前言
在mysql的查询优化中,索引是一项至关重要的技术,它能够大大提升数据检索的效率。本文将讨论这11种常见情况,帮助开发者更好地理解索引的使用及优化。
图示
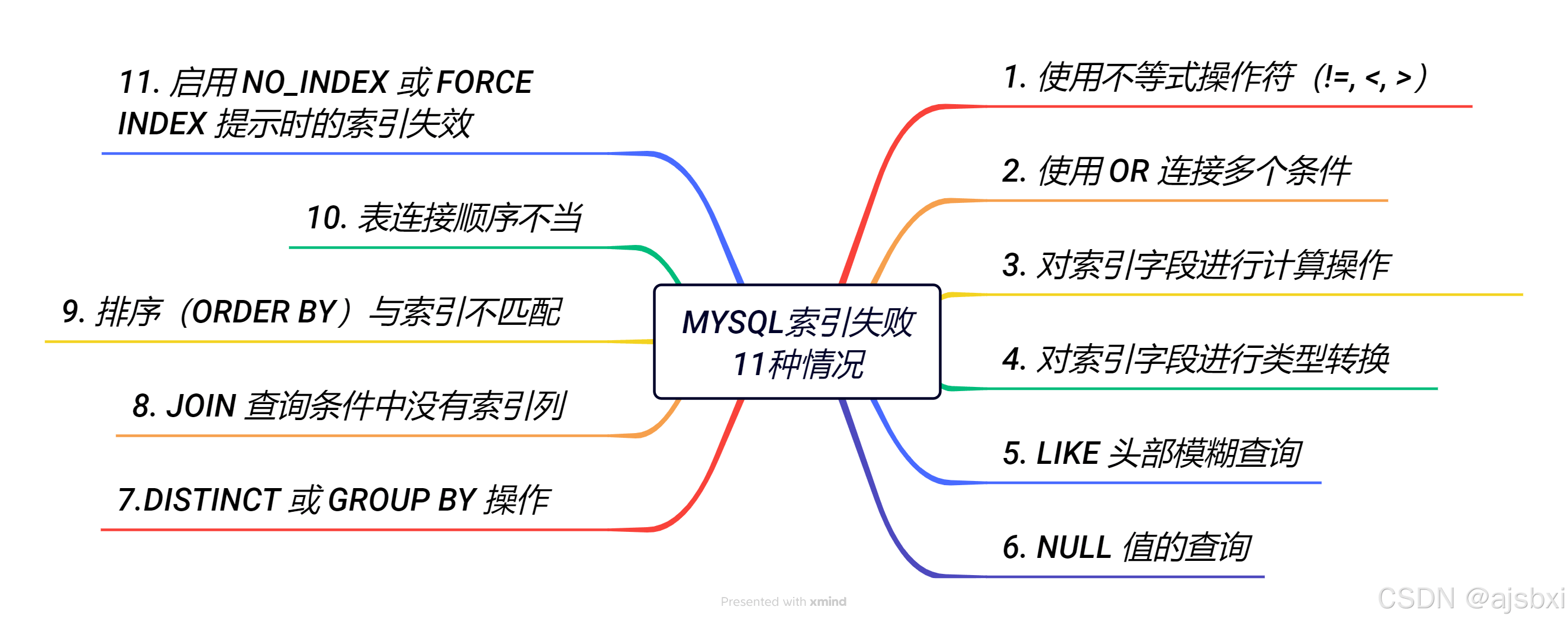
1. 使用不等式操作符(!=, <, >)
- 例子:
select * from users where age != 30;
- 原理:索引通常用于等值查询(
=)或范围查询(>,<),不等式操作无法有效利用索引。 - 解决方案:避免使用不等式条件,改用范围查询。
select * from users where age not between 30 and 30; select * from users where`age > 30`and`age < 30;
2. 使用 or 连接多个条件
- 例子:
select * from users where age = 30 or gender = 'male';
- 原理:
or会导致多个独立查询,尤其当每个条件涉及不同列时,索引不会完全失效,会快速定位有索引列部分,无索引列进行全部扫描。 - 解决方案:使用
union替代or、创建联合索引。--创建联合索引 create index idx_users_age_gender on users(age,gender); select * from users where age = 30 or gender = 'male'; --使用union合并子查询 select * from users where age = 30 union select * from users where gender = 'male';
3. 对索引字段进行计算操作
- 例子:
select * from orders where year(order_date) = 2024;
- 原理:计算和函数操作会改变数据的表现形式,索引无法直接应用。这个查询中,使用了
year(order_date)函数来提取order_date字段的年份,与 2024 进行比较。 - 解决方案:1.改为直接存储处理后的数据。2.直接改为当前字段的范围查询。
--范围查询 select * from orders where order_date >= '2024-01-01' and order_date < '2025-01-01'; --直接存储处理后的数据 alter table orders add column order_year int; -- 新增字段 order_year update orders set order_year = year(order_date); select * from orders where order_year = 2024;
4. 对索引字段进行类型转换
- 例子:
select * from users where cast(age as char) = '30';
- 原理:类型转换会导致数据类型与索引数据类型不匹配,索引失效。
- 解决方案:确保查询条件的数据类型与索引数据类型一致,避免使用类型转换。
5. like 头部模糊查询
- 例子:
select * from users where name like '%john';
- 原理:
like查询以%开头时,索引无法使用,因为数据库无法提前确定匹配的范围。 - 解决方案:避免在
like查询中使用前缀%,改为like 'john%'。select * from users where name like 'john%';
6. null 值的查询
- 例子:
select * from users where age is null;
- 原理:索引对
null值的查询支持有限,可能无法高效利用。 - 解决方案:避免频繁查询
null值,或者为包含null值的字段设计专门的索引、将null值替换为其他默认值。-- 使用ifnull() 函数 select * from users where ifnull(age, -1) = -1; -- 使用coalesce() 函数 select * from users where coalesce(age, -1) = -1; --使用 not null 约束,修改字段默认值为 0 alter table users modify age not null default 0;
7. distinct 或 group by 操作
- 例子:
select distinct age from users; select age, count(*) from users group by age;
- 原理:
distinct和group by操作需要去重或聚合数据。这些操作不能直接利用索引来返回唯一结果,通常会导致数据库扫描整个表(即全表扫描),尤其是在没有合适索引的情况下。 - 解决方案:使用合适的索引(例如
group by列上创建索引),或者将查询分解成多个步骤。--创建索引 create index idx_users_age on users(age); select age, count(*) from users group by age; --子查询获取去重结果集再查询 select age, count(*) from users where age in ( select distinct age from users where age is not null ) group by age;
8. join 查询中没有适当的索引
- 例子:
select * from users u join orders o on u.id = o.user_id;
- 原理:如果连接条件没有索引,
join查询可能会导致全表扫描。 - 解决方案:为连接字段创建索引,确保连接操作高效执行。
create index idx_user_id on orders(user_id); create index idx_user_id_users on users(id);
- 使用合适的连接类型:在某些情况下,使用
inner join、left join或其他连接类型可以影响查询性能,选择最合适的连接方式可以帮助优化性能。
9. 排序(order by)与索引不匹配
- 例子:
select * from users order by name desc,age asc;
- 原理:如果索引的顺序与查询的排序要求不匹配,可能无法利用索引。
- 解决方案:确保查询的排序方式与索引的顺序一致,使用复合索引支持多种排序需求。
-- 创建复合索引 create index idx_name_age on users(name desc, age asc); select * from users order by name desc, age asc;
10. 表连接顺序不当
- 例子:
select * from users u join orders o on u.id = o.user_id where o.order_date > '2024-01-01';
- 原理:连接顺序不当可能导致某些表的索引无法使用,从而降低查询性能。
- 解决方案:根据数据量和索引设计优化
join顺序。-- 使用子查询(筛选大表后再去连接) select * from (select * from orders where order_date > '2024-01-01') o join users u on u.id = o.user_id; -- 小表驱动大表(如果users表有100条,orders有20万数据) -- 使用 straight_join 强制左表为驱动表 select * from users u straight_join orders o on u.id = o.user_id where o.order_date > '2024-01-01';
11. 启用 no_index 或 force index 提示时的索引失效
- 例子:
select * from users force index (idx_name) where age = 30;
- 原理:强制索引或禁止索引可能导致查询优化器无法选择最优的执行计划。
- 解决方案:避免使用
force index或no_index,让数据库自动选择最优索引。
总结
在 sql 查询优化中,合适的索引设计和查询结构调整是提高性能的关键。通过以下措施可以避免常见的性能瓶颈:
- 使用适当的索引来加速
distinct、group by、join和order by操作。 - 优化连接顺序,确保合理使用索引。
- 避免强制使用或禁用索引,允许查询优化器自动选择最优执行计划。
到此这篇关于mysql进阶之路索引失效的11种情况的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关mysql索引失效情况内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论