pytorch上/下采样函数torch.nn.functional.interpolate插值
torch.nn.functional.interpolate(input_tensor, size=none, scale_factor=8, mode='bilinear', align_corners=false) ''' down/up samples the input to either the given size or the given scale_factor the algorithm used for interpolation is determined by mode. currently temporal, spatial and volumetric sampling are supported, i.e. expected inputs are 3-d, 4-d or 5-d in shape. the input dimensions are interpreted in the form: mini-batch x channels x [optional depth] x [optional height] x width. the modes available for resizing are: nearest, linear (3d-only), bilinear, bicubic (4d-only), trilinear (5d-only), area '''
这个函数是用来上采样或下采样tensor的空间维度(h,w):
input_tensor支持输入3d (b, c, w)或(batch,seq_len,dim)、4d (b, c, h, w)、5d (b, c, f, h, w)的 tensor shape。其中b表示batch_size,c表示channel,f表示frames,h表示height,w表示weight。
size是目标tensor的(w)/(h,w)/(f,h,w)的形状;scale_factor是采样tensor的saptial shape(w)/(h,w)/(f,h,w)的缩放系数,size和scale_factor两个参数只能定义一个,具体是上采样,还是下采样根据这两个参数判断。如果size或者scale_factor是list序列,则必须匹配输入的大小。
- 如果输入3d,则它们的序列长度必须是1(只缩放最后1个维度w)。
- 如果输入4d,则它们的序列长度必须是2(缩放最后2个维度h,w)。
- 如果输入是5d,则它们的序列长度必须是3(缩放最后3个维度f,h,w)。
插值算法mode可选:最近邻(nearest, 默认)、线性(linear, 3d-only)、双线性(bilinear, 4d-only)、三线性(trilinear, 5d-only)等等。
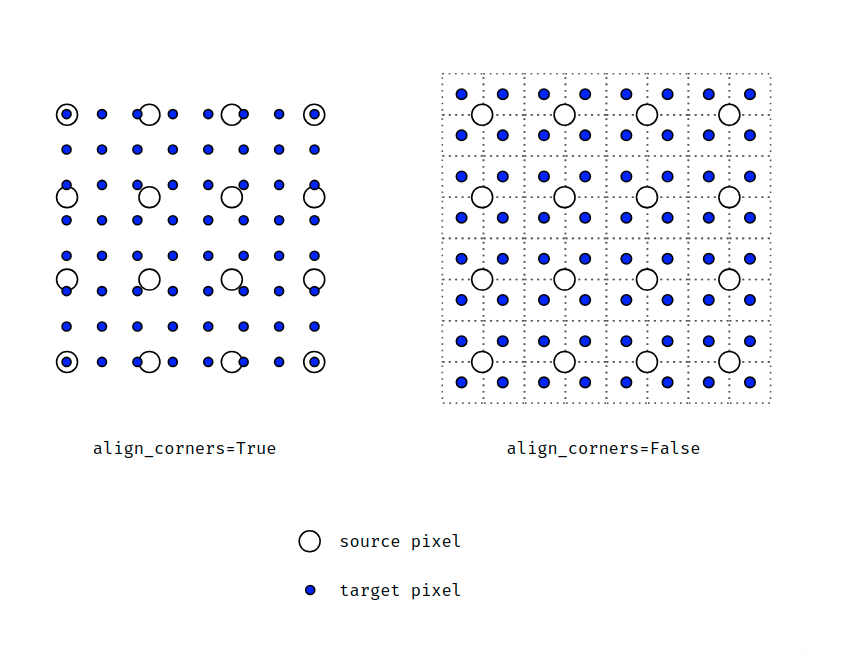
是否align_corners对齐角点:可选的bool值, 如果 align_corners=true,则对齐 input 和 output 的角点像素(corner pixels),保持在角点像素的值. 只会对 mode=linear, bilinear, trilinear 有作用. 默认是 false。一图看懂align_corners=true与false的区别,从4×4上采样成8×8。
一个是按四角的像素点中心对齐,另一个是按四角的像素角点对齐:
import torch import torch.nn.functional as f b, c, f, h, w = 1, 3, 8, 64, 64
1. upsample/downsample 3d tensor
# interpolate 3d tensor x = torch.randn([b, c, w]) ## downsample to (b, c, w/2) y0 = f.interpolate(x, scale_factor=0.5, mode='nearest') y1 = f.interpolate(x, size=[w//2], mode='nearest') y2 = f.interpolate(x, scale_factor=0.5, mode='linear') # only 3d y3 = f.interpolate(x, size=[w//2], mode='linear') # only 3d print(y0.shape, y1.shape, y2.shape, y3.shape) # torch.size([1, 3, 32]) torch.size([1, 3, 32]) torch.size([1, 3, 32]) torch.size([1, 3, 32]) ## upsample to (b, c, w*2) y0 = f.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest') y1 = f.interpolate(x, size=[w*2], mode='nearest') y2 = f.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='linear') # only 3d y3 = f.interpolate(x, size=[w*2], mode='linear') # only 3d print(y0.shape, y1.shape, y2.shape, y3.shape) # torch.size([1, 3, 128]) torch.size([1, 3, 128]) torch.size([1, 3, 128]) torch.size([1, 3, 128])
2. upsample/downsample 4d tensor
# interpolate 4d tensor x = torch.randn(b, c, h, w) ## downsample to (b, c, h/2, w/2) y0 = f.interpolate(x, scale_factor=0.5, mode='nearest') y1 = f.interpolate(x, size=[h//2, w//2], mode='nearest') y2 = f.interpolate(x, scale_factor=0.5, mode='bilinear') # only 4d y3 = f.interpolate(x, size=[h//2, w//2], mode='bilinear') # only 4d print(y0.shape, y1.shape, y2.shape, y3.shape) # torch.size([1, 3, 32, 32]) torch.size([1, 3, 32, 32]) torch.size([1, 3, 32, 32]) torch.size([1, 3, 32, 32]) ## upsample to (b, c, h*2, w*2) y0 = f.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest') y1 = f.interpolate(x, size=[h*2, w*2], mode='nearest') y2 = f.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear') # only 4d y3 = f.interpolate(x, size=[h*2, w*2], mode='bilinear') # only 4d print(y0.shape, y1.shape, y2.shape, y3.shape) # torch.size([1, 3, 128, 128]) torch.size([1, 3, 128, 128]) torch.size([1, 3, 128, 128]) torch.size([1, 3, 128, 128])
3. upsample/downsample 5d tensor
# interpolate 5d tensor x = torch.randn(b, c, f, h, w) ## downsample to (b, c, f/2, h/2, w/2) y0 = f.interpolate(x, scale_factor=0.5, mode='nearest') y1 = f.interpolate(x, size=[f//2, h//2, w//2], mode='nearest') y2 = f.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='trilinear') # only 5d y3 = f.interpolate(x, size=[f//2, h//2, w//2], mode='trilinear') # only 5d print(y0.shape, y1.shape, y2.shape, y3.shape) # torch.size([1, 3, 4, 32, 32]) torch.size([1, 3, 4, 32, 32]) torch.size([1, 3, 16, 128, 128]) torch.size([1, 3, 4, 32, 32]) ## upsample to (b, c, f*2, h*2, w*2) y0 = f.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest') y1 = f.interpolate(x, size=[f*2, h*2, w*2], mode='nearest') y2 = f.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='trilinear') # only 5d y3 = f.interpolate(x, size=[f*2, h*2, w*2], mode='trilinear') # only 5d print(y0.shape, y1.shape, y2.shape, y3.shape) # torch.size([1, 3, 16, 128, 128]) torch.size([1, 3, 16, 128, 128]) torch.size([1, 3, 16, 128, 128]) torch.size([1, 3, 16, 128, 128])
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持代码网。





发表评论