cloud体系中,可以在网关层统一实现ip白名单:
@bean
public routelocator customroutelocator(routelocatorbuilder builder) {
return builder.routes()
.route("secure-service", r -> r.path("/api/secure/**")
.filters(f -> f.filter(new ipwhitelistgatewayfilter()))
.uri("lb://secure-service"))
.build();
}
8.2 kubernetes环境适配
在k8s中需要考虑pod ip动态变化的问题:
apiversion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: networkpolicy
metadata:
name: api-whitelist
spec:
podselector:
matchlabels:
app: spring-boot-app
ingress:
- from:
- ipblock:
cidr: 192.168.1.0/24
ports:
- protocol: tcp
port: 8080
8.3 未来演进方向
- 机器学习分析:自动识别异常ip并动态调整白名单
- 区块链存证:将白名单变更记录上链确保不可篡改
- 零信任整合:与零信任架构深度集成
- iot扩展:支持设备指纹等更多维度的认证
- 量子安全:为后量子时代提前准备加密方案
九、总结与展望
本文详细探讨了在spring boot应用中实现ip白名单控制的多种方案,从基础的interceptor实现到基于spring security的专业方案,再到生产级的增强功能和分布式环境适配。通过本教程,您应该能够:
- 深入理解ip白名单的原理和价值
- 掌握在spring boot中实现ip控制的多种技术
- 具备构建生产级ip白名单系统的能力
- 了解相关的最佳实践和优化策略
ip白名单作为网络安全的基础设施之一,在云原生和微服务架构不断演进的今天,仍然发挥着不可替代的作用。未来,随着边缘计算和5g技术的普及,ip白名单技术可能会与更多新兴技术融合,形成更智能、更灵活的访问控制体系。
到此这篇关于springboot中ip白名单控制实现限制接口访问的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关springboot ip白名单 内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论