前言
runtime 是使用 c 和汇编实现的运行时代码库,objective-c 中有很多语言特性都是通过它来实现。了解 runtime 开发可以帮助我们更灵活的使用 objective-c 这门语言,我们可以将程序功能推迟到运行时再去决定怎么做,还可以利用 runtime 来解决项目开发中的一些设计和技术问题,使开发过程更加具有灵活性。
一些关键字
- self:类的隐藏参数变量,指向当前调用方法的对象
- super:是编译器的标示符,通过 super 调用方法会被翻译成 objc_msgsendsuper(self, _cmd,…)
- sel:以方法名为内容的 c 字符串
- imp:指向方法实现的函数指针
- id:指向类对象或实例对象的指针
- isa:为 id 对象所属类型 (objc_class),objc 中的继承就是通过 isa 指针找到 objc_class,然后再通过 super_class 去找对应的父类
- metaclass:在 objc 中,类本身也是对象,实例对象的 isa 指向它所属的类,而类对象的 isa 指向元类 (metaclass),元类的 isa 直接指向根元类,根元类的isa指向它自己,它们之间的关系如下图所示。
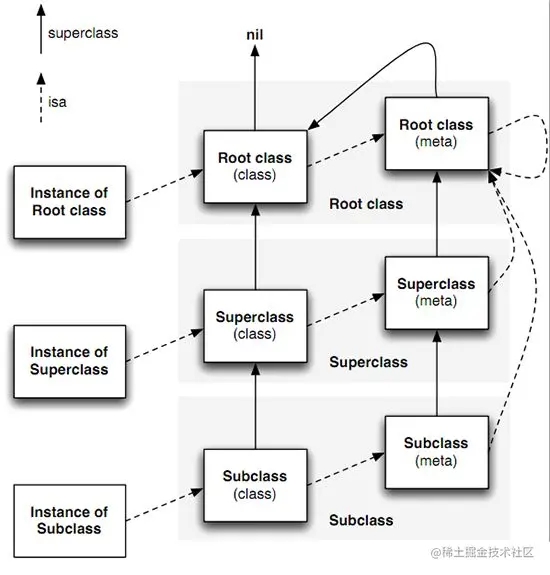
消息传递 (messaging)
objective-c 对于调用对象的某个方法这种行为叫做给对象发送消息,实际上就是沿着它的 isa 指针去查找真正的函数地址。下面我们来了解一下这个过程:
我们写一个给对象发送消息的代码
[array insertobject:obj atindex:5];
编译器首先会将上面代码翻译成这种样子
objc_msgsend(array, @selector(insertobject:atindex:), obj, 5);
系统在运行时会通过 array 对象的 isa 指针找到对应的 class(如果是给类发消息,则找到的是metaclass),然后在 class 的 cache 方法列表中用 sel 去找对应 method,如果找不到便去 class 的方法列表中去找,如果在方法列表中也找不对对应 method 时,便沿着继承体系继续向上查找,找到后将 method 放入 cache,以便下次能快速定位,然后再去执行 method 的 imp,找不到时系统便报错:unrecognized selector sent to insertobject:atindex:
runtime 提供了三种方法避免因为找不到方法而崩溃
当找不到方法实现时,runtime 会先发送 +resolveinstancemethod: 或 +resolveclassmethod: 消息,我们可以重写它然后为对象指定一个处理方法。
void dynamicxxxmethod(id obj, sel _cmd) {
nslog(@"ok...");
}
+ (bool)resolveinstancemethod:(sel)asel {
if(asel == @selector(xxx:)) {
class_addmethod([self class], asel, (imp)dynamicxxxmethod, "v@:");
return yes;
}
return [super resolveinstancemethod];
}
class_addmethod 方法的最后一个参数用来指定所添加方法的参数及返回值,叫 type encodings。
如果 resolve 方法返回 no,runtime 会发送 -forwardingtargetforselector: 消息,允许我们将消息转发给能处理它的其它对象。
- (id)forwardingtargetforselector:(sel)aselector {
if(aselector == @selector(xxx:)){
return otherobject;
}
return [super forwardingtargetforselector:aselector];
}
当 -forwardingtargetforselector: 返回 nil 时,runtime 会发送 -methodsignatureforselector: 和 -forwardinvocation: 消息。我们可以选择忽略消息、抛出异常、将消息转由当前对象或其它对象的任意消息来处理。
//根据 sel 生成 nsinvocation 对象,然后再由 -forwardinvocation: 方法进行转发。
- (nsmethodsignature *)methodsignatureforselector:(sel)aselector {
nsmethodsignature *signature = [super methodsignatureforselector:aselector];
if (!signature) {
signature = [otherobject instancemethodsignatureforselector:aselector];
}
return signature;
}
- (void)forwardinvocation:(nsinvocation *)invocation {
sel sel = invocation.selector;
if([otherobject respondstoselector:sel]) {
[invocation invokewithtarget:otherobject]; // 转发消息
}
else {
[self doesnotrecognizeselector:sel]; // 抛出异常
}
}
kvo
当我们为对象添加观察者后,runtime 会在运行时创建这个对象所在类的子类,并且将该对象的 isa 指针指向这个子类,然后重写监听属性的 set 方法并在方法中调用 -willchangevalueforkey: 和 -didchangevalueforkey: 来通知观察者,所以如果直接修改实例变量便不会触发监听方法。当移除观察者后,runtime 便会将这个子类删除。
所以 isa 指针并不总是指向实例对象所属的类,也有可能指向一个中间类,所以不能依靠它来确定类型,而是应该用 class 方法来确定实例对象的类。
关联对象 (associated objects)
在 category 中可以为类添加实例方法或类方法,但是不支持添加实例变量,所以即使我们在 category 中为类添加了 property,也不能直接使用它,runtime 可以解决这个问题,我们只需要定义一个指针,然后通过 objc_setassociatedobject 方法将指针与对象进行关联并指定内存管理方式,数据以 keyvalue 的形式存储在一个 hashmap 里。
objc 中的类和对象都是结构体,category 也是这样,定义的方法和属性在结构体中的存储,并在运行时按倒序添加到主类中(添加的方法会放在方法列表的上面),所以如果添加的方法与原类中的一样,那么在调用此方法时,优先找到的便是我们添加的这个方法。如果有多个 category 添加同样名称的方法,那么这些方法在方法列表中的顺序取决于他们的编译顺序,也就是这些 category 文件在 compile sources 中的顺序。
@interface nsobject (jc)
@property (nonatomic, copy) nsstring *id;
@end
@implementation nsobject (jc)
static const void *idkey;
- (nsstring *)id {
return objc_getassociatedobject(self, &idkey);
}
- (void)setid:(nsstring *)id {
objc_setassociatedobject(self, &idkey, id, objc_association_copy_nonatomic);
}
@end
aop(method swizzling)
我们可以通过继承、category、aop 方式来扩展类的功能。
- 继承比较适合在设计底层代码架构时使用,不适当的使用会让代码看起来很啰嗦,并且增加维护难度。
- category 适合为现有类添加方法。
- 当需要修改现有类的方法并且拿不到源码时,继承和 aop 都能解决问题,但是用 aop 来解决代码耦合度更低。其实就算能拿到源码,往往直接去改源码也不是个好办法。
在 objective-c 中,可以通过 method swizzling 技术来实现 aop,下面我们通过交换两个方法的实现代码来向已存在的方法中添加其它功能。
#import <objc/runtime.h>
@implementation uiviewcontroller (tracking)
+ (void)load {
static dispatch_once_t oncetoken;
dispatch_once(&oncetoken, ^{
class aclass = [self class];
sel originalselector = @selector(viewwillappear:);
sel swizzledselector = @selector(swizzled_viewwillappear:);
method originalmethod = class_getinstancemethod(aclass, originalselector);
method swizzledmethod = class_getinstancemethod(aclass, swizzledselector);
// 如果要对类方法进行交换,使用下面注释的代码
// class aclass = object_getclass((id)self);
//
// method originalmethod = class_getclassmethod(aclass, originalselector);
// method swizzledmethod = class_getclassmethod(aclass, swizzledselector);
// 交换两个方法的实现
// 防止 aclass 不存在 originalselector,所以添加一下试试,但指向地址为新方法地址
bool didaddmethod = class_addmethod(aclass, originalselector, method_getimplementation(swizzledmethod), method_gettypeencoding(swizzledmethod));
if (didaddmethod) {
// 添加成功,说明 aclass 不存在 originalselector,所以替换 swizzledselector 的 imp 为 originalmethod,实质上它们都指向 swizzledmethod
class_replacemethod(aclass, swizzledselector, method_getimplementation(originalmethod), method_gettypeencoding(originalmethod));
}
else {
// 添加失败,说明 aclass 存在 originalselector,直接交换
method_exchangeimplementations(originalmethod, swizzledmethod);
}
});
}
#pragma mark - method swizzling
// 由于方法实现已经被交换,所以系统在调用 viewwillappear: 时,实际上会调用 swizzled_viewwillappear:
- (void)swizzled_viewwillappear:(bool)animated {
// 下面代码表面上看起来会引起递归调用,由于函数实现已经被交换,实际上会调用 viewwillappear:
[self swizzled_viewwillappear:animated];
// 在原有基础上添加其它功能(写日志等)
}
@end
使用 method swizzling 需要注意下面几个问题
- 需要在 +load 方法中执行 method swizzling,+initialize 方法有可能不会被调用
- 避免父类与子类同时 hook 父类的某方法,避免不了时至少要保证不在 +load 方法中执行 super.load(),否则父类中的 +load 方法会被执行两次
- 需要在 dispatch_once 中执行,避免因多线程等问题倒致的偶数次交换后失效的问题
- 如果你用了 swizzled_viewwillappear 作为方法名,那么如果你引用的第三方 sdk 中也用了这个方法名来做方法交换,那会造成方法的递归调用,所以你最好换一个不太会被重复使用的方法名,例如 mx_swizzled_viewwillappear
- 即便使用 mx_swizzled_viewwillappear 尽量避免了与第三方库或自己项目中别的地方对 viewwillappear 交换倒致的递归调用问题,仍然会存在调用顺序问题,解决办法就是在 build phases 中调整类文件的顺序
其它
我们可以通过 runtime 特性来获得类的所有属性名称和类型,然后再通过 kvc 将 json 中的值填充给该类的对象。还可以在程序运行时为类添加方法或替换方法从而使对象能够更灵活的根据需要来选择实现方法。总之 runtime 库就象一堆积木,只要发挥想象力便能实现各种各样的功能,但前提是你需要了解它。
以上就是objective-c runtime 开发示例详解的详细内容,更多关于objective-c runtime 开发的资料请关注代码网其它相关文章!



发表评论