0 、前言
在写sql语句的时候常常会有很多疑问,那就是当单表的数据量很大的时候,查询性能怎么样,以及索引对数据查询的影响,今天用navicat批量造了很多重复数据来对mysq在数据量大的时候查询的性能的测试。
1 、使用navicat批量插入数据
函数—>新建函数–>填写名,选择函数,点击完成
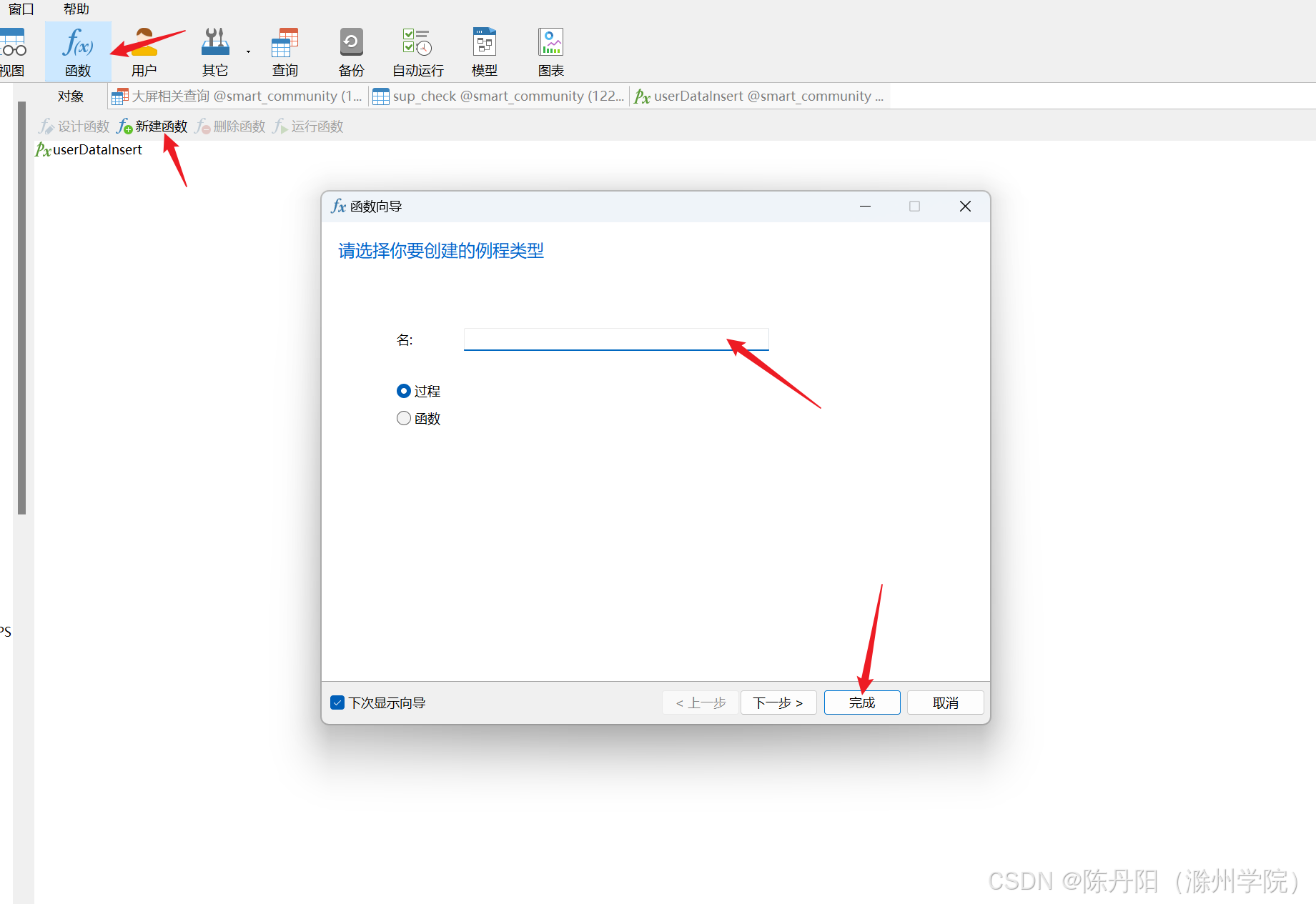
填写函数
create definer=`root`@`%` procedure `userdatainsert`() begin # 设置循环变量 declare i int default 0; while i<=100000 do insert into sup_check(advertiser_id,check_time,record_types_id,dept_id) values(20,'2024-04-09',1,203); set i = i + 1; end while; end
保存后点击运行即可,此处会执行时间较长,主要看你的主机性能,磁盘的读写速度等,最好在自己的本地虚拟机中去跑,节省时间。
2、编写sql测试
此sql就是单表的查询(嵌套子查询),根据年份然后按照年月去对数据进行一个分组,问gpt的时候,gpt说使用函数的时候进行的是全表的扫描,不走索引,此时很慌,很想测试一下,走索引和不走索引到底有什么区别
select year(check_time) as year ,month(check_time) as month ,count(*) as checknum
from sup_check
where
(dept_id = 100 or dept_id in (select t.dept_id from sys_dept t where find_in_set(100,ancestors)))
and year(check_time) = 2024
group by year,month
order by year,month;
3、索引相关
单列索引
create index idx_check_time on sup_check (check_time);
复合索引
create index idx_column1_column2 on sup_check (check_time, record_type_id);
唯一索引
create unique index uidx_column_name on table_name (column_name);
全文索引
create fulltext index ftx_column_name on table_name (column_name);
使用表名 ,在某些情况下,你可能还想在索引名称中包含表名,尤其是在大型数据库中,这有助于避免索引名称冲突:
create index idx_table_name_column_name on table_name (column_name);
注意事项
避免使用特殊字符:不要在索引名称中使用特殊字符,如 !, @, #, $, %, ^, &, *, (, ), -, +, =, {, }, [, ], |, , ;, :, ', ", , <, >, /, ?`。
长度限制:mysql索引名称的最大长度是64个字符
查看索引
这将返回以下列:
- table:表名
- non_unique:如果索引不能包含重复值,则为0;如果可以,则为1。
- key_name:索引的名称。
- seq_in_index:索引中的列序列号。
- column_name:列名。
- collation:列如何排序,如果是定序的,则显示排序顺序;如果是未排序的,则显示null。
- cardinality:索引中唯一值的估计数量。
- sub_part:如果列只是部分索引,则为索引的字符数。如果是整个列被索引,则为null。
- packed:指示关键字如何被压缩,如果没有被压缩,则为null。
- null:如果列含有null,则显示yes。
- index_type:索引类型,如btree、fulltext、hash等。
- comment:索引的备注信息。
show index from table_name;
4、查询测试
建立完索引之后,我发现当查询出的数据量比较大的时候,查询指定数据的速度确实快了,但是当所查询出的字段多或者数据条数多的时候还是会耗费很长时间,那解决办法就是分页,一下查询出这么多条数据肯定慢,分页的话就特别快了。
select year(check_time) as year ,month(check_time) as month ,count(*) as checknum
from sup_check
where
(dept_id = 100 or dept_id in (select t.dept_id from sys_dept t where find_in_set(100,ancestors)))
and year(check_time) = 2024
group by year,month
order by year,month;
limit 20 offset 0;
5、提升sql的办法
优化sql,经常查询的字段使用索引,查询出需要使用的字段,分页查询
6、探讨分页查询的基本实现原理
首先使用count(*) 查询出数据总条数,此查询是经过mysql优化过的,速度比较快,或者你去count(索引列)然后就是根据每页的数据大小计算出总的页数(int totalpages = (totalrecords + pagesize - 1) / pagesize;),然后就是执行分页查询,查询指定页的数据
到此这篇关于mysql数据库数据批量插入的实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关mysql 数据批量插入内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!







发表评论