参数校验是一个常见的问题,比如字段非空,字段长度限制,邮箱格式、手机格式验证等等。
避免校验规则,写一大串步骤,繁琐重复。
hibernate validator为此提供了一套比较完善、便捷的验证实现方式。
一、自动校验
第一步,导入依赖
项目已经引入spring-boot-starter-web包里面有hibernate-validator包,不需要引用hibernate validator依赖。
项目还未引入spring-boot-starter-web包可以引入以下依赖:
<dependency>
<groupid>org.hibernate</groupid>
<artifactid>hibernate-validator</artifactid>
<version>4.3.1.final</version>
</dependency>第二步,统一异常处理
validateexceptioncontroller
import com.central.common.model.result;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.slf4j;
import org.springframework.core.ordered;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.order;
import org.springframework.validation.bindingresult;
import org.springframework.web.bind.methodargumentnotvalidexception;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.exceptionhandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.restcontrolleradvice;
import java.util.hashmap;
import java.util.map;
/**
* 统一异常处理
*/
@slf4j
@restcontrolleradvice
@order(ordered.highest_precedence)
public class validateexceptioncontroller {
//如果能精确匹配到该异常就会执行这个方法,后续执行下面的方法
@exceptionhandler(value = methodargumentnotvalidexception.class)
public result handelvalidateexception(methodargumentnotvalidexception e) {
log.error("数据校验出现问题:{},异常类型:{}", e.getmessage(), e.getclass());
map<string, string> map = new hashmap<>();
//1.获取校验错误结果
bindingresult result = e.getbindingresult();
result.getfielderrors().foreach(fielderror -> {
//获取每个错误的属性名字
string field = fielderror.getfield();
//获取每个错误提示信息
string defaultmessage = fielderror.getdefaultmessage();
map.put(field, defaultmessage);
});
return result.failed(map, "数据校验错误");
}
}第三步,定义接口接收实体dto
定义校验规则,可以参考
关于java validation (验证注解) 见文末补充介绍。
import io.swagger.annotations.apimodel;
import io.swagger.annotations.apimodelproperty;
import lombok.data;
import javax.validation.valid;
import javax.validation.constraints.notblank;
import javax.validation.constraints.notnull;
import javax.validation.constraints.size;
import java.io.serializable;
import java.util.list;
@data
@apimodel("售后申请接口-接收实体dto")
public class afterserviceapplydto implements serializable {
@notblank(message = "订单编号不为空")
@apimodelproperty(value = "订单编号", required = true)
private string grandsonordercode;
@notnull(message = "申请售后类型不为空")
@apimodelproperty(value = "申请售后类型: 10:退货 20:换货 30:维修", required = true)
private integer customerexpect;
@notblank(message = "产品问题描述不为空")
@apimodelproperty(value = "产品问题描述", required = true)
private string questiondesc;
@apimodelproperty("问题描述图片链接地址,多个图片以“,”分隔")
private string questionpic;
@valid
@notnull(message = "客户信息实体不为空")
@apimodelproperty("客户信息实体")
private aftersalecustomerdto ascustomerdto;
@valid
@size(min = 1, max = 1, message = "只能申请1个商品")
@notnull(message = "申请单明细列表不为空")
@apimodelproperty("申请单明细列表")
private list<aftersaledetaildto> asdetaildtos;
}第四步,在contoller接口中增加参数注解@validated
表示只校验当前参数
@api(tags = "【售后】订单售后api接口")
@restcontroller
public class afterserviceapicontroller {
/**
* 售后申请接口
* @param afterserviceapplydto 售后申请参数
* @return 操作结果
*/
@apioperation("售后申请接口")
@postmapping("/afterservice/api/apply")
public result apply(@validated @requestbody afterserviceapplydto afterserviceapplydto) {
// todo
return null;
}
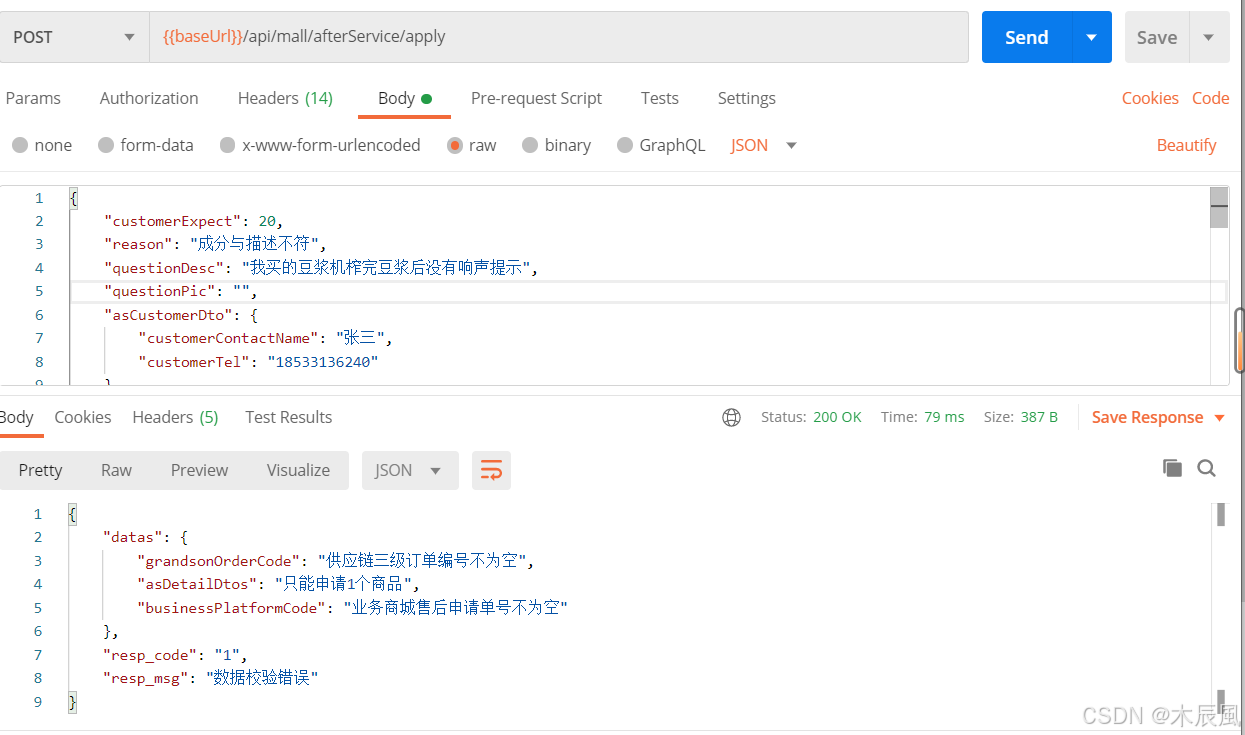
}第五步,测试结果
postman发送错误数据触发验证测试
二、手动校验
第一步,校验工具类
validatorutils
import com.central.business.afterservice.dto.afterserviceapplydto;
import com.central.common.model.result;
import javax.validation.constraintviolation;
import javax.validation.validation;
import javax.validation.validator;
import java.util.arraylist;
import java.util.hashmap;
import java.util.list;
import java.util.map;
import java.util.set;
/**
* 校验工具类
*/
public class validatorutils {
private static final validator validator;
// 第一种方式创建validator
static {
// 普通模式(默认是这个模式)
// 普通模式(会校验完所有的属性,然后返回所有的验证失败信息)
validator = validation.builddefaultvalidatorfactory().getvalidator();
}
//第二种方式创建validator
// static {
// // 1.普通模式(默认是这个模式)
// // 普通模式(会校验完所有的属性,然后返回所有的验证失败信息)
// // .failfast(false)
// // 或 .addproperty("hibernate.validator.fail_fast", "false")
//
// // 2.快速失败返回模式
// // 快速失败返回模式(只要有一个验证失败,则返回)
// // .addproperty("hibernate.validator.fail_fast", "true")
// // 或 .failfast(true)
// validatorfactory validatorfactory = validation.byprovider(hibernatevalidator.class)
// .configure()
// .failfast(true)
.addproperty("hibernate.validator.fail_fast", "true")
// .buildvalidatorfactory();
// validator = validatorfactory.getvalidator();
// }
/**
* 校验对象,返回校验失败list信息
*
* @param object 对象
* @param groups 组
* @return 校验失败list信息
*/
public static list<string> validateentity(object object, class<?>... groups) {
list<string> list = new arraylist<>();
set<constraintviolation<object>> validate = validator.validate(object, groups);
for (constraintviolation<object> violation : validate) {
list.add(violation.getmessage());
}
return list;
}
/**
* 校验对象,返回校验失败map信息
*
* @param object 对象
* @param groups 组
* @return 校验失败map信息,key为属性(字段名),value为校验失败信息
*/
public static map<string, string> validateentityproperty(object object, class<?>... groups) {
map<string, string> map = new hashmap<>();
set<constraintviolation<object>> validate = validator.validate(object, groups);
for (constraintviolation<object> violation : validate) {
map.put(violation.getpropertypath().tostring(), violation.getmessage());
}
return map;
}
/**
* 校验对象,返回校验失败result信息
*
* @param object 对象
* @param groups 组
* @return 校验失败result,校验失败返回错误信息,成功返回成功信息
*/
public static result<map<string, string>> validateentityresult(object object, class<?>... groups) {
map<string, string> map = new hashmap<>();
set<constraintviolation<object>> validate = validator.validate(object, groups);
for (constraintviolation<object> violation : validate) {
map.put(violation.getpropertypath().tostring(), violation.getmessage());
}
if (map.size() > 0) {
return result.failed(map, "数据校验错误!");
}
return result.succeed("数据校验成功!");
}
public static void main(string[] args) {
afterserviceapplydto afterserviceapplydto = new afterserviceapplydto();
system.out.println(validateentityresult(afterserviceapplydto));
}
}第二步,测试结果
result(datas={questiondesc=产品问题描述不为空, grandsonordercode=供应链三级订单编号不为空, reason=售后原因不为空, ascustomerdto=客户信息实体不为空, asdetaildtos=申请单明细列表不为空, businessplatformcode=业务商城售后申请单号不为空, customerexpect=申请售后类型不为空}, resp_code=1, resp_msg=数据校验错误!)补充:java validation (验证注解)
| 验证注解 | 验证的数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| @assertfalse | boolean,boolean | 验证注解的元素值是false |
| @asserttrue | boolean,boolean | 验证注解的元素值是true |
| @notnull | 任意类型 | 验证注解的元素值不是null |
| @null | 任意类型 | 验证注解的元素值是null |
| @min(value=值) | bigdecimal,biginteger, byte,short, int, long,等任何number或charsequence(存储的是数字)子类型 | 验证注解的元素值大于等于@min指定的value值 |
| @max(value=值) | 和@min要求一样 | 验证注解的元素值小于等于@max指定的value值 |
| @decimalmin(value=值) | 和@min要求一样 | 验证注解的元素值大于等于@ decimalmin指定的value值 |
| @decimalmax(value=值) | 和@min要求一样 | 验证注解的元素值小于等于@ decimalmax指定的value值 |
| @digits(integer=整数位数, fraction=小数位数) | 和@min要求一样 | 验证注解的元素值的整数位数和小数位数上限 |
| @size(min=下限, max=上限) | 字符串、collection、map、数组等 | 验证注解的元素值的在min和max(包含)指定区间之内,如字符长度、集合大小 |
| @past | java.util.date,java.util.calendar;joda time类库的日期类型 | 验证注解的元素值(日期类型)比当前时间早 |
| @future | 与@past要求一样 | 验证注解的元素值(日期类型)比当前时间晚 |
| @notblank | charsequence子类型 | 验证注解的元素值不为空(不为null、去除首位空格后长度为0),不同于@notempty,@notblank只应用于字符串且在比较时会去除字符串的首位空格 |
| @length(min=下限, max=上限) | charsequence子类型 | 验证注解的元素值长度在min和max区间内 |
| @notempty | charsequence子类型、collection、map、数组 | 验证注解的元素值不为null且不为空(字符串长度不为0、集合大小不为0) |
| @range(min=最小值, max=最大值) | bigdecimal,biginteger,charsequence, byte, short, int, long等原子类型和包装类型 | 验证注解的元素值在最小值和最大值之间 |
| @email(regexp=正则表达式,flag=标志的模式) | charsequence子类型(如string) | 验证注解的元素值是email,也可以通过regexp和flag指定自定义的email格式 |
| @pattern(regexp=正则表达式,flag=标志的模式) | string,任何charsequence的子类型 | 验证注解的元素值与指定的正则表达式匹配 |
| @valid | 任何非原子类型 | 指定递归验证关联的对象如用户对象中有个地址对象属性,如果想在验证用户对象时一起验证地址对象的话,在地址对象上加@valid注解即可级联验证 |
到此这篇关于java spring validation 自动、手动校验的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关java spring validation校验内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论