1.什么是 future 模式?java 中是如何实现的?
(1)future 模式是一种并发编程模式,它允许异步执行代码并在未来获取其结果。在 future 模式中,调用线程可以提交一个任务给另一个线程或线程池,并立即返回一个 future 对象作为任务的代理。future 对象表示了尚未完成的任务,并允许调用线程在未来的某个时刻获取任务的结果。future 模式通常用于处理长时间运行的任务,例如网络请求或耗时的计算。通过使用 future 模式,调用线程可以避免阻塞并继续执行其他任务,同时仍然能够获得任务的结果。
(2)在 java 中,future 模式是通过 future 接口来实现的。java 还提供了 completablefuture 类,它是 future 接口的实现,并提供了更丰富的功能,例如异步回调和异常处理。java 设计到的相关接口和类如下图所示:
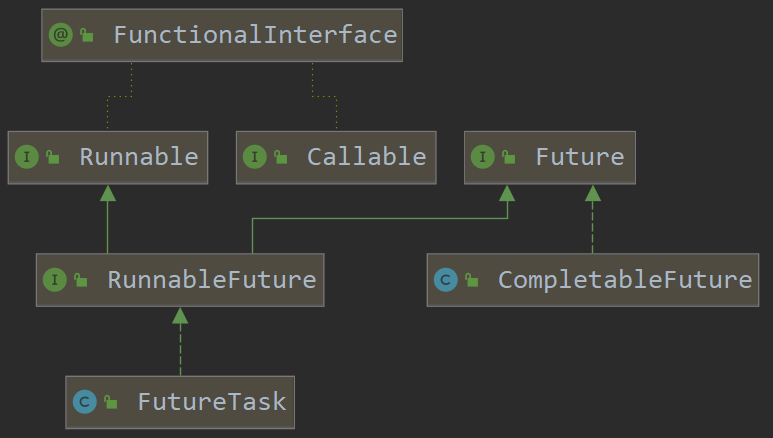
2.callable、future 与 futuretask 分别是什么?
通常来说,我们使用 runnable 和 thread 来创建一个新的线程。但是它们有一个弊端,就是 run() 是没有返回值的。而有时候我们希望开启一个线程去执行一个任务,并且这个任务执行完成后有一个返回值。jdk 提供了 callable 接口与 future 类为我们解决这个问题,这也是所谓的“异步”模型。
2.1.callable 接口
(1)callable 与 runnable 类似,同样是只有⼀个抽象方法的函数式接看。不同的是, callable 提供的方法是有返回值的,而且支持泛型。callable 接口的特点如下:
- 为了实现 runnable,需要实现不返回任何内容的 run() 方法,而对于callable,需要实现在完成时返回结果的 call() 方法;
- call() 方法可以引发异常,而 run() 则不能;
- 为实现 callable 而必须重写 call() 方法;
- 不能直接替换 runnable,因为 thread 类的构造方法根本没有 callable;
@functionalinterface
public interface callable<v> {
v call() throws exception;
}class mythread1 implements runnable {
@override
public void run() {
//无返回值
}
}
class mythread2 implements callable {
@override
public object call() throws exception {
return 1;
}
}(2)那⼀般是怎么使用 callable 的呢? callable⼀般配合线程池工具 executorservice 来使用。这里只介绍 executorservice 可以使用 submit 方法来让⼀个 callable 接口执行。它会返回⼀个 future ,我们后续的程序可以通过这个 future 的 get 方法得到结果。这里可以看⼀个简单的使用案例:
class task implements callable<integer> {
@override
public integer call() throws exception {
// 模拟计算需要 3 秒
thread.sleep(3000);
return 2;
}
public static void main(string args[]) throws executionexception, interruptedexception {
// 使⽤
executorservice executor = executors.newcachedthreadpool();
task task = new task();
// executorservice.submit() 方法返回的其实就是 future 的实现类 futuretask
future<integer> result = executor.submit(task);
//注意调⽤ get ⽅法会阻塞当前线程,直到得到结果,所以实际编码中建议使⽤可以设置超时时间的重载 get ⽅法
system.out.println(result.get());
}
}输出结果:
2
此外,callable 可以配合 futuretask 使用:
class task implements callable<integer> {
@override
public integer call() throws exception {
// 模拟计算需要 3 秒
thread.sleep(3000);
return 2;
}
public static void main(string[] args) throws executionexception, interruptedexception {
futuretask<integer> task = new futuretask<>(new task());
new thread(task).start();
integer res = task.get();
//注意调⽤ get ⽅法会阻塞当前线程,直到得到结果,所以实际编码中建议使⽤可以设置超时时间的重载 get ⽅法
system.out.println(res);
}
}2.2.future 接口
(1)在 java 中,future 类是一个泛型接口,位于 java.util.concurrent 包下,其包含的方法如下:
package java.util.concurrent;
// v 表示任务返回值的类型
public interface future<v> {
//成功取消任务返回 true,否则返回 false
boolean cancel(boolean mayinterruptifrunning);
//判断任务是否被取消
boolean iscancelled();
//判断任务是否已经执行完成
boolean isdone();
//获取任务执行结果
v get() throws interruptedexception, executionexception;
//指定时间内没有返回计算结果就抛出 timeoutexception 异常
v get(long timeout, timeunit unit)
throws interruptedexception, executionexception, timeoutexception;
}简单理解 future:现在有一个任务,提交给了 future 来处理。任务执行期间我自己可以去做任何想做的事情。并且,在这期间我还可以取消任务以及获取任务的执行状态。一段时间之后,我就可以 future 那里直接取出任务执行结果。
(2)cancel 方法是试图取消⼀个线程的执行。 注意是试图取消,并不⼀定能取消成功。因为任务可能已完成、已取消、或者⼀些其它因素不能取消,存在取消失败的可能。boolean 类型的返回值是“是否取消成功”的意思。参数 paramboolean 表示是否采用中断的方式取消线程执行。 所以有时候为了让任务有能够取消的功能,就使用 callable 来代替 runnable 。 如果为了可取消性而使用 future 但又不提供可用的结果,则可以声明 future<?> 形式类型、并返回 null 作为底层任务的结果。
2.3.futuretask 类
(1)上面介绍了 future 接口。这个接口有⼀个实现类叫 futuretask 。 futuretask 是实现的 runnablefuture 接口的,而 runnablefuture 接口同时继承了 runnable 接口和 future 接口:
public interface runnablefuture<v> extends runnable, future<v> {
/**
* sets this future to the result of its computation
* unless it has been cancelled.
*/
void run();
}(2)那 futuretask 类有什么用?前面说到了 future 只是⼀个接口,而它里面的 cancel、get、isdone 等方法要自己实现起来都是非常复杂的。所以 jdk 提供了⼀个 futuretask 类来供我们使用。futuretask 有两个构造函数,可传入 callable 或者 runnable 对象。实际上,传入 runnable 对象也会在方法内部转换为 callable 对象:
public class futuretask<v> implements runnablefuture<v> {
//...
public futuretask(callable<v> callable) {
if (callable == null)
throw new nullpointerexception();
this.callable = callable;
this.state = new;
}
public futuretask(runnable runnable, v result) {
// 通过适配器 runnableadapter 来将 runnable 对象 runnable 转换成 callable 对象
this.callable = executors.callable(runnable, result);
this.state = new;
}
}futuretask 相当于对 callable 进行了封装,管理着任务执行的情况,存储了 callable 的 call 方法的任务执行结果。
(3)示例代码如下:
class task implements callable<integer> {
@override
public integer call() throws exception {
//模拟计算需要⼀秒
thread.sleep(1000);
return 2;
}
public static void main(string args[]) throws executionexception, interruptedexception {
executorservice executor = executors.newcachedthreadpool();
futuretask<integer> futuretask = new futuretask<>(new task());
executor.submit(futuretask);
system.out.println(futuretask.get());
}
}使用上与第⼀个 demo 有⼀点小的区别:
- 此处调用 submit 方法是没有返回值的,因为这里实际上是调用的
submit(runnable task)方法,而上面的 demo,调用的是submit(callable<t> task)方法。 - 这里是使用 futuretask 的 get 方法来获取返回值,而上面的 demo 是通过 submit 方法返回的 future 去取值。 在很多高并发的环境下,有可能 callable 和 futuretask 会创建多次。futuretask 能够在高并发环境下确保任务只执行⼀次。
(4)核心原理
- 在主线程中需要执行比较耗时的操作时,但又不想阻塞主线程时,可以把这些作业交给 future 对象在后台完成;
- 当主线程将来需要时,就可以通过 future 对象获得后台作业的计算结果或者执行状态;
- 一般 futuretask 多用于耗时的计算,主线程可以在完成自己的任务后,再去获取结果;
- 仅在计算完成时才能检索结果;如果计算尚未完成,则阻塞 get() 方法,一旦计算完成,就不能再重新开始或取消计算;
- get() 方法而获取结果只有在计算完成时获取,否则会一直阻塞直到任务转入完成状态,然后会返回结果或者抛出异常;
- get() 只计算一次,因此 get() 方法放到最后。
//比较 runnable 和 callable 这两个接口
class mythread1 implements runnable {
@override
public void run() {
//无返回值
}
}
class mythread2 implements callable {
@override
public object call() throws exception {
return 1;
}
}
public class callabledemo {
public static void main(string[] args) throws executionexception, interruptedexception {
//使用 runnable 创建线程
new thread(new mythread1(), "aa").start();
/*
使用 callable 创建线程
不能像上面那样直接创建 new thread(new mythread2(), "bb").start();
*/
//futuretask
futuretask<integer> futuretask1 = new futuretask<>(new mythread2());
//使用 lambda 表达式进行简化
futuretask<integer> futuretask2 = new futuretask<>(()->{
system.out.println(thread.currentthread().getname() + " enters the callable .");
return 1;
});
//创建一个线程
new thread(futuretask2, "luck").start();
while (!futuretask2.isdone()) {
system.out.println("wait...");
}
//调用 futuretask 的get()
system.out.println(futuretask2.get());
//只进行一次计算
system.out.println(futuretask2.get());
system.out.println(thread.currentthread().getname() + " is over !");
}
}(5)futuretask 的几种状态
/** * state 可能的状态转变路径如下: * new -> completing -> normal * new -> completing -> exceptional * new -> cancelled * new -> interrupting -> interrupted */ private volatile int state; private static final int new = 0; private static final int completing = 1; private static final int normal = 2; private static final int exceptional = 3; private static final int cancelled = 4; private static final int interrupting = 5; private static final int interrupted = 6;
state 表示任务的运行状态,初始状态为 new。运行状态只会在 set、setexception、cancel 方法中终止。completing、interrupting 是任务完成后的瞬时状态。
3.completablefuture 类有什么用?
(1)future 在实际使用过程中存在一些局限性,例如不支持异步任务的编排组合、获取计算结果的 get() 方法为阻塞调用等。java 8 才被引入 completablefuture 类可以解决 future 的这些缺陷。completablefuture 除了提供了更为好用和强大的 future 特性之外,还提供了函数式编程、异步任务编排组合(可以将多个异步任务串联起来,组成一个完整的链式调用)等能力。
public class completablefuture<t> implements future<t>, completionstage<t> {
//...
}(2)可以看到,completablefuture 同时实现了 future 接口 和 completionstage 接口。其中,completionstage 接口描述了一个异步计算的阶段。很多计算可以分成多个阶段或步骤,此时可以通过它将所有步骤组合起来,形成异步计算的流水线。completionstage 接口中的方法比较多,completablefuture 的函数式能力就是这个接口赋予的。从这个接口的方法参数可以发现其大量使用了 java 8 引入的函数式编程。
到此这篇关于java 并发编程面试题 future 模式的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关java future 模式内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论