1. 简介
webclient是spring 5引入的响应式web客户端,用于执行http请求。相比传统的resttemplate,webclient提供了非阻塞、响应式的方式来处理http请求,是spring推荐的新一代http客户端工具。本文将详细介绍如何在springboot 3.x中配置和使用webclient。
2. 环境准备
2.1 依赖配置
在 pom.xml中添加必要的依赖:
<parent>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactid>
<version>3.2.10</version>
<relativepath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactid>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactid>
</dependency>3. webclient配置
3.1 基础配置
@configuration
public class webclientconfig {
@bean
public webclient webclient() {
return webclient.builder()
.baseurl("https://echo.apifox.com")
.defaultheader(httpheaders.content_type, mediatype.application_json_value)
.defaultheader(httpheaders.accept, mediatype.application_json_value)
.build();
}
}3.2 高级配置
package com.coderjia.boot3webflux.config;
import io.netty.channel.channeloption;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.readtimeouthandler;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.writetimeouthandler;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.slf4j;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.configuration;
import org.springframework.http.httpheaders;
import org.springframework.http.mediatype;
import org.springframework.http.client.reactive.reactorclienthttpconnector;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.exchangefilterfunction;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.webclient;
import reactor.core.publisher.mono;
import reactor.netty.http.client.httpclient;
import reactor.netty.resources.connectionprovider;
import java.time.duration;
/**
* @author coderjia
* @create 2024/12/3 下午 09:42
* @description
**/
@slf4j
@configuration
public class webclientconfig {
@bean
public webclient webclient() {
// 配置http连接池
connectionprovider provider = connectionprovider.builder("custom")
.maxconnections(500)
.maxidletime(duration.ofseconds(20))
.build();
// 配置http客户端
httpclient httpclient = httpclient.create(provider)
.option(channeloption.connect_timeout_millis, 5000)
.responsetimeout(duration.ofseconds(5))
.doonconnected(conn ->
conn.addhandlerlast(new readtimeouthandler(5))
.addhandlerlast(new writetimeouthandler(5)));
// 构建webclient实例
return webclient.builder()
.clientconnector(new reactorclienthttpconnector(httpclient))
.baseurl("https://echo.apifox.com")
.defaultheader(httpheaders.content_type, mediatype.application_json_value)
.defaultheader(httpheaders.accept, mediatype.application_json_value)
// 添加请求日志记录功能
.filter(exchangefilterfunction.ofrequestprocessor(
clientrequest -> {
log.debug("request: {} {}",
clientrequest.method(),
clientrequest.url());
return mono.just(clientrequest);
}
))
// 添加响应日志记录功能
.filter(exchangefilterfunction.ofresponseprocessor(
clientresponse -> {
log.debug("response status: {}",
clientresponse.statuscode());
return mono.just(clientresponse);
}
))
.build();
}
}3.3 retrieve()和exchange()区别
在使用 webclient 进行 http 请求时,retrieve() 和 exchange() 方法都可以用来处理响应,但它们有不同的用途和行为。以下是它们的主要区别:
retrieve()
- 用途:retrieve() 方法用于简化响应处理,特别是当你只需要响应体时。
- 自动错误处理:retrieve() 会自动处理 http 错误状态码(例如 4xx 和 5xx),并抛出 webclientresponseexception 及其子类。
- 返回值:通常用于直接获取响应体,例如 bodytomono(string.class) 或 bodytoflux(string.class)。
- 适用场景:适用于大多数常见的请求处理场景,特别是当你不需要手动处理响应状态码时。
exchange()
- 用途:exchange() 方法提供了更底层的控制,允许你手动处理响应,包括响应状态码和响应头。
- 手动错误处理:exchange() 不会自动处理 http 错误状态码,你需要手动检查响应状态码并进行相应的处理。
- 返回值:返回 clientresponse 对象,你可以从中提取响应状态码、响应头和响应体。
- 适用场景:适用于需要手动处理响应状态码或响应头的复杂场景。
示例对比
retrieve()
public mono<jsonobject> get(string q1) {
return webclient.get()
.uri(uribuilder -> uribuilder
.path("/get")
.queryparam("q1", q1)
.build())
.accept(mediatype.application_json)
.retrieve()
.bodytomono(jsonobject.class);
}exchange()
public mono<jsonobject> get(string q1) {
return webclient.get()
.uri(uribuilder -> uribuilder
.path("/get")
.queryparam("q1", q1)
.build())
.accept(mediatype.application_json)
.exchangetomono(response -> {
if (response.statuscode().is2xxsuccessful()) {
return response.bodytomono(jsonobject.class);
} else {
return mono.error(new runtimeexception("request failed with status code: " + response.statuscode()));
}
});
}4. 使用示例
4.1 基本请求操作
package com.coderjia.boot3webflux.service;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.jsonobject;
import jakarta.annotation.resource;
import org.springframework.http.mediatype;
import org.springframework.stereotype.service;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.webclient;
import reactor.core.publisher.mono;
/**
* @author coderjia
* @create 2024/12/3 下午 10:22
* @description
**/
@service
public class apiservice {
@resource
private webclient webclient;
// get请求
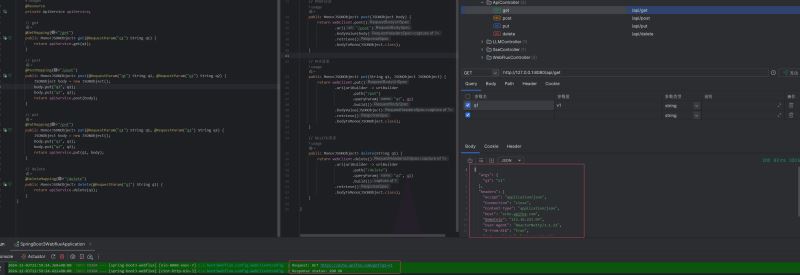
public mono<jsonobject> get(string q1) {
return webclient.get()
.uri(uribuilder -> uribuilder
.path("/get")
.queryparam("q1", q1)
.build())
.accept(mediatype.application_json)
.retrieve()
.bodytomono(jsonobject.class);
}
// post请求
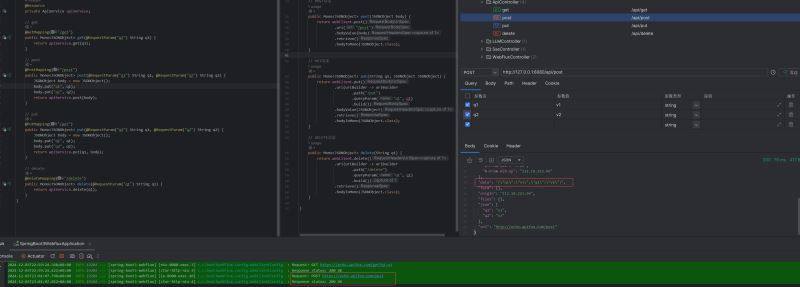
public mono<jsonobject> post(jsonobject body) {
return webclient.post()
.uri("/post")
.bodyvalue(body)
.retrieve()
.bodytomono(jsonobject.class);
}
// put请求
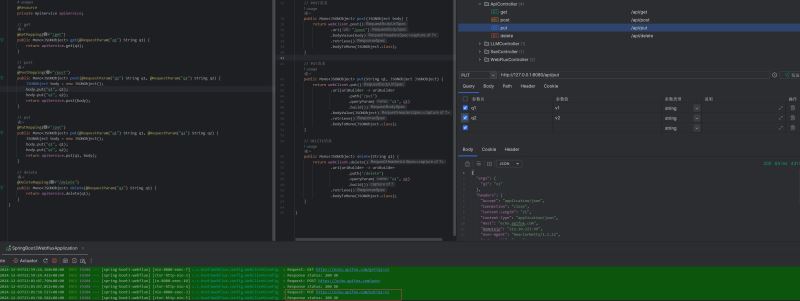
public mono<jsonobject> put(string q1, jsonobject jsonobject) {
return webclient.put()
.uri(uribuilder -> uribuilder
.path("/put")
.queryparam("q1", q1)
.build())
.bodyvalue(jsonobject)
.retrieve()
.bodytomono(jsonobject.class);
}
// delete请求
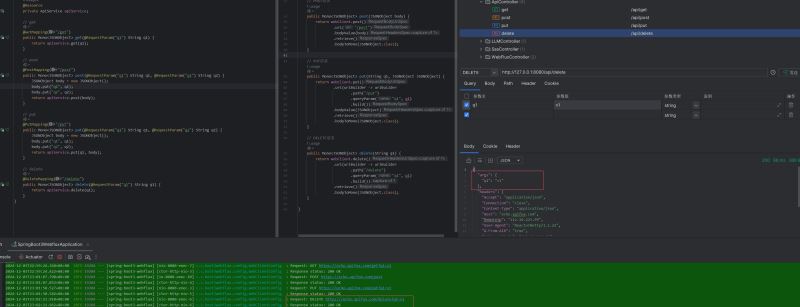
public mono<jsonobject> delete(string q1) {
return webclient.delete()
.uri(uribuilder -> uribuilder
.path("/delete")
.queryparam("q1", q1)
.build())
.retrieve()
.bodytomono(jsonobject.class);
}
}效果展示
4.2 处理复杂响应
@service
public class apiservice {
// 获取列表数据
public flux<jsonobject> getallusers() {
return webclient.get()
.uri("/users")
.retrieve()
.bodytoflux(jsonobject.class);
}
// 处理错误响应
public mono<jsonobject> getuserwitherrorhandling(long id) {
return webclient.get()
.uri("/users/{id}", id)
.retrieve()
.onstatus(httpstatuscode::is4xxclienterror, clientresponse -> mono.error(new runtimeexception("客户端错误")))
.onstatus(httpstatuscode::is5xxservererror, clientresponse -> mono.error(new runtimeexception("服务器错误")))
.bodytomono(jsonobject.class);
}
// 使用exchange()方法获取完整响应
public mono<responseentity<jsonobject>> getuserwithfullresponse(long id) {
return webclient.get()
.uri("/users/{id}", id)
.accept(mediatype.application_json)
.exchange()
.flatmap(response -> response.toentity(jsonobject.class));
}
}4.3 高级用法
@service
public class apiservice {
// 带请求头的请求
public mono<jsonobject> getuserwithheaders(long id, string token) {
return webclient.get()
.uri("/users/{id}", id)
.header("authorization", "bearer " + token)
.retrieve()
.bodytomono(jsonobject.class);
}
// 带查询参数的请求
public flux<jsonobject> searchusers(string name, int age) {
return webclient.get()
.uri(uribuilder -> uribuilder
.path("/users/search")
.queryparam("name", name)
.queryparam("age", age)
.build())
.retrieve()
.bodytoflux(jsonobject.class);
}
// 文件上传
public mono<string> uploadfile(filepart filepart) {
return webclient.post()
.uri("/upload")
.contenttype(mediatype.multipart_form_data)
.body(bodyinserters.frommultipartdata("file", filepart))
.retrieve()
.bodytomono(string.class);
}
}5. 最佳实践
合理使用响应式类型
- 使用 mono 用于单个对象
- 使用 flux 用于集合数据
- 注意背压处理
错误处理
public mono<jsonobject> getuserwithretry(long id) {
return webclient.get()
.uri("/users/{id}", id)
.retrieve()
.bodytomono(jsonobject.class)
.retrywhen(retry.backoff(3, duration.ofseconds(1)))
.timeout(duration.ofseconds(5))
.onerrorresume(timeoutexception.class,
e -> mono.error(new runtimeexception("请求超时")));
}资源管理
- 使用连接池
- 设置适当的超时时间
- 实现优雅关闭
6. 注意事项
- webclient 是非阻塞的,需要注意响应式编程的特性
- 合理配置连接池和超时参数
- 在生产环境中实现适当的错误处理和重试机制
- 注意内存使用,特别是处理大量数据时
7. 与resttemplate对比
| 特性 | webclient | resttemplate |
|---|---|---|
| 编程模型 | 响应式、非阻塞 | 同步、阻塞 |
| 性能 | 更好 | 一般 |
| 资源利用 | 更高效 | 一般 |
| 学习曲线 | 较陡 | 平缓 |
| 适用场景 | 高并发、响应式系统 | 简单应用、传统系统 |
8. 总结
webclient 作为 spring 推荐的新一代 http 客户端,提供了强大的响应式编程能力和更好的性能。虽然相比 resttemplate 有一定的学习曲线,但在现代微服务架构中,其带来的好处远超过学习成本。建议在新项目中优先考虑使用webclient,特别是在需要处理高并发请求的场景下。
参考资料
到此这篇关于springboot3-webclient配置与使用详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关springboot3 webclient使用内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论