1.前言
接口请求重试机制是保证系统稳定性和容错能力的重要手段之一。当接口请求发生失败或暂时性错误时,通过重试机制可以提高请求的成功率。本文将详细介绍接口请求重试机制的几种常见方法。
2.几种方法
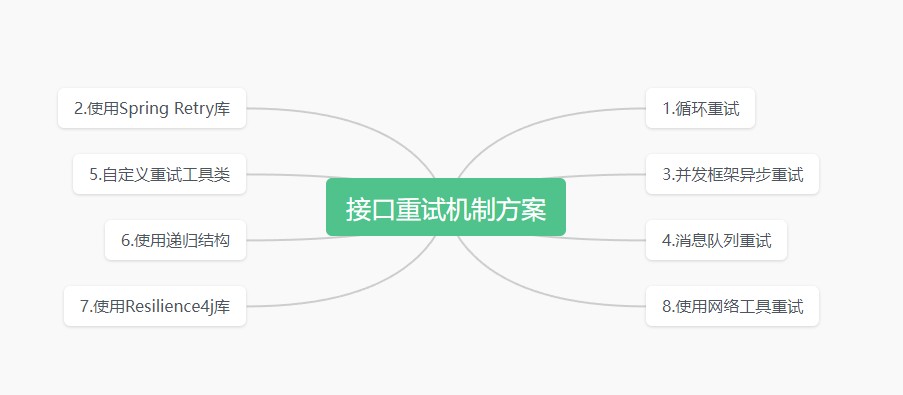
2.1循环重试
它的基本思路是:
- 定义重试次数,如最大重试5次
- 发送请求,如果失败则进入重试逻辑
- 在循环内部,记录当前已重试次数,如当前已重试2次
- 判断当前重试次数是否达到最大次数,如果达到则终止循环,否则进行重试
- 在循环内部,可以添加定时重试间隔,也可以使用指数退避算法
- 发送重试请求,重复判断是否成功,直到成功、达到最大次数或其他终止条件
示例
public class retry {
private static final int max_retries = 5;
public static response request() throws exception {
int retries = 0;
while (true) {
try {
// 发送请求,返回响应
response response = httpclient.sendrequest();
// 请求成功则返回响应
if (response.issuccess()) {
return response;
}
} catch (exception e) {
// 请求失败进行重试
}
// 判断是否超过最大重试次数
if (++retries >= max_retries) {
throw new exception("exceeded max retries");
}
// 增加间隔后重试
int interval = (int) (math.random() * 1000);
thread.sleep(interval);
}
}
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
response response = request();
// ...
}
}
2.2 使用spring retry库
使用 spring retry 库可以很方便地实现接口请求的重试机制。
2.2.1 添加 maven 依赖
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.retry</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-retry</artifactid>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
2.2.2 添加 @enableretry 注解启用重试功能
2.2.3 在需要重试的方法上添加 @retryable 注解
@retryable(value = exception.class, maxattempts = 3, backoff = @backoff(delay = 5000))
public user getuser(string id) {
// 远程调用接口
}
@retryable 定义了重试规则:- value - 重试的异常类型
- maxattempts - 最大重试次数
- backoff - 重试等待策略
2.2.4. 还可以自定义 retrytemplate 进行更复杂的重试控制
retrytemplate template = new retrytemplate();
template.execute(context -> {
// 可在此处自定义重试逻辑
return remoteclient.invoke();
});
spring retry 为接口请求重试提供了完善和易用的解决方案,可以灵活控制各种重试参数,适用于复杂系统的容错要求。
2.3 并发框架异步重试
使用并发框架的异步请求方式可以较简单地实现接口请求的重试机制。以completablefuture为例:
2.3.1 发送请求使用completablefuture封装:
completablefuture<response> future = completablefuture.supplyasync(() -> {
return service.call();
});
2.3.2 当请求失败时,使用retryasync自动完成重试:
future = future.exceptionally(e -> {
return service.retryasync();
});
2.3.3 可以链式调用,自定义重试逻辑:
future
.exceptionally(e -> {
// 处理异常
})
.thenapplyasync(resp -> {
// 处理响应
})
.retryasync(retrycount, delay);
主要优点是:
- 线程安全的异步请求
- 自动重试失败任务
- 简洁的链式编程方式
- 避免阻塞主线程
使用并发框架可以便捷地实现异步重试机制,提高系统容错性。其他框架如rxjava也有类似的重试机制。
2.4 消息队列重试
使用消息队列可以实现接口请求的异步重试机制。
基本思路是:
- 接口请求发送失败后,将请求信息封装为消息,发送到请求重试的队列中。
- 消息消费者从队列中获取失败的请求,根据策略进行重试。
- 重复重试直到成功、重试次数用尽或其他终止条件。
- 成功后将消息移除队列,失败则保留消息供再次重试。
主要步骤:
- 创建请求重试队列,如“request.retry.queue”
- 接口请求失败后,生成重试消息,发送到队列
- 消费者启动线程从队列中取消息重试
- 根据重试策略进行定时重试或最大重试数
- 成功则确认消息,失败则重新入队
使用消息队列进行重试有利于:
- 异步重试,不阻塞主线程
- 可靠地完成重试任务
- 灵活控制重试策略
示例
// 1. 创建队列
queue retryqueue = new queue("request.retry.queue");
// 2. 请求失败,发送重试消息
public void request() {
try {
// 调用接口
httpclient.post(url, payload);
} catch (exception e) {
// 发送重试消息
message msg = new message(url, payload, maxretries);
retryqueue.send(msg);
}
}
// 3. 消费者线程进行重试
class retryconsumer implements runnable {
public void run() {
while (true) {
message msg = retryqueue.take();
for (int i = 0; i < msg.getmaxretries(); i++) {
try {
// 重试请求
httpclient.post(msg.geturl(), msg.getpayload());
// 请求成功,结束循环
break;
} catch (exception e) {
// 等待后继续重试
}
}
// 重试完成后,确认消息
retryqueue.confirm(msg);
}
}
}
这就是使用消息队列实现接口重试的基本流程,可以根据需求扩展重试策略、异常处理等逻辑。
2.5 自定义重试工具类
使用自定义的重试工具类来实现接口请求的重试机制,提高代码的复用性和可维护性。
重试工具类的实现思路:
- 提供重试方法,参数包括请求函数、重试策略等
- 在重试方法内部执行循环请求
- 每次请求失败时,根据策略等待一段时间
- 记录当前重试次数,与最大次数比较
- 请求成功或者达到最大重试次数则结束循环
示例:
public class retryutil {
public static <t> t retry(retrycallable<t> callable, retrypolicy policy) {
int retries = 0;
while(true) {
try {
return callable.call();
} catch(exception e) {
if (retries >= policy.maxretries) {
throw e;
}
// 等待
policy.delay();
// 重试次数加1
retries++;
}
}
}
}
// 执行请求的函数接口
interface retrycallable<t> {
t call();
}
// 重试策略
class retrypolicy {
int maxretries;
int delay;
}
// 使用示例
retryutil.retry(() -> {
// 接口请求
return httpclient.get(url);
}, policy);
这样可以提高重试相关逻辑的复用性,避免写重复代码。
2.6 使用递归结构
使用递归结构也可以实现接口请求的重试机制。
基本思路是设计一个递归函数,在函数内部发送请求,如果失败则继续递归调用自身再次重试。
示例:
public class retryrequest {
private static final int max_retries = 3;
public static response request(int retries) {
try {
// 发送请求
response response = httpclient.get("http://example.com");
return response;
} catch (exception e) {
// 处理异常
// 判断是否需要重试
if (retries < max_retries) {
// 增加重试次数
retries++;
// 延迟1秒钟
thread.sleep(1000);
// 递归调用自身进行重试
return request(retries);
}
// 重试失败
throw new runtimeexception("request failed after " + max_retries + " retries!");
}
}
public static void main(string[] args) {
response response = request(0);
// 处理响应
}
}
主要逻辑是通过递归不断调用自身来实现重试。优点是逻辑较简单清晰,缺点是递归层次过深时可能会导致堆栈溢出。需要合理设置最大递归深度,也可以通过循环改写递归来避免深层递归。
2.7 使用resilience4j
resilience4j是一个很好的java重试库,可以用它来实现接口请求的重试机制。
主要步骤:
2.7.1添加resilience4j依赖
<dependency> <groupid>io.github.resilience4j</groupid> <artifactid>resilience4j-retry</artifactid> </dependency>
2.7.2 定义重试逻辑
retryconfig config = retryconfig.custom()
.maxattempts(3)
.waitduration(duration.ofmillis(500))
.build();
retry retry = retry.of("backend", config);
2.7.3 使用重试逻辑调用接口
string result = retry.executesupplier(() -> {
// 发送请求
return backendservice.callapi();
});
2.7.4 自定义重试异常predicate
retryconfig config = retryconfig.custom() .retryonexception(e -> isretryable(e)) .build();
resilience4j提供了线程安全的重试 decorator,可以通过配置灵活控制重试策略,很好地支持了接口请求重试。
2.8 使用网络工具重试
我们常用的一些网络工具来做重试
示例
public class retryexample {
private static final int max_retries = 3;
public static string request(string url) throws exception {
int retries = 0;
while (true) {
try {
// 使用httpclient发送请求
return httpclientutils.get(url);
} catch (exception e) {
if (retries >= max_retries) {
throw e;
}
// 增加重试次数
retries++;
// 延迟1秒钟
timeunit.seconds.sleep(1);
}
}
}
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception {
string result = request("http://example.com/api");
system.out.println(result);
}
}
// 网络工具类
class httpclientutils {
public static string get(string url) throws ioexception {
// 发送get请求并返回结果
}
}
主要通过循环和网络工具类来实现重试逻辑,延时控制也可以用random来实现指数退避。这种 utilities + 循环 的组合可以实现灵活可复用的重试机制。
3.注意事项
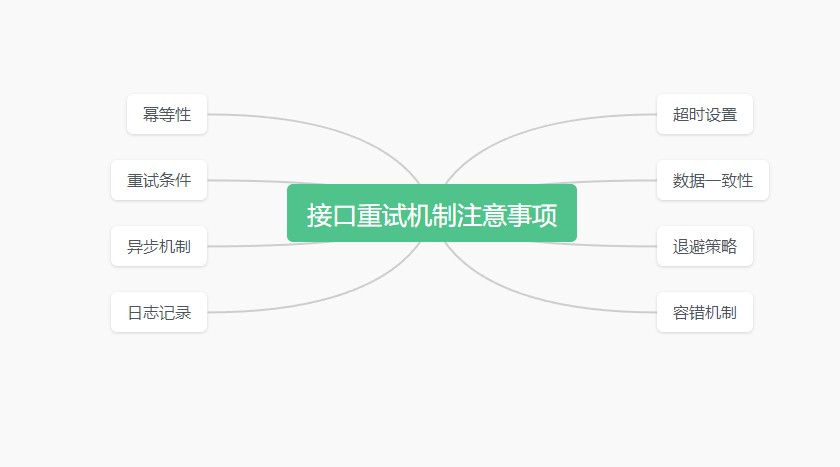
接口请求重试时需要注意以下几点:
3.1 幂等性
接口需要是幂等的,多次调用结果相同,避免重复执行带来副作用。
3.2 资源竞争
重试可能对服务端造成更大压力,需要考虑限流等措施。
3.3 超时设置
合理设置重试最大次数和总超时时间,避免长时间等待。
3.4 重试条件
明确哪些异常情况下需要重试,不能无脑重试所有错误。
3.5 数据一致性
请求成功后要幂等更新状态,避免重复数据。
3.6 异步机制
重试过程不要阻塞主业务线程。
3.7 退避策略
失败后延迟一段时间再重试,可选避免集群重试。
3.8 日志记录
记录重试的次数、错误原因等信息,方便排查问题。
3.9 容错机制
重试失败后的降级处理,避免级联失败。
总结
接口请求重试机制对保证系统高可用非常关键,需要根据业务需求选择合适的重试策略。常用的组合策略包括带最大次数的定时/指数退避重试、故障转移重试等。重试机制需要综合设置以达到容错效果又避免产生过大的系统负载。
到此这篇关于聊聊java中接口重试机制的几种解决方案的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关java接口重试机制内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论