在处理大型文件时(如内存只有4g却要读取8g的文件),我们需要采用特殊的技术来避免内存溢出。以下是几种高效读取大文件的方法。
一、基本方法:逐行读取
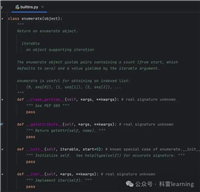
1. 使用文件对象的迭代器
最简单的方法是直接迭代文件对象,python会自动使用缓冲io以高效的方式处理:
with open('large_file.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f: # 逐行读取,内存友好
process_line(line) # 处理每一行
2. 明确使用 readline()
with open('large_file.txt', 'r') as f:
while true:
line = f.readline()
if not line: # 到达文件末尾
break
process_line(line)
二、分块读取方法
对于非文本文件或需要按块处理的情况:
1. 指定缓冲区大小
buffer_size = 1024 * 1024 # 1mb的缓冲区
with open('large_file.bin', 'rb') as f:
while true:
chunk = f.read(buffer_size)
if not chunk: # 文件结束
break
process_chunk(chunk)
2. 使用 iter 和 partial
更pythonic的分块读取方式:
from functools import partial
chunk_size = 1024 * 1024 # 1mb
with open('large_file.bin', 'rb') as f:
for chunk in iter(partial(f.read, chunk_size), b''):
process_chunk(chunk)
三、内存映射文件 (mmap)
对于需要随机访问的大型文件:
import mmap
with open('large_file.bin', 'r+b') as f:
# 创建内存映射
mm = mmap.mmap(f.fileno(), 0)
# 像操作字符串一样操作文件
print(mm[:100]) # 读取前100字节
# 可以搜索内容
index = mm.find(b'some_pattern')
if index != -1:
print(f"found at position {index}")
mm.close() # 记得关闭映射
四、使用生成器处理
将文件处理逻辑封装为生成器:
def read_large_file(file_path, chunk_size=1024*1024):
"""生成器函数,逐块读取大文件"""
with open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
while true:
chunk = f.read(chunk_size)
if not chunk:
break
yield chunk
# 使用生成器
for chunk in read_large_file('huge_file.bin'):
process_chunk(chunk)
五、处理压缩文件
对于大型压缩文件,可以使用流式解压:
1. gzip 文件
import gzip
import shutil
with gzip.open('large_file.gz', 'rb') as f_in:
with open('large_file_extracted', 'wb') as f_out:
shutil.copyfileobj(f_in, f_out) # 流式复制
2. zip 文件
import zipfile
with zipfile.zipfile('large_file.zip', 'r') as z:
with z.open('file_inside.zip') as f:
for line in f:
process_line(line)
六、多线程/多进程处理
对于需要并行处理的情况:
1. 多线程处理不同块
from concurrent.futures import threadpoolexecutor
import os
def process_chunk(start, end, file_path):
"""处理文件的指定部分"""
with open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
f.seek(start)
chunk = f.read(end - start)
# 处理chunk...
def parallel_file_processing(file_path, num_threads=4):
file_size = os.path.getsize(file_path)
chunk_size = file_size // num_threads
with threadpoolexecutor(max_workers=num_threads) as executor:
futures = []
for i in range(num_threads):
start = i * chunk_size
end = start + chunk_size if i != num_threads - 1 else file_size
futures.append(executor.submit(process_chunk, start, end, file_path))
# 等待所有任务完成
for future in concurrent.futures.as_completed(futures):
future.result()
七、使用第三方库
1. dask - 用于超大型数据集
import dask.dataframe as dd
# 创建延迟计算的dataframe
df = dd.read_csv('very_large_file.csv', blocksize=25e6) # 25mb每块
# 执行操作(惰性计算)
result = df.groupby('column').mean().compute() # 实际计算
2. pytables - 处理hdf5格式
import tables
# 打开hdf5文件
h5file = tables.open_file('large_data.h5', mode='r')
# 访问数据集
table = h5file.root.data.table
for row in table.iterrows(): # 迭代访问
process_row(row)
h5file.close()
八、数据库替代方案
对于需要频繁查询的大型数据,考虑使用数据库:
1. sqlite
import sqlite3
# 将数据导入sqlite
conn = sqlite3.connect(':memory:') # 或磁盘数据库
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('create table data (col1, col2, col3)')
# 批量插入数据
with open('large_file.csv') as f:
# 使用生成器避免内存问题
data_gen = (line.strip().split(',') for line in f)
cursor.executemany('insert into data values (?, ?, ?)', data_gen)
conn.commit()
九、性能优化技巧
缓冲区大小选择:
- 通常8kb到1mb之间效果最好
- 可通过实验找到最佳大小
二进制模式 vs 文本模式:
- 二进制模式(
'rb')通常更快 - 文本模式(
'r')需要处理编码,但更方便
- 二进制模式(
操作系统缓存:
- 现代os会自动缓存频繁访问的文件部分
- 多次读取同一大文件时,第二次会快很多
避免不必要的处理:
- 尽早过滤掉不需要的数据
- 使用生成器保持内存效率
十、完整示例:处理超大csv文件
import csv
from collections import namedtuple
from itertools import islice
def process_large_csv(file_path, batch_size=10000):
"""分批处理大型csv文件"""
# 定义行结构
csvrow = namedtuple('csvrow', ['id', 'name', 'value'])
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
headers = next(reader) # 跳过标题行
while true:
# 读取一批行
batch = list(islice(reader, batch_size))
if not batch:
break # 文件结束
# 处理批次
rows = [csvrow(*row) for row in batch]
process_batch(rows)
# 可选:显示进度
print(f"processed {len(batch)} rows")
def process_batch(rows):
"""处理一批数据"""
# 这里添加实际处理逻辑
pass
# 使用
process_large_csv('huge_dataset.csv')
十一、总结
处理大文件的关键原则:
- 不要一次性加载到内存:始终使用迭代或分块方式
- 选择合适的数据结构:根据需求选择逐行、分块或内存映射
- 考虑并行处理:对于cpu密集型处理
- 利用生成器:保持内存效率
- 考虑专业工具:如dask、pytables等
通过以上技术,即使内存有限,也能高效处理远大于内存的文件。记住,正确的i/o策略可以显著影响程序性能,特别是对于大型数据集。
到此这篇关于python中几种高效读取大文件的完整指南的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python 读取大文件内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论