前言
postgresql 数据库是最常用的关系型数据库之一,最吸引人的一点是它作为开源数据库且具有可拓展性,能够提供丰富的应用。运用python可以很简单的建立postgresql 数据库连接,其中最受欢迎的就是psycopg。
1. 安装psycopg2
psycopy是针对python的postgres 数据库的适配模块,安装psycopg2可以整合python和postgres 。使用cmd输入命令进行安装:
pip install psycopg2
也可以在pycharm中查找psycopg2安装包:
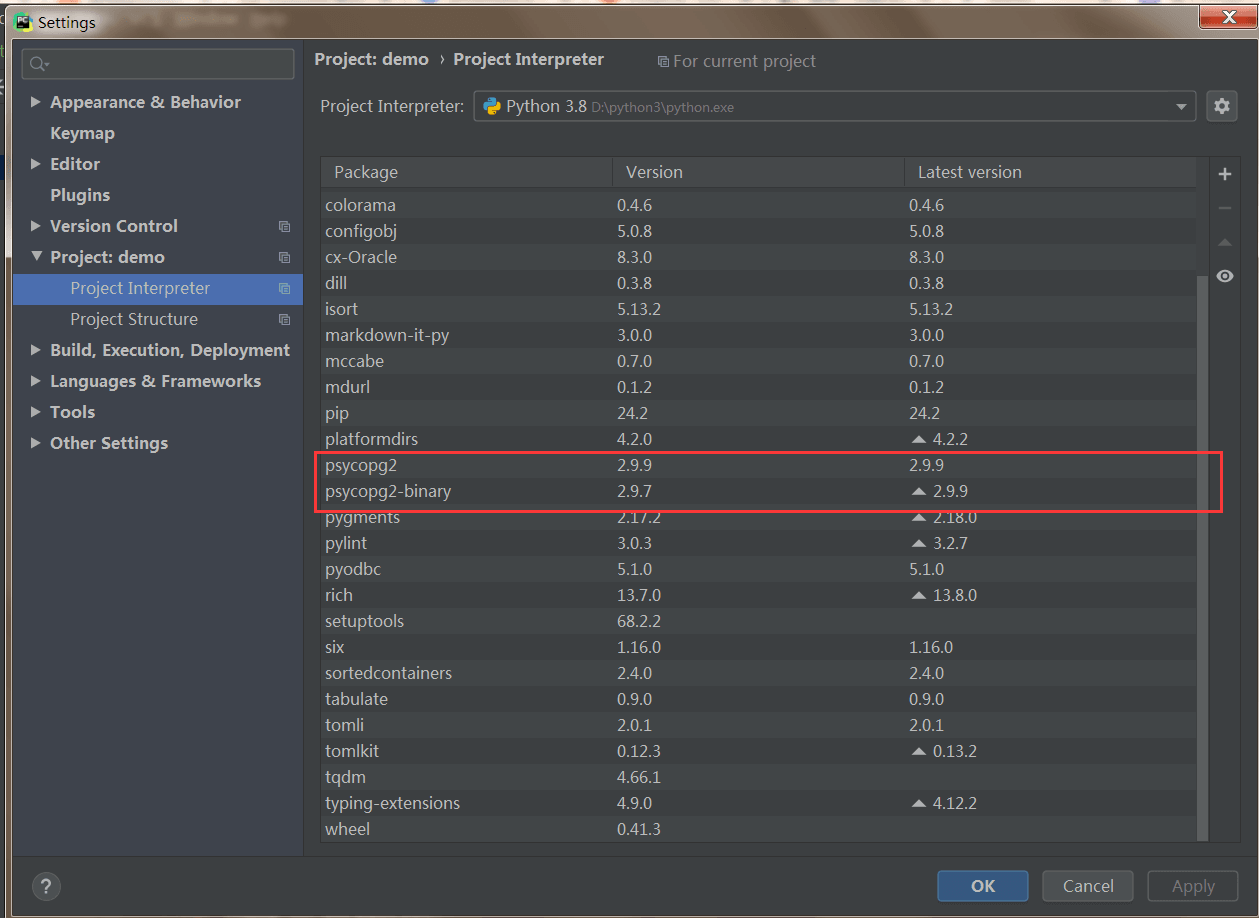
2. 图形化连接数据库
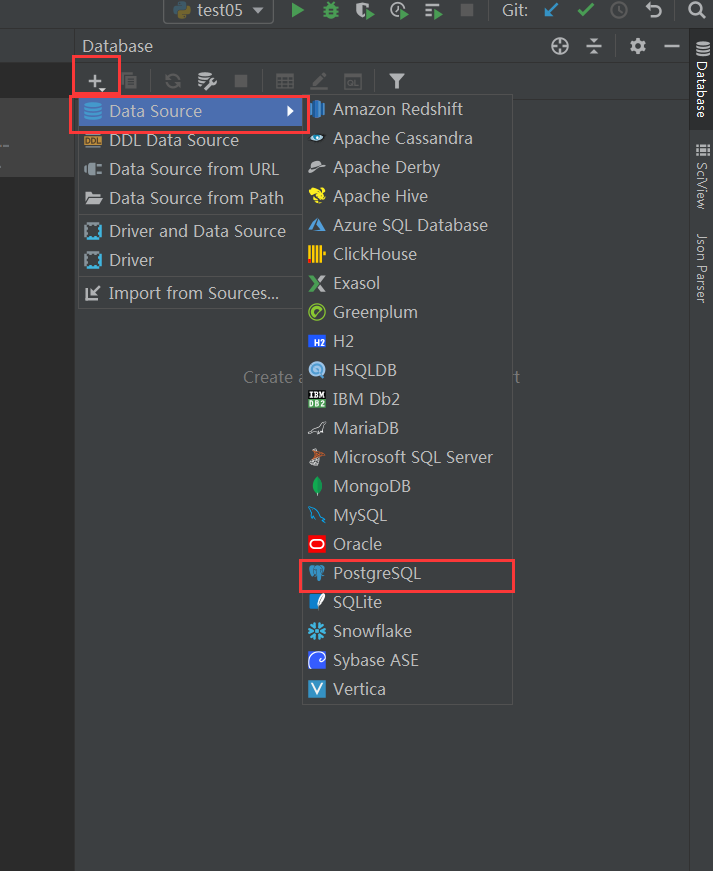
在pycharm中选择database,点击左上角的+添加数据库,选择postgresql:
创建数据库连接后点击apply,数据库会显示在右侧窗格中。
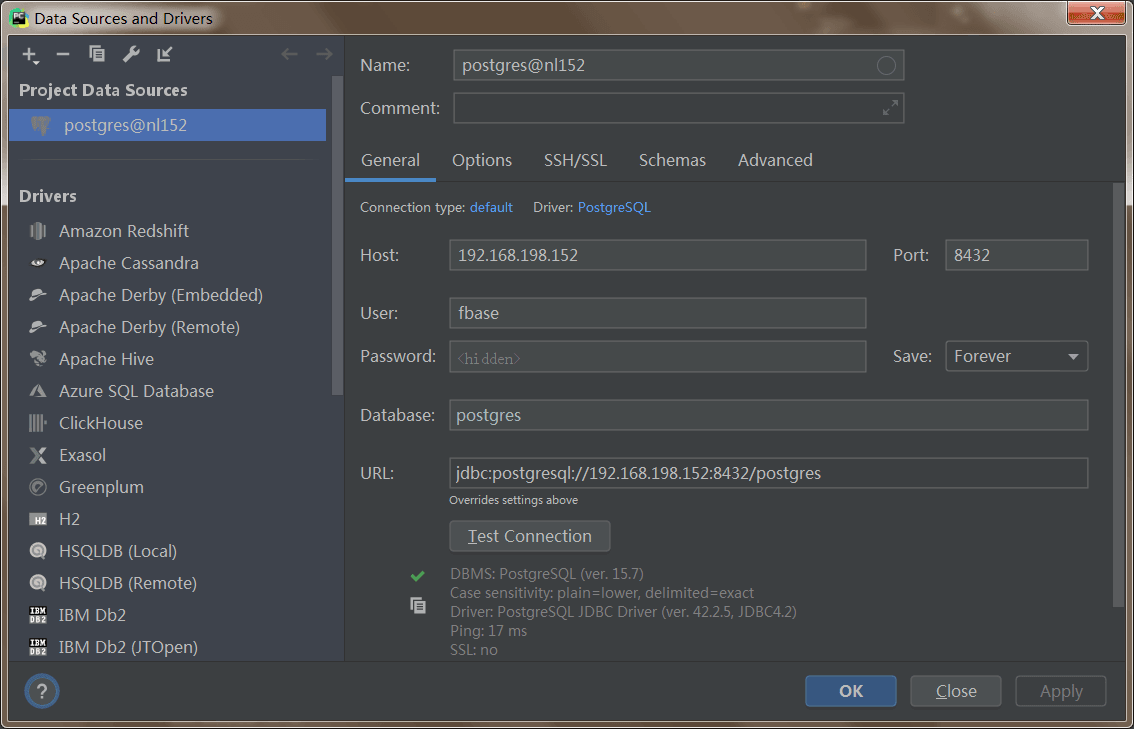
3. 代码连接数据库
3.1 不使用配置文件
下面使用 psycopy2.connect()方法连接到postgresql数据库。通过调用cursor类中的execute()方法对数据库进行操作。在execute()中用sql语句创建表。使用commit()将数据发送到数据库服务器,最后使用close()关闭数据库。commit()能够对数据库进行改变,且不可逆。
connect() 方法的参数一般包括:
- database: 要连接的数据库名称
- user:连接数据库的用户名
- password: 连接数据库的密码
- host: 数据库端口的地址,一般为 “localhost”,或者主机的ip地址
- port: 门户 默认为5432.
import psycopg2
con = psycopg2.connect(database="postgres",
user="fbase",
password="123456",
host="192.168.198.152",
port="8432")
print(con)
print("database opened successfully")
cur = con.cursor()
cur.execute('select version()')
db_version = cur.fetchone()
print(db_version)
con.close()
运行结果如下:

3.2 使用配置文件
可以使用配置文件来存储所有连接参数。
database.ini文件的内容如下:
[postgresql] host = 192.168.198.152 database = postgres user = fbase password = 123456 port = 8432
下面的config()函数会读取database.ini文件并返回连接参数。该config()函数放置在config.py文件中:
from configparser import configparser
def config(filename='../../resource/database.ini', section='postgresql'):
# create a parser
parser = configparser()
# read config file
parser.read(filename)
# get section, default to postgresql
db = {}
if parser.has_section(section):
params = parser.items(section)
for param in params:
db[param[0]] = param[1]
else:
raise exception('section {0} not found in the {1} file'.format(section, filename))
return db下面的connect()函数连接到suppliers数据库并打印出 postgresql 数据库版本。
import psycopg2
from demo.pgdemo.config import config
def connect():
""" connect to the postgresql database server """
conn = none
try:
# read connection parameters
params = config()
# connect to the postgresql server
print('connecting to the postgresql database...')
conn = psycopg2.connect(**params)
# create a cursor
cur = conn.cursor()
# execute a statement
print('postgresql database version:')
cur.execute('select version()')
# display the postgresql database server version
db_version = cur.fetchone()
print(db_version)
# close the communication with the postgresql
cur.close()
except (exception, psycopg2.databaseerror) as error:
print(error)
finally:
if conn is not none:
conn.close()
print('database connection closed.')
if __name__ == '__main__':
connect()怎么运行的。
- 首先,从
database.ini文件中读取数据库连接参数。 - 接下来,通过调用
connect()函数创建一个新的数据库连接。 - 然后,新建一个
cursor并执行sql语句来获取 postgresql 数据库版本。 - 之后,通过调用游标对象的
fetchone()方法读取结果集。 - 最后,通过调用
cursor和connection对象的close()方法关闭与数据库服务器的通信。
4. dml语句测试
4.1 创建表
使用sql(structured query language)语句create table添加新的表:
import psycopg2
# 建立数据库连接
con = psycopg2.connect(database="postgres",
user="fbase",
password="123456",
host="192.168.198.152",
port="8432")
print("database opened successfully")
# 调用游标对象
cur = con.cursor()
# 用cursor中的execute 使用ddl语句创建一个名为 student 的表,指定表的字段以及字段类型
cur.execute('''
create table if not exists student
(admission int primary key not null,
name text not null,
age int not null,
course char(50),
department char(50));''')
# 提交更改,增添或者修改数据只会必须要提交才能生效
con.commit()
con.close()
结果查看:
postgres=# \d
list of relations
schema | name | type | owner
--------+---------+-------+-------
public | student | table | fbase
(1 row)
4.2 表插入数据
使用insert into 在以经生成的表中插入数据
import psycopg2
# 建立数据库连接
con = psycopg2.connect(database="postgres",
user="fbase",
password="123456",
host="192.168.198.152",
port="8432")
print("database opened successfully")
# 调用游标对象
cur = con.cursor()
# 在表中插入一条数据
cur.execute("insert into student (admission,name,age,course,department) "
"values (3420, 'john', 18, 'computer science', 'ict')")
# 提交更改,增添或者修改数据只会必须要提交才能生效
con.commit()
con.close()
结果查看:
postgres=# select * from student ;
admission | name | age | course | department
-----------+------+-----+----------------------------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------
3420 | john | 18 | computer science | ict
(1 row)
4.3 表更新数据
同样使用sql语句更新目标字段,使用commit()更新数据库
import psycopg2
# 建立数据库连接
con = psycopg2.connect(database="postgres",
user="fbase",
password="123456",
host="192.168.198.152",
port="8432")
print("database opened successfully")
# 调用游标对象
cur = con.cursor()
# 更新表中的数据
cur.execute("update student set name = 'joe' where admission = 3420")
# 提交更改,增添或者修改数据只会必须要提交才能生效
con.commit()
con.close()
结果查看:
postgres=# select * from student ;
admission | name | age | course | department
-----------+------+-----+----------------------------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------
3420 | john | 18 | computer science | ict
(1 row)
postgres=# select * from student ;
admission | name | age | course | department
-----------+------+-----+----------------------------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------
3420 | joe | 18 | computer science | ict
(1 row)
4.4 表删除数据
同样使用sql语句更新目标字段,使用commit()更新数据库
import psycopg2
# 建立数据库连接
con = psycopg2.connect(database="postgres",
user="fbase",
password="123456",
host="192.168.198.152",
port="8432")
print("database opened successfully")
# 调用游标对象
cur = con.cursor()
# 删除表中的数据
cur.execute("delete from student where admission = 3420")
# 提交更改,增添或者修改数据只会必须要提交才能生效
con.commit()
con.close()
结果查看:
postgres=# select * from student ;
admission | name | age | course | department
-----------+------+-----+----------------------------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------
3420 | joe | 18 | computer science | ict
(1 row)
postgres=# select * from student ;
admission | name | age | course | department
-----------+------+-----+--------+------------
(0 rows)
5. dql语句测试
5.1 查看表中的数据
同样使用sql语句更新目标字段,使用commit()更新数据库
import psycopg2
# 建立数据库连接
con = psycopg2.connect(database="postgres",
user="fbase",
password="123456",
host="192.168.198.152",
port="8432")
print("database opened successfully")
# 调用游标对象
cur = con.cursor()
# 删除表中的数据
cur.execute("select * from student")
rows = cur.fetchall()
for row in rows:
print("admission =", row[0])
print("name =", row[1])
print("age =", row[2])
print("course =", row[3])
print("department =", row[4], "\n")
# 提交更改,增添或者修改数据只会必须要提交才能生效
con.commit()
con.close()
结果查看:
d:\python3\python.exe d:/project/python/demo/demo/pgdemo/dql_select_1.py
database opened successfully
admission = 3420
name = john
age = 18
course = computer science
department = ict
w[3])
print("department =", row[4], "\n")
# 提交更改,增添或者修改数据只会必须要提交才能生效
con.commit()
con.close()
结果查看:
d:\python3\python.exe d:/project/python/demo/demo/pgdemo/dql_select_1.py database opened successfully admission = 3420 name = john age = 18 course = computer science department = ict
总结
到此这篇关于使用python进行postgresql数据库连接的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python连接postgresql数据库内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论