前言
在web应用中,确保前后端之间的数据传输安全是非常重要的。这通常涉及到使用https协议、数据加密、令牌验证等安全措施。本文通过将前后端之间的传输数据进行加密,用于在spring boot应用中实现前后端传输加密设计。
一、数据加密方案
即使使用了https,也可能需要在应用层对数据进行额外的加密。这可以通过以下方式实现:
- 对称加密:加密解密是同一个密钥,速度快,数据接收方需要公布其私钥给数据传输方进行数据加密,安全性完全依赖于该密钥。适合做大量数据或数据文件的加解密。
- 使用aes、des等对称加密算法对敏感数据进行加密和解密。
- 前后端需要共享一个密钥(key)用于加密和解密。
- 密钥的管理和传输需要特别注意安全性。
- 非对称加密:加密用公钥,解密用私钥。公钥和私钥是成对的(可借助工具生成,如openssl等),即用公钥加密的数据,一定能用其对应的私钥解密,能用私钥解密的数据,一定是其对应的公钥加密。对大量数据或数据文件加解密时,效率较低。数据接收方需公布其公钥给数据传输方,私钥自己保留,安全性更高。
- 使用rsa、ecc等非对称加密算法。
- 私钥用于加密数据,公钥用于解密数据。
- 公钥可以公开,而私钥需要安全存储。
- 混合加密
- 结合使用对称加密和非对称加密。
- 使用非对称加密算法交换对称加密的密钥(会话密钥),然后使用会话密钥进行实际的数据加密和解密。
这里就赘述介绍每种加密的实现方式和原理。
1.1 数据加密实现方式
如果数据传输较大,密钥不需要进行网络传输,数据不需要很高的安全级别,则采用对称加密,只要能保证密钥没有人为外泄即可;
如果数据传输小,而且对安全级别要求高,或者密钥需要通过internet交换,则采用非对称加密;
本文采用了两者结合的方式(混合加密模式),这样是大多数场景下采用的加密方式。加密时序图如下所示:
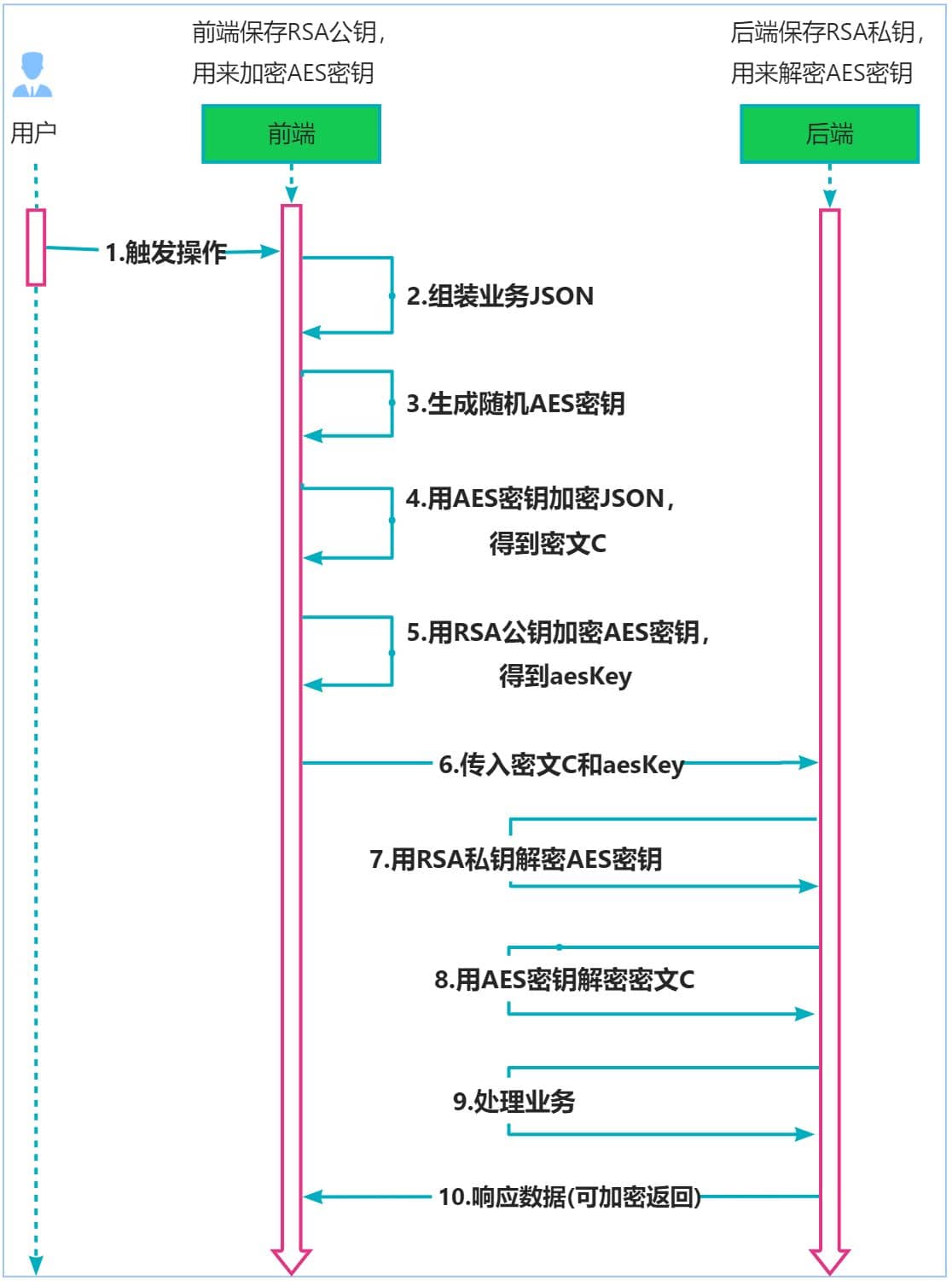
通过使用对称加密(aes) 和 非对称加密(rsa) 的方式来实现对数据的加密;即通过对称加密进行业务数据体的加密,通过非对称加密进行对称加密密钥的加密;它结合了对称加密的高效性 和 非对称加密的安全性。
注意事项:
- 确保rsa公钥在传输过程中是安全的,因为任何拥有这个公钥的人都可以用它来加密aes密钥,但只有拥有私钥的人才能解密它。
- 确保在加密和解密过程中使用安全的加密库和最新的加密算法标准。
- 定期更换密钥对和对称密钥,以降低密钥泄露的风险。
这种混合加密模式提供了安全性和效率之间的平衡。对称加密(如aes)用于加密大量数据,因为它通常比非对称加密更快。而非对称加密(如rsa)用于加密密钥,因为它提供了更强的安全性,特别是当密钥需要在不安全的通道上传输时。
1.2 aes加密工具类创建
- 封装aesutil工具类时 pom.xml 中运用到的 依赖:
<!-- hutool-all工具类依赖 --> <dependency> <groupid>cn.hutool</groupid> <artifactid>hutool-all</artifactid> <version>5.8.18</version> </dependency>
- aes加解密工具类 aesutil 代码:
package com.example.api_security_demo.utils;
import cn.hutool.core.codec.base64;
import javax.crypto.cipher;
import javax.crypto.keygenerator;
import javax.crypto.spec.secretkeyspec;
import java.io.unsupportedencodingexception;
import java.security.key;
import java.security.nosuchalgorithmexception;
import java.security.securerandom;
import java.util.random;
/**
* @classname : aesutil
* @description : aes加密工具类
* @author : ad
*/
public class aesutil {
public static final string char_encoding = "utf-8";
/**
* [常见算法]aes、des、rsa、blowfish、rc4 等等
* [常见的模式] ecb (电子密码本模式)、cbc (密码分组链接模式)、ctr (计数模式) 等等
* [常见的填充] nopadding、pkcs5padding、pkcs7padding 等等
*
* [aes算法]可以有以下几种常见的值:
* aes:标准的aes算法。
* aes/cbc/pkcs5padding:使用cbc模式和pkcs5填充的aes算法。
* aes/ecb/pkcs5padding:使用ecb模式和pkcs5填充的aes算法。
* aes/gcm/nopadding:使用gcm模式的aes算法,不需要填充。
* aes/ccm/nopadding:使用ccm模式的aes算法,不需要填充。
* aes/cfb/nopadding:使用cfb模式的aes算法,不需要填充。
* */
public static final string aes_algorithm = "aes";
public static char[] hexchar = {'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'};
/**
* description: 随机生成 aeskey密钥
*
* @param length 随机生成密钥长度
* @return java.lang.string
*/
public static string getaeskey(int length) throws exception
{
/*
* random类用于生成伪随机数。
* */
random random = new random();
stringbuilder ret = new stringbuilder();
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
// 选择生成数字还是字符
boolean ischar = (random.nextint(2) % 2 == 0);
/* 0随机生成一个字符*/
if (ischar)
{
// 选择生成大写字母 / 小写字母
int choice = (random.nextint(2) % 2 == 0) ? 65 : 97;
ret.append((char) (choice+random.nextint(26)));
/* 1随机生成一个数字 */
}else
{
ret.append( random.nextint(10));
}
}
return ret.tostring();
}
/**
* description: 加密
*
* @param data 待加密数据内容
* @param aeskey 加密密钥
* @return byte[]
*/
public static byte[] encrypt(byte[] data,byte[] aeskey)
{
if (aeskey.length != 16)
{
throw new runtimeexception("invalid aes key length (must be 16 bytes) !");
}
try{
/*
* 创建一个secretkeyspec对象来包装aes密钥。
* 它使用了aeskey字节数组作为密钥,并指定算法为"aes"。
* 这个对象用来提供对称加密算法的密钥。
* */
secretkeyspec secretkey = new secretkeyspec(aeskey, "aes");
/*
* 获取secretkeyspec对象中的编码形式,将其存储在encodedformat字节数组中。
* 这个编码形式可以被用来重新构造密钥。
* */
byte[] encodedformat = secretkey.getencoded();
/*
* 使用encodedformat字节数组创建了另一个secretkeyspec对象seckey。
* 这个对象也用来提供对称加密算法的密钥。
* */
secretkeyspec seckey = new secretkeyspec(encodedformat, "aes");
/*
* 使用cipher类的getinstance()方法获取了一个cipher对象(创建密码器)。
* 这个对象用来完成加密或解密的工作。
* */
cipher cipher = cipher.getinstance(aes_algorithm);
/*
* 码调用init()方法来初始化cipher对象(初始化)。
* 它要求传入操作模式和提供密钥的对象,这里使用cipher.encrypt_mode代表加密模式,以及之前创建的seckey对象作为密钥。
* */
cipher.init(cipher.encrypt_mode,seckey);
/*
* 用cipher对象对data进行加密操作,得到加密后的结果存储在result字节数组中。
* */
byte[] result = cipher.dofinal(data);
return result;
}catch (exception e){
throw new runtimeexception(" encrypt fail! ",e);
}
}
/**
* description: 解密
*
* @param data 解密数据
* @param aeskey 解密密钥
* @return byte[]
*/
public static byte[] decrypt(byte[] data,byte[] aeskey)
{
if (aeskey.length != 16)
{
throw new runtimeexception(" invalid aes key length ( must be 16 bytes)");
}
try {
secretkeyspec secretkeyspec = new secretkeyspec(aeskey, "aes");
byte[] encodedformat = secretkeyspec.getencoded();
secretkeyspec seckey = new secretkeyspec(encodedformat, "aes");
/* 创建密码器 */
cipher cipher = cipher.getinstance(aes_algorithm);
/* 初始化密码器 */
cipher.init(cipher.decrypt_mode,seckey);
byte[] result = cipher.dofinal(data);
return result;
}catch (exception e){
throw new runtimeexception(" decrypt fail !",e);
}
}
/**
* description:加密数据,并转换为base64编码格式!
*
* @param data 待加密数据
* @param aeskey 加密密钥
* @return java.lang.string
*/
public static string encrypttobase64(string data,string aeskey)
{
try {
byte[] valuebyte = encrypt(data.getbytes(char_encoding), aeskey.getbytes(char_encoding));
/* 加密数据转 byte[]--> 换为base64 --> string */
return base64.encode(valuebyte);
}catch (unsupportedencodingexception e){
throw new runtimeexception(" encrypt fail !",e);
}
}
/**
* description: 解密数据,将basse64格式的加密数据进行解密操作
*
* @param data
* @param aeskey
* @return java.lang.string
*/
public static string decryptfrombase64(string data,string aeskey)
{
try {
byte[] originaldata = base64.decode(data.getbytes());
byte[] valuebyte = decrypt(originaldata,aeskey.getbytes(char_encoding));
return new string(valuebyte,char_encoding);
}catch (unsupportedencodingexception e){
throw new runtimeexception("decrypt fail !",e);
}
}
/**
* description:加密数据,aeskey为base64格式时,并将加密后的数据转换为base64编码格式
*
* @param data
* @param aeskey
* @return java.lang.string
*/
public static string encryptwithkeybase64(string data,string aeskey)
{
try{
byte[] valuebyte = encrypt(data.getbytes(char_encoding), base64.decode(aeskey.getbytes()));
return base64.encode(valuebyte);
}catch (unsupportedencodingexception e){
throw new runtimeexception("encrypt fail!",e);
}
}
/**
* description: 解密数据,数据源为base64格式,且 aeskey为base64编码格式
*
* @param data
* @param aeskey
* @return java.lang.string
*/
public static string decryptwithkeybase64(string data,string aeskey)
{
try {
byte[] originaldate = base64.decode(data.getbytes());
byte[] valuebyte = decrypt(originaldate,base64.decode(aeskey.getbytes()));
return new string(valuebyte,char_encoding);
}catch (unsupportedencodingexception e){
throw new runtimeexception("decrypt fail !",e);
}
}
/**
* description:通过密钥生成器生成一个随机的 aes 密钥,并将其以字节数组的形式返回。
* 主要功能是生成并返回一组随机的密钥字节数组,这些字节数组可用于加密和解密数据。
*
* @param
* @return byte[]
*/
public static byte[] generaterandomaeskey()
{
keygenerator keygenerator = null;
try{
/*
* keygenerator是java cryptography architecture(jca)提供的主要密钥生成器类之一,用于生成对称加密算法的密钥。
* 获取一个用于生成aes算法密钥的keygenerator实例,以便在加密和解密操作中使用该密钥。
* */
keygenerator = keygenerator.getinstance(aes_algorithm);
}catch (nosuchalgorithmexception e){
throw new runtimeexception("generaterandomkey fail !",e);
}
/*
* securerandom 类提供了一种用于生成加密强随机数的实现。
* */
securerandom securerandom = new securerandom();
/*
* 初始化密钥生成器 keygenerator。
* 初始化密钥生成器时使用了 securerandom 实例,以确保生成的密钥具有足够的随机性。
* */
keygenerator.init(securerandom);
/*
* 调用 generatekey() 方法,使用初始化后的 keygenerator 生成密钥对象 key。
* */
key key = keygenerator.generatekey();
//返回生成的密钥的字节数组表示。
return key.getencoded();
}
/**
* description: 通过密钥生成器生成一个随机的 aes 密钥,并转化为base64格式
*
* @param
* @return java.lang.string
*/
public static string generaterandomaeskeywithbase64()
{
return base64.encode(generaterandomaeskey());
}
/* !!当get请求进行加密时,地址上的加密参数就以16进制字符串的方式进行传输,否则特殊符号路径无法解析[ +、/、=]等base64编码格式 */
/**
* description: 从byte[] 数组转 16进制字符串
*
* @param b
* @return java.lang.string
*/
public static string tohexstring(byte[] b)
{
/*
* 每个字节都可以用两个十六进制字符来表示,因此初始化的容量是字节数组长度的两倍。
* */
stringbuilder sb = new stringbuilder(b.length * 2);
for (int i = 0; i<b.length ;i++)
{
/*
* 首先取字节的高四位,然后查找对应的十六进制字符,并将其追加到stringbuilder中
* */
sb.append(hexchar[(b[i] & 0xf0) >>> 4]);
/*
* 取字节的低四位,找到对应的十六进制字符,并追加到stringbuilder中。
* */
sb.append(hexchar[b[i] & 0x0f]);
}
return sb.tostring();
}
/**
* description: 从16进制字符串转 byte[] 数组
*
* @param s
* @return byte[]
*/
public static final byte[] tobytes(string s)
{
byte[] bytes;
bytes = new byte[s.length() / 2];
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length ; i++)
{
bytes[i] = (byte) integer.parseint(s.substring(2*i,2*i+2),16);
}
return bytes;
}
}
aes加解密工具类方法代码解析(为了方便自己理解和使用,有必要简单分类记录一下工具类中的方法接口):
aesutil工具类中的方法封装的比较杂乱,通过梳理之后更加能理清每个方法的具体用法和功能!
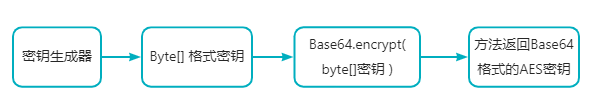
- 生成aes密钥的方法:
该工具类中总共封装了两种 生成 aes密钥的方法 string getaeskey(int length) 和 string generaterandomaeskeywithbase64()
getaeskey 方法生成的密钥是 由数字(0-9)、小写字母、大写字母随机组成的普通字符串;
generaterandomaeskeywithbase64() 方法生成的密钥是 通过 **javax.crypto.keygenerator 密钥生成器 **生成byte[] 类型的数据 在将该 byte[] 转换为 **base64编码 **格式。
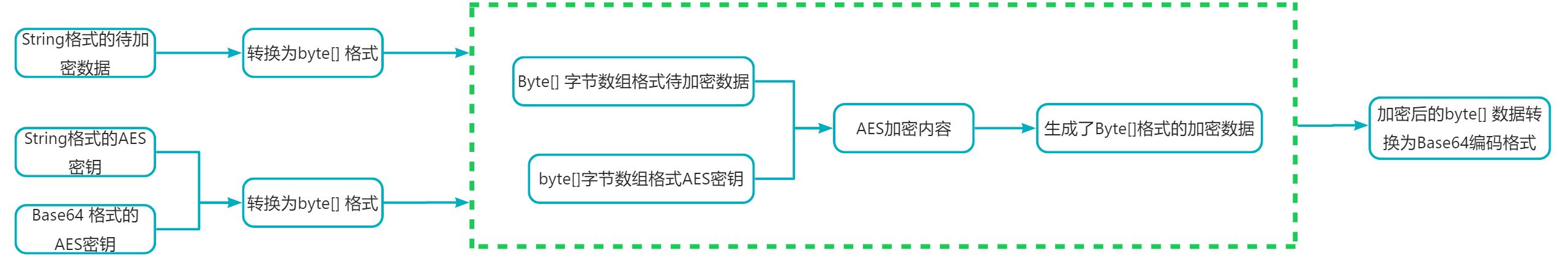
- aes加密数据方法:
aes工具类封装的加密数据方法有以下几种 byte[] encrypt(byte[] data,byte[] aeskey)、 string encrypttobase64(string data,string aeskey) 和 string encryptwithkeybase64(string data,string aeskey) 共三种加密方式:
byte[] encrypt(byte[] data,byte[] aeskey)该aes加密方法为最基础的加密方式,需要传入加密数据的 byte[] 格式数据,以及 aes密钥的byte[] 格式数据。加密之后的数据会以 byte[]格式返回。
注:其实其余加密方法都是基于该方法进行封装的。也可以根据自己需求来调整,注意区别在于传入的数据格式有所区别!!
string encrypttobase64(string data,string aeskey)该aes加密方法是通过传入加密数据的字符串,同时传入字符格式的aes密钥key(通过getaeskey生成的密钥); 方法内部会将传入进来的 待加密数据 data 和 aeskey密钥转换为 byte[] 格式,然后在调用第一种加密方法;最后生成的加密数据byte[] 也会在内部自动转换为base64编码格式 然后返回。
string encryptwithkeybase64(string data,string aeskey)该aes加密方法,需要传入 字符串形式的加密数据,以及 **base64编码格式的aes密钥 (**该密钥主要是通过generaterandomaeskeywithbase64() 方法生成的密钥数据 为base64编码格式 **)。**加密方法内部在接收到 待加密数据后会自动转换为byte[]格式;在接收到base64编码格式的aes密钥后,通过base64.decode() 将其解码为 byte[]。然后在调用原始的加密方法对待加密数据进行加密操作。最终加密后的数据byte[] 通过 new string(valuebyte,“utf-8”) 的方式转换为字符串返回。
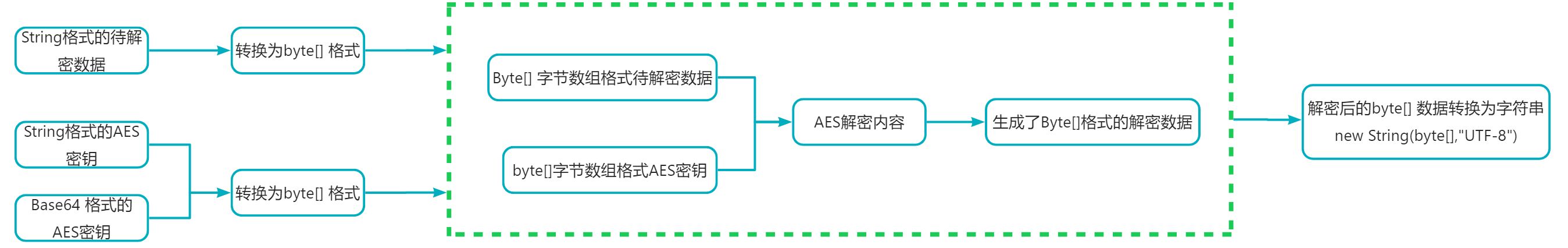
- aes解密数据方法:
aes工具类中封装的解密方法,对应于加密方法:byte[] decrypt(byte[] data,byte[] aeskey)、 string decryptfrombase64(string data,string aeskey) 和 string decryptfrombase64(string data,string aeskey)。三种方式。
该三种方式分别与上面三种加密方式是对应的。需要注意传入的数据封装格式就行。
第一种解密方法就需要传入 加密后数据格式 byte[],密钥格式 byte[]
第二种解密方法对应于上面的第二种加密方法。需要传入的加密数据为base64编码格式( 通过加密方法生成byte[] 后 在转换为 base64格式 ),需要传入aes密钥格式就为普通字符串格式(通过 string getaeskey(int length) 方法生成的密钥)。
第三种解密方法,需要传入的待解密数据 为base64编码格式,需要传入的aes密钥也为base64编码格式
- string tohexstring(byte[] b) 方法
该方法是将byte[] 字节数据转换为16进制的字符串数据,后续会利用到。 比如在get请求种传输加密数据,如果前端加密后的数据需要放入地址中进行传输到后端;若采用base64编码格式数加密数据进行传输时,加密内容会包含 +、\、= 三个符号,无法在地址中进行传输了。所有这里封装了该方法,通过调用该方法,将加密后的byte[] 字节数据数据转换为 hexstring 16进制字符串格式(只包含了 0~9、a、b、c、d、e、f)。这样get请求中的加密数据就可以通过地址进行传输了
- byte[] tobytes(string s) 方法
该方法于 tohexstring 方法相对应,将转换为hexstring十六进制的字符串 还原为字节数据byte[]。
1.3 rsa加密工具类创建
rsa加密工具类,同样引用了 hutool-all 依赖工具类。
package com.example.api_security_demo.utils;
import cn.hutool.core.codec.base64encoder;
import javax.crypto.cipher;
import java.io.bytearrayoutputstream;
import java.security.*;
import java.security.interfaces.rsaprivatekey;
import java.security.interfaces.rsapublickey;
import java.security.spec.pkcs8encodedkeyspec;
import java.security.spec.x509encodedkeyspec;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @classname : rsautil
* @description : rsa加密工具类
* @author : ad
*/
public class rsautil {
/**
* "sha256withrsa" 是一种使用 sha-256 哈希算法和 rsa 加密算法结合的数字签名算法。
* 在这种算法中,数据首先会通过 sha-256 进行哈希处理,得到一个固定长度的摘要,然后使用 rsa 私钥对这个摘要进行加密,从而生成数字签名。
* */
public static final string algorithm_sha256withrsa = "sha256withrsa";
public static final string key_algorithm ="rsa";
//rsa最大加密明文大小
public static final int max_encrypt_block = 117;
//rsa最大解密密文大小
public static final int max_decrypt_block = 128;
private static char[] hexchar = { '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f' };
/**
* description: 公钥分段加密
*
* @param data 待加密源数据
* @param publickey 公钥(base64编码)
* @param length 段长 1024长度的公钥最大取117
* @return byte[]
*/
public static byte[] encryptbypublickey(byte[] data,string publickey,int length) throws exception
{
/*
* 将base64编码格式 publickey进行解码
* */
byte[] publickeybyte = decryptbase64(publickey);
/*
* 使用x509encodedkeyspec类创建了一个x.509编码的keyspec对象,并将publickeybyte作为参数传入。
* 将公钥 [字符串] 解码成 [公钥对象] ,以便用于加密数据。
* */
x509encodedkeyspec x509encodedkeyspec = new x509encodedkeyspec(publickeybyte);
/*
* 通过keyfactory获取了rsa的实例
* */
keyfactory keyfactory = keyfactory.getinstance(key_algorithm);
/*
* 调用generatepublic方法使用之前创建的x509encodedkeyspec对象来生成公钥。
* */
key generatepublickey = keyfactory.generatepublic(x509encodedkeyspec);
/*
* 创建一个cipher实例,它是用于加密或解密数据的对象。cipher类提供了加密和解密功能,并支持许多不同的加密算法。
* 在这里,getinstance 方法中传入了keyfactory.getalgorithm()[获取与指定密钥工厂相关联的算法名称。],它用于获取与指定算法关联的 cipher 实例。
* */
cipher cipher = cipher.getinstance(keyfactory.getalgorithm());
/*
* 初始化 cipher 对象。
* 在初始化过程中,指定加密模式为 encrypt_mode,并传入了之前生成的公钥 generatepublickey。
* */
cipher.init(cipher.encrypt_mode,generatepublickey);
int inputlen = data.length;
bytearrayoutputstream out = new bytearrayoutputstream();
//段落起始位置
int offset = 0;
byte[] cache;
int i = 0;
//对数据进行分段加密
while (inputlen - offset > 0)
{
if (inputlen - offset > length) {
cache = cipher.dofinal(data,offset,length);
} else {
cache = cipher.dofinal(data,offset,inputlen-offset);
}
out.write(cache,0,cache.length);
i++;
offset = i * length;
}
byte[] encryptdate = out.tobytearray();
out.close();
return encryptdate;
}
/**
* description:
*
* @param data 待解密数据
* @param privatekey 私密(buse64编码)
* @param length 分段解密长度 128
* @return byte[]
*/
public static byte[] decryptbyprivatekey(byte[] data,string privatekey,int length) throws exception
{
byte[] privatekeybyte = decryptbase64(privatekey);
pkcs8encodedkeyspec pkcs8encodedkeyspec = new pkcs8encodedkeyspec(privatekeybyte);
keyfactory keyfactory = keyfactory.getinstance(key_algorithm);
key generateprivatekey = keyfactory.generateprivate(pkcs8encodedkeyspec);
cipher cipher = cipher.getinstance(keyfactory.getalgorithm());
cipher.init(cipher.decrypt_mode,generateprivatekey);
int inputlen = data.length;
bytearrayoutputstream out = new bytearrayoutputstream();
int offset = 0;
byte[] cache;
int i = 0;
//对数据进行分段解密
while (inputlen - offset > 0)
{
if (inputlen - offset > length)
{
cache = cipher.dofinal(data,offset,length);
} else {
cache = cipher.dofinal(data,offset,inputlen - offset);
}
out.write(cache,0,cache.length);
i++;
offset = i * length;
}
byte[] decryptdata = out.tobytearray();
out.close();
return decryptdata;
}
/**
* description: base64解码
*
* @param src
* @return byte[]
*/
public static byte[] decryptbase64(string src)
{
sun.misc.base64decoder decoder = new sun.misc.base64decoder();
try{
return decoder.decodebuffer(src);
}catch (exception ex){
return null;
}
}
/**
* description: base64编码
*
* @param src
* @return java.lang.string
*/
public static string encryptbase64(byte[] src)
{
sun.misc.base64encoder encoder = new sun.misc.base64encoder();
return encoder.encode(src);
}
/**
* description: 从byte[] 数组转 16进制字符串
*
* @param b
* @return java.lang.string
*/
public static string tohexstring(byte[] b)
{
/*
* 每个字节都可以用两个十六进制字符来表示,因此初始化的容量是字节数组长度的两倍。
* */
stringbuilder sb = new stringbuilder(b.length * 2);
for (int i = 0; i<b.length ;i++)
{
/*
* 首先取字节的高四位,然后查找对应的十六进制字符,并将其追加到stringbuilder中
* */
sb.append(hexchar[(b[i] & 0xf0) >>> 4]);
/*
* 取字节的低四位,找到对应的十六进制字符,并追加到stringbuilder中。
* */
sb.append(hexchar[b[i] & 0x0f]);
}
return sb.tostring();
}
/**
* description: 从16进制字符串转 byte[] 数组
*
* @param s
* @return byte[]
*/
public static final byte[] tobytes(string s)
{
byte[] bytes;
bytes = new byte[s.length() / 2];
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length ; i++)
{
bytes[i] = (byte) integer.parseint(s.substring(2*i,2*i+2),16);
}
return bytes;
}
/**
* description: 判断对象是否为null
*/
public static boolean isempty(object str) {
return (str == null || "".equals(str));
}
/**
* rsa 公钥私钥生成器
* */
public static map generaterandomtobase64key() throws exception{
string key_algorithm ="rsa";
keypairgenerator keypairgenerator = keypairgenerator.getinstance(key_algorithm);
//密钥位数
keypairgenerator.initialize(1024);
//创建公钥/私钥
keypair keypair = keypairgenerator.generatekeypair();
rsapublickey publickey = (rsapublickey) keypair.getpublic();
rsaprivatekey privatekey = (rsaprivatekey) keypair.getprivate();
byte[] publickeyencoded = publickey.getencoded();
byte[] privatekeyencoded = privatekey.getencoded();
hashmap<string,string> map = new hashmap<>();
map.put("publickey", base64encoder.encode(publickeyencoded));
map.put("privatekey",base64encoder.encode(privatekeyencoded));
return map;
}
/**
* description: 根据请求参数map集合,排号顺序sort,组装生成对应请求中的签名参数sign
*
* @param map 请求参数map集合
* @param allowvaluenull 是否允许map中的值为null; true允许:若允许为空则会出现a=&b=
* @return java.lang.string
*/
public static string generatesortsign(map<string,string> map,boolean allowvaluenull)
{
list<string> keys = new arraylist<>(map.size());
for ( string key : map.keyset() )
{
/*
* 排除下列参数数据
* 1.不允许出现空value 且 map中为null 的键值对
* 2.参数签名内容键值对
* */
if ( (!allowvaluenull && isempty(map.get(key))) || "sign".equals(key) || "signvalue".equals(key) )
{
continue;
}
keys.add(key);
}
/*
* sort静态方法用于按自然顺序或自定义顺序对list进行排序
* */
collections.sort(keys);
stringbuffer stringbuffer = new stringbuffer();
boolean isfirst = true;
for (string key : keys){
if (isfirst){
stringbuffer.append(key).append("=").append(map.get(key));
isfirst = false;
continue;
}
stringbuffer.append("&").append(key).append("=").append(map.get(key));
}
return stringbuffer.tostring();
}
/**
* description: 用于生成数据的数字签名,并将签名数据转换为十六进制字符串格式返回
*
* @param rawdate 签名裸数据
* @param privatekey 私钥
* @param algorithm 签名验算算法
* @return java.lang.string
*/
public static string generatesign(byte[] rawdate,string privatekey,string algorithm) throws exception
{
byte[] privatekeybytes = decryptbase64(privatekey);
pkcs8encodedkeyspec pkcs8encodedkeyspec = new pkcs8encodedkeyspec(privatekeybytes);
keyfactory keyfactory = keyfactory.getinstance(key_algorithm);
privatekey generateprivate = keyfactory.generateprivate(pkcs8encodedkeyspec);
/*
* 使用指定的签名算法algorithm,通过signature实例获取签名对象signature。
* */
signature signature = signature.getinstance(algorithm);
/*
* 初始化签名对象,传入生成的私钥generateprivate。
* */
signature.initsign(generateprivate);
/*
* 将要签名的裸数据rawdata传入签名对象。
* */
signature.update(rawdate);
/*
* 生成签名数据sign
* */
byte[] sign = signature.sign();
return tohexstring(sign);
}
/**
* description: 验证签名
*
* @param data 请求数据
* @param publickey 公钥
* @param sign 签名数据
* @param algorithm 签名验算算法
* @return boolean
*/
public static boolean verify(byte[] data,string publickey,string sign,string algorithm) throws exception
{
byte[] publickeybytes = decryptbase64(publickey);
x509encodedkeyspec x509encodedkeyspec = new x509encodedkeyspec(publickeybytes);
keyfactory keyfactory = keyfactory.getinstance(key_algorithm);
publickey generatepublickey = keyfactory.generatepublic(x509encodedkeyspec);
signature signature = signature.getinstance(algorithm);
signature.initverify(generatepublickey);
signature.update(data);
return signature.verify( tobytes(sign) );
}
}
rsautil加解密工具类方法代码解析(为了方便自己理解和使用,有必要简单分类记录一下工具类中的方法接口):
- 生成密钥对方法:
map generaterandomtobase64key() - byte[] 与 base64编码互相转换的方法:
byte[] decryptbase64(string src)string encryptbase64(byte[] src)
- hexstring 十六进制字符串 与 byte[] 字节数组 互相转换的方法:
string tohexstring(byte[] b)byte[] tobytes(string s)
- rsa加密/解密方法:
byte[] encryptbypublickey(byte[] data,string publickey,int length)rsautil工具类中的加密接口就只有 一个,最终加密后的数据会以字节数组 byte[] 格式返回。最终用户想将密文以什么形式传输都可以( string() 字符串形式、base64编码格式、hexstring十六进制字符串形式 )。byte[] decryptbyprivatekey(byte[] data,string privatekey,int length)在解码数据时,必须将密文数据根据对应的数据格式转换为 byte[] 后传入解码方法。
- base64格式编码解码方法:
byte[] decryptbase64(string src)string encryptbase64(byte[] src)
二、解密传输数据实现方案
依托与springboot进行开发,在后台中需要解密的请求接口,是采用了filter来实现解密操作。
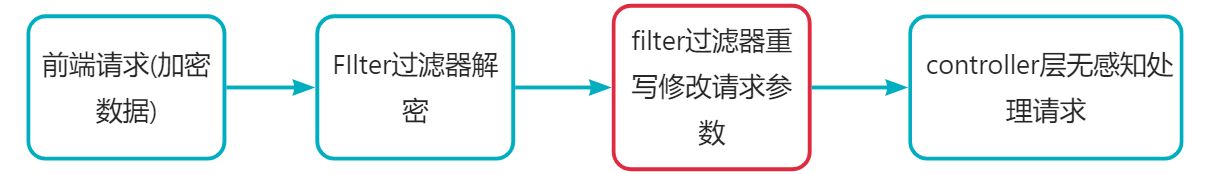
采用 filter 来对加密数据进行解密的好处之一是:filter 获取到参数后,可以将密文参数解密之后,重新重写请求参数。这样在controller层处理业务逻的接口可以按照正常方式进行开发,@requestbody、@requestparam 等注解都能正常使用。
2.1 request 流只能读取一次的问题
在接口调用连接中,request的请求流只能调用一次,处理之后,如果之后还需要用到请求流获取数据,就会发现数据为空。比如使用了filter或者aop在接口处理之前,获取了request中的数据,对参数进行了校验,那么之后就不能在获取request请求流了。
- 解决办法:
继承httpservletrequestwrapper,将请求中的流copy一份,复写getinputstream和getreader等方法供外部使用。每次调用后的getinputstream方法都是从复制出来的二进制数组中进行获取,这个二进制数组在对象存在期间一致存在。通过httpservletrequestwrapper可以获取到前端加密的请求参数,同时也可以将解密后的参数设置进去。
post请求:采用filter来实现 加密传输数据的解密功能,在解密对应request请求流中的数据之后。将解密后的数据替换至自定义封装的requestwrapper对象中 body中。
get请求:地址栏中添加了加密数据,在filter进行解密之后,会将请求数据存入自定义封装的 requestwrapper 对象中的 map集合数据中。在重写父类的 getparament() 等方法。
这里需要特别注意;对于multipartrequest请求如果不做处理httpservletrequestwrapper中是获取不到参数的;
- 自定义 requestwrapper对象:
package com.example.api_security_demo.common.core.wrapper;
import com.alibaba.fastjson2.jsonobject;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.multipartrequest;
import javax.servlet.readlistener;
import javax.servlet.servletinputstream;
import javax.servlet.servletrequest;
import javax.servlet.http.httpservletrequest;
import javax.servlet.http.httpservletrequestwrapper;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.charset.charset;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @classname : requestwrapper
* @description : 自定义request,解决request请求流中的数据二次或多次使用问题
* 继承httpservletrequestwrapper,将请求体中的流copy一份,覆写getinputstream()和getreader()方法供外部使用。
* 每次调用覆写后的getinputstream()方法都是从复制出来的二进制数组中进行获取,这个二进制数组在对象存在期间一直存在,这样就实现了流的重复读取。
* @author : ad
*/
@slf4j
public class requestwrapper extends httpservletrequestwrapper {
/**
* 存储body数据
* */
private byte[] body;
//============
/**
* 保存原始request对象,当请求为 multipartrequest 文件上传类的请求操作
*/
private httpservletrequest request;
/**
* 额外参数可以加到这个里面 重写getparameter() 方法 ,从而使请求中不存在的参数,通过该map集合中获取!!
*/
private map<string, string[]> parametermap = new linkedhashmap<>();
/**
* description: requestwrapper 请求包装类的构造方法
*
* @param request
* @return
*/
public requestwrapper(httpservletrequest request)throws ioexception
{
super(request);
//[文件上传相关的操作]
this.request = request;
if(request instanceof multipartrequest){
// 如果是[文件上传类]请求
this.parsebody(request);
}else{
//[普通请求类]将body数据存储起来
string bodystring = getbodystring(request);
body = bodystring.getbytes(charset.defaultcharset());
}
}
/* [multipartrequest 文件上传]相关操作接口 */
/**
* 如果是 multipartrequest,需要解析参数信息
*/
private void parsebody(httpservletrequest request) {
map<string,object> parametermap = new linkedhashmap<>();
enumeration<string> parameternames = request.getparameternames();
while(parameternames.hasmoreelements()){
string name = parameternames.nextelement();
string[] values = request.getparametervalues(name);
parametermap.put(name, (values !=null && values.length == 1) ? values[0] : values);
}
// 将解析出来的参数,转换成json并设置到body中保存
this.body = jsonobject.tojsonstring(parametermap).getbytes(charset.defaultcharset());
}
public void setbody(byte[] body)
{
this.body = body;
try {
if(this.request instanceof multipartrequest){
//[文件上传请求相关的操作]
//todo 将json格式body数据转换为mp
//this.setparametermap(jsonutil.json2map(body));
string bodystr = new string(body, "utf-8");
com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.objectmapper objectmapper = new com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.objectmapper();
map<string, object> bodymap = objectmapper.readvalue(bodystr, map.class);
this.setparametermap(bodymap);
}
} catch (exception e) {
log.error("转换参数异常,参数:{},异常:{}",body, e);
}
}
/**
* description:读取请全体body中数据 [从 requestwrapper中读取]
*
* @param
* @return java.lang.string
*/
public string getbodystring(){
final inputstream inputstream = new bytearrayinputstream(body);
return inputstreamtostring(inputstream);
}
/**
* description: 读取请求体body中数据 [从httpservletrequest中读取]
*
* @param request
* @return java.lang.string
*/
public string getbodystring(final servletrequest request)
{
try {
return inputstreamtostring(request.getinputstream());
}catch (ioexception e){
log.error("read request body io_stream fail !",e);
throw new runtimeexception(e);
}
}
/**
* description: 将inputstream流里面的数据读取出来并转换为字符串形式
*
* @param inputstream
* @return java.lang.string
*/
private string inputstreamtostring(inputstream inputstream){
stringbuilder sb = new stringbuilder();
bufferedreader reader = null;
try {
reader = new bufferedreader(new inputstreamreader(inputstream, charset.defaultcharset()));
string line;
while ((line = reader.readline()) != null){
sb.append(line);
}
}catch (ioexception e){
log.error("bufferedreader is fail !",e);
throw new runtimeexception(e);
}finally {
if (reader != null){
try {
reader.close();
} catch (ioexception e) {
throw new runtimeexception(e);
}
}
}
return sb.tostring();
}
@override
public bufferedreader getreader() throws ioexception {
return new bufferedreader(new inputstreamreader(getinputstream()));
}
@override
public servletinputstream getinputstream() throws ioexception {
final bytearrayinputstream inputstream = new bytearrayinputstream(body);
return new servletinputstream() {
@override
public boolean isfinished() {
return false;
}
@override
public boolean isready() {
return false;
}
@override
public void setreadlistener(readlistener readlistener) {
}
@override
public int read() throws ioexception {
return inputstream.read();
}
};
}
// [get请求相关操作,封装request.getparameter()中的相关参数 ]
/**
* description: the default behavior of this method is to return getparameter(stringname) on the wrapped request object.
*
* @param name
* @return java.lang.string
* @date 2024-05-13
*/
@override
public string getparameter(string name) {
string result = super.getparameter(name);
// 如果参数获取不到则尝试从参数(自定义封装的存贮零时请求数据的集合)map中获取,并且只返回第一个
if(result==null && this.parametermap.containskey(name)){
result = this.parametermap.get(name)[0];
}
return result;
}
/**
* the default behavior of this method is to return getparametermap() on the
* wrapped request object.
*/
@override
public map<string, string[]> getparametermap() {
// 需要将原有的参数加上新参数 返回
map<string,string[]> map = new hashmap<>(super.getparametermap());
for(string key: this.parametermap.keyset()){
map.put(key, this.parametermap.get(key));
}
return collections.unmodifiablemap(map);
}
/**
* the default behavior of this method is to return
* getparametervalues(string name) on the wrapped request object.
*
* @param name
*/
@override
public string[] getparametervalues(string name) {
string[] result = super.getparametervalues(name);
if(result == null && this.parametermap.containskey(name)){
result = this.parametermap.get(name);
}
return result;
}
/**
* the default behavior of this method is to return getparameternames() on
* the wrapped request object.
*/
@override
public enumeration<string> getparameternames() {
enumeration<string> parameternames = super.getparameternames();
set<string> names = new linkedhashset<>();
if(parameternames !=null){
while(parameternames.hasmoreelements()){
names.add(parameternames.nextelement());
}
}
// 添加后期设置的参数map
if(!this.parametermap.isempty()){
names.addall(this.parametermap.keyset());
}
return collections.enumeration(names);
}
/**
* 设置参数map
* @param json2map
*/
public void setparametermap(map<string, object> json2map) {
if(json2map != null && !json2map.isempty()) {
for (string key : json2map.keyset()){
//获取map中对应key的value
object value = json2map.get(key);
if(this.parametermap.containskey(key)){
//如果额外参数hashlink中包含该参数,则在赋值加入到string[] 中
string[] originalarray = this.parametermap.get(key);
int originallength = originalarray.length;
originalarray = arrays.copyof(originalarray,originallength + 1);
originalarray[originallength] = string.valueof(value);
//this.parametermap.put(key, collection.add(this.parametermap.get(key), value));
this.parametermap.put(key,originalarray);
}else{
this.parametermap.put(key, new string[]{string.valueof(value)});
}
}
}
}
}requestwrapper类方法代码解析(为了方便自己理解和使用,有必要简单分类记录一下工具类中的方法接口):这里自定义封装的 requestwrapper对象,继承 httpservletrequestwrapper。
- 通过重写 getreader() 、getinputstream() 等方法,从而可以实现通过request对象读取body数据时,能够直接获取到该对象中我们自己封装的用于存放请求体数据的属性byte[] body。
- **void setbody(byte[] body) **方法可以用来给自定义封装的属性body进行赋值,在 解密请求数据的 filter中,解密了body数据后,通过调用该方法将解密后的body数据存入requestwrapper对象。这样在后续的业务操作中直接通过request对象获取到的body数据就是已经解密的数据。实现了业务无感知!
- **void setparametermap(map<string, object> json2map) ** 在解密filter中,将get请求中地址上的加密数据进行解密之后,调用该方法就将解密后的get请求数据封装到 requestwrapper对象中的map集合中实现后续调用request.getparameter() 方法时能够获取到解密后的参数。
- 重写父类 getparameter(string name)、map<string, string[]> getparametermap()、 string[] getparametervalues(string name)等方法,实习在getrequestparameter()数据时,也能够在requestwrapper对象中的map集合中获取参数数据。
2.2 过滤器filter解密请求参数
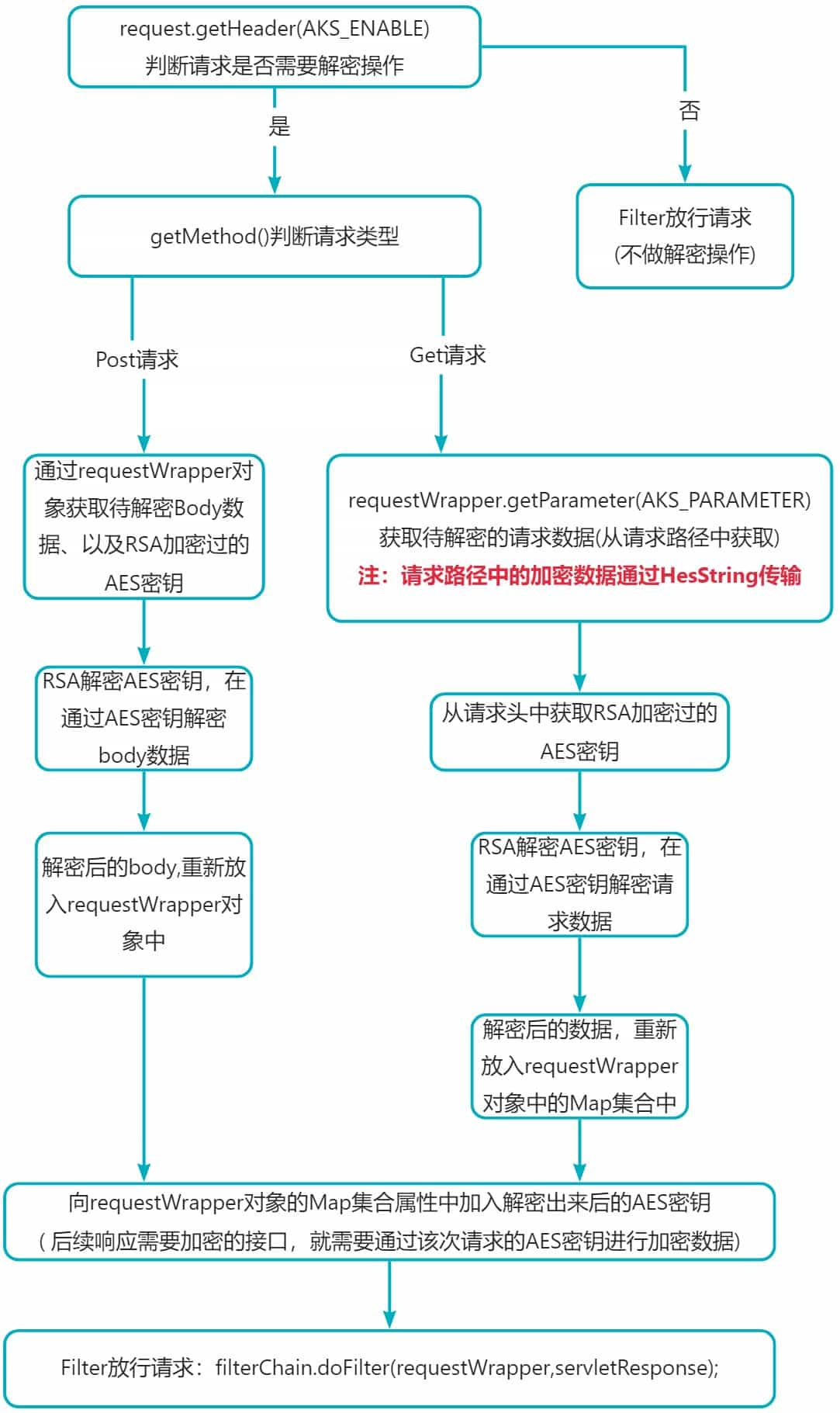
这里封装的解密参数过滤器filter中,首先需要通过请求头中的 aksencrypt数据判断该请求是否为加密请求,如果不是则直接放行不做解密操作。如果需要解密的请求,首先判断请求类型在进行对应的解密处理。
filter解密数据过滤器代码:
package com.example.api_security_demo.filter;
import com.alibaba.fastjson2.jsonobject;
import com.example.api_security_demo.common.core.wrapper.requestwrapper;
import com.example.api_security_demo.utils.aesutil;
import com.example.api_security_demo.utils.rsautil;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.value;
import org.springframework.util.objectutils;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.httpservletrequest;
import java.io.bufferedreader;
import java.io.ioexception;
import java.util.arrays;
import java.util.hashmap;
import java.util.map;
/**
* @classname : decryptreplacestreamfilter
* @description :filter过滤器 解密请求参数。同时替换请求体,使后续操作无感知加密!!
* @author : ad
*/
@slf4j
public class decryptreplacestreamfilter implements filter {
/*
* aks(authentication key management system),采用无明文密钥的方式对数据进行加密保护,加解密运算由统一的安全计算中心完成,aks系统以接口的方式为对各个业务线提供加密解服务。
* 各个系统不再使用明文密钥,只使用密钥别名,调用简单的加解密函数,完成对数据的保护。
* */
//请求头标签开关:是否需要加密解密
private static final string aks_enable = "aksencrypt";
//get请求加密数据key
public static final string aks_parameter = "encryptdata";
private static final string method_get = "get";
private static final string method_post ="post";
//post请求加密数据key
private static final string aks_body ="content";
//aes密钥key
private static final string aes_key = "aeskey";
/**
* feign是声明式web service客户端,它让微服务之间的调用变得更简单,类似controller调用service。
* feign内部调用时,请求头中标注请求源
* */
public static final string source_key = "api-source";
public static final string source_value = "inner-api";
@value("${rsa.privatekey}")
private string privatekey;
@value("${api.security.enable}")
private boolean securityenable;
@override
public void dofilter(servletrequest servletrequest, servletresponse servletresponse, filterchain filterchain) throws ioexception, servletexception {
//转换为自己wrapper,实现多次读写
requestwrapper requestwrapper = new requestwrapper((httpservletrequest) servletrequest);
string contenttype = requestwrapper.getcontenttype(); //请求头中获取content-type数据
string requesturi = requestwrapper.getrequesturi();
//配置文件配置是否开启加解密功能
if (!securityenable)
{
log.info("未开启接口安全加密传输! 无需解密请求参数!");
filterchain.dofilter(requestwrapper,servletresponse);
return;
}
//通过请求头参数判断该请求是否需要解密处理
if (!needaks(requestwrapper)){
log.info("请求:{},非加密请求,无需解密操作!",requesturi);
filterchain.dofilter(requestwrapper,servletresponse);
return;
}
/*
* [该功能暂时不用管,因为在请求头中不添加 aksencrypt:true 键值对,请求接口时同样不会去进行解密请求数据的操作]
* */
//feign服务端调用内部请求,按照不加密的逻辑放行[feign是声明式web service客户端,它让微服务之间的调用变得更简单,类似controller调用service。]
//前端 --> a --> b --> c
string sourcekey = requestwrapper.getheader(source_key);
if (!objectutils.isempty(sourcekey) && sourcekey.equals(source_value) ){
log.info("内部请求,无效加密解密接口数据!");
filterchain.dofilter(requestwrapper,servletresponse);
return;
}
/*
* post请求进行解密工作
* */
if (requestwrapper.getmethod().equalsignorecase(method_post)){
//读取json请求体数据
stringbuffer bodyinfo = new stringbuffer();
string line = null;
bufferedreader reader = null;
reader = requestwrapper.getreader();
while ( ( line = reader.readline() ) != null ){
bodyinfo.append(line);
}
//解密请求体数据
jsonobject jsonobject = jsonobject.parseobject(bodyinfo.tostring());
log.info("post请求:{},待解密请求参数:{}", requesturi, jsonobject.tojsonstring(jsonobject));
//获取通过aes加密之后的密文
string content = jsonobject.getstring(aks_body);
//获取通过rsa加密之后的aes密钥key
string aeskey = jsonobject.getstring(aes_key);
//rsautil解密出aes密钥key
try {
aeskey = new string(rsautil.decryptbyprivatekey(rsautil.tobytes(aeskey),privatekey,rsautil.max_decrypt_block),"utf-8");
} catch (exception e) {
throw new runtimeexception(e);
}
/*
* 方式1.将解密之后的数据+aeskey [放入body中,弃:会影响body结构] ( 满足在aop操作中对出参数据进行加密 ) 一并交给下游业务。
*/
//jsonobject requestbody = jsonobject.parseobject(data);
//requestbody.put(aes_key,aeskey);
/*
* 方式2.将其放入[请求对象属性中中],不影响请求体结构!
*/
//requestwrapper.setattribute(aes_key,aeskey);
/*
* 方式3.将其放入[放入requestwrapper封装的额外参数map中],不影响请求体结构!
* */
hashmap<string, object> map = new hashmap<>();
map.put(aes_key,aeskey);
requestwrapper.setparametermap(map);
//aesutil + aeskey 解密json数据
string decryptdata = aesutil.decryptfrombase64(content, aeskey);
log.info("get请求:{},解密之后参数:{}", requesturi, decryptdata);
//重置json请求体,保证下游业务无感知获取数据
//requestwrapper.setbody(requestbody.tojsonstring().getbytes());
requestwrapper.setbody(decryptdata.getbytes());
}
/*
* get请求解密处理:[aes密钥key放置在请求头中]
* */
else if (requestwrapper.getmethod().equalsignorecase(method_get))
{
//get请求中 获取到指定加密的参数 然后进行解密操作
string encryptdata = requestwrapper.getparameter(aks_parameter);
log.info("get请求:{},待解密请求参数:{}", requestwrapper.getrequesturi(), encryptdata);
// 先解密 存放在请求头中且经过rsa加密过的aes密钥
string aeskey = requestwrapper.getheader(aes_key);
if (encryptdata != null && !encryptdata.isempty() && aeskey != null && !aeskey.isempty()){
try {
byte[] aeskeybyte = rsautil.decryptbyprivatekey(rsautil.tobytes(aeskey), privatekey, rsautil.max_decrypt_block);
aeskey = new string(aeskeybyte,"utf-8");
system.out.println("aeskey.tostring() = " + aeskey.tostring());
} catch (exception e) {
throw new runtimeexception(e);
}
//get请求中的加密数据是以16进制字符串方式传输
byte[] encryptdatabyte = aesutil.tobytes(encryptdata);
system.out.println("arrays.tostring(encryptdatabyte) = " + arrays.tostring(encryptdatabyte));
// 解密数据操作 aks_parameter
string decryptdata = new string(aesutil.decrypt(encryptdatabyte,aeskey.getbytes("utf-8")),"utf-8");
log.info("get请求:{},解密之后参数:{}", requesturi, decryptdata);
//将get请求中的parameter参数赋值入requestwrapper中封装的其它参数存放集合map中
com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.objectmapper objectmapper = new com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.objectmapper();
map<string, object> map = objectmapper.readvalue(decryptdata, map.class);
//将asekey数据也存入map额外参数中
map.put("aeskey",aeskey);
requestwrapper.setparametermap(map);
}
}
filterchain.dofilter(requestwrapper,servletresponse);
}
@override
public void init(filterconfig filterconfig) throws servletexception {
filter.super.init(filterconfig);
}
@override
public void destroy() {
filter.super.destroy();
}
/**
* description: 判断当前请求是否需要加密解密数据
*
* @param request
* @return boolean
*/
private boolean needaks(httpservletrequest request){
string enableaks = request.getheader(aks_enable);
return (enableaks != null && enableaks.equalsignorecase("true"))? true: false;
}
}代码解析:
- 代码中通过三重方式放到是否需要解密请求接口。一个是配置文件中读取的开关配置、一个是通过请求头中是否开启加密传输的标识(也就是在发送加密接口时,都需要在请求头上封装该开关)、feign服务端调用内部请求,按照不加密的逻辑放行。
- 解密方式按照文章开头采用的方案,先用rsa密钥解密出随机的aes密钥,在通过密钥解密密文。
- 对应get请求和post请求的解密方式两点区别。post整个请求体都是加密参数即body数据通过base64方式传输进来的;get请求中的加密参数需要使用:encryptdata,由于需要放入路径中,base64编码格式中含有
+、\、=等特殊符号无法进行传输和解析,所以get请求中的加密数据是采用hexstring格式进行传输的,在解密时也需要对应的方法进行转换为byte[]后在进行解密操作。 - 关于aes密钥的存放位置。post请求中的aes密钥是存入body中存入过来的,而get请求中的aes密钥是存放在请求头中传递过来的,所以在解密对应请求方式的密文时,注意aes密钥的获取方式。
- 关键解密后的aes密钥,需要一并交给下游业务。满足在aop操作中对出参数据进行加密,所以解密出来的aes密钥也需要存入requestwrapper对象的map集合中,方便下游业务获取。
filter过滤器注册配置类:
需要注意解密过滤器filter 的优先级一点要设置为最高优先级registration.setorder(1);,首先需要该过滤器对加密数据进行解密后在重新封装请求,才能使后续的业务数据能直接获取到解密后的数据,达到无感知的效果。
package com.example.api_security_demo.filter;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.filterregistrationbean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.configuration;
import javax.servlet.filter;
/**
* @classname : weballhandlerconfig
* @description : 过滤器、监听器、拦截器 前置处理配置类
* @author : ad
*/
@configuration
public class weballhandlerconfig {
/**
* 注册过滤器
* */
@bean
public filterregistrationbean allfilterregistration(){
filterregistrationbean<filter> registration = new filterregistrationbean<>();
registration.setfilter(decryptreplacestreamfilter());
registration.addurlpatterns("/*");
registration.setname("apisecurityfilter");
registration.setorder(1);
return registration;
}
@bean(name = "decryptreplacestreamfilter")
public filter decryptreplacestreamfilter(){
return new decryptreplacestreamfilter();
}
}三、响应数据加密实现方案
响应数据加密的实现方式是采用aop来实现,可以对返回的结果对象进行处理,而filter只能拿到request与response对象,处理不方便;
这里的响应数据加密方案就简单采用的是aes加密,通过前端传来的随机aes进行加密响应数据后在响应给前端!
这里响应加密的开启方式是通过自定义注解来实现的,创建自定义一个自定义注解,作为响应数据加密的切点,就实现了响应数据是否加密的开启。

3.1 自定义注解(开启加密的注解):
package com.example.api_security_demo.common.core.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* @classname : responseencrypt
* @description : 响应数据加密开启注解
* @author : ad
*/
@target(elementtype.method)
@retention(retentionpolicy.runtime)
//@documented
public @interface responseencrypt {
}3.2 aop实现响应数据加密功能:
需要注意,这里的响应加密aop的优先级也要设置为最高@order(value = 0),从而使最先开始的aop能最后结束,这样才能保证 加密响应的aop最终处理的响应数据是所以业务逻辑都处理结束后最终的响应结果,然后进行加密处理后响应给前端。
package com.example.api_security_demo.aop;
import com.example.api_security_demo.common.r;
import com.example.api_security_demo.common.core.annotation.responseencrypt;
import com.example.api_security_demo.utils.aesutil;
import org.aspectj.lang.proceedingjoinpoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.pointcut;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.requestcontextholder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.servletrequestattributes;
import javax.servlet.http.httpservletrequest;
import javax.servlet.http.httpservletresponse;
/**
* @classname : responseencryptaop
* @description : 传输加密模块aop,对接口的出参进行加密,注意顺序不能乱,
* 此aop必须第一个执行,因为最先执行的最后结束,这样才能在各个aop都执行完毕之后完成最后的加密
* @author : ad
*/
@order(value = 0)
@aspect
@component
public class responseencryptaop {
@pointcut("@annotation(com.example.api_security_demo.common.core.annotation.responseencrypt)")
public void point(){}
/**
* 环绕增强,加密出参
* */
@around(value = "point() && @annotation(responseencrypt)")
public object aroundencrypt(proceedingjoinpoint joinpoint, responseencrypt responseencrypt) throws throwable {
//返回的结合
object returnvalue = null;
//从上下文中提取
httpservletrequest request = ((servletrequestattributes) requestcontextholder.getrequestattributes()).getrequest();
httpservletresponse response = ((servletrequestattributes) requestcontextholder.getrequestattributes()).getresponse();
//业务执行返回结果
returnvalue = joinpoint.proceed();
system.out.println("returnvalue.tostring() = " + returnvalue.tostring());
//获取到前端传递过来的aes密钥,然后对响应数据进行aes加密操作
string aeskey = request.getparameter("aeskey");
system.out.println("aeskey = " + aeskey);
string encrypttobase64data = aesutil.encrypttobase64(returnvalue.tostring(), aeskey);
returnvalue = r.ok(encrypttobase64data);
return returnvalue;
}
}
四、测试相关的类
4.1 测试类实体封装
package com.example.api_security_demo.controller;
import lombok.data;
import lombok.tostring;
import lombok.experimental.accessors;
/**
* @classname : tbstudenentity
* @description : 测试实体类
* @author : ad
*/
@data
@accessors(chain = true)
@tostring
public class tbstudententity {
int id;
string name;
string sex;
int age;
}4.2 测试接口controller层封装
package com.example.api_security_demo.controller;
import com.example.api_security_demo.common.r;
import com.example.api_security_demo.common.core.annotation.responseencrypt;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import javax.servlet.http.httpservletrequest;
/**
* @classname : tbstudentcontroller
* @description : 前端控制器controller测试类
* @author : ad
*/
@restcontroller
@requestmapping("/demo")
@slf4j
public class tbstudentcontroller {
@postmapping("/encryptpost")
@responseencrypt
public r postdemo(@requestbody tbstudententity tbstudententity,httpservletrequest request){
system.out.println("request.getparameter(\"aeskey\") = " + request.getparameter("aeskey"));
//system.out.println("request.getattribute(\"aeskey\") = " + request.getattribute("aeskey"));
system.out.println("tbstudententity = " + tbstudententity);
return r.ok(tbstudententity.tostring());
}
@getmapping("/encryptget")
@responseencrypt
public r postdemoget(httpservletrequest request,@requestparam string id,@requestparam string name,@requestparam string aeskey ){
system.out.println("id = " + id);
system.out.println("name = " + name);
system.out.println("aeskey = " + aeskey);
system.out.println("request.getparameter(\"age\") = " + request.getparameter("age"));
//system.out.println("request.getattribute(decryptreplacestreamfilter.aks_parameter) = " + request.getattribute(decryptreplacestreamfilter.aks_parameter));
return r.ok();
}
}
4.3 前端模拟生成加密数据
package com.example.api_security_demo.utils;
import com.alibaba.fastjson2.jsonobject;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.jsonprocessingexception;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.slf4j;
import org.junit.test;
import java.io.unsupportedencodingexception;
import java.util.arrays;
import java.util.hashmap;
import java.util.map;
/**
* @classname : utilstestclass
* @description : 工具类测试类
* @author : ad
*/
@slf4j
public class utilstestclass {
/**
* 可以将其放入配置文件中进行读取
* */
string publickey = "migfma0gcsqgsib3dqebaquaa4gnadcbiqkbgqdi7he0aw9ilcmkfoajymag+5rbrhu2itebf04gutnymur6rl1gjkec7jkum/8xsindh4jn6vz3oartjbcn4cxjbtqpys5i8vexxgzzqhe34ly0rt62qy8uvs113454dtwzzr9bjmpqsxmaftqhmgedjxvwlut0a6cmrizkojw8wqidaqab";
string privatekey = "miicdqibadanbgkqhkig9w0baqefaascal8wggjbageaaogbamjsctrpb0gsiyr+galiyab7lefgftyi15t/tgzs2dgy5hpgxuykp5zskq4z/zfkkd0fiofpxpegbfonskfglgnu1a/kzmlxv5fgdpoqetfgtjrg3rzdlxrvlxxfjngnpbllh0goy9blexp+1acyb4ondxats3rrokzgjko6pdxzagmbaaecgybruhdkkcnypwi188gnhbuu18qhqpa1crbpbi90obwwlmqqvcdj6to2y3t1au+9z/fxxzrn+ic6apu1p2m2hab4ipdw+2vm0darn7xjpzbdjqvasyvj2owwlwckg05ms2pagcmlxv3tlen7ibfktjgzhdlial8jygyi6xwdnlataqjbapjctpmxuas9luyxo2exeaukec2uc06fezqgm6u1rtqsque5kgpmj1dieruocqxn8i+mlnj1urmw8ltmxmnjaiecqqdoxvbjuxwolwrf8lsoez9xggc/45pe7j8dubev0ii1rvckmytkxmgnaupe7xq9cgnmpnbruqednzshha8rqgm5akbuwwrbac6rtcplprwl+s3uptne01fpzxgkyy1+rw5qsg1puazfgooathz92wa16lxnj1mwrmvdp03qnpc8pdvhakboqwd6vv/2d0l9enh4cj2iy1rx7whgfrncwmd1rtguf94tf6pd4jl+5ivaie6h+c8nw5uknzskmqx/nmxlz/ezakbdxrx7ygmg4plxcjpt4ot6dejdjusvb1lhwucl6qffyhzloh3/9xqs3t9xb/2f61tdh5jd3facd7wexjczw+64";
/**
* description: 测试获取密钥的方法
*/
@test
public void testgetask() throws exception {
// aes密钥
string aeskey = aesutil.getaeskey(16);
system.out.println("aeskey = " + aeskey);
// aes base64类型密钥
string base64aeskey = aesutil.generaterandomaeskeywithbase64();
system.out.println("base64aeskey = " + base64aeskey);
//rsa 私钥公钥
map map = rsautil.generaterandomtobase64key();
system.out.println("map.get(\"privatekey\") = " + map.get("privatekey"));
system.out.println("map.get(\"publickey\") = " + map.get("publickey"));
}
/**
* description: post请求加密传输,请求体body封装测试
*
* @param
* @return void
*/
@test
public void postrequestbodyencrypttest() throws exception {
//自定义方式获取 aeskey
string aeskey = aesutil.getaeskey(16);
//内部方式获取 base64aeskey
string base64aeskey = aesutil.generaterandomaeskeywithbase64();
//创建请求体body数据 content
//模拟业务数据json,并用aes密钥key进行加密
map<string, object> datamap = new hashmap<>();
datamap.put("id", 15);
datamap.put("name", "张三");
datamap.put("sex", "男");
datamap.put("age", 20);
jsonobject datajson = new jsonobject(datamap);
string contentjson = jsonobject.tojsonstring(datajson);
//aes 加密业务数据
string content = aesutil.encrypttobase64(contentjson, aeskey);
log.info("aes加密数据操作: \naes加密之前的数据 = {} \naes加密之后的数据 content= {}",contentjson,content);
//rsa 加密aes密钥
byte[] bytes = rsautil.encryptbypublickey(aeskey.getbytes("utf-8"), publickey, rsautil.max_encrypt_block);
string encryptaeskey = rsautil.tohexstring(bytes);
log.info("rsa加密aes密钥操作: \nrsa加密之前的aes密钥= {} \nrsa加密之后的aes密钥 aeskey={}",aeskey,encryptaeskey);
/**
* 09:08:42.376 [main] info com.example.api_security_demo.utils.utilstestclass - aes加密数据操作:
* aes加密之前的数据 = {"sex":"男","name":"张三","id":15,"age":20}
* aes加密之后的数据 content= u/vrpwktlao12atyfa1rb14ehnfthfvhyefy7r+dojzo6jzxs4bwuj0xny8rju8f
* 09:08:42.380 [main] info com.example.api_security_demo.utils.utilstestclass - rsa加密aes密钥操作:
* rsa加密之前的aes密钥= 9rag41fie8uk7l3k
* rsa加密之后的aes密钥 aeskey=c7eccef1d112075ee64eec65163b8b1dcb1a54ea6c8b51875174f6d34fc4ac7d50d2977b7519d275ee610d717d594228e132b053a70cdad9f925701a728ed794684d12097cfb8bea598c561393cb69de384b2ec83aa8ddb9a98a5adb3ed51ee1b9aaab2cf7bc5b49712a95e40ac4ea17421f5250d34b8e629e58db0b26e54b39
* */
}
/**
* description: get请求加密传输,请求体requestparameter数据封装测试
* 注意: 通过aes加密之后的数据 byte[] 需要转换为 hexstring十六进制字符串后才能在 请求地址中传输,不能在用base64编码格式的方式进行传输!
*/
@test
public void getrequestbodyencrypttest() throws exception {
//自定义方式获取 aeskey
string aeskey = aesutil.getaeskey(16);
//内部方式获取 base64aeskey
string base64aeskey = aesutil.generaterandomaeskeywithbase64();
//创建请求体body数据 content
//模拟业务数据json,并用aes密钥key进行加密
map<string, object> datamap = new hashmap<>();
datamap.put("id", 15);
datamap.put("name", "张三");
datamap.put("sex", "男");
datamap.put("age", 20);
jsonobject datajson = new jsonobject(datamap);
string contentjson = jsonobject.tojsonstring(datajson);
//aes 加密业务数据
byte[] contentbyte = aesutil.encrypt(contentjson.getbytes("utf-8"), aeskey.getbytes("utf-8"));
string content = aesutil.tohexstring(contentbyte);
log.info("aes加密数据操作: \naes加密之前的数据 = {} \naes加密之后的byte[]数据 = {} \naes加密后的数据转换为hexstring十六进制字符串数据encryptdata={}",contentjson,arrays.tostring(contentbyte),content);
//rsa 加密aes密钥
byte[] bytes = rsautil.encryptbypublickey(aeskey.getbytes("utf-8"), publickey, rsautil.max_encrypt_block);
string encryptaeskey = rsautil.tohexstring(bytes);
log.info("rsa加密aes密钥操作: \nrsa加密之前的aes密钥= {} \nrsa加密之后的aes密钥aeskey={}",aeskey,encryptaeskey);
/**
* 09:09:13.172 [main] info com.example.api_security_demo.utils.utilstestclass - aes加密数据操作:
* aes加密之前的数据 = {"sex":"男","name":"张三","id":15,"age":20}
* aes加密之后的byte[]数据 = [73, 19, 107, 60, 29, 109, 100, 119, -81, -117, -84, -85, 19, 28, 86, 18, 123, 48, 58, 37, -28, -65, -93, -124, -50, 89, -10, -101, 48, 48, -104, -18, -109, 127, -19, 80, 62, -122, -80, -122, 94, 72, -16, -89, -1, -128, 22, -92]
* aes加密后的数据转换为hexstring十六进制字符串数据encryptdata=49136b3c1d6d6477af8bacab131c56127b303a25e4bfa384ce59f69b303098ee937fed503e86b0865e48f0a7ff8016a4
* 09:09:13.177 [main] info com.example.api_security_demo.utils.utilstestclass - rsa加密aes密钥操作:
* rsa加密之前的aes密钥= 868e9fma727s9w5q
* rsa加密之后的aes密钥aeskey=2ab5531c7814201b4eaef3802ca883e79ffffd4c4ec32e698403189c0954718fd5cebd0ac5e66e856ec4f95a408442fc76276586a8fdb94c14c8f311f30ad061d6928315078736e6633113cdba255870a78e9077b2f18bdc4b2730804e5d6181df4b0ecf51597f71c8e0ccb89a5e160f1216a7bde5386b42171577db400d5a54
* */
}
@test
public void testbytebase64string(){
/*
* 创建字节数组的方式
* */
byte[] testbytes = new byte[]{0,1,2,3,4};
/*
* 读取字节数组的方式:
* */
system.out.println("arrays.tostring(bytes1) = " + arrays.tostring(testbytes));
//模拟业务数据json,并用aes密钥key进行加密
map<string, string> datamap = new hashmap<>(2);
datamap.put("name", "张三");
datamap.put("age", "20");
jsonobject datajson = new jsonobject(datamap);
string jsonstr = jsonobject.tojsonstring(datajson);
com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.objectmapper objectmapper = new com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.objectmapper();
try {
map<string, object> map = objectmapper.readvalue(jsonstr, map.class);
system.out.println("map.tostring() = " + map.tostring());
system.out.println("map.get(\"name\") = " + map.get("name"));
system.out.println("map.get(\"age\") = " + map.get("age"));
} catch (jsonprocessingexception e) {
throw new runtimeexception(e);
}
byte[] jsonbyte = datajson.tostring().getbytes();
system.out.println("new string(jsonbyte) = " + new string(jsonbyte));
//[两种方式不一样!]
string hexstr = "0123456789abcdef";
system.out.println("arrays.tostring(hexstr.getbytes()) = " + arrays.tostring(hexstr.getbytes()));
system.out.println("arrays.tostring(rsautil.tobytes(hexstr)) = " + arrays.tostring(rsautil.tobytes(hexstr)));
}
/**
* description: 解密操作测试
*/
@test
public void testaesdecrypt() throws exception {
string encryptaeskey = "868dbf00b6849a1189f186f18bc98eca65981829e12d3bad21f4a64c139a6fe6953729e488af642cb5bf7104459a4fbf084bb536f251e2d9fa39747037715da6a73caf23e1d68bd5338d51dd207ebe9c4a72749d87d73eb96fc193adac45e6b8b6b7fcc211ee47efd0d54ea97dcfdbc221ac0bd7664d32becbdd654c3d9b2446";
string encryptdate = "8ee240b806a571f0f7ef5568d9cf5e36d999686acabfa4d5425d73ef7e546c8c1e9147c084269a6884cfeebf6759bd60";
//解密之后的aeskey 56x8817grc2p33w0
byte[] decryptaeskey = rsautil.decryptbyprivatekey(rsautil.tobytes(encryptaeskey), privatekey, rsautil.max_decrypt_block);
string decryptaeskeystr = new string(decryptaeskey, "utf-8");
system.out.println("decryptaeskeystr = " + decryptaeskeystr);
//get请求数据解密 [加密数据为hexstr十六进制字符串形式]
byte[] encryptdatabyte = aesutil.tobytes(encryptdate);
system.out.println("arrays.tostring(encryptdatabyte) 加密数据byte[]形式 = " + arrays.tostring(encryptdatabyte));
string decryptdata = new string(aesutil.decrypt(encryptdatabyte,decryptaeskeystr.getbytes("utf-8")),"utf-8");
system.out.println("decryptdata解密后的数据 = " + decryptdata);
/* //post请求数据解密 [加密数据为base64编码格式]
string decryptdata2 = aesutil.decryptfrombase64(encryptdate, decryptaeskeystr);
system.out.println("decryptdata2 解密后的数据 = " + decryptdata2);*/
/**
* aes加密之前的数据 = {"sex":"男","name":"张三","id":15,"age":20}
* aes加密之后的byte[]数据 = [-114, -30, 64, -72, 6, -91, 113, -16, -9, -17, 85, 104, -39, -49, 94, 54, -39, -103, 104, 106, -54, -65, -92, -43, 66, 93, 115, -17, 126, 84, 108, -116, 30, -111, 71, -64, -124, 38, -102, 104, -124, -49, -18, -65, 103, 89, -67, 96]
* aes加密后的数据转换为hexstring十六进制字符串数据encryptdata=8ee240b806a571f0f7ef5568d9cf5e36d999686acabfa4d5425d73ef7e546c8c1e9147c084269a6884cfeebf6759bd60
* 16:48:25.095 [main] info com.example.api_security_demo.utils.utilstestclass - rsa加密aes密钥操作:
* rsa加密之前的aes密钥= 8c0n9032214lj139
* rsa加密之后的aes密钥aeskey=868dbf00b6849a1189f186f18bc98eca65981829e12d3bad21f4a64c139a6fe6953729e488af642cb5bf7104459a4fbf084bb536f251e2d9fa39747037715da6a73caf23e1d68bd5338d51dd207ebe9c4a72749d87d73eb96fc193adac45e6b8b6b7fcc211ee47efd0d54ea97dcfdbc221ac0bd7664d32becbdd654c3d9b2446
* */
}
/**
* description: 响应数据加密后,模拟前端进行解密操作
*/
@test
public void responseencrypttodecrypt() throws unsupportedencodingexception {
string aeskeypost = "9rag41fie8uk7l3k";
string aeskeyget = "0303f71572405ef1";
string encryptdata = "cf156ddc9cd9fde2a8287fa3b8eadca258ce063130d29d7d9c1b949a4628c42e497b4e1db76244bdd075cb37b8ef0212";
//解密后的数据
string decryptdata = "";
//base64编码格式的数据解密
//decryptdata = aesutil.decryptfrombase64(encryptdata, aeskeyget);
//hexstring格式的数据转换后在解密
byte[] decrypt = aesutil.decrypt(aesutil.tobytes(encryptdata), aeskeyget.getbytes("utf-8"));
decryptdata = new string(decrypt, "utf-8");
system.out.println("decryptdata = " + decryptdata);
}
}
4.4 模拟加密请求调用接口
4.4.1 post请求的封装
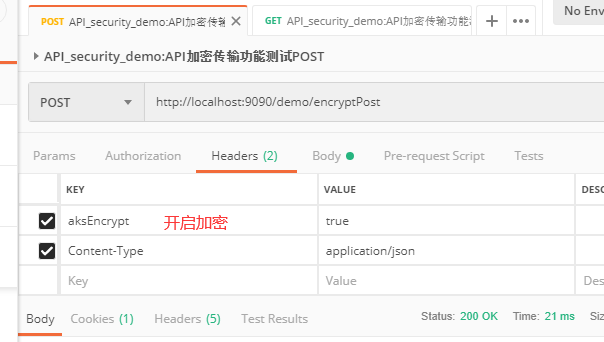
- 请求头中封装数据:
aksencrypt: true 开启解密功能
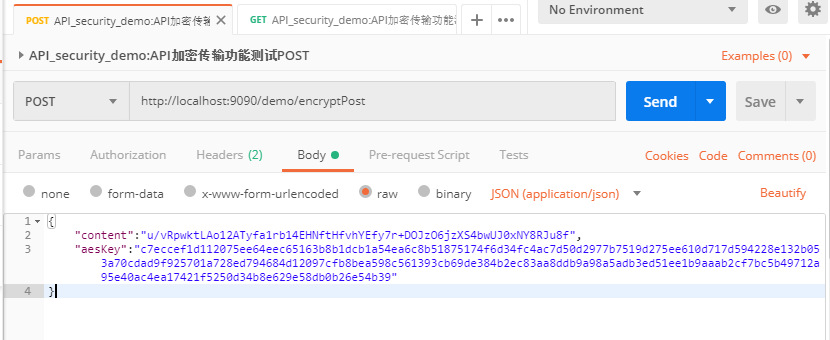
- 请求体body(application/json格式)的封装:
content:通过随机aes密钥加密后的请求数据
aeskey: 通过rsa加密后的随机aes密钥
- post请求后响应数据
可以看出 请求数据解密后,通过 requestwrapper重新封装后的请求数据,能直接通过@requestbody 等注解直接获取到相请求体中的数据。 同时也可以通过 request.getparameter()中存放的参数。
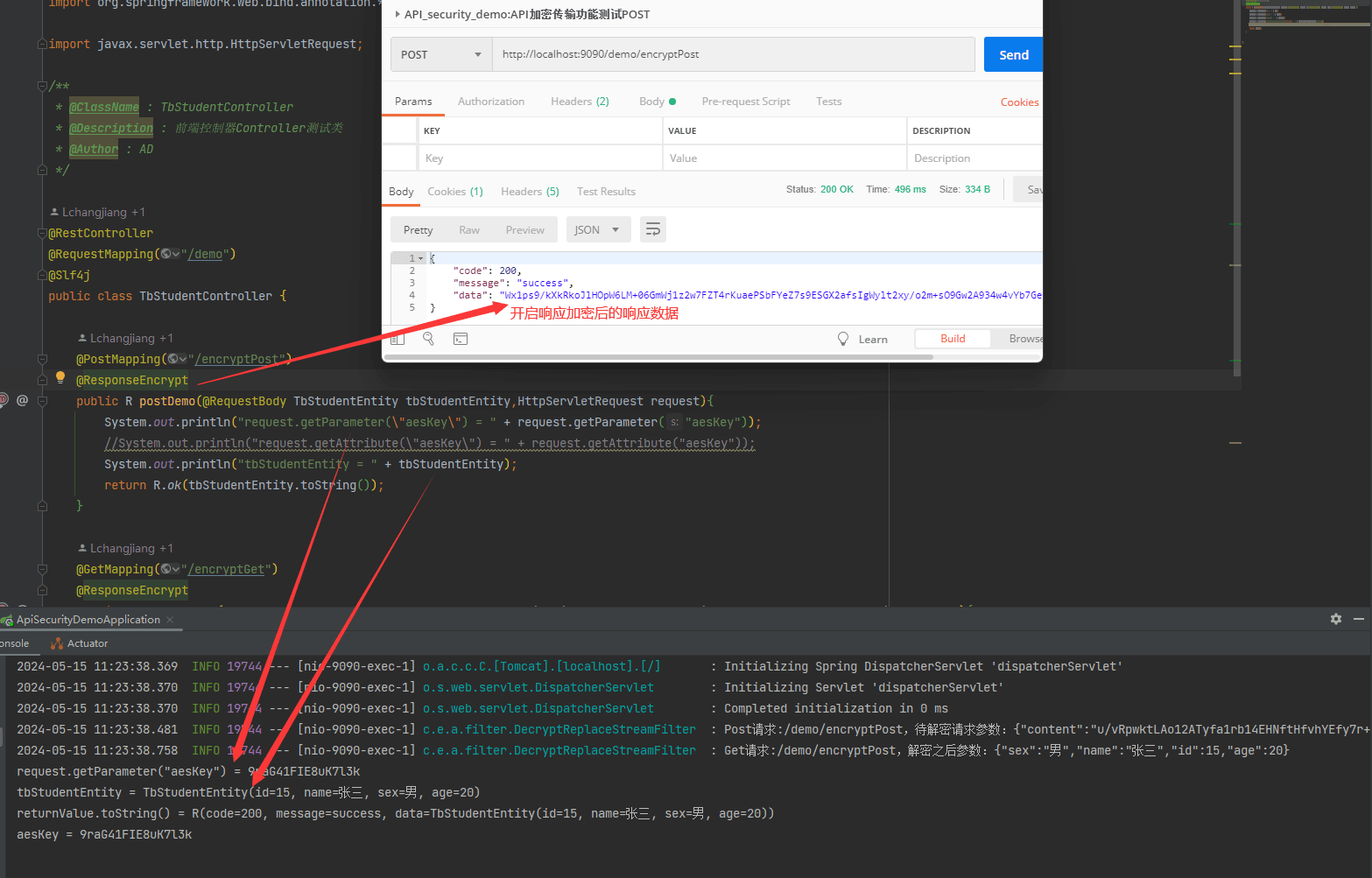
4.4.2 get请求的封装
- get请求的封装
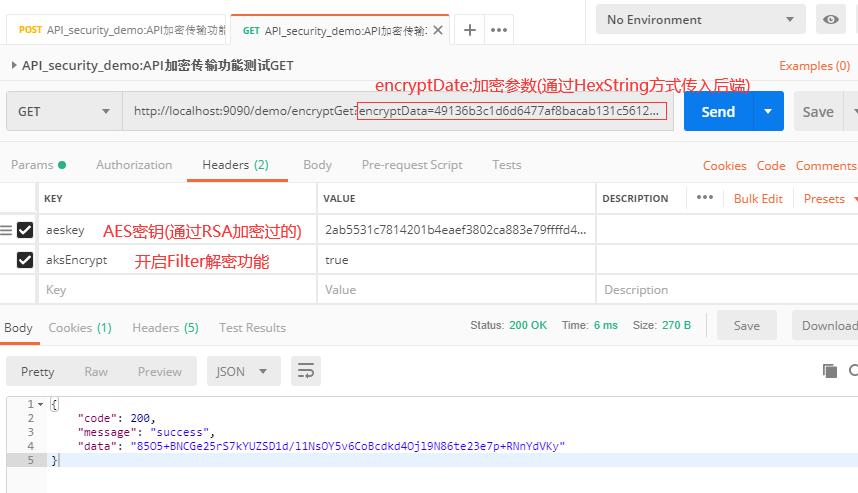
- get请求响应结果:
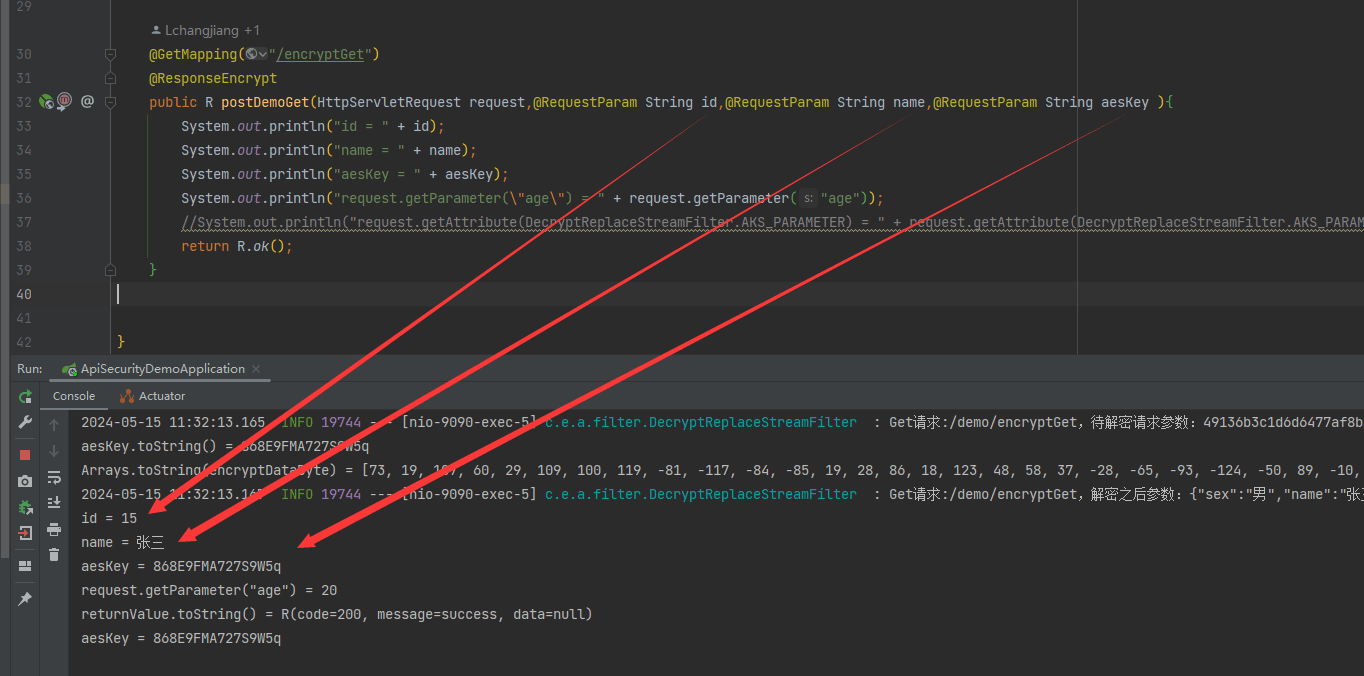
可以看出 请求数据解密后,通过 requestwrapper重新封装后的请求数据,能直接通过@requestparam等注解直接获取到get请求中的数据。 同时也可以通过 request.getparameter()中存放的参数。
总结
到此这篇关于springboot前后端传输加密设计实现方案的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关springboot前后端传输加密内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论