正文
efcore是微软官方的一款orm框架,主要是用于实体和数据库对象之间的操作。功能非常强大,在老版本的时候叫做ef,后来.net core问世,efcore也随之问世。
本文我们将用一个控制台项目host一个web服务,并且使用本地mysql作为数据库,使用efcore的code first模式进行数据操作。
dbset清除计划
以前使用ef/efcore的开发者应该都记得,需要在dbcontext里写好多dbset,一个表对应一个dbset,然后在其他地方操作这些dbset对相关的表进行增删改查。作为一个开发,这些重复操作都是我们希望避免的,我们可以利用反射机制将这些类型通过框架自带的方法循环注册进去。
1.ef实体继承统一的接口,方便我们反射获取所有ef实体,接口可以设置一个泛型,来泛化我们的主键类型,因为可能存在不同的表的主键类型也不一样。
统一的ef实体接口
public interface iefentity<tkey>
{
public tkey id { get; set; }
}
统一的接口实现类
public abstract class aggregateroot<tkey> : iefentity<tkey>
{
public tkey id { get; set; }
}
用户实体类
public class user : aggregateroot<string>
{
public string username { get; set; }
public datetime birthday { get; set; }
public virtual icollection<book> books { get; set; }
}
2.利用反射获取某个程序集下所有的实体类
public class efentityinfo
{
public (assembly assembly, ienumerable<type> types) efentitiesinfo => (gettype().assembly, getentitytypes(gettype().assembly));
private ienumerable<type> getentitytypes(assembly assembly)
{
//获取当前程序集下所有的实现了iefentity的实体类
var efentities = assembly.gettypes().where(m => m.fullname != null
&& array.exists(m.getinterfaces(), t => t.isgenerictype && t.getgenerictypedefinition() == typeof(iefentity<>))
&& !m.isabstract && !m.isinterface).toarray();
return efentities;
}
}
3.dbcontext实现类中onmodelcreating方法中注册这些类型
protected override void onmodelcreating(modelbuilder modelbuilder)
{
//循环实体类型,并且通过entity方法注册类型
foreach (var entitytype in types)
{
modelbuilder.entity(entitytype);
}
base.onmodelcreating(modelbuilder);
}
至此为止所有的实体类都被注册到dbcontext中作为dbsets,再也不需要一个个写dbset了,可以用过dbcontext.set<user>()获取用户的dbset。
ientitytypeconfiguration(表配置)
用数据库创建过表的同学都知道,在设计表的时候,可以给表添加很多配置和约束,在code first模式中,很多同学都是在对象中通过注解的方式配置字段。如下就配置了用户名是不能为null和最大长度为500
[required]
[maxlength(500)]
public string username { get; set; }
也有的同学在dbcontext中的onmodelcreating方法配置
modelbuilder.entity<user>().property(x => x.username).isrequired();
这两种方法,前者入侵行太强,直接代码耦合到实体类中了,后者不够清楚,把一大堆表的配置写在一个方法里,当然了很多人说可以拆分不同的方法或者使用注释分开。但是!不够优雅!
我们可以使用ientitytypeconfiguration接口实现我们所想的优雅的表配置。
1.创建一个配置基类,继承自ientitytypeconfiguration,做一些通用的配置,比如设置主键,一般都是id啦,还有软删除等。
public abstract class entitytypeconfiguration<tentity, tkey> : ientitytypeconfiguration<tentity>
where tentity : aggregateroot<tkey>
{
public virtual void configure(entitytypebuilder<tentity> builder)
{
var entitytype = typeof(tentity);
builder.haskey(x => x.id);
if (typeof(isoftdelete).isassignablefrom(entitytype))
{
builder.hasqueryfilter(d => ef.property<bool>(d, "isdeleted") == false);
}
}
}
2.创建用户实体/表独有的配置,比如设置用户名的最大长度,以及seed一些数据
public class userconfig : entitytypeconfiguration<user, string>
{
public override void configure(entitytypebuilder<user> builder)
{
base.configure(builder);
builder.property(x => x.username).hasmaxlength(50);
//mock一条数据
builder.hasdata(new user()
{
id = "090213204",
username = "bruce",
birthday = datetime.parse("1996-08-24")
});
}
}
当然还有很多配置可以设置,比如索引,导航属性,唯一键等。如下图书实体
public class bookconfig : entitytypeconfiguration<book, long>
{
public override void configure(entitytypebuilder<book> builder)
{
base.configure(builder);
builder.property(x => x.id).valuegeneratedonadd(); //设置book的id自增
builder.property(x => x.bookname).hasmaxlength(500).isrequired();
builder.hasindex(x => x.author);//作者添加索引
builder.hasindex(x => x.sn).isunique();//序列号添加唯一索引
builder.hasone(r => r.user).withmany(x=>x.books)
.hasforeignkey(r => r.userid).isrequired();//导航属性,本质就是创建外键,虽然查询很方便,生产中不建议使用!!!
}
}
3.dbcontext中应用配置
protected override void onmodelcreating(modelbuilder modelbuilder)
{
modelbuilder.hascharset("utf8mb4 ");
var (assembly, types) = _efentitysinfo.efentitiesinfo;
foreach (var entitytype in types)
{
modelbuilder.entity(entitytype);
}
//只需要将配置类所在的程序集给到,它会自动加载
modelbuilder.applyconfigurationsfromassembly(assembly);
base.onmodelcreating(modelbuilder);
}
repository(仓储)
这个不过分介绍,特别是基于http的微服务中基本都有这个。
1.创建一个仓储基类,对于不同的实体,创建一样的增删改查方法。
简单写几个查询的方法定义。
public interface iasyncrepository<tentity, tkey> where tentity : class
{
iqueryable<tentity> all();
iqueryable<tentity> all(string[] propertiestoinclude);
iqueryable<tentity> where(expression<func<tentity, bool>> filter);
iqueryable<tentity> where(expression<func<tentity, bool>> filter, string[] propertiestoinclude);
}
2.创建仓储实现类,将dbcontext注入到构造中
public class genericrepository<tentity, tkey> : iasyncrepository<tentity, tkey> where tentity : class
{
protected readonly librarydbcontext _dbcontext;
public genericrepository(librarydbcontext dbcontext)
{
_dbcontext = dbcontext;
}
~genericrepository()
{
_dbcontext?.dispose();
}
public virtual iqueryable<tentity> all()
{
return all(null);
}
public virtual iqueryable<tentity> all(string[] propertiestoinclude)
{
var query = _dbcontext.set<tentity>().asnotracking();
if (propertiestoinclude != null)
{
foreach (var property in propertiestoinclude.where(p => !string.isnullorwhitespace(p)))
{
query = query.include(property);
}
}
return query;
}
}
autofac
1.注入dbcontext到repository的构造方法中,并且注入repository
public class efcoreeleganceuseefcoremodule : module
{
protected override void load(containerbuilder builder)
{
base.load(builder);
builder.registermodule<efcoreeleganceusedomainmodule>(); //注入domain模块
builder.registergeneric(typeof(genericrepository<,>))//将dbcontext注入到仓储的构造中
.usingconstructor(typeof(librarydbcontext))
.asimplementedinterfaces()
.instanceperdependency();
builder.registertype<workunit>().as<iworkunit>().instanceperdependency();
}
}
2.domain注入efentityinfo
public class efcoreeleganceusedomainmodule : module
{
protected override void load(containerbuilder builder)
{
builder.registertype<efentityinfo>().singleinstance();
}
}
数据库配置
1.注入dbcontext,从配置文件读取数据库配置,然后根据开发/生产环境做一些特殊处理
var mysqlconfig = hostcontext.configuration.getsection("mysql").get<mysqloptions>();
var serverversion = new mariadbserverversion(new version(mysqlconfig.version));
services.adddbcontextfactory<librarydbcontext>(options =>
{
options.usemysql(mysqlconfig.connectionstring, serverversion, optionsbuilder =>
{
optionsbuilder.minbatchsize(4);
optionsbuilder.commandtimeout(10);
optionsbuilder.migrationsassembly(mysqlconfig.migrationassembly);//迁移文件所在的程序集
optionsbuilder.usequerysplittingbehavior(querysplittingbehavior.splitquery);
}).usequerytrackingbehavior(querytrackingbehavior.notracking);
//开发环境可以打开日志记录和显示详细的错误
if (hostcontext.hostingenvironment.isdevelopment())
{
options.enablesensitivedatalogging();
options.enabledetailederrors();
}
});
项目架构和源码
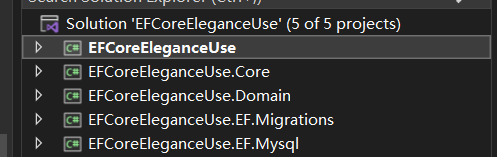
项目只是一个demo架构,并不适用于生产,主程序是一个控制台项目,只需要引用相关的包和模块,就可以启动一个web host.
全部代码已经全部上传到github:https://github.com/bruceqiu1996/efcoredemo该项目是一个可以启动运行的基于.net6的控制台项目,启动后会启动一个web host和一个swagger页面。
以上就是.net如何优雅的使用efcore实例详解的详细内容,更多关于.net使用efcore的资料请关注代码网其它相关文章!




发表评论