1、c#类型
类型(type)又叫数据类型(data type)。
a data type is a homogeneous collection of values,effectively prensented,equipped with a set of operations which manipulate these values.
- 数据类型是由相同类型的值组成的集合。比如int[]是整数的集合。
- 数据类型配备有专门针对自己的值的一组运算操作,比如int类型的数据可以进行加法、减法、乘法、除法操作。深层的意思是,这一组操作是专门为这一种数据类型准备的,我们不能拿数据类型a的操作去对数据类型b进行操作。
- 数据类型的“类型”二字包含有“型号”的意思,也就是说,一个数据类型代表着这种数据类型的值在内存中存储时需要占多少的内存,比如对于int来说,它可存储-2,147,483,648 到 2,147,483,647范围内的值,需要占4个字节。我们在存储数据时,应该选择合适的数据类型,比如我们想要存储100这个数据,如果使用int的话显得太浪费了,使用byte就够用了,byte只占一个字节;而如果我们想要存储256这个数据,使用byte就不行了,因为byte只能存储0~255的整数。所以说,大内存存储小尺寸的数据会导致浪费,小内存存储大尺寸的数据会导致丢失精度。举一个现实中的例子,有一个盒子,如果我们拿一个橡皮丢进去,空间完全足够而且还有很多空出来的空间没有得到利用,而如果我们拿一把椅子丢进去就不行了,这时候如果想强制丢进去,只能把椅子的一部分放进去,椅子就会被损坏了。
- 数据类型会被有效地表示,包括存储在内存中的位置、占内存的大小、类型包含的成员(方法、字段、事件等)、类型所继承的基类型。
- c#是一种强类型的语言,这意味着每个变量和常量都必须有一个明确的数据类型。这样编译器就能保证代码中执行的所有运算都是类型安全的。例如,如果定义了一个 int 类型的变量,则编译器允许在加法和减法运算中使用此变量, 如果尝试在一个 string 类型的变量上执行相同的运算,则编译器会产生错误。
// c#代码 int a = 10; string str = "hello, world!"; int b = a + str; //输出结果为: //无法将类型“string”隐式转换为“int”
# python代码 a = 10 a = "hello, world!"
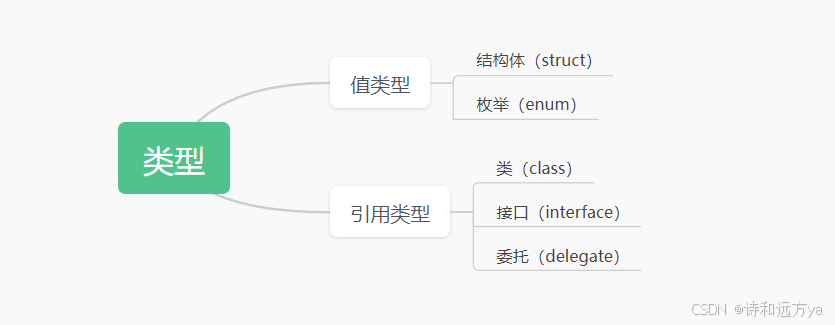
c#类型分为值类型和引用类型,值类型有结构体和枚举,引用类型有类、接口、委托。
struct mystruct // 定义结构体
{
}
type type = typeof(int); //使用typeof关键字获取int的类型
console.writeline(type.basetype); //打印int的基类型
console.writeline(type.basetype.basetype); //打印int的基类型的基类型
console.writeline("---------");
type = typeof(mystruct); //使用typeof关键字获取mystruct的类型
console.writeline(type.basetype); //打印mystruct的基类型
console.writeline(type.basetype.basetype); //打印mystruct的基类型的基类型
//输出结果为:
//system.valuetype
//system.object
//---------
//system.valuetype
//system.object
2、值类型
值类型的变量存储数据,而引用类型的变量存储对实际数据的引用。
2.1 结构体
结构体和类很相似,结构体通常用来封装小型相关变量组。
与类相比,结构体有一些限制,例如它不能声明为抽象的或密封的,它也不能声明默认构造函数(没有参数的构造函数)和析构函数。结构体通常用于小型、不可变的数据结构,而类更适合用于需要更复杂行为的对象。
结构体在c#中是实现轻量级数据结构的强大工具,它在性能上通常优于类,因为它避免了垃圾回收的开销。然而,它也有一定的限制,比如不能被声明为可空的,并且当结构体包含引用类型字段时,可能会引入垃圾回收的开销。
结构体可以包含构造函数、 常量、 字段、 方法、 属性、 索引器、 运算符、 事件和嵌套类型,但如果同时需要上述几种成员,则应当考虑改为使用类作为类型。
struct student
{
public int age;
public int height;
public double weight;
public string name;
}
我们不能在结构体中初始化实例字段,可以在结构体中初始化静态字段以及常量。
struct student
{
public static int avgage = 10; //可以在结构体中初始化静态字段
public const int height = 100; //可以在结构体中初始化常量
public int age; //不能在结构体中初始化实例字段
}
要想初始化实例字段,有两种方法:一是使用参数化构造函数,二是在声明结构后分别访问成员。
struct student
{
public student(int x)
{
age = x;
}
//public static int avgage = 10;
public int age;
}
student stu = new student(10); //使用参数化构造函数初始化实例字段
console.writeline(stu.age);
stu.age = 20; //声明结构后访问实例字段
console.writeline(stu.age);
//输出结果为:
//10
//20
与类不同,结构的实例化可以使用new运算符,也可以不使用。如果使用的话,会创建该结构的对象,并调用构造函数,构造函数不传入参数的话,调用的是默认构造函数,默认构造函数会对结构体的成员进行初始化;如果不使用的话,就不会调用构造函数,在初始化所有字段之前,字段将保持未赋值状态且对象不可用。
struct student
{
public int age;
public int height;
}
student stu1; //不使用new创建对象
student stu2 = new student(); //使用new创建对象,并调用构造函数
struct student
{
public int age;
public int height;
}
student stu1; //不使用new创建对象
console.writeline(stu1.age);
//输出结果为:
//使用了可能未赋值的字段"age"
所以正确的做法应该是:
struct student
{
public int age;
public int height;
}
student stu1;
stu1.age = 10;
stu1.height = 130;
console.writeline(stu1.age);
console.writeline(stu1.height);
struct student
{
public int age;
public int height;
}
student stu2 = new student();
console.writeline(stu1.age);
console.writeline(stu1.height);
2.2 枚举
枚举类型用enum关键字进行声明,它是一种由一组称为枚举数列表的命名常量组成的独特类型。
通常情况下,最好是在命名空间内直接定义枚举,以便该命名空间中的所有类都能够同样方便地访问它。 但是,还可以将枚举嵌套在类或结构中。
默认情况下,第一个枚举数的值为 0,后面每个枚举数的值依次递增 1。
namespace consoleapp1
{
enum days { mon, tue, wed, thu, fri, sat, sun };
class program
{
static void main(string[] args)
{
console.writeline((int)days.mon);
console.writeline((int)days.tue);
console.writeline((int)days.wed);
}
}
}
//输出结果为:
//0
//1
//2
当然,也可以强制元素序列从1开始。
namespace consoleapp1
{
enum days { mon=1, tue, wed, thu, fri, sat, sun };
class program
{
static void main(string[] args)
{
console.writeline((int)days.mon);
console.writeline((int)days.tue);
console.writeline((int)days.wed);
}
}
}
//输出结果为:
//1
//2
//3
枚举类型的默认基础类型是int,所以,上述代码中定义枚举类型变量的完整表达为:
enum days:int { mon=1, tue, wed, thu, fri, sat, sun };
枚举类型变量可赋以基础类型范围内的任何值,准许使用的枚举类型有 byte、 sbyte、 short、 ushort、 int、 uint、 long 或 ulong。
namespace consoleapp1
{
enum days:byte { mon=1, tue=2, wed=10, thu=20, fri=30, sat=100, sun=255 };
class program
{
static void main(string[] args)
{
console.writeline((byte)days.mon);
console.writeline((byte)days.tue);
console.writeline((byte)days.wed);
console.writeline((byte)days.thu);
console.writeline((byte)days.fri);
console.writeline((byte)days.sat);
console.writeline((byte)days.sun);
}
}
}
//输出结果为:
//1
//2
//10
//20
//30
//100
//255
在switch语句中使用枚举值。
namespace consoleapp1
{
enum days { mon, tue, wed, thu, fri, sat, sun };
class program
{
static void main(string[] args)
{
days day = (days)1;
switch (day)
{
case days.mon:
console.writeline("today is mon");
break;
case days.tue:
console.writeline("today is tue");
break;
case days.wed:
console.writeline("today is wed");
break;
case days.thu:
console.writeline("today is thu");
break;
case days.fri:
console.writeline("today is fri");
break;
case days.sat:
console.writeline("today is sat");
break;
case days.sun:
console.writeline("today is sun");
break;
}
}
}
}
使用枚举类型的好处:
- 明确变量可以存储的值。
enum days:byte { mon=1, tue=2, wed=10, thu=20, fri=30, sat=100, sun=255 };
days day = days.mon;
在这个程序中,一个星期只能包含从星期一到星期日的7天,所以只能取枚举中的值。
我们可以使用扩展方法为枚举类型添加功能。
namespace consoleapp1
{
// 在非泛型静态类中定义扩展方法
public static class extensions
{
public static grades minpassing = grades.d;
// this关键字在方法定义中用于指定这是一个扩展方法
//this关键字后面跟着的是类型参数,表示这个扩展方法可以被任何grade类型的实例调用
public static bool passing(this grades grade)
{
return grade >= minpassing;
}
}
public enum grades { f = 0, d=1, c=2, b=3, a=4 };
class program
{
static void main(string[] args)
{
grades g1 = grades.d;
grades g2 = grades.f;
console.writeline("first {0} a passing grade.", g1.passing() ? "is" : "is not");
console.writeline("second {0} a passing grade.", g2.passing() ? "is" : "is not");
extensions.minpassing = grades.c;
console.writeline("\r\nraising the bar!\r\n");
console.writeline("first {0} a passing grade.", g1.passing() ? "is" : "is not");
console.writeline("second {0} a passing grade.", g2.passing() ? "is" : "is not");
}
}
}
}
/* 输出结果为:
first is a passing grade.
second is not a passing grade.
raising the bar!
first is not a passing grade.
second is not a passing grade.
*/
实际上,通过枚举类型实例对扩展方法的调用,等效于调用普通非扩展方法的方式。也就是说,调用扩展方法与调用在类型中实际定义的方法之间没有明显的差异。
console.writeline("first {0} a passing grade.", g1.passing() ? "is" : "is not");
console.writeline("second {0} a passing grade.", g2.passing() ? "is" : "is not");
// 等效于
console.writeline("first {0} a passing grade.", extensions.passing(g1) ? "is" : "is not");
console.writeline("first {0} a passing grade.", extensions.passing(g2) ? "is" : "is not");到此这篇关于c# 值类型的实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关c# 值类型内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!







发表评论