对话实录
小白:(苦恼)我在遍历列表时,想知道每个元素的位置,只能用个计数器变量,好繁琐,有没有更简单的办法?
专家:(掏出法宝)用enumerate函数,遍历同时获取索引,轻松解决你的困扰!
enumerate函数基础直击
1. 基本用法
enumerate函数用于将一个可迭代对象(如列表、字符串、元组等)组合为一个索引序列,同时列出数据和数据下标。
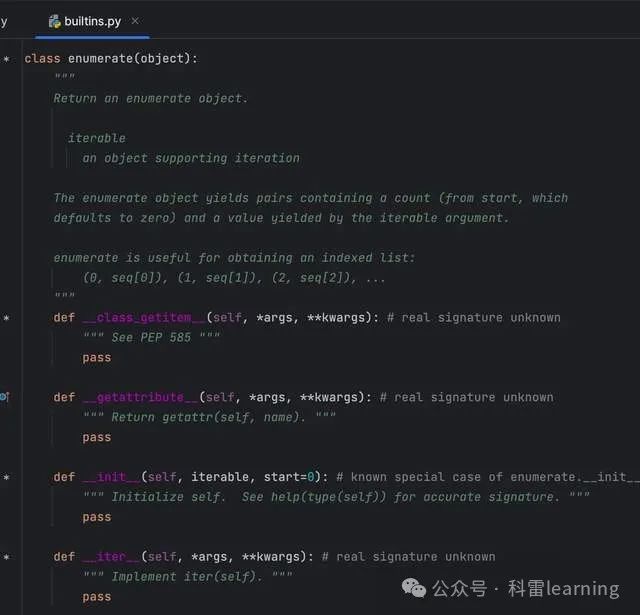
源代码中大家可以看到enumerate类定义了__iter__ 和__next__魔法方法,之前文章我们也说过定义了这两种方法的可以作为迭代器使用。
函数可以接收2个参数
1)iterable(必填):可迭代对象,如列表、元组、字符串等。
2)start(可选):默认为0。不为0 意思是指定索引的起始值,比如start=1代表索引从1开始而不是从0开始。
fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
for index, fruit in enumerate(fruits):
print(f"索引 {index} 对应的水果是 {fruit}")
# 输出:
# 索引 0 对应的水果是 apple
# 索引 1 对应的水果是 banana
# 索引 2 对应的水果是 cherry这里enumerate函数就像给每个水果贴上了对应的位置标签,让我们在遍历水果列表时,轻松知道它们的位置。
2. 起始索引设定
enumerate函数还可以指定起始索引,默认从 0 开始,若需要从其他数字开始计数,可传入第二个参数。
students = ['alice', 'bob', 'charlie']
for rank, student in enumerate(students, start = 1):
print(f"排名第 {rank} 的学生是 {student}")
# 输出:
# 排名第 1 的学生是 alice
# 排名第 2 的学生是 bob
# 排名第 3 的学生是 charlie在这种场景下,将起始索引设为 1,更符合日常排名的习惯。
常用功能及案例
案例 1:修改特定位置元素
在处理列表时,有时需要根据索引修改特定位置的元素,enumerate函数能精准定位。
scores = [85, 90, 78, 95]
for index, score in enumerate(scores):
if index == 2:
scores[index] = 80 # 将索引为2的成绩修改为80
print(scores)
# 输出:[85, 90, 80, 95]案例 2:查找特定元素位置
利用enumerate函数可以快速找到列表中某个元素的所有位置。
colors = ['red', 'blue', 'green', 'blue', 'yellow'] blue_positions = [index for index, color in enumerate(colors) if color == 'blue'] print(blue_positions) # 输出:[1, 3]
这里通过列表推导式结合enumerate函数,高效筛选出所有蓝色元素的索引。
案例 3:文本处理中的行号标注
在处理文本文件时,enumerate函数可用于给每一行添加行号。
with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
for line_number, line in enumerate(file, start = 1):
print(f"第 {line_number} 行: {line.strip()}")这样在查看文本内容时,能清晰知道每一行的行号,方便定位和处理文本数据。
闭坑指南
对不可迭代对象使用
enumerate函数只能用于可迭代对象,如果传入不可迭代对象,会报错。
number = 123 # 错误示范,会抛出 typeerror: 'int' object is not iterable for index, value in enumerate(number): pass
确保传入enumerate函数的是列表、字符串、元组、文件对象等可迭代对象。
误解索引和元素顺序
在for循环中,接收enumerate返回值时,索引在前,元素在后,顺序不能错。
words = ['hello', 'world'] # 错误示范,会导致变量赋值错误 for word, index in enumerate(words): pass
正确写法是for index, word in enumerate(words): ,保持索引在前,元素在后的顺序。
不恰当的起始索引
设置起始索引时,要根据实际需求合理设定。如果起始索引设置不当,可能导致逻辑错误。
# 假设要统计学生考试排名,从1开始更合理
ranks = [1, 2, 3]
# 错误示范,起始索引设为0不符合排名习惯
for rank, student in enumerate(ranks, start = 0):
print(f"排名第 {rank} 的学生成绩是 {student}")应根据实际场景,如排名场景,将起始索引设为 1 。
专家工具箱
1. 与zip函数联用
enumerate和zip函数结合,可以在遍历多个可迭代对象时,同时获取索引和对应元素。
names = ['alice', 'bob', 'charlie']
ages = [25, 30, 35]
for index, (name, age) in enumerate(zip(names, ages), start = 1):
print(f"序号 {index},姓名 {name},年龄 {age}")
# 输出:
# 序号 1,姓名 alice,年龄 25
# 序号 2,姓名 bob,年龄 30
# 序号 3,姓名 charlie,年龄 352. 结合lambda函数
在一些需要对索引和元素进行复杂操作的场景中,结合lambda函数能实现更灵活的处理。
nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] result = list(map(lambda x: x[0] * x[1], enumerate(nums))) print(result) # 输出:[0, 2, 6, 12, 20]
这里lambda函数将索引和对应元素相乘,map函数应用这个操作到整个列表。
3. 用于while循环模拟for循环遍历
虽然enumerate函数常与for循环搭配,但在某些情况下,也可以在while循环中模拟类似功能。
my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c']
index = 0
while index < len(my_list):
value = my_list[index]
print(f"索引 {index} 处的值是 {value}")
index += 1这种方式在一些需要更复杂循环控制逻辑,但又想实现类似enumerate功能的场景中比较有用。
小白:(恍然大悟)原来enumerate函数有这么多巧妙用法!
专家:(微笑)记住:掌握enumerate函数,遍历数据时获取索引将变得轻松又高效!
常用操作速查表
操作 | 代码示例 | 说明 |
基本遍历获取索引 | for index, value in enumerate([1, 2, 3]) | 遍历列表同时获取索引 |
设定起始索引 | for index, value in enumerate([1, 2, 3], start = 1) | 从指定数字开始计数 |
修改特定位置元素 | for index, value in enumerate([1, 2, 3]): if index == 1: list[index] = 5 | 根据索引修改列表元素 |
查找元素位置 | [index for index, value in enumerate([1, 2, 1, 3]) if value == 1] | 找到特定元素的所有索引 |
总结
到此这篇关于python中enumerate函数详解之遍历中的索引神器的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python遍历索引enumerate函数内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!




发表评论