mysql分页查询
在mysql中,分页查询通常使用 limit 关键字来实现。
limit [offset,] rows 其中,offset表示偏移量(从结果集的第几行开始返回,默认从 0 开始计数),rows表示要返回的行数。
常规版
# 查询第一页(假设每页显示 10 条记录): select * from users limit 0, 10; #这里0是偏移量,表示从第 1 行(偏移量为 0)开始,10是要返回的行数。 #查询第二页: select * from users limit 10, 10; #此时偏移量为10,即跳过前面 10 行,然后返回 10 行。
升级版
更灵活的分页查询如果你需要更灵活地处理分页,可以使用变量来动态设置 offset 和 rows:
set @page_size := 10;
set @page_number := 2;
set @offset := (@page_size * (@page_number - 1));
select *
from employees
limit @offset, @page_size;
# 在存储过程中使用 limit 进行分页查询,以下是一个简单的存储过程示例,用于实现分页查询:
delimiter $$
create procedure get_page(in page_number int, in page_size int)
begin
set @offset = (page_number - 1) * page_size;
set @limit = page_size;
set @sql = concat('select * from your_table limit ', @offset, ', ', @limit);
prepare stmt from @sql;
execute stmt;
deallocate prepare stmt;
end$$
delimiter ;
使用 join 或子查询进行分页有时候,你可能需要在复杂的查询中进行分页,例如包含 join 或子查询:
select e.*
from employees e
join (
select employee_id
from employees
order by hire_date
limit @offset, @page_size
) as sub_query on e.employee_id = sub_query.employee_id;
mysql 8.0 引入了窗口函数,可以使用 row_number() 来实现分页:
select *
from (
select *, row_number() over (order by hire_date) as row_num
from employees
) as paginated_results
where row_num between @offset + 1 and @offset + @page_size;
oracle分页查询
在oracle数据库中,分页查询通常使用rownum伪列或者数据库12c及更高版本中的fetch first和offset子句来实现。
常规版
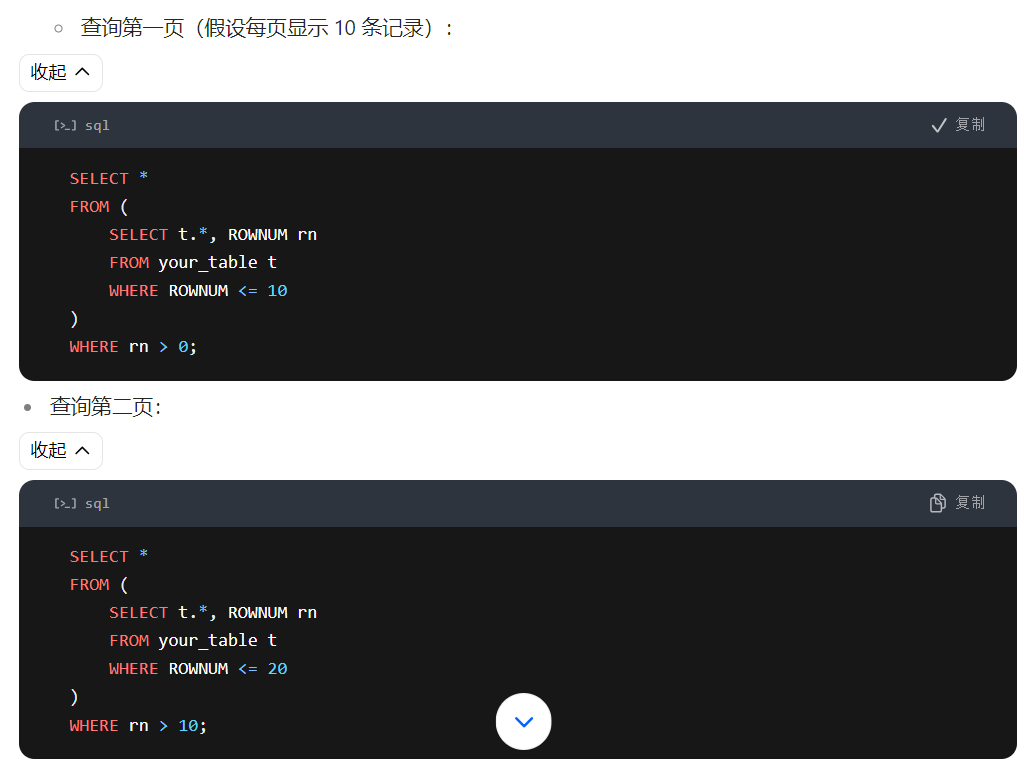
在oracle 12c之前的版本,分页查询通常依赖于rownum伪列。rownum为结果集中的每一行分配一个唯一的行号。
select * from (
select temp.*, rownum rnum from (
select * from your_table where conditions order by some_column
) temp where rownum <= :upper_bound
) where rnum > :lower_bound;
# :upper_bound是上界值,通常是(页码 * 每页显示的行数)。
# :lower_bound是下界值,通常是(页码 - 1) * 每页显示的行数 + 1。
# 假设你有一个名为employees的表,你想查询第2页的数据,每页显示10行数据。
select * from (
select temp.*, rownum rnum from (
select * from employees order by employee_id
) temp where rownum <= 20
) where rnum > 10;
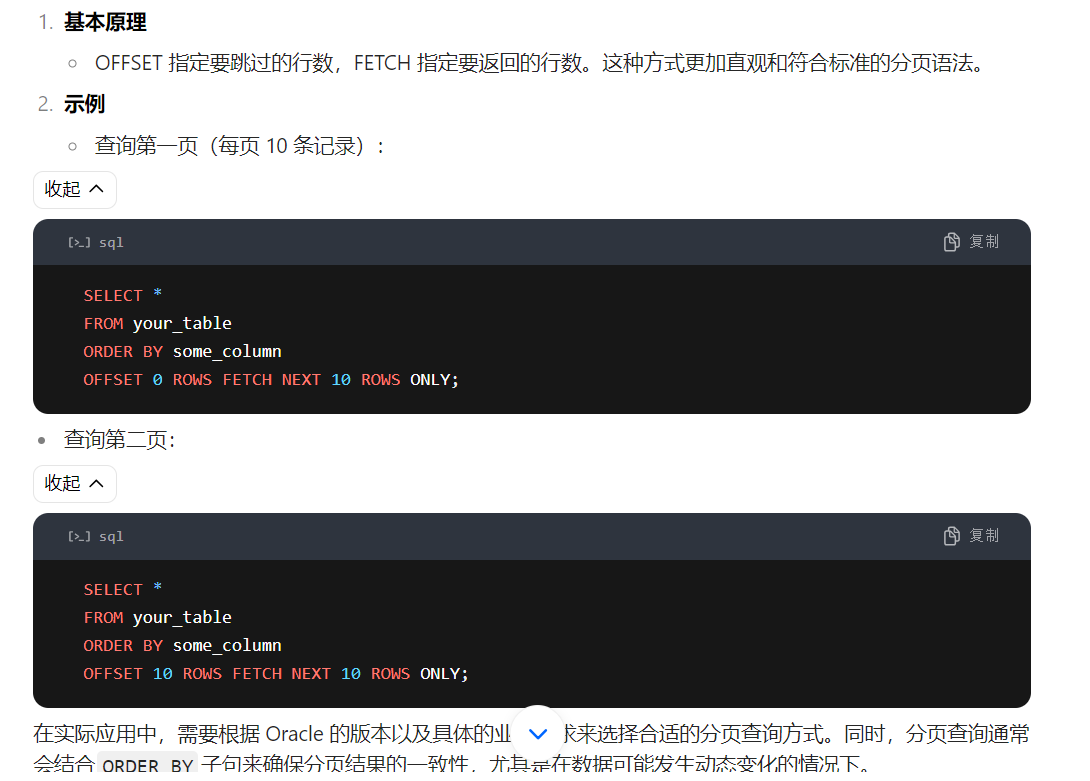
oracle 12c及更高版本使用offset和fetch进行分页
select * from your_table where conditions order by some_column offset :lower_bound rows fetch next :page_size rows only; # :lower_bound是分页的起始行,通常是(页码 - 1) * 每页显示的行数。 # :page_size是每页显示的行数。 # 假设你有一个名为employees的表,你想查询第2页的数据,每页显示10行数据。 select * from employees order by employee_id offset 10 rows fetch next 10 rows only; # 这里,offset 10 rows跳过前10行,fetch next 10 rows only则返回接下来的10行。
升级版
动态分页查询有时候我们可能需要根据用户输入或者业务逻辑动态地确定每页显示的记录数和页码。
例如,假设我们有一个存储过程,接受两个参数:p_page_number(页码)和p_page_size(每页记录数)。
在这个存储过程中,首先计算偏移量v_offset,然后在内部子查询中使用分析函数row_number()对表中的数据按照some_column(根据实际需求替换为排序依据的列)进行排序和编号。接着在中层子查询中根据计算得到的偏移量和每页记录数限制rownum,最后在外层子查询中根据rn(行号)筛选出真正需要的页面数据。
create or replace procedure dynamic_paging(p_page_number in number, p_page_size in number) as
v_offset number := (p_page_number - 1) * p_page_size;
begin
-- 使用分析函数和rownum进行分页
select *
from (
select t.*, rownum rn
from (
select col1, col2, col3, -- 这里列出实际表中的列
-- 使用分析函数(例如row_number)对数据进行排序和编号
row_number() over (order by some_column) as row_num
from your_table
) t
where rownum <= v_offset + p_page_size
)
where rn > v_offset;
end;
多表连接与分页结合当查询涉及多个表连接时,分页操作需要考虑连接结果的顺序和数量。
假设有table1和table2两个表,我们要查询连接后的结果并进行分页。
这里先进行table1和table2的连接操作,然后使用order by对连接结果进行排序,接着在内部子查询中使用rownum进行初步的分页筛选,最后在外层子查询中根据行号rn进行调整以得到正确的第一页数据。对于多表连接的分页查询,确保连接的正确性以及排序的合理性是很重要的,这样才能得到准确的分页结果。
select *
from (
select t.*, rownum rn
from (
select col1, col2, col3 -- 这里列出连接后的列
from table1
join table2 on table1.key = table2.key
order by some_column
) t
where rownum <= 10
)
where rn > 0;
分区表的分页优势如果数据存储在分区表中,可以利用分区的特性更高效地进行分页查询。
假设我们有一个按照日期分区的表partitioned_table,要查询某个日期分区内的数据并进行分页。
通过指定分区名,可以直接在该分区内进行分页查询,减少了查询的数据量,提高了查询效率,尤其是在处理大型表时这种优势更加明显。
select *
from (
select t.*, rownum rn
from (
select col1, col2, col3
from partitioned_table partition (partition_name) -- 替换为实际分区名
order by some_column
) t
where rownum <= 10
)
where rn > 0;
postgresql分页查询
在postgresql中,分页查询通常使用 limit 和 offset 子句来实现。这两个子句可以限制查询结果的数量,并指定返回结果的起始点。
常规版
使用 limit 和 offset 关键字
# column_name是用于排序的列(如果不指定排序顺序,分页结果可能会不稳定), # count 是要返回的行数(即每页的行数), # offset_value是偏移量(表示从结果集的第几行开始返回)。 select * from table_name where condition order by column_name limit count offset offset_value; # 查询第一页(假设每页显示 10 条记录) # 这里查询users表,按照user_id排序,返回前 10 条记录(偏移量为 0 表示从第一行开始)。 select * from users order by user_id limit 10 offset 0; # 查询第二页 select * from users order by user_id limit 10 offset 10;
使用 fetch 和 offset(postgresql 8.4 及以上版本支持 fetch)
select * from your_table order by some_column offset offset_value fetch first num_rows rows only; select * from users order by user_id offset 0 fetch first 10 rows only; select * from users order by user_id offset 10 fetch first 10 rows only;
升级版
更灵活的分页查询
set @page_size = 10;
set @page_number = 2;
set @offset = (@page_size * (@page_number - 1));
select *
from employees
order by employee_id
limit @page_size offset @offset;
# 在这个函数中,根据传入的页码p_page_number和每页大小p_page_size构建动态 sql 语句。
#然后使用return query execute执行动态 sql 并返回结果。这种方式使得分页查询更加灵活,能够适应不同的需求。
create or replace function dynamic_paging(p_page_number int, p_page_size int)
returns setof your_table_type as
$body$
declare
v_sql text;
begin
v_sql := format('select * from your_table order by some_column limit %s offset %s', p_page_size, (p_page_number - 1) * p_page_size);
return query execute v_sql;
end;
$body$
language plpgsql;多表连接后的分页
# 当查询涉及多个表的连接时,分页操作需要考虑连接结果集的顺序和结构。
# 例如,假设有三个表table1、table2和table3,要对它们连接后的结果进行分页:
select *
from (
select sub.*, rownum as row_num
from (
select t1.col1, t2.col2, t3.col3
from table1 t1
join table2 t2 on t1.key = t2.key
join table3 t3 on t2.other_key = t3.other_key
order by t1.some_column
) sub
)
where row_num between start_row and end_row;
#首先在内部子查询中进行多表连接并按照table1中的some_column排序。
#然后在中层子查询中使用rownum(这里rownum类似 oracle 中的概念,
#在 postgresql 中是自定义的行号)为结果集编号。
#最后在外层子查询中根据计算出的开始行start_row和结束行
#end_row(可以根据页码和每页大小计算得出)进行分页筛选。
使用窗口函数进行分页postgresql 8.4及以上版本支持窗口函数,可以使用 row_number() 窗口函数来实现更复杂的分页逻辑:
with paginated as (
select *, row_number() over (order by employee_id) as rn
from employees
)
select *
from paginated
where rn between 11 and 20;
#窗口函数可以在不改变结果集行数的情况下对每一行进行计算,这在复杂的分页场景中很有用。
#例如,假设要对一个包含员工信息的表employees进行分页,并且在分页结果中显示每个员工在部门内的排名:
select department, employee_name, salary,
row_number() over (partition by department order by salary desc) as rank_in_department
from employees
order by department, rank_in_department
limit page_size offset offset;
# 这里使用row_number()窗口函数计算每个员工在其所属部门内按照薪资降序排列的排名。
# 然后按照部门和部门内排名进行排序,最后进行分页操作。这种方式可以在分页结果中提供更多的信息和分析价值。
sql server分页查询
在 sql server 中,分页查询可以通过使用 offset 和 fetch 子句来实现。这些子句在 sql server 2012 及更高版本中被引入,提供了一种简单且直观的方式来进行分页。
常规版
使用offset - fetch子句(sql server 2012 及以上版本)
select * from your_table order by some_column offset offset_rows rows fetch next fetch_rows rows only; # 其中,your_table是要查询的表名, # some_column是用于排序的列(如果不指定排序顺序,分页结果可能会不稳定), # offset_rows是偏移量(表示从结果集的第几行开始返回), # fetch_rows是要返回的行数(即每页的行数)。 # 查询第一页(假设每页显示 10 条记录) select * from users order by user_id offset 0 rows fetch next 10 rows only; # 查询第二页 select * from users order by user_id offset 10 rows fetch next 10 rows only;
使用top关键字结合子查询(适用于旧版本)
# 查询第一页(假设每页显示 10 条记录)
select top 10 * from your_table order by some_column;
# 查询第二页(假设每页显示 10 条记录)
# 这个方法相对复杂一些,在子查询中获取前 20 条记录,然后通过外部查询排除前 10 条记录来得到第二页的数据。
select * from (
select top 20 * from your_table order by some_column
) as subquery
where not exists (select top 10 * from your_table order by some_column)
order by some_column;
升级版
使用动态 sql 实现灵活分页
# 例如,创建一个存储过程,接受页码@pagenumber和每页行数@pagesize作为参数:
create procedure dynamicpaging
@pagenumber int,
@pagesize int
as
begin
declare @sql nvarchar(max);
set @sql = n'select * from (
select *, row_number() over (order by some_column) as row_num
from your_table
) as subquery
where row_num between ' + cast((@pagenumber - 1) * @pagesize + 1 as nvarchar(10)) + ' and ' + cast(@pagenumber * @pagesize as nvarchar(10));
exec sp_executesql @sql;
end;
# 在这个存储过程中,首先构建动态 sql 语句。使用row_number()函数为结果集中的每一行分配一个行号(按照some_column排序),
# 然后根据传入的页码和每页行数计算出要获取的行号范围,最后通过sp_executesql执行动态 sql 语句来实现分页查询。
多表连接后的分页
# 例如,假设有表table1和table2,要对它们连接后的结果进行分页:
select *
from (
select sub.*, row_number() over (order by some_column) as row_num
from (
select t1.col1, t2.col2
from table1 t1
join table2 t2 on t1.key = t2.key
order by some_column
) as sub
) as final
where row_num between start_row and end_row;
# 首先在内部子查询中进行table1和table2的连接,并按照some_column排序。
#然后在中层子查询中使用row_number()函数为连接后的结果集分配行号。
#最后在外层子查询中根据计算出的起始行start_row和结束行
#end_row(可以根据页码和每页行数计算得出)进行分页筛选。
与窗口函数结合的分页查询
# 例如,要查询员工表employees中的数据并进行分页,同时显示每个部门内员工的排名:
select department, employee_name, salary,
row_number() over (partition by department order by salary desc) as rank_in_department
from employees
order by department, rank_in_department
offset offset_rows rows fetch next fetch_rows rows only;
#这里使用row_number()窗口函数在每个部门内按照薪资降序为员工分配排名。
#然后按照部门和部门内排名进行排序,最后再进行分页操作。这种方式可以在分页结果中提供更详细的部门内员工信息。总结
到此这篇关于常见数据库中sql分页语法整理大全的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关数据库sql分页语法内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论