前言
在 oracle 数据库操作中,查询数据是最频繁、最核心的操作之一。单表查询,即仅从一个表中检索信息,是所有复杂查询的基础。本笔记将系统梳理单表查询的关键子句及其用法,并特别介绍oracle中伪列的使用。
思维导图
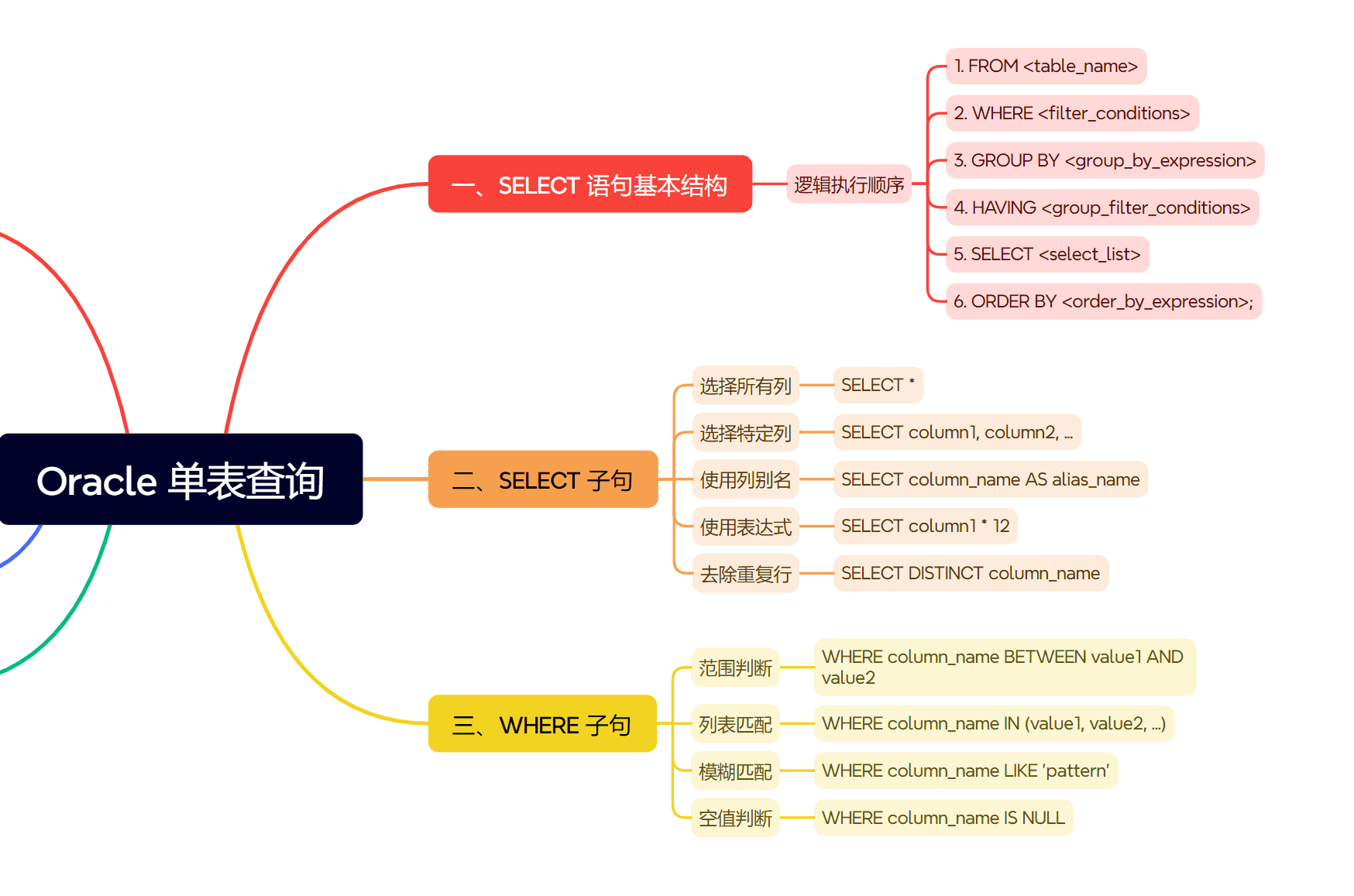
一、select 语句基本结构
一个完整的单表查询语句通常包含以下按执行顺序排列 (逻辑上) 的子句:
select <select_list> -- 5. 选择要显示的列或表达式 from <table_name> -- 1. 指定数据来源表 [where <filter_conditions>] -- 2. 行过滤条件 [group by <group_by_expression>] -- 3. 分组依据 [having <group_filter_conditions>] -- 4. 分组后的过滤条件 [order by <order_by_expression>]; -- 6. 结果排序
- from 子句:最先执行,确定查询的数据源表。
- where 子句:其次执行,根据指定条件筛选满足要求的行。
- group by 子句:在
where过滤后执行,将符合条件的行按一个或多个列的值进行分组。 - having 子句:在
group by分组后执行,用于过滤分组后的结果集 (通常与聚合函数配合使用)。 - select 子句:在上述操作完成后,选择最终要显示的列、表达式或聚合函数结果。
- order by 子句:最后执行,对最终结果集进行排序。
二、select 子句:选择列与表达式
- 选择所有列:
select *
select * from employees;
- 选择特定列:
select column1, column2, ...
select employee_id, first_name, salary from employees;
- 使用列别名 (as): 提高可读性或避免重名。
select employee_id as "员工编号", first_name "名", salary "月薪" from employees; select salary * 12 as annual_salary from employees;
- 计算列/表达式: 可以在
select中进行算术运算、字符串拼接、函数调用等。
select last_name || ', ' || first_name as full_name, salary / 30 as daily_rate from employees; select sysdate - hire_date as days_employed from employees; select upper(first_name) as upper_first_name from employees;
- 去除重复行 (distinct): 只显示唯一的行组合。
select distinct department_id from employees; select distinct department_id, job_id from employees;
- 常量值: 可以在查询结果中包含常量。
select first_name, salary, 'oracle corp' as company_name from employees;
三、from 子句:指定表
对于单表查询,from 子句非常简单,就是指定要查询的那个表名。
from employees;
可以为表指定别名,在单表查询中不常用,但在多表连接或子查询中非常有用。
from employees e;
四、where 子句:行过滤
where 子句用于根据指定的条件筛选出满足要求的行。
常用比较运算符:= (等于), > (大于), < (小于), >= (大于等于), <= (小于等于), <> 或 != (不等于)。
逻辑运算符:and (与), or (或), not (非)。
其他常用条件:
between ... and ...: 范围判断 (包含边界值)。
select first_name, salary from employees where salary between 5000 and 10000;
in (value1, value2, ...): 匹配列表中的任何一个值。
select first_name, department_id from employees where department_id in (10, 20, 30);
like: 模糊匹配字符串。%: 匹配任意数量 (包括零个) 的字符。_: 匹配任意单个字符。escape 'char': 定义转义字符,用于匹配%或_本身。
select first_name from employees where first_name like 'a%'; select last_name from employees where last_name like '_o%'; select note from notes where note like '100\%%' escape '\';
is null/is not null: 判断是否为空值。
select first_name, commission_pct from employees where commission_pct is null;
代码案例:查询薪水大于8000且部门id为90的员工:
select employee_id, first_name, salary, department_id from employees where salary > 8000 and department_id = 90;
查询部门id为10或20,或者职位id以 ‘sa_’ 开头的员工:
select employee_id, department_id, job_id from employees where department_id in (10, 20) or job_id like 'sa\_%';
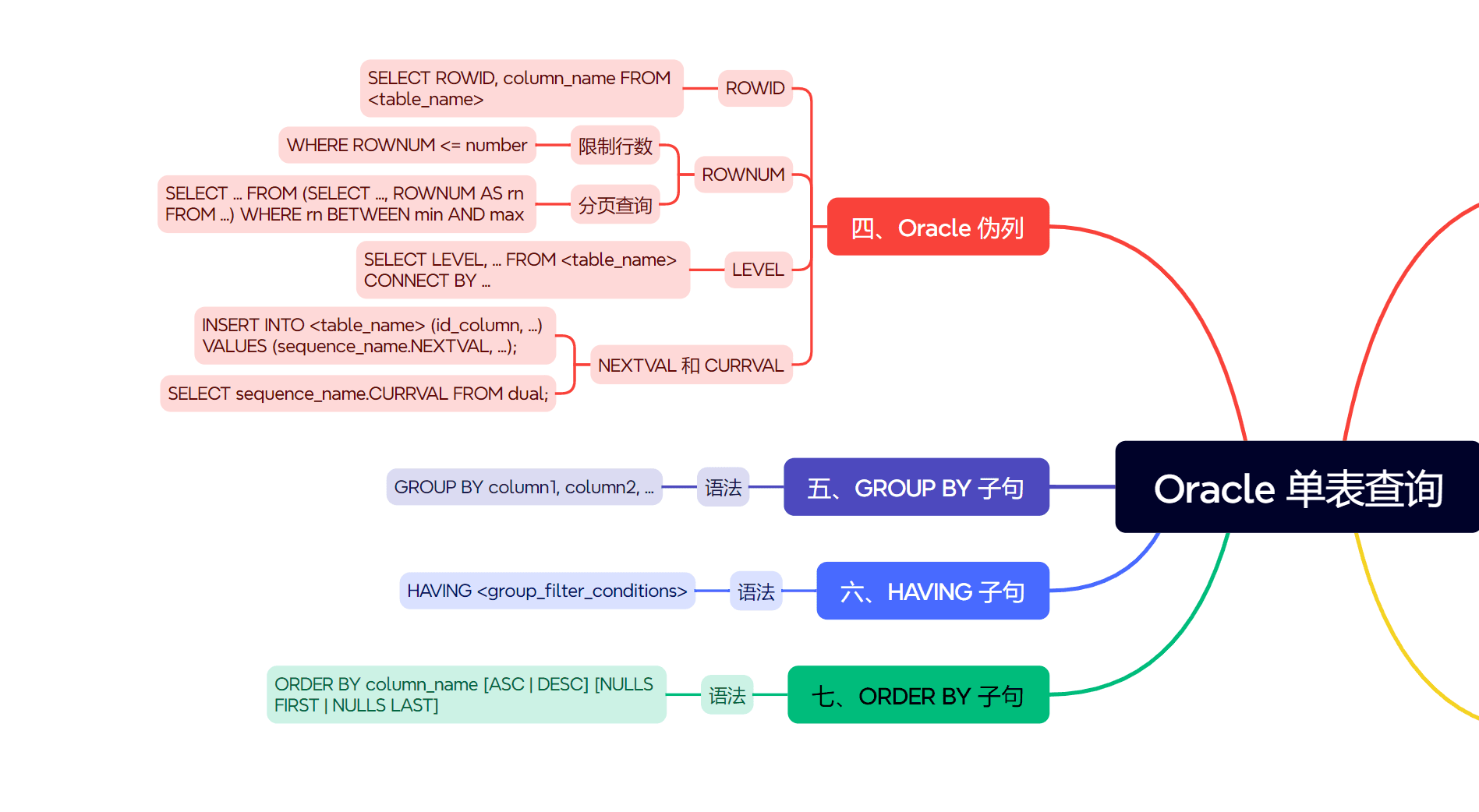
五、oracle 伪列 (pseudocolumns)
oracle 提供了一些特殊的列,它们不实际存储在表中,但可以像普通列一样在sql语句中引用。这些被称为伪列。
常用的伪列:
rowid:- 唯一标识数据库中每一行的物理地址。
- 它是访问表中行的最快方式。
rowid的值看起来像一串十六进制字符。- 虽然唯一,但如果表发生重组或迁移,行的
rowid可能会改变。因此,不建议将其作为持久的行标识符。
select rowid, employee_id, first_name from employees where rownum <= 5;
rownum:- 对于查询返回的每一行,
rownum会按顺序分配一个从1开始的数字。 rownum是在数据被检索出来之后,但在任何order by子句应用之前分配的。- 常用于限制查询结果的行数 (分页查询的基础)。
- 重要:不能直接在
where子句中使用rownum > n(n>1) 来获取第n行之后的数据,因为rownum是逐行分配的。如果第一行不满足rownum > 1,那么就没有第二行可以被分配rownum = 2。
- 对于查询返回的每一行,
-- 获取前5名员工 (基于默认顺序或order by之前的顺序)
select employee_id, first_name, salary from employees where rownum <= 5;
-- 错误的方式尝试获取第6到第10名员工
-- select * from employees where rownum > 5 and rownum <= 10; (通常不会返回任何结果)
-- 正确的分页方式 (使用子查询)
select *
from (select employee_id, first_name, salary, rownum as rn
from (select employee_id, first_name, salary
from employees
order by salary desc)) -- 内层先排序
where rn between 6 and 10;
level:- 与层次查询 (hierarchical queries) 一起使用 (
connect by子句)。 - 表示当前行在层次结构中的级别。根节点为
level 1。
- 与层次查询 (hierarchical queries) 一起使用 (
-- 假设employees表有 manager_id 列,形成层级关系 select level, employee_id, first_name, manager_id from employees start with manager_id is null -- 定义根节点 connect by prior employee_id = manager_id; -- 定义父子关系
nextval和currval(与序列 sequence 相关):sequence_name.nextval: 获取序列的下一个值。每次调用都会使序列递增。sequence_name.currval: 获取序列的当前值 (必须在当前会话中至少调用过一次nextval之后才能使用)。- 常用于在
insert语句中为主键列生成唯一值。
-- 假设存在一个名为 employee_seq 的序列 create sequence employee_seq start with 200 increment by 1; insert into employees (employee_id, first_name, last_name, email) values (employee_seq.nextval, 'new', 'employee', 'new.emp@example.com'); select employee_seq.currval from dual; -- 查看当前会话中序列的当前值
六、group by 子句:数据分组
group by 子句将具有相同值的行组织成一个摘要组。通常与聚合函数 (如 count(), sum(), avg(), max(), min()) 一起使用,对每个组进行计算。
聚合函数: (与之前版本相同)
count(*),count(column_name),count(distinct column_name)sum(column_name),avg(column_name)max(column_name),min(column_name)
使用规则:
select列表中所有未包含在聚合函数中的列,都必须出现在group by子句中。where子句先于group by执行;having子句后于group by执行。
代码案例:查询每个部门的员工人数:
select department_id, count(*) as num_employees from employees group by department_id;
七、having 子句:分组过滤
having 子句用于在数据分组后对分组结果进行进一步筛选。它通常包含聚合函数。
代码案例:查询平均薪水大于8000的部门:
select department_id, avg(salary) as avg_salary from employees group by department_id having avg(salary) > 8000;
八、order by 子句:结果排序
order by 子句用于对最终查询结果集进行排序。它是查询语句中逻辑上最后执行的部分。
排序方式: (与之前版本相同)
asc(升序, 默认),desc(降序)- 多列排序, 列别名排序, 列序号排序 (不推荐)
nulls first/nulls last
代码案例:按薪水降序排列员工信息:
select employee_id, first_name, salary from employees order by salary desc;
总结: 单表查询是 oracle sql 的基石。熟练掌握各子句的功能、用法、执行顺序,以及伪列 (特别是 rownum 和 rowid) 的特性,是编写高效、准确查询的关键。
练习题
背景表:假设我们有一个 products 表,结构如下:
create table products ( product_id number primary key, product_name varchar2(100) not null, category_id number, supplier_id number, unit_price number(10,2), units_in_stock number, discontinued char(1) default 'n' -- 'y' or 'n' ); -- 插入一些样例数据 (请自行补充更多数据以测试所有题目) insert into products values (1, 'chai', 10, 1, 18.00, 39, 'n'); insert into products values (2, 'chang', 10, 1, 19.00, 17, 'n'); insert into products values (3, 'aniseed syrup', 20, 1, 10.00, 13, 'n'); insert into products values (4, 'chef anton''s cajun seasoning', 20, 2, 22.00, 53, 'n'); insert into products values (5, 'chef anton''s gumbo mix', 20, 2, 21.35, 0, 'y'); insert into products values (6, 'grandma''s boysenberry spread', 30, 3, 25.00, 120, 'n'); insert into products values (7, 'northwoods cranberry sauce', 20, 3, 40.00, 6, 'n'); insert into products values (8, 'mishi kobe niku', 40, 4, 97.00, 29, 'y'); insert into products values (9, 'ikura', 40, 4, 31.00, 31, 'n'); insert into products values (10, 'queso cabrales', 40, 5, 21.00, 22, 'n'); commit;
假设 category_id 10=‘beverages’, 20=‘condiments’, 30=‘confections’, 40=‘dairy products’。
请为以下每个场景编写相应的sql查询语句。
题目:
- 查询
products表中所有产品的rowid和product_name。 - 查询
products表中前5条记录的product_id,product_name,unit_price(基于它们在表中的物理存储顺序,不指定特定排序)。 - 查询
products表中按unit_price降序排列后的第3到第5条产品记录的product_name和unit_price。 - 查询每个
category_id下有多少种产品,并为每个类别结果行分配一个行号 (基于category_id的默认分组顺序)。 - 查询所有
category_id为 20 (condiments) 的产品名称和库存量 (units_in_stock),并给product_name列起别名为 “调味品名称”,units_in_stock列起别名为 “当前库存”。 - 查询单价 (
unit_price) 大于等于20且小于50的所有产品信息 (使用between或比较运算符均可)。 - 查询产品名称 (
product_name) 以 “chef anton” 开头的所有产品id和产品名称。 - 统计每个
supplier_id供应的产品中,已停产 (discontinued= ‘y’) 的产品数量。只显示供应了已停产产品的供应商id及其对应的已停产产品数量。 - 查询所有产品信息,并按
category_id升序排序,在同一类别中再按units_in_stock降序排序,并将库存量为null的产品排在最后。 - (与序列相关,假设已创建序列
product_pk_seq) 使用序列product_pk_seq.nextval作为product_id,插入一条新产品记录:product_name=‘new test product’, category_id=10, unit_price=15.00, units_in_stock=100。然后查询该序列的当前值。(只需写insert和查询序列的语句)
答案与解析:
- 查询 rowid 和 product_name:
select rowid, product_name from products;
- 解析:
rowid是一个伪列,可以直接在select列表中引用。
- 查询前5条记录 (基于物理顺序):
select product_id, product_name, unit_price from products where rownum <= 5;
- 解析:
rownum在where子句中用于限制返回的行数。此时的顺序是oracle获取数据的自然顺序,不保证特定排序。
- 分页查询 (排序后取特定范围):
select product_name, unit_price
from (select product_name, unit_price, rownum as rn
from (select product_name, unit_price
from products
order by unit_price desc))
where rn between 3 and 5;
- 解析: 这是oracle分页的标准写法。最内层查询先按价格降序排序,中间层查询为排序后的结果分配
rownum(并赋予别名rn),最外层查询根据rn筛选出第3到第5条记录。
- 分组并为组结果分配行号 (分析函数):(严格来说,为分组结果分配行号通常使用分析函数如
row_number() over(),rownum在group by之后应用是对聚合后的结果行进行编号)
如果题目意图是统计后给结果行编号:
select category_id, count(*) as product_count, rownum as group_row_num from products group by category_id;
- 解析: 先按
category_id分组并用count(*)统计。然后对这个聚合后的结果集中的每一行分配rownum。
如果意图是在每个组内部分配行号,则需要分析函数(超出单表查询基础范围,但可作了解):
-- select product_name, category_id, row_number() over (partition by category_id order by product_name) as rn_in_category -- from products;
- 使用列别名并过滤 (同前):
select product_name as "调味品名称", units_in_stock as "当前库存" from products where category_id = 20;
- 范围查询 (多种写法):使用
between and:
select * from products where unit_price between 20 and 49.99;
使用比较运算符:
select * from products where unit_price >= 20 and unit_price < 50;
- 解析:
between包含边界。如果题目是大于等于20且小于50,则用第二种更精确。
- 模糊查询 (like):
select product_id, product_name from products where product_name like 'chef anton%';
- 解析:
like 'chef anton%'匹配以 “chef anton” 开头的所有字符串。
- 分组统计已停产产品:
select supplier_id, count(*) as discontinued_product_count from products where discontinued = 'y' group by supplier_id having count(*) > 0; -- 或者直接不加having,如果没有已停产的供应商则不会显示
- 解析: 先用
where筛选出已停产产品,然后按supplier_id分组并用count(*)统计。having count(*) > 0确保只显示那些确实有已停产产品的供应商。
- 多列排序与nulls last:
select * from products order by category_id asc, units_in_stock desc nulls last;
- 解析: 先按
category_id升序,再按units_in_stock降序,nulls last确保units_in_stock为null的记录排在每个类别的最后。
- 使用序列插入并查询当前值:(假设序列
product_pk_seq已创建:create sequence product_pk_seq start with 11 increment by 1;)
insert into products (product_id, product_name, category_id, unit_price, units_in_stock) values (product_pk_seq.nextval, 'new test product', 10, 15.00, 100); select product_pk_seq.currval from dual;
- 解析:
product_pk_seq.nextval获取序列的下一个值并用于插入。product_pk_seq.currval从dual表查询当前会话中该序列的当前值 (必须在同一会话中先调用过nextval)。
总结
到此这篇关于oracle数据库查询之单表查询的关键子句及其用法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关oracle单表查询内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!



发表评论