在 mysql 中,_rowid 是一个虚拟列,可以用来查询 innodb 表的内部行 id(当表没有显式定义主键时)。以下是使用 _rowid 的 sql 查询示例:
1. 基本查询(适用于没有主键的表)
select
_rowid as internal_row_id, -- 显示内部行id
t.* -- 查询所有列
from your_table_name t
limit 10;2. 检查表是否支持 _rowid
-- 检查表是否有主键或唯一索引 show index from your_table_name; -- 如果表没有主键,且至少有一个非空的唯一整数列,`_rowid` 会指向该列 -- 否则,mysql 会使用内部隐藏的 rowid
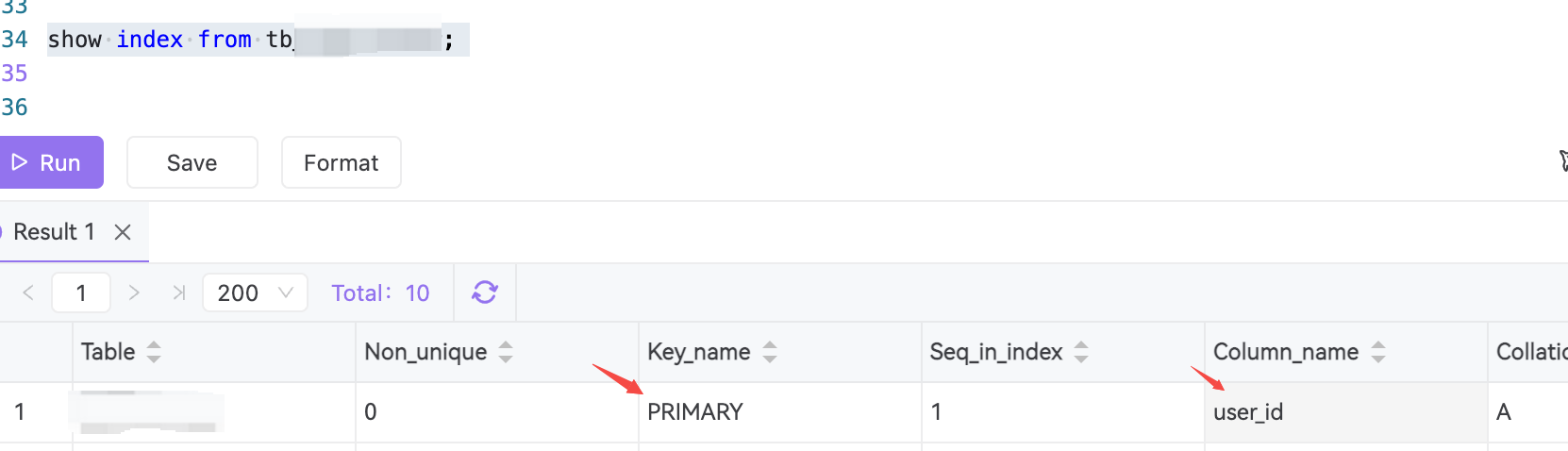
3. 注意事项
_rowid的限制:- 仅适用于 innodb 表。
- 如果表有主键,
_rowid会指向主键列。 - 如果表没有主键但有唯一非空整数列,
_rowid会指向该列。 - 如果表既没有主键也没有唯一非空整数列,
_rowid会显示内部隐藏的行 id(但可能不稳定,不建议依赖它)。
替代方案:
如果 _rowid 不可用,可以使用 row_number()(mysql 8.0+):
select
row_number() over (order by (select null)) as row_num,
other_columns
from your_table_name;或者使用变量模拟行号(mysql 5.7+):
set @row_number = 0;
select
(@row_number:=@row_number + 1) as row_num,
other_columns
from your_table_name;4. 最佳实践
- 显式定义主键:建议在表中添加
id int auto_increment primary key,避免依赖_rowid。 - 避免依赖内部行 id:
_rowid可能因数据重组(如optimize table)而变化,不适合用作业务逻辑。
补充:mysql 根据时间自动创建分区脚本
以下是一个mysql脚本示例,用于根据时间自动创建和管理分区表:
-- 1. 首先创建一个按时间分区的表(如果尚未存在)
create table if not exists time_partitioned_data (
id int auto_increment,
data_value varchar(255),
created_at datetime not null,
primary key (id, created_at)
)
partition by range (to_days(created_at)) (
partition p_min values less than (to_days('2023-01-01'))
);
-- 2. 创建存储过程来自动管理分区
delimiter //
create procedure auto_manage_partitions(in table_name varchar(64), in days_ahead int)
begin
declare done int default false;
declare partition_name varchar(64);
declare partition_value varchar(64);
declare max_value date;
declare new_partition_date date;
declare new_partition_name varchar(64);
declare new_partition_value int;
declare alter_sql text;
-- 获取当前最大分区值
select max(to_days(created_at)) into @max_day
from time_partitioned_data;
set max_value = ifnull(from_days(@max_day), curdate());
-- 创建未来分区
set new_partition_date = max_value;
while datediff(date_add(new_partition_date, interval 1 month), max_value) <= days_ahead do
set new_partition_date = date_add(new_partition_date, interval 1 month);
set new_partition_name = concat('p_', date_format(new_partition_date, '%y%m'));
set new_partition_value = to_days(new_partition_date);
-- 检查分区是否已存在
select count(*) into @partition_exists
from information_schema.partitions
where table_schema = database()
and table_name = 'time_partitioned_data'
and partition_name = new_partition_name;
if @partition_exists = 0 then
set alter_sql = concat('alter table ', table_name,
' add partition (partition ', new_partition_name,
' values less than (', new_partition_value, '))');
prepare stmt from alter_sql;
execute stmt;
deallocate prepare stmt;
select concat('created partition: ', new_partition_name, ' for date: ', new_partition_date) as message;
end if;
end while;
-- 可选:删除旧分区(例如保留最近12个月的数据)
/*
select partition_name, partition_description into @old_partition, @old_value
from information_schema.partitions
where table_schema = database()
and table_name = 'time_partitioned_data'
and partition_name != 'p_min'
order by partition_description asc
limit 1;
if to_days(curdate()) - @old_value > 365 then
set @drop_sql = concat('alter table ', table_name, ' drop partition ', @old_partition);
prepare stmt from @drop_sql;
execute stmt;
deallocate prepare stmt;
select concat('dropped old partition: ', @old_partition) as message;
end if;
*/
end //
delimiter ;
-- 3. 创建事件定期执行分区管理
create event if not exists manage_partitions_event
on schedule every 1 month
starts current_timestamp
do
call auto_manage_partitions('time_partitioned_data', 90); -- 提前创建未来90天的分区
-- 启用事件调度器
set global event_scheduler = on;到此这篇关于mysql查询使用_rowid虚拟列的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关mysql查询_rowid虚拟列内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论