本篇主要是基于go来实现一个压测的工具,关于压测的内容可以参考其他的文章,这里默认了解压测的基本概念
整体架构
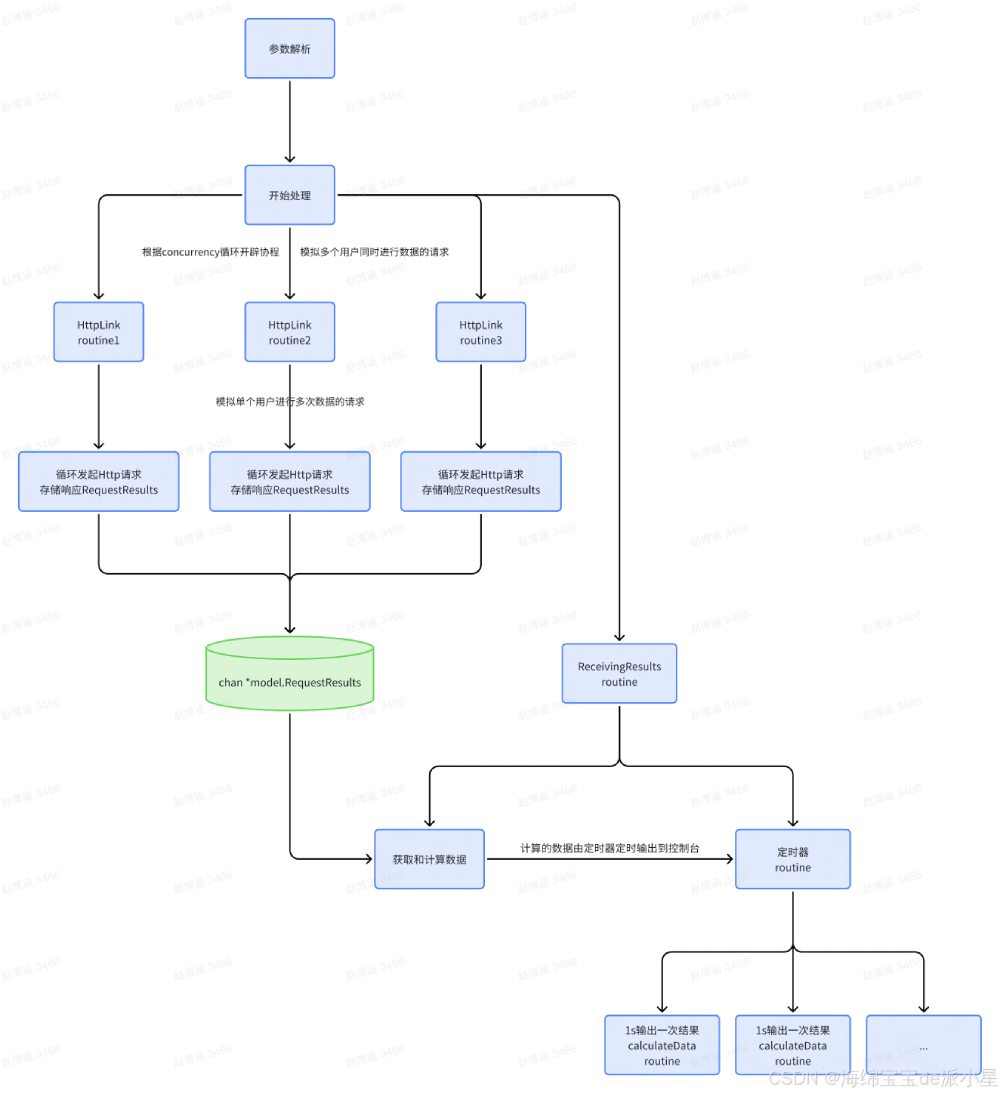
整体系统架构比较简单
通用数据处理模块
http请求响应数据处理
本项目支持http协议、websocket协议、grpc协议、remote authentication dial-in user service协议,因此需要构造出一个通用的http请求和响应的结构体,进行一个通用的封装:
// request 请求数据
type request struct {
url string // url
form string // http/websocket/tcp
method string // 方法 get/post/put
headers map[string]string // headers
body string // body
verify string // 验证的方法
timeout time.duration // 请求超时时间
debug bool // 是否开启debug模式
maxcon int // 每个连接的请求数
http2 bool // 是否使用http2.0
keepalive bool // 是否开启长连接
code int // 验证的状态码
redirect bool // 是否重定向
}
这当中值得注意的是验证的方法,这里是因为在进行压测中,要判断返回的响应是否是正确的响应,因此要进行判断响应是否正确,所以要进行相应的函数的注册,因此对于一个请求,是有必要找到一个对应的请求方法来判断这个请求正确,之后进行记录
这个model的核心功能,就是生成一个http请求的结构体,来帮助进行存储
// newrequest 生成请求结构体
// url 压测的url
// verify 验证方法 在server/verify中 http 支持:statuscode、json websocket支持:json
// timeout 请求超时时间
// debug 是否开启debug
// path curl文件路径 http接口压测,自定义参数设置
func newrequest(url string, verify string, code int, timeout time.duration, debug bool, path string,
reqheaders []string, reqbody string, maxcon int, http2, keepalive, redirect bool) (request *request, err error) {
var (
method = "get"
headers = make(map[string]string)
body string
)
if path != "" {
var curl *curl
curl, err = parsethefile(path)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if url == "" {
url = curl.geturl()
}
method = curl.getmethod()
headers = curl.getheaders()
body = curl.getbody()
} else {
if reqbody != "" {
method = "post"
body = reqbody
}
for _, v := range reqheaders {
getheadervalue(v, headers)
}
if _, ok := headers["content-type"]; !ok {
headers["content-type"] = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=utf-8"
}
}
var form string
form, url = getform(url)
if form == "" {
err = fmt.errorf("url:%s 不合法,必须是完整http、websocket连接", url)
return
}
var ok bool
switch form {
case formtypehttp:
// verify
if verify == "" {
verify = "statuscode"
}
key := fmt.sprintf("%s.%s", form, verify)
_, ok = verifymaphttp[key]
if !ok {
err = errors.new("验证器不存在:" + key)
return
}
case formtypewebsocket:
// verify
if verify == "" {
verify = "json"
}
key := fmt.sprintf("%s.%s", form, verify)
_, ok = verifymapwebsocket[key]
if !ok {
err = errors.new("验证器不存在:" + key)
return
}
}
if timeout == 0 {
timeout = 30 * time.second
}
request = &request{
url: url,
form: form,
method: strings.toupper(method),
headers: headers,
body: body,
verify: verify,
timeout: timeout,
debug: debug,
maxcon: maxcon,
http2: http2,
keepalive: keepalive,
code: code,
redirect: redirect,
}
return
}
之后是对于对应的响应的封装,结构体定义为:
// requestresults 请求结果
type requestresults struct {
id string // 消息id
chanid uint64 // 消息id
time uint64 // 请求时间 纳秒
issucceed bool // 是否请求成功
errcode int // 错误码
receivedbytes int64
}
curl参数解析处理
对于这个模块,本项目中实现的逻辑是根据一个指定的curl的文件,对于文件中的curl进行解析,即可解析出对应的http请求的参数,具体代码链接如下
https://gitee.com/zhaobohan/stress-testing/blob/master/model/curl_model.go
客户端模块
http客户端处理
在该模块中主要是对于http客户端进行处理,对于普通请求和http2.0请求进行了特化处理,支持根据客户端id来获取到指定的客户端,建立映射关系
具体的核心成员为:
var (
mutex sync.rwmutex
// clients 客户端
// key 客户端id - value 客户端
clients = make(map[uint64]*http.client)
)
再具体的,对于客户端的封装,主要操作是,对于client的构造
// createlanghttpclient 初始化长连接客户端参数
// 创建了一个配置了长连接的 http 客户端传输对象
func createlanghttpclient(request *model.request) *http.client {
tr := &http.transport{
// 使用 net.dialer 来建立 tcp 连接
// timeout 设置为 30 秒,表示如果连接在 30 秒内没有建立成功,则超时
// keepalive 设置为 30 秒,表示连接建立后,如果 30 秒内没有数据传输,则发送一个 keep-alive 探测包以保持连接
dialcontext: (&net.dialer{
timeout: 30 * time.second,
keepalive: 30 * time.second,
}).dialcontext,
maxidleconns: 0, // 最大连接数,默认0无穷大
maxidleconnsperhost: request.maxcon, // 对每个host的最大连接数量(maxidleconnsperhost<=maxidleconns)
idleconntimeout: 90 * time.second, // 多长时间未使用自动关闭连接
// insecureskipverify 设置为 true,表示不验证服务器的 ssl 证书
tlsclientconfig: &tls.config{insecureskipverify: true},
}
if request.http2 {
// 使用真实证书 验证证书 模拟真实请求
tr = &http.transport{
dialcontext: (&net.dialer{
timeout: 30 * time.second,
keepalive: 30 * time.second,
}).dialcontext,
maxidleconns: 0, // 最大连接数,默认0无穷大
maxidleconnsperhost: request.maxcon, // 对每个host的最大连接数量(maxidleconnsperhost<=maxidleconns)
idleconntimeout: 90 * time.second, // 多长时间未使用自动关闭连接
// 配置 tls 客户端设置,insecureskipverify 设置为 false,表示验证服务器的 ssl 证书
tlsclientconfig: &tls.config{insecureskipverify: false},
}
// 将 tr 配置为支持 http/2 协议
_ = http2.configuretransport(tr)
}
client := &http.client{
transport: tr,
}
// 禁止 http 客户端自动重定向,而是让客户端在遇到重定向时停止并返回最后一个响应
if !request.redirect {
client.checkredirect = func(req *http.request, via []*http.request) error {
return http.erruselastresponse
}
}
return client
}https://gitee.com/zhaobohan/stress-testing/blob/master/server/client/http_client.go
grpc客户端处理
对于grpc的构造来说,主要实现的功能是建立连接等,这些操作是较为简单的操作,因此这里不具体讲述
// grpcsocket grpc
type grpcsocket struct {
conn *grpc.clientconn
address string
}
conn和address主要都是借助于两个类的成员函数来完成,解析地址和建立连接
其余模块可在代码中查看,这里不进行过多讲述
https://gitee.com/zhaobohan/stress-testing/blob/master/server/client/grpc_client.go
websocket客户端处理
// websocket websocket
type websocket struct {
conn *websocket.conn
urllink string
url *url.url
isssl bool
httpheader map[string]string
}
其余模块可在代码中查看,这里不进行过多讲述
https://gitee.com/zhaobohan/stress-testing/blob/master/server/client/websocket_client.go
连接处理模块
grpc
对于grpc的测试,这里模拟了一个rpc调用,执行了一个hello world的函数,之后填充相应的数据作为请求的响应,最后将结果返回
// grpcrequest 请求
func grpcrequest(chanid uint64, ch chan<- *model.requestresults, i uint64, request *model.request,
ws *client.grpcsocket) {
var (
starttime = time.now()
issucceed = false
errcode = model.httpok
)
// 获取连接
conn := ws.getconn()
if conn == nil {
errcode = model.requesterr
} else {
c := pb.newapiserverclient(conn)
var (
ctx = context.background()
req = &pb.request{
username: request.body,
}
)
// 发送请求,获得响应
rsp, err := c.helloworld(ctx, req)
if err != nil {
errcode = model.requesterr
} else {
// 200 为成功
if rsp.code != 200 {
errcode = model.requesterr
} else {
issucceed = true
}
}
}
requesttime := uint64(helper.diffnano(starttime))
requestresults := &model.requestresults{
time: requesttime,
issucceed: issucceed,
errcode: errcode,
}
requestresults.setid(chanid, i)
ch <- requestresults
}http
对于http的测试,效果也基本类似,原理也基本相同
// http 请求
func http(ctx context.context, chanid uint64, ch chan<- *model.requestresults, totalnumber uint64, wg *sync.waitgroup,
request *model.request) {
defer func() {
wg.done()
}()
for i := uint64(0); i < totalnumber; i++ {
if ctx.err() != nil {
break
}
list := getrequestlist(request)
issucceed, errcode, requesttime, contentlength := sendlist(chanid, list)
requestresults := &model.requestresults{
time: requesttime,
issucceed: issucceed,
errcode: errcode,
receivedbytes: contentlength,
}
requestresults.setid(chanid, i)
ch <- requestresults
}
return
}
统计数据模块
下面来看计算统计数据模块
统计原理
这里需要统计的数据有以下:
耗时、并发数、成功数、失败数、qps、最长耗时、最短耗时、平均耗时、下载字节、字节每秒、状态码
其中这里需要注意的,计算的数据有qps,其他基本都可以经过简单的计算得出
那qps该如何进行计算呢?这里来这样进行计算:
qps = 服务器每秒钟处理请求数量 (req/sec 请求数/秒)
定义:单个协程耗时t, 所有协程压测总时间 sumt,协程数 n
如果:只有一个协程,假设接口耗时为 2毫秒,每个协程请求了10次接口,每个协程耗总耗时210=20毫秒,sumt=20
qps = 10/201000=500
如果:只有十个协程,假设接口耗时为 2毫秒,每个协程请求了10次接口,每个协程耗总耗时210=20毫秒,sumt=2010=200
qps = 100/(200/10)*1000=5000
上诉两个示例现实中总耗时都是20毫秒,示例二 请求了100次接口,qps应该为 示例一 的10倍,所以示例二的实际总qps为5000
除以协程数的意义是,sumt是所有协程耗时总和
实现过程
这个模块主要是定时进行一个统计压测的结论并进行打印的工作,依赖的函数是
// calculatedata 计算数据
func calculatedata(concurrent, processingtime, requesttime, maxtime, mintime, successnum, failurenum uint64,
chanidlen int, errcode *sync.map, receivedbytes int64) {
if processingtime == 0 {
processingtime = 1
}
var (
qps float64
averagetime float64
maxtimefloat float64
mintimefloat float64
requesttimefloat float64
)
// 平均 qps 成功数*总协程数/总耗时 (每秒)
if processingtime != 0 {
qps = float64(successnum*concurrent) * (1e9 / float64(processingtime))
}
// 平均时长 总耗时/总请求数/并发数 纳秒=>毫秒
if successnum != 0 && concurrent != 0 {
averagetime = float64(processingtime) / float64(successnum*1e6)
}
// 纳秒=>毫秒
maxtimefloat = float64(maxtime) / 1e6
mintimefloat = float64(mintime) / 1e6
requesttimefloat = float64(requesttime) / 1e9
// 打印的时长都为毫秒
table(successnum, failurenum, errcode, qps, averagetime, maxtimefloat, mintimefloat, requesttimefloat, chanidlen,
receivedbytes)
}
以上就是基于go语言实现一个压测工具的详细内容,更多关于go压测工具的资料请关注代码网其它相关文章!







发表评论