前言
文件操作与数据处理是python编程中最基础也是最重要的技能之一。无论是数据分析、web开发还是自动化脚本编写,都离不开对文件的读写和各种数据处理操作。本文将全面介绍python中的文件操作方法和常用数据处理技巧,帮助开发者高效地处理各类数据任务。
一、python基础文件操作
1.1 文件打开与关闭
python使用内置的open()函数进行文件操作,基本语法如下:
file = open(filename, mode='r', encoding=none)
常用模式参数:
‘r’:只读(默认)
‘w’:写入,会覆盖已有文件
‘a’:追加,在文件末尾添加
‘x’:独占创建,文件已存在则失败
‘b’:二进制模式
‘t’:文本模式(默认)
‘+’:更新(可读可写)
推荐使用上下文管理器(with语句):
with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
content = file.read()
# 文件会在with块结束后自动关闭
1.2 文件读写方法
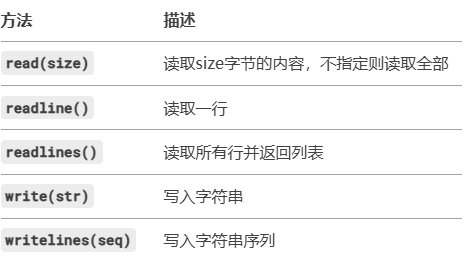
示例代码:
# 写入文件
with open('data.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write('第一行内容\n')
f.write('第二行内容\n')
f.writelines(['第三行\n', '第四行\n'])
# 读取文件
with open('data.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
print(f.read()) # 读取全部内容
f.seek(0) # 重置文件指针到开头
print(f.readline()) # 读取一行
f.seek(0)
print(f.readlines()) # 读取所有行到列表
二、常见文件格式处理
2.1 csv文件处理
使用标准库csv:
import csv
# 写入csv文件
data = [
['姓名', '年龄', '城市'],
['张三', 25, '北京'],
['李四', 30, '上海']
]
with open('people.csv', 'w', newline='', encoding='utf-8') as f:
writer = csv.writer(f)
writer.writerows(data)
# 读取csv文件
with open('people.csv', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
for row in reader:
print(row)
# 字典形式读写
with open('people_dict.csv', 'w', newline='', encoding='utf-8') as f:
fieldnames = ['name', 'age', 'city']
writer = csv.dictwriter(f, fieldnames=fieldnames)
writer.writeheader()
writer.writerow({'name': '王五', 'age': 28, 'city': '广州'})
with open('people_dict.csv', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
reader = csv.dictreader(f)
for row in reader:
print(row['name'], row['age'])
2.2 json文件处理
import json
# python对象转json
data = {
"name": "张三",
"age": 25,
"hobbies": ["读书", "游泳"],
"married": false
}
# 写入json文件
with open('data.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(data, f, ensure_ascii=false, indent=2)
# 读取json文件
with open('data.json', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
loaded_data = json.load(f)
print(loaded_data['name'])
2.3 excel文件处理(使用openpyxl)
from openpyxl import workbook, load_workbook
# 创建excel文件
wb = workbook()
ws = wb.active
ws.title = "员工信息"
# 写入数据
ws.append(['姓名', '部门', '工资'])
ws.append(['张三', '技术部', 15000])
ws.append(['李四', '市场部', 12000])
# 保存文件
wb.save('employees.xlsx')
# 读取excel文件
wb = load_workbook('employees.xlsx')
ws = wb.active
for row in ws.iter_rows(values_only=true):
print(row)
三、高效数据处理技巧
3.1 使用pandas进行数据处理
pandas是python中最强大的数据处理库之一,特别适合处理结构化数据。
import pandas as pd
# 从csv创建dataframe
df = pd.read_csv('people.csv')
print(df.head())
# 基本数据处理
print(df.describe()) # 统计描述
print(df.sort_values('年龄', ascending=false)) # 排序
print(df[df['年龄'] > 25]) # 条件筛选
# 数据清洗
df.dropna() # 删除空值
df.fillna(0) # 填充空值
df['年龄'] = df['年龄'].astype(int) # 类型转换
# 保存处理结果
df.to_excel('processed_data.xlsx', index=false)
3.2 大数据文件处理策略
对于大文件,应避免一次性读取全部内容:
# 逐行处理大文本文件
with open('large_file.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
process_line(line) # 自定义处理函数
# 分块读取大csv文件
chunk_size = 10000
for chunk in pd.read_csv('large_data.csv', chunksize=chunk_size):
process_chunk(chunk)
# 使用生成器处理数据
def read_large_file(file_path):
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
while true:
data = f.read(1024) # 每次读取1kb
if not data:
break
yield data
for chunk in read_large_file('very_large_file.txt'):
process_chunk(chunk)
四、高级文件操作
4.1 目录遍历与文件操作
import os
from pathlib import path
# 使用os模块
print(os.listdir('.')) # 列出当前目录文件
os.makedirs('new_dir', exist_ok=true) # 创建目录
# 使用更现代的pathlib
base_path = path('.')
for file in base_path.glob('*.txt'): # 查找所有txt文件
print(file.name, file.stat().st_size) # 文件名和大小
# 递归遍历目录
for root, dirs, files in os.walk('some_directory'):
for file in files:
print(os.path.join(root, file))
4.2 文件压缩与解压
import zipfile
import gzip
import shutil
# zip文件处理
with zipfile.zipfile('archive.zip', 'w') as zf:
zf.write('file1.txt')
zf.write('file2.txt')
with zipfile.zipfile('archive.zip', 'r') as zf:
zf.extractall('extracted_files')
# gzip压缩
with open('large_file.txt', 'rb') as f_in:
with gzip.open('large_file.txt.gz', 'wb') as f_out:
shutil.copyfileobj(f_in, f_out)
4.3 内存文件操作(stringio/bytesio)
from io import stringio, bytesio
# 内存文本文件
string_io = stringio()
string_io.write('hello ')
string_io.write('world!')
print(string_io.getvalue()) # hello world!
# 内存二进制文件
bytes_io = bytesio()
bytes_io.write(b'binary data')
print(bytes_io.getvalue())
五、实战案例:日志文件分析
import re
from collections import counter
def analyze_logs(log_file):
# 统计ip访问次数
ip_pattern = re.compile(r'\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}')
ip_counter = counter()
# 统计状态码
status_pattern = re.compile(r'http/1.\d" (\d{3})')
status_counter = counter()
with open(log_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
# 提取ip
ip_match = ip_pattern.search(line)
if ip_match:
ip_counter[ip_match.group()] += 1
# 提取状态码
status_match = status_pattern.search(line)
if status_match:
status_counter[status_match.group(1)] += 1
# 输出结果
print("top 10 ips:")
for ip, count in ip_counter.most_common(10):
print(f"{ip}: {count}次")
print("\n状态码统计:")
for status, count in status_counter.most_common():
print(f"{status}: {count}次")
# 使用示例
analyze_logs('web_server.log')
六、最佳实践与注意事项
编码问题:
始终明确指定文件编码(推荐utf-8)
处理不同编码文件时使用chardet检测编码
路径处理:
使用os.path.join()或pathlib构建跨平台路径
避免硬编码路径,使用配置文件或命令行参数
资源管理:
始终确保文件正确关闭(推荐使用with语句)
大文件处理时注意内存使用
错误处理:
捕获和处理文件操作可能抛出的异常(filenotfounderror, permissionerror等)
实现重试机制处理临时性io错误
性能优化:
批量读写优于单次操作
考虑使用内存映射文件处理超大文件
结语
python提供了丰富而强大的文件操作和数据处理能力,从简单的文本文件到复杂的excel表格,从基本的字符串处理到高级的数据分析,python都能优雅地完成任务。掌握这些技能将大大提高您的开发效率和数据处理能力。
以上就是python文件操作与数据处理实战指南的详细内容,更多关于python文件操作与数据处理的资料请关注代码网其它相关文章!





发表评论