1 - 概述
所有的集合类和集合接口都在java.util包下。
在内存中申请一块空间用来存储数据,在java中集合就是替换掉定长的数组的一种引用数据类型。
2 - 集合与数组的区别
长度区别
数组长度固定,定义长了造成内存空间的浪费,定义短了不够用。
集合大小可以变,用多少空间拿多少空间。
内容区别
数组可以存储基本数据类型和引用数据类型
集合中能存储引用数据类型(存储的为对象的内存地址)
list.add(100);//为自动装箱,100为integer包装的
元素区别
数组中只能存储同一种类型成员
集合中可以存储不同类型数据(一般情况下也只存储同一种类型的数据)
集合结构
在java中每一个不同的集合,底层会对应不同的数据结构。往不同的集合中
存储元素,等于将数据放到了不同的数据结构当中。什么是数据结构?数据存储的
结构就是数据结构。不同的数据结构,数据存储方式不同。
- 单列集合 collection
- list可以重复:arraylist/linkedlist
- set不可重复:hashset/treeset
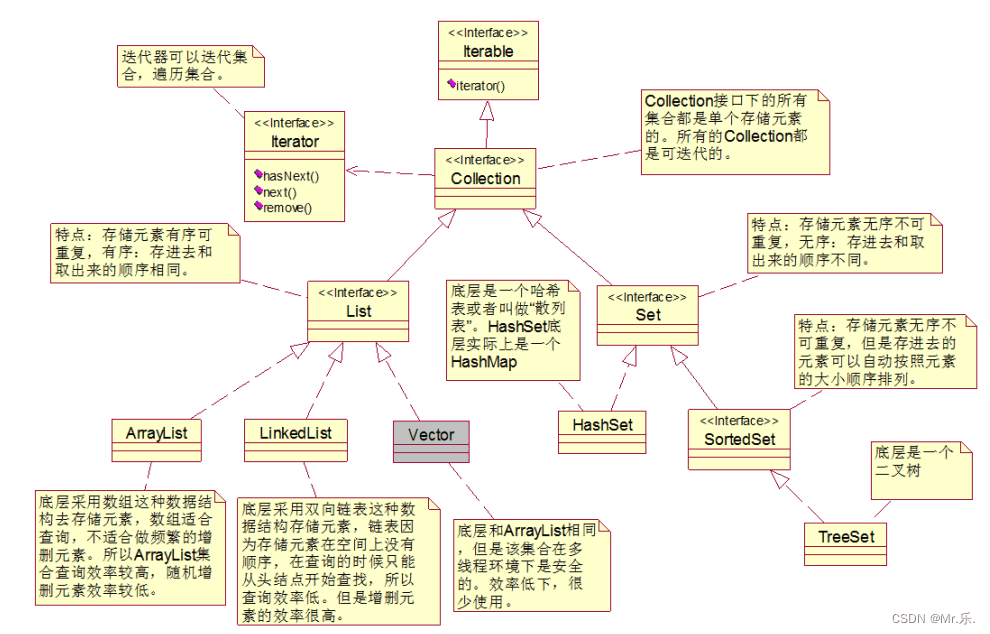
(大量文字插入会导致图片不清,所以在此进行更详细的描述)
- list特点:此处顺序并不是大小顺序,而是存入数据的先后顺序。有序因为list集合都有下标,下标从0开始,以递增。
- set特点:取出顺序不一定为存入顺序,另外set集合没有下标。
- arraylist是非线程安全的。
- hashset集合在new的时候,底层实际上new了一个hashmap集合。向hashset集合中存储元素,实际上是存储到了hashmap的key中了。hashmap集合是一个hash表数据结构。
- sortedset集合存储元素的特点:由于继承了set集合,所以他的特点也是无序不可重复,但是放在sortedset集合中的元素可以自动排序。放到该集合中的元素是自动按照大小顺序排序的。
- treeset集合底层实际上是treemap。treeset集合在new的时候,底层实际上new了一个treemap集合。向treeset集合中存储元素,实际上是存储到了treemap的key中了。treemap集合是一个二叉树数据结构。
双列集合map:hashmap/treemap
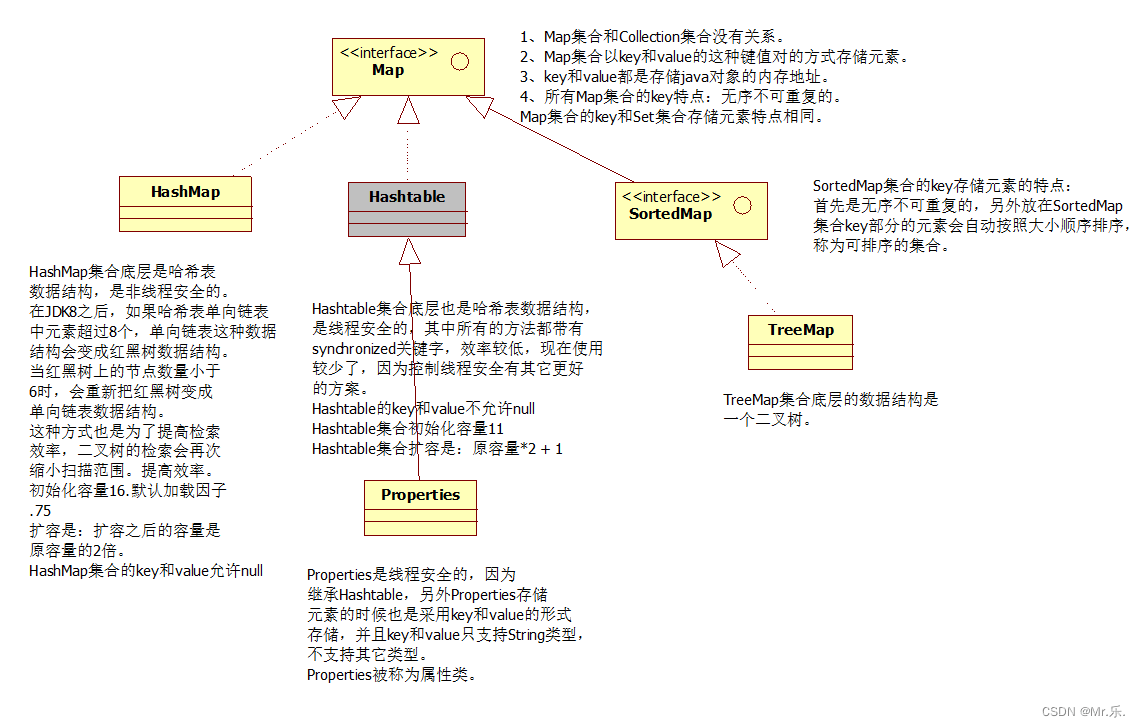
粗体是接口 斜体是实现类
3- collection集合
3.1 - 概述
单列集合的顶层接口,既然是接口就不能直接使用,需要通过实现类!~
3.2 - collection集合的的常用方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
boolean add(e e) | 添加元素到集合的末尾(追加) |
boolean remove(object o) | 删除指定的元素,成功则返回true(底层调用equles) |
void clear() | 清空集合 |
boolean contains(object o) | 判断元素在集合中是否存在,存在则返回true(底层调用equles) |
boolean isempty() | 判断集合是否为空,空则返回true |
int size() | 返回集合中元素个数 |
import java.util.arraylist;
import java.util.collection;
/**
* @author mr.乐
* @description
*/
public class collection_01 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
//父类的引用指向子类的对象,形成多态
collection<string> con = new arraylist<>();
//追加的方式添加元素
con.add("东邪");
con.add("西毒");
con.add("南帝");
con.add("北丐");
con.add("中神通");
//删除,通过元素名称删除元素
system.out.println(con.remove("西毒"));
//判断集合中是否包含指定参数元素
system.out.println(con.contains("西毒")); //false
system.out.println(con.contains("东邪")); //true
//获取集合中元素个数
system.out.println(con.size());
//判断是否为空
system.out.println(con.isempty());//false
//清空集合
con.clear();
//判断是否为空
system.out.println(con.isempty());//true
system.out.println(con);//打印集合的元素
}
}3.3 - collection集合的遍历
以下迭代方式,是所有collection通用的一种方式。在map集合中不能使用,在所有的collection以及子类中使用。
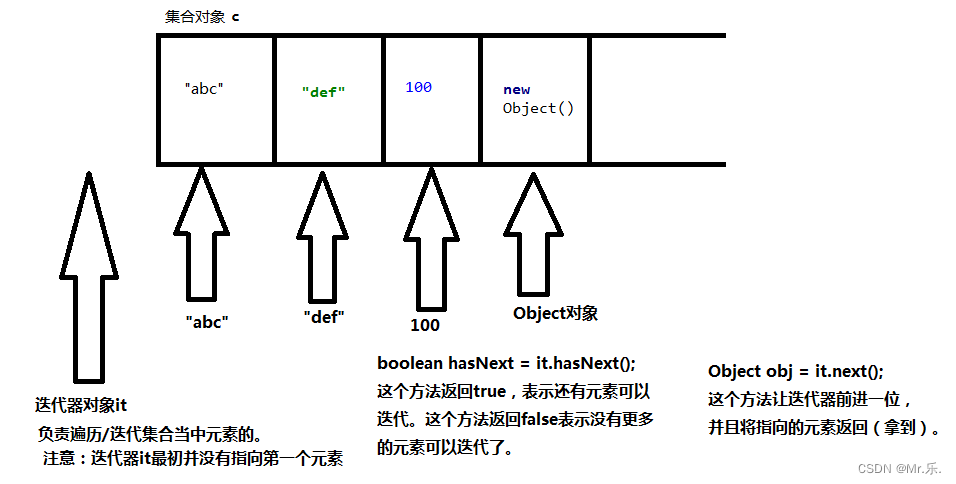

import java.util.arraylist;
import java.util.collection;
import java.util.iterator;
/**
* @author mr.乐
* @description collection 集合的遍历
*/
public class connection_02 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
//多态
collection<string> con = new arraylist<>();
//添加元素
con.add("abc");
con.add("def");
con.add("100");
con.add("444");
//collection集合的遍历方式
//因为没有索引的概念,所以collection集合不能使用fori进行遍历
//增强版for循环,其实底层使用的也是迭代器,在字节码文件中查看
for (string str : con) {
system.out.print(str + "\t");
}
system.out.println();//换行
//迭代器,集合专属的遍历工具
iterator<string> it = con.iterator();//创建迭代器对象
while (it.hasnext()){//判断下一个位置是否有元素
system.out.print(it.next() + "\t");//获取到下一个位置的元素
}
}
}3.4-iterator的remove
import java.util.arraylist;
import java.util.collection;
import java.util.iterator;
/**
* @author mr.乐
* @description
*/
public class connection_remove {
public static void main(string[] args) {
// 创建集合
collection c = new arraylist();
// 注意:此时获取的迭代器,指向的是那是集合中没有元素状态下的迭代器。
// 一定要注意:集合结构只要发生改变,迭代器必须重新获取。
// 当集合结构发生了改变,迭代器没有重新获取时,调用next()方法时:java.util.concurrentmodificationexception
iterator it = c.iterator();
// 添加元素
c.add(1); // integer类型
c.add(2);
c.add(3);
// 获取迭代器
//iterator it = c.iterator();
/*while(it.hasnext()){
// 编写代码时next()方法返回值类型必须是object。
// integer i = it.next();
object obj = it.next();
system.out.println(obj);
}*/
collection c2 = new arraylist();
c2.add("abc");
c2.add("def");
c2.add("xyz");
iterator it2 = c2.iterator();
while(it2.hasnext()){
object o = it2.next();
// 删除元素
// 删除元素之后,集合的结构发生了变化,应该重新去获取迭代器
// 但是,循环下一次的时候并没有重新获取迭代器,所以会出现异常:java.util.concurrentmodificationexception
// 出异常根本原因是:集合中元素删除了,但是没有更新迭代器(迭代器不知道集合变化了)
//c2.remove(o); // 直接通过集合去删除元素,没有通知迭代器。(导致迭代器的快照和原集合状态不同。)
// 使用迭代器来删除可以吗?
// 迭代器去删除时,会自动更新迭代器,并且更新集合(删除集合中的元素)。
it2.remove(); // 删除的一定是迭代器指向的当前元素。
system.out.println(o);
}
system.out.println(c2.size()); //0
}
}4-list
原型arraylist<e>
- arraylist是一个list接口的实现类,底层使用的是一个可以调整大小的数组实现的。
<e>:是一种特殊的数据类型(引用数据类型) -- 泛型- arraylist<string> 或者 arraylist<integer> 或者 arraylist<student>
4.1 - arraylist构造和添加方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
public arraylist<e>() | 创建一个空集合 |
public boolean add(e e) | 将指定的参数元素追加到集合的末尾 |
public void add(int index ,e e) | 在集合的指定位置添加指定的元素(插入元素) |
public void addall(e object) | 用于将指定集合中所有元素添加到当前集合中 |
/**
* @author mr.乐
* @description arraylist构造和添加方法
*/
public class arraylist_01 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
//创建空集合
arraylist<string> list = new arraylist<>();//泛型定义为string
//采用默认追加的方式添加元素
system.out.println(list.add("刘德华"));
system.out.println(list.add("张学友"));
system.out.println(list.add("郭富城"));
system.out.println(list.add("黎明"));
//插入的方式添加元素
// list.add(10,"谭咏麟");//插入元素方法索引值不能大于集合中元素个数
// list.add(4,"谭咏麟");//表示在集合中最后位置插入元素,与追加相同
list.add(1,"谭咏麟");//指定位置插入元素,索引位置之后的元素会自动向后进行移动
arraylist<string> newlist = new arraylist<>();//创建新的集合
newlist.add("小沈阳");
newlist.add("宋小宝");
newlist.add("赵四");
newlist.add("刘能");
//查看集合中的元素
system.out.println("原集合内部元素:" + list);
system.out.println("新集合内部元素:" + newlist);
list.addall(newlist); //将新集合全部元素添加到原集合中
system.out.println("原集合内部元素:" + list);
}
}4.2 - arraylist集合常用方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
public boolean remove(object o) | 删除指定的元素,成功则返回true |
public e remove(int index) | 删除指定索引位置的元素,返回被删除的元素 |
public e set(int index,e e) | 修改指定索引位置的元素,返回修改前的元素 |
public e get(int index) | 获取指定索引对应的元素 |
public int size() | 获取结合中元素个数 |
import java.util.arraylist;
import java.util.iterator;
/**
* @author mr.乐
* @description arraylist集合常用方法
*/
public class arraylist_02 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
arraylist<string> list = new arraylist<>();
//追加方式添加元素
list.add("东邪");
list.add("西毒");
list.add("南帝");
list.add("北丐");
list.add("中神通");
//删除
system.out.println(list.remove("西毒"));//通过元素名称删除,返回boolean
system.out.println(list.remove(1));//通过索引删除元素,返回被删除元素名
//修改
system.out.println(list.set(1,"西毒"));//指定索引位置修改元素,并返回被修改元素
system.out.println("原集合中元素有:" + list);
//获取方法
system.out.println(list.get(1));//通过指定索引位置获取集合元素
//获取集合元素个数
system.out.println(list.size());
//集合的遍历,普通for循环
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
system.out.print(list.get(i) + "\t");
}
system.out.println();
//增强版for循环
for (string name : list) {
system.out.print(name+ "\t");
}
system.out.println();
//迭代器
iterator<string> it = list.iterator();//创建迭代器
while (it.hasnext()){//判断下一个位置是否有元素
system.out.print(it.next() + "\t"); //next方法表示获取下一个位置的元素
}
system.out.println();
//stream流
list.stream().foreach(system.out::println);
}
}4.3 -arraylist实现原理
底层代码:
属性:
default_capacity = 10 默认长度,初始化容量为10object[] empty_elementdata = {} //有参构造所创建object[] defaultcapacity_empty_elementdata = {} //无参构造所创建的object[] elementdata;底层为object类型的数组,存储的元素都在此。int size 实际存放的个数构造方法 :
//一个参数的构造
public arraylist(int initialcapacity) {
if (initialcapacity > 0) {
this.elementdata = new object[initialcapacity];
} else if (initialcapacity == 0) {
this.elementdata = empty_elementdata;
} else {
throw new illegalargumentexception("illegal capacity: "+
initialcapacity);
}
}
//参数如果大于零,则为创建数组的长度;
//参数如果等于零,empty_elementdata;
//参数如果小于0,抛出异常。
//无参构造
public arraylist() {
this.elementdata = defaultcapacity_empty_elementdata;
}
//defaultcapacity_empty_elementdata new对象时默认为0 当添加第一个元素的时候,数组扩容至10add方法源码:(jdk1.8与之不同,此处为jdk16)
//源码
public boolean add(e e) {
modcount++;//操作次数
add(e, elementdata, size);
//e 操作对象; elementdata 底层操作的数组;size 默认大小0
return true;
}
------------------------------------------------
private void add(e e, object[] elementdata, int s) {
if (s == elementdata.length)//ture
elementdata = grow();
elementdata[s] = e; //存数据
size = s + 1; //最小需要长度
}
----------------------------------------------------------
private object[] grow() {
return grow(size + 1);
}
-----------------------------------------------------
private object[] grow(int mincapacity) { //初始传入为size+1 为1
int oldcapacity = elementdata.length; //初始为0
if (oldcapacity > 0 || elementdata != defaultcapacity_empty_elementdata) {
//if条件为初始数组长度>0或者数组不是无参构造构建的
int newcapacity = arrayssupport.newlength(oldcapacity, //旧数组的长度
mincapacity - oldcapacity, /* minimum growth */
//最小需要长度-旧数组的长度 大于0代表空间不足
oldcapacity >> 1 /* preferred growth */);
//二进制位右移1位 位旧数组长度/2
return elementdata = arrays.copyof(elementdata, newcapacity);
将数据放入新数组中
} else {
return elementdata = new object[math.max(default_capacity, mincapacity)];
//数组长度 default_capacity为10 此处代表无参构造默认长度为10
}
}
----------------------------------------------------
public static int newlength(int oldlength, int mingrowth, int prefgrowth) {
// assert oldlength >= 0
// assert mingrowth > 0
int newlength = math.max(mingrowth, prefgrowth) + oldlength;
//如果prefgrowth>mingrowth 扩容1.5倍 mingrowth>prefgrowth为需要多少给多少
if (newlength - max_array_length <= 0) {
//max_array_length为int最大值 表示新数组长度如果小于int的最大值
return newlength;
}
return hugelength(oldlength, mingrowth);
//返回int最大值
}arraylist集合底层是数组,怎么优化?
尽可能少的扩容。因为数组扩容效率比较低,建议在使用arraylist集合 的时候预估计元素的个数,给定一个初始化容量。数组优点:
检索效率比较高。(每个元素占用空间大小相同,内存地址是连续的,知道首元素内存地址,
然后知道下标,通过数学表达式计算出元素的内存地址,所以检索效率最高。)数组缺点:
随机增删元素效率比较低。
另外数组无法存储大数据量。(很难找到一块非常巨大的连续的内存空间。)向数组末尾添加元素,效率很高,不受影响。
4.4 -linkedlist实现原理
底层代码
属性:
transient int size = 0;//初始长度
transient node<e> first;//头节点
transient node<e> last;//尾节点add方法源码:(jdk1.8与之不同,此处为jdk16)
public boolean add(e e) {
linklast(e);
return true;
}
--------------------------------------
void linklast(e e) {
final node<e> l = last; //初始为null
final node<e> newnode = new node<>(l, e, null);
//参数1:位上一个节点的内存地址,参数2:e为插入的数据,参数3:下一个节点的内存地址
last = newnode; // 最后节点为新节点
if (l == null) //如果newnode的前一个节点为null,则将新节点赋给first
first = newnode;
else
l.next = newnode; //尾节点下一个节点为新节点
size++;//大小
modcount++;//操作数
}4.5-linkedlist和arraylist
linkedlist和arraylist方法一样,只是底层实现不一样。arraylist底层为数组存储,linkedlist是以双向链表存储。linkedlist集合没有初始化容量。最初这个链表中没有任何元素。first和last引用都是null。
链表的优点:
由于链表上的元素在空间存储上内存地址不连续。
所以随机增删元素的时候不会有大量元素位移,因此随机增删效率较高。
在以后的开发中,如果遇到随机增删集合中元素的业务比较多时,建议
使用linkedlist。
链表的缺点:
不能通过数学表达式计算被查找元素的内存地址,每一次查找都是从头
节点开始遍历,直到找到为止。所以linkedlist集合检索/查找的效率
较低。
arraylist:把检索发挥到极致。(末尾添加元素效率还是很高的。)
linkedlist:把随机增删发挥到极致。
加元素都是往末尾添加,所以arraylist用的比linkedlist多。
4.6 -vector
1、底层也是一个数组。
2、初始化容量:10
3、怎么扩容的?
扩容之后是原容量的2倍。
10--> 20 --> 40 --> 80
4、vector中所有的方法都是线程同步的,都带有synchronized关键字,
是线程安全的。效率比较低,使用较少了。
5、怎么将一个线程不安全的arraylist集合转换成线程安全的呢?
使用集合工具类:
java.util.collections;
java.util.collection 是集合接口。
java.util.collections 是集合工具类。
collections.synchronizedlist();//将及格转换为线程安全的。
5-set
5.1 -概述
- set集合也是一个接口,继承自collection,与list类似,都需要通过实现类来进行操作。
- 特点
- 不允许包含重复的值
- 没有索引(就不能使用普通的for循环进行遍历)
import java.util.hashset;
import java.util.set;
/**
* @author mr.乐
* @description set集合
*/
public class demo01 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
//使用多态,父类的引用指向子类对象
set<string> set = new hashset<>();
//添加元素
set.add("黄固");
set.add("欧阳锋");
set.add("段智兴");
set.add("洪七公");
set.add("段智兴");
system.out.println(set);//打印集合
//[洪七公, 黄固, 欧阳锋, 段智兴]
//hashset集合对于元素的读写顺序不做保证
//相同的元素,多次存储,只能保留一个,并且不会报错
//list集合可以存储重复元素,set集合不行
}
}例:双色球
import java.util.random;
import java.util.treeset;
/**
* @author mr.乐
* @description 双色球 -set版
*/
public class demo02 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
random ran = new random();//创建随机类对象
int blueball = ran.nextint(16) + 1;
// hashset<integer> redballs = new hashset<>();//创建集合用来存储红球
treeset<object> redballs = new treeset<>();//treeset集合自带排序规则
while (redballs.size() < 6){
redballs.add(ran.nextint(33) + 1);//将当前生成的红球直接存进集合中
//因为set集合不能存储重复的元素,所以去重的操作可以省略不做。
}
system.out.println("红球:" + redballs + "篮球 [" + blueball + "]");
}
}5.2 -哈希值
set集合的去重原理使用的是哈希值。
哈希值就是jdk根据对象地址 或者 字符串 或者数值 通过自己内部的计算出来的一个整数类型数据
public int hashcode()- 用来获取哈希值,来自于object顶层类- 对象的哈希值特点
- 同一个对象多次调用
hashcode()方法,得到的结果是相同的。- 默认情况下,不同的对象的哈希值也是不同的(特殊情况除外)
/**
* @author mr.乐
* @description 哈希值
*/
public class demo03 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
//相同对象哈希值相同
system.out.println("张三".hashcode());//774889
system.out.println("张三".hashcode());//774889
//不同对象哈希值不同
system.out.println(new object().hashcode());
system.out.println(new object().hashcode());
//不同的对象的哈希值也有可能相同,例外情况
system.out.println("辂鹅".hashcode());//1179395
system.out.println("较鸦".hashcode());//1179395
system.out.println("辄鸇".hashcode());//1179395
system.out.println("辅鷨".hashcode());//1179395
}
}5.3 -hashset去重原理
- hashset集合的特点
- 底层结构是“哈希表”
- 集合对于读写顺序不做保证
- 没有索引
- set集合中的内容不能重复
/**
* @author mr.乐
* @description hashset去重原理
*/
public class demo04 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
hashset<student> set = new hashset<>();
//添加元素
set.add(new student("黄固",28));
set.add(new student("欧阳锋",38));
set.add(new student("段智兴",48));
set.add(new student("洪七公",40));
set.add(new student("段智兴",48));
//从程序的角度来考虑,两个段智兴不是同一个对象,都有自己的存储空间,所以哈希值也不一样。
for (student stu : set) {
system.out.println(stu);
}
/*
重写hashcode和equals
student{name='段智兴', age=48}
student{name='欧阳锋', age=38}
student{name='洪七公', age=40}
student{name='黄固', age=28}
*/
}
}5.4 -linkedhashset
- 特点
- linkedhashset是哈希表和链表实现的set接口,具有可预测的读写顺序。
- 有链表来保证元素有序
- 有哈希表来保证元素的唯一性
/**
* @author mr.乐
* @description linkedhashset
*/
public class demo05 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
linkedhashset<string> set = new linkedhashset<>();
//添加元素
set.add("黄固");
set.add("欧阳锋");
set.add("段智兴");
set.add("洪七公");
set.add("段智兴");//重复的元素不能存进去
system.out.println(set);//打印集合 [黄固, 欧阳锋, 段智兴, 洪七公]
}
}5.5 -treeset
1、treeset集合底层实际上是一个treemap
2、treemap集合底层是一个二叉树。
3、放到treeset集合中的元素,等同于放到treemap集合key部分了。
4、treeset集合中的元素:无序不可重复,但是可以按照元素的大小顺序自动排序。
import java.util.treeset;
public class treesettest02 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
// 创建一个treeset集合
treeset<string> ts = new treeset<>();
// 添加string
ts.add("zhangsan");
ts.add("lisi");
ts.add("wangwu");
ts.add("zhangsi");
ts.add("wangliu");
// 遍历
for(string s : ts){
// 按照字典顺序,升序!
system.out.println(s);
}
/*
lisi
wangliu
wangwu
zhangsan
zhangsi
*/
treeset<integer> ts2 = new treeset<>();
ts2.add(100);
ts2.add(200);
ts2.add(900);
ts2.add(800);
ts2.add(600);
ts2.add(10);
for(integer elt : ts2){
// 升序!
system.out.println(elt);
}
}
}5.5.1 -自定义排序规则
对于自定义的类无法排序,因为类中对象之间没有比较规则,不知道谁大谁小。
/**
* @author mr.乐
* @description 自定义比较器
*/
import java.util.treeset;
public class treesettest04 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
customer c1 = new customer(32);
customer c2 = new customer(20);
customer c3 = new customer(30);
customer c4 = new customer(25);
// 创建treeset集合
treeset<customer> customers = new treeset<>();
// 添加元素
customers.add(c1);
customers.add(c2);
customers.add(c3);
customers.add(c4);
// 遍历
for (customer c : customers){
system.out.println(c);
}
}
}
// 放在treeset集合中的元素需要实现java.lang.comparable接口。
// 并且实现compareto方法。equals可以不写。
class customer implements comparable<customer>{
int age;
public customer(int age){
this.age = age;
}
// 需要在这个方法中编写比较的逻辑,或者说比较的规则,按照什么进行比较!
// k.compareto(t.key)
// 拿着参数k和集合中的每一个k进行比较,返回值可能是>0 <0 =0
// 比较规则最终还是由程序员指定的:例如按照年龄升序。或者按照年龄降序。
@override
public int compareto(customer c) { // c1.compareto(c2);
return c.age - this.age;
}
public string tostring(){
return "customer[age="+age+"]";
}
}匿名内部类方式
public class treesettest05 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
// treeset<student> ts = new treeset<>();//默认排序规则
treeset<student> ts = new treeset<>(new comparator<student>() {
@override
public int compare(student o1, student o2) {
int res = o1.getage() - o2.getage();
return 0 == res ? o1.getname().compareto(o2.getname()) : res;
//三目运算符 等于零用姓名排序
}
});//默认排序规则
//添加元素
ts.add(new student("andy",19));
ts.add(new student("jack",18));
ts.add(new student("tom",21));
ts.add(new student("lucy",17));
ts.add(new student("bob",21)); //当年龄相同时,按照姓名的字典顺序排序
for (student stu : ts) {
system.out.println(stu);
}
}
}comparable和comparator怎么选择呢?
当比较规则不会发生改变的时候,或者说当比较规则只有1个的时候,建议实现comparable接口。
如果比较规则有多个,并且需要多个比较规则之间频繁切换,建议使用comparator接口。
6 -map
6.1 -概述
- 双列集合:用来存储键值对的集合。
interface map<k,v>: k(key)键 ,v(value)值- 将键映射到值的对象,不能出现重复的键,每个键最多可以映射到一个值
1、map和collection没有继承关系。
2、map集合以key和value的方式存储数据:键值对
key和value都是引用数据类型。
key和value都是存储对象的内存地址。
key起到主导的地位,value是key的一个附属品。
例子:
| 学号(key) | 姓名(value) |
|---|---|
| stu001 | 张三 |
| stu002 | 李四 |
| stu003 | 张三 |
6.2 -map的基本方法
| 学号(key) | 姓名(value) |
|---|---|
| stu001 | 张三 |
| stu002 | 李四 |
| stu003 | 张三 |
import java.util.hashmap;
import java.util.map;
/**
* @author mr.乐
* @description 集合的基本方法
*/
public class map01 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
map<string,string> map = new hashmap<>();
map.put("stu001","andy");
map.put("stu002","jack");
map.put("stu003","tom");
map.put("stu004","bob");
map.put("stu004","smith");//设置(修改)
//如果键不存在,则表示添加元素。如果键存在,则表示设置值。
//删除
system.out.println(map.remove("stu003")); //tom
//判断是否包含
system.out.println(map.containskey("stu003")); //false
system.out.println(map.containskey("stu004")); //true
system.out.println("-----------------------");
system.out.println(map.containsvalue("tom")); //false
system.out.println(map.containsvalue("smith")); //true
system.out.println("-----------------------");
system.out.println(map.isempty());//判断集合是否为空 false
map.clear();//清空集合
system.out.println(map.isempty()); //true
system.out.println(map); //{}
}
}6.3 -map集合的获取功能
import java.util.collection;
import java.util.hashmap;
import java.util.map;
import java.util.set;
/**
* @author mr.乐
* @description
*/
public class map_get {
public static void main(string[] args) {
map<string,string> map = new hashmap<>();
map.put("stu001","andy");
map.put("stu002","jack");
map.put("stu003","tom");
map.put("stu004","bob");
//get通过键获取值
system.out.println(map.get("stu003"));
system.out.println("------------------");
//keyset 获取所有键的set集合
set<string> keyset = map.keyset();
system.out.println(keyset);
//values 获取所有值的collection集合
collection<string> values = map.values();
system.out.println(values);
//entryset 获取所有键值对对象的set集合
set<map.entry<string, string>> es = map.entryset();
//map集合通过entryset()方法转换成的这个set集合,set集合中元素的类型是 map.entry<k,v>
//map.entry和string一样,都是一种类型的名字,只不过:map.entry是静态内部类,是map中的静态内部类
system.out.println(es);
//[stu001=andy, stu003=tom, stu002=jack, stu004=bob]
for (map.entry<string, string> entry:es){
system.out.println("key:"+entry.getkey()+" "+"value:"+entry.getvalue());
}
/*
key:stu001 value:andy
key:stu003 value:tom
key:stu002 value:jack
key:stu004 value:bob
*/
}
}6.4 -哈希表
通过 数组 + 链表 实现的一种数据结构
哈希表的构造方法的参数是一个长度为16个元素的数组,通过哈希值 % 16 的值,作为头节点在数组中选择对应的位置,就形成了哈希表。
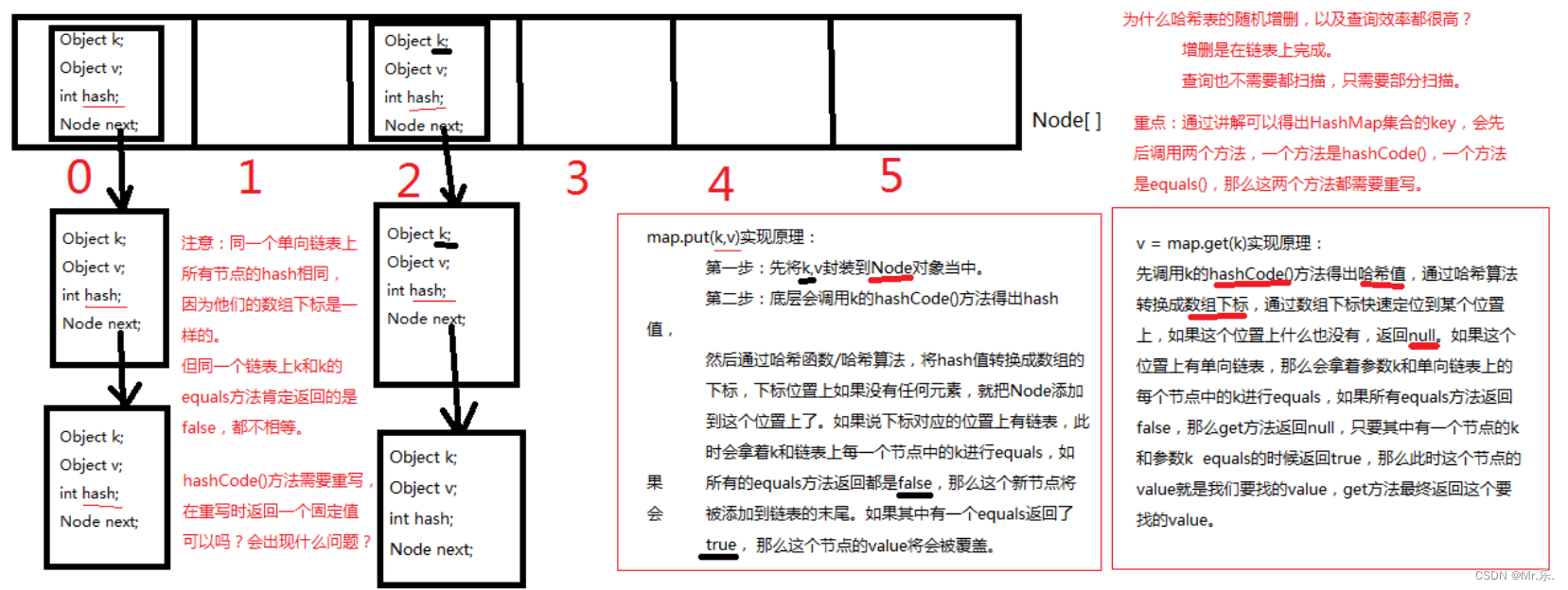
注:图转自动力节点。
6.5 -hashmap
6.5.1 -底层源码
public class hashmap{
// hashmap底层实际上就是一个数组。(一维数组)
node<k,v>[] table;
// 静态的内部类hashmap.node
static class node<k,v> {
final int hash; // 哈希值(哈希值是key的hashcode()方法的执行结果。hash值通过哈希函数/算法,可以转换存储成数组的下标。)
final k key; // 存储到map集合中的那个key
v value; // 存储到map集合中的那个value
node<k,v> next; // 下一个节点的内存地址。
}
}6.5.2 -特点
1、无序,不可重复。
为什么无序? 因为不一定挂到哪个单向链表上。
不可重复是怎么保证的? equals方法来保证hashmap集合的key不可重复。
如果key重复了,value会覆盖。
2、放在hashmap集合key部分的元素其实就是放到hashset集合中了。
所以hashset集合中的元素也需要同时重写hashcode()+equals()方法。
3、hashmap集合的默认初始化容量是16,默认加载因子是0.75
这个默认加载因子是当hashmap集合底层数组的容量达到75%的时候,数组以二叉树开始扩容。
重点,记住:hashmap集合初始化容量必须是2的倍数,这也是官方推荐的,
这是因为达到散列均匀,为了提高hashmap集合的存取效率,所必须的。
6.5.3 -注意
1.向map集合中存,以及从map集合中取,都是先调用key的hashcode方法,然后再调用equals方法!
equals方法有可能调用,也有可能不调用。
拿put(k,v)举例,什么时候equals不会调用? k.hashcode()方法返回哈希值, 哈希值经过哈希算法转换成数组下标。 数组下标位置上如果是null,equals不需要执行。 拿get(k)举例,什么时候equals不会调用? k.hashcode()方法返回哈希值, 哈希值经过哈希算法转换成数组下标。 数组下标位置上如果是null,equals不需要执行。
4.假设将所有的hashcode()方法返回值固定为某个值,那么会导致底层哈希表变成了 纯单向链表。
这种情况我们成为:散列分布不均匀。
什么是散列分布均匀?
假设有100个元素,10个单向链表,那么每个单向链表上有10个节点,这是最好的, 是散列分布均匀的。假设将所有的hashcode()方法返回值都设定为不一样的值,可以吗,有什么问题? 不行,因为这样的话导致底层哈希表就成为一维数组了,没有链表的概念了。 也是散列分布不均匀。散列分布均匀需要你重写hashcode()方法时有一定的技巧。
7 -properties
properties是一个map集合,继承hashtable,properties的key和value都是string类型。 properties被称为属性类对象。 properties是线程安全的。
7.1 -方法
import java.io.ioexception;
import java.util.properties;
import java.util.set;
/**
* @author mr.乐
* @description properties特有方法
*/
public class properties01 {
public static void main(string[] args) throws ioexception {
properties prop = new properties();
final string src = "./myconf.ini";//定义配置信息存储路径
// mysave(prop,src);//存储配置文件
myload(prop,src);//加载配置文件信息
//password<--->123456
//database<--->yx2115
//port<--->3306
//username<--->root
}
private static void myload(properties prop, string src) throws ioexception {
filereader fr = new filereader(src);
prop.load(fr);//通过流,加载指定路径的配置文件
fr.close();
//遍历
set<string> keyset = prop.stringpropertynames();//获取对象键的set集合
for (string key : keyset) {
system.out.println(key + "<--->" + prop.getproperty(key));//通过键拿到值
}
}
private static void mysave(properties prop, string src) throws ioexception {
//将配置信息存储到对象中
prop.setproperty("username","root");
prop.setproperty("password","123456");
prop.setproperty("database","yx2115");
prop.setproperty("port","3306");
//写入文件
filewriter fw = new filewriter(src);//创建输出流对象
prop.store(fw,"mydatabase configure!~");
fw.close();
}
}8 -总结
本篇文章介绍了集合的常用方法以及个别集合的底层是如何实现的。介绍了集合的继承与实现结构。各个集合的扩容方式及扩容大小以及各个集合的优点和用途。希望大家可以根据本篇文章可以更加深刻的理解java中的集合。
到此这篇关于java集合超详细的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关java集合内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!



发表评论