一、适合建立索引的字段特征
1.1 高选择性的字段
选择性公式:
选择性 = 不重复的值数量(distinct) / 总记录数
选择性越接近1,索引效果越好
示例分析:
-- 查看字段选择性 select count(distinct gender)/count(*) as gender_selectivity, count(distinct phone)/count(*) as phone_selectivity from users;
1.2 常用查询条件的字段
| 查询类型 | 索引效果 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| where条件 | ★★★ | where user_id = 1001 |
| join条件 | ★★★ | on a.order_id = b.id |
| 排序字段 | ★★ | order by create_time desc |
| 分组字段 | ★★ | group by department |
1.3 具体推荐场景
1.3.1 应当建索引的字段
- 主键和外键字段(自动创建)
- 高频查询的where条件字段
- 多表join的关联字段
- 排序和分组字段(特别是组合排序)
- 区分度高的状态字段(如订单状态)
1.3.2 数值类型优先
-- 好的索引字段 alter table products add index idx_category_id (category_id); -- 整型 alter table users add index idx_phone (phone); -- 定长字符串 -- 较差的索引选择 alter table logs add index idx_content (content(255)); -- 长文本前缀索引
二、索引失效的8大常见场景
2.1 违反最左前缀原则
联合索引结构示例:
alter table orders add index idx_user_status (user_id, status);
失效案例:
-- 有效使用索引 explain select * from orders where user_id = 1001 and status = 1; -- 部分失效(只用到了user_id) explain select * from orders where user_id = 1001; -- 完全失效(跳过了user_id) explain select * from orders where status = 1;
2.2 对索引列使用函数或运算
失效示例:
-- 索引失效 explain select * from users where date(create_time) = '2023-01-01'; explain select * from products where price + 100 > 500; -- 优化方案 explain select * from users where create_time between '2023-01-01 00:00:00' and '2023-01-01 23:59:59';
2.3 隐式类型转换
常见陷阱:
-- phone字段是varchar类型 explain select * from users where phone = 13800138000; -- 失效 explain select * from users where phone = '13800138000'; -- 有效 -- 枚举值比较 explain select * from orders where status = '1'; -- 可能失效 explain select * from orders where status = 1; -- 有效
2.4 使用不等于(!=或<>)
失效分析:
-- 索引失效 explain select * from users where age != 30; -- 优化方案(范围查询+union) explain select * from users where age < 30 union all select * from users where age > 30;
2.5 like以通配符开头
对比示例:
-- 索引失效
explain select * from users where name like '%张%';
-- 索引有效(前缀匹配)
explain select * from users where name like '张%';
-- 特殊优化方案(全文索引)
alter table users add fulltext index ft_idx_name (name);
explain select * from users where match(name) against('张*' in boolean mode);
2.6 or条件使用不当
失效场景:
-- 索引失效(其中一个条件无索引) explain select * from users where user_id = 1001 or register_ip = '192.168.1.1'; -- 优化方案 explain select * from users where user_id = 1001 union all select * from users where register_ip = '192.168.1.1' and user_id != 1001;
2.7 数据分布不均匀
案例演示:
-- 当status=1占90%数据时 explain select * from orders where status = 1; -- 可能全表扫描 -- 查看数据分布 select status, count(*) from orders group by status;
2.8 索引列参与is null判断
特殊情况:
-- mysql 5.7+可以走索引 explain select * from users where phone is null; -- 通常需要结合其他条件 explain select * from users where phone is null and create_time > '2023-01-01';
三、高级索引失效场景
3.1 索引合并导致的性能问题
-- 可能不如预期高效 explain select * from users where username = 'admin' or email = 'admin@example.com'; -- 优化方案 create index idx_username_email on users(username, email);
3.2 范围查询后的索引失效
-- 只有user_id和status能用索引,age失效 explain select * from orders where user_id = 1001 and status > 0 and age = 30; -- 优化索引顺序 alter table orders add index idx_user_age_status (user_id, age, status);
3.3 不同字符集比较
-- 不同字符集比较导致失效 explain select * from users u join logs l on u.username = l.operator where u.charset = 'utf8mb4' and l.charset = 'latin1';
四、索引使用最佳实践
4.1 索引设计黄金法则
三星索引原则:
- 一星:where条件列是索引前缀
- 二星:order by/group by列在索引中
- 三星:select列被索引覆盖
索引维护成本:
- 写操作需要更新索引
- 每个表最佳索引数通常为3-5个
4.2 实战案例解析
电商系统优化:
-- 原始查询 select product_id, product_name, price from products where category_id = 5 and status = 1 and stock > 0 order by sales_volume desc limit 20; -- 优化方案 alter table products add index idx_cat_status_stock_sales (category_id, status, stock, sales_volume desc);
4.3 监控与调优工具
索引使用分析:
-- 查看未使用的索引 select * from sys.schema_unused_indexes; -- 索引统计信息 show index from products; -- 查询性能分析 explain analyze select * from orders where user_id = 1001;
五、mysql 8.0索引新特性
5.1 倒序索引
alter table orders add index idx_create_time (create_time desc);
5.2 隐藏索引
-- 测试删除索引的影响 alter table users alter index idx_email invisible; alter table users alter index idx_email visible;
5.3 函数索引
-- 对json字段建立索引 alter table products add index idx_price_data ((cast(price_data->'$.price' as decimal(10,2))));
六、总结与决策流程图
6.1 索引创建决策流程
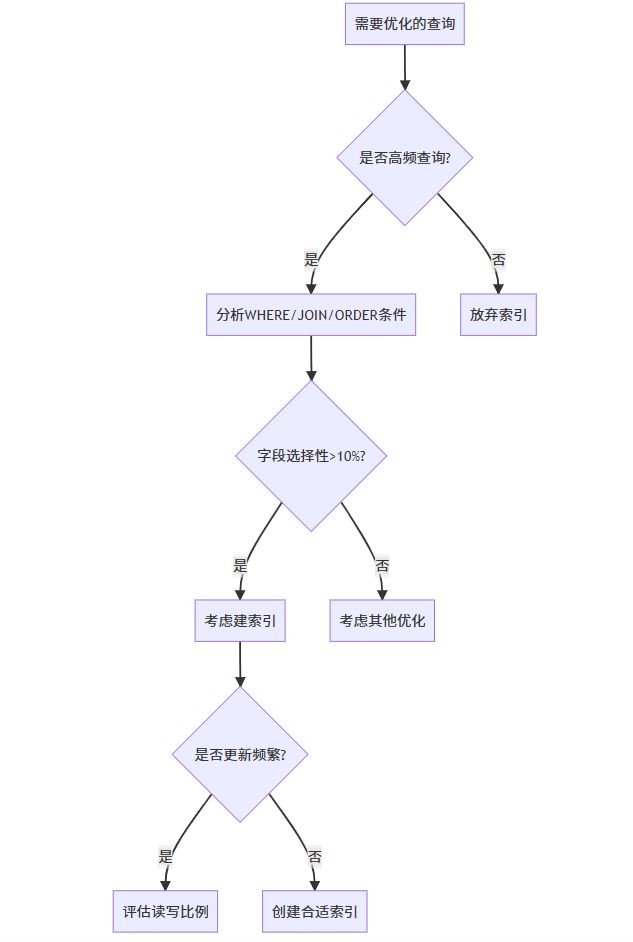
6.2 索引失效排查清单
- 检查explain执行计划
- 验证sql是否遵循最左前缀原则
- 检查是否有隐式类型转换
- 排查是否使用了函数或运算
- 分析数据分布情况
- 确认字符集和排序规则一致性
通过系统性地理解索引适用场景和失效原理,可以显著提升数据库查询性能。实际应用中应当结合业务特点和数据分布,定期审查索引效果,避免过度索引和索引滥用。
以上就是mysql索引选择与失效场景全解析的详细内容,更多关于mysql索引选择与失效的资料请关注代码网其它相关文章!






发表评论