aop动态代理源码剖析
aop增强逻辑的执行时机是在initializebean方法中
protected object initializebean(string beanname, object bean, @nullable rootbeandefinition mbd) {
if (beanname.indexof("my") >= 0) {
system.out.println("============= [initializebean] beanname=" + beanname + " =============");
}
if (system.getsecuritymanager() != null) {
accesscontroller.doprivileged((privilegedaction<object>) () -> {
invokeawaremethods(beanname, bean);
return null;
}, getaccesscontrolcontext());
}
else {
invokeawaremethods(beanname, bean);
}
object wrappedbean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.issynthetic()) {
wrappedbean = applybeanpostprocessorsbeforeinitialization(wrappedbean, beanname);
}
try {
invokeinitmethods(beanname, wrappedbean, mbd);
}
catch (throwable ex) {
throw new beancreationexception(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getresourcedescription() : null),
beanname, "invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.issynthetic()) {
// aop增强逻辑的执行时机
// 说白了就是在beanpostprocessor#postprocessafterinitialization
wrappedbean = applybeanpostprocessorsafterinitialization(wrappedbean, beanname);
}
return wrappedbean;
}org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.abstractautoproxycreator#postprocessafterinitialization
@override
public object postprocessafterinitialization(@nullable object bean, string beanname) {
if (bean != null) {
object cachekey = getcachekey(bean.getclass(), beanname);
if (this.earlyproxyreferences.remove(cachekey) != bean) {
// 如果它有资格被代理
return wrapifnecessary(bean, beanname, cachekey);
}
}
return bean;
}protected object wrapifnecessary(object bean, string beanname, object cachekey) {
// 以下三种情况,判断,如果不需要增强,就直接返回
if (stringutils.haslength(beanname) && this.targetsourcedbeans.contains(beanname)) {
return bean;
}
if (boolean.false.equals(this.advisedbeans.get(cachekey))) {
return bean;
}
// 如果是 基础设施类(pointcut、advice、advisor 等) 或 需要 skip, 则不需要增强
if (isinfrastructureclass(bean.getclass()) || shouldskip(bean.getclass(), beanname)) {
this.advisedbeans.put(cachekey, boolean.false);
return bean;
}
// create proxy if we have advice.
// 为目标 bean 查找合适的通知器,并封装成一个排好顺序的list<advisor>集合
// 底层是基于拓扑排序
object[] specificinterceptors = getadvicesandadvisorsforbean(bean.getclass(), beanname, null);
if (specificinterceptors != do_not_proxy) {
this.advisedbeans.put(cachekey, boolean.true);
// 创建代理
object proxy = createproxy(
bean.getclass(), beanname, specificinterceptors, new singletontargetsource(bean));
this.proxytypes.put(cachekey, proxy.getclass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedbeans.put(cachekey, boolean.false);
return bean;
}protected boolean isinfrastructureclass(class<?> beanclass) {
// 下面这些是基础设施类,说白了就是aop的一些配置类,是不需要被增强的
boolean retval = advice.class.isassignablefrom(beanclass) ||
pointcut.class.isassignablefrom(beanclass) ||
advisor.class.isassignablefrom(beanclass) ||
aopinfrastructurebean.class.isassignablefrom(beanclass);
if (retval && logger.istraceenabled()) {
logger.trace("did not attempt to auto-proxy infrastructure class [" + beanclass.getname() + "]");
}
return retval;
}创建动态代理底层逻辑createproxy()
protected object createproxy(class<?> beanclass, @nullable string beanname,
@nullable object[] specificinterceptors, targetsource targetsource) {
if (this.beanfactory instanceof configurablelistablebeanfactory) {
autoproxyutils.exposetargetclass((configurablelistablebeanfactory) this.beanfactory, beanname, beanclass);
}
// 通过代理工厂创建代理
proxyfactory proxyfactory = new proxyfactory();
proxyfactory.copyfrom(this);
// 设置代理模式
// 在enableaspectjautoproxy注解中,有一个属性proxytargetclass
// boolean proxytargetclass() default false;
// 表示默认使用的是jdk动态代理,如果设置为true则会使用cglib动态代理
if (proxyfactory.isproxytargetclass()) {
// explicit handling of jdk proxy targets and lambdas (for introduction advice scenarios)
if (proxy.isproxyclass(beanclass) || classutils.islambdaclass(beanclass)) {
// must allow for introductions; can't just set interfaces to the proxy's interfaces only.
for (class<?> ifc : beanclass.getinterfaces()) {
proxyfactory.addinterface(ifc);
}
}
}
else {
// no proxytargetclass flag enforced, let's apply our default checks...
// 如果没有接口,则会赋值为true,强制使用cglib动态代理
if (shouldproxytargetclass(beanclass, beanname)) {
proxyfactory.setproxytargetclass(true);
}
else {
evaluateproxyinterfaces(beanclass, proxyfactory);
}
}
advisor[] advisors = buildadvisors(beanname, specificinterceptors);
proxyfactory.addadvisors(advisors);
proxyfactory.settargetsource(targetsource);
customizeproxyfactory(proxyfactory);
proxyfactory.setfrozen(this.freezeproxy);
if (advisorsprefiltered()) {
proxyfactory.setprefiltered(true);
}
// use original classloader if bean class not locally loaded in overriding class loader
classloader classloader = getproxyclassloader();
if (classloader instanceof smartclassloader && classloader != beanclass.getclassloader()) {
classloader = ((smartclassloader) classloader).getoriginalclassloader();
}
// 使用工厂模式真正创建动态代理
return proxyfactory.getproxy(classloader);
}proxyfactory.getproxy(classloader);底层逻辑
public object getproxy(@nullable classloader classloader) {
// 创建 aopproxy 对象
// 调用 aopproxy.getproxy 创建代理对象
return createaopproxy().getproxy(classloader);
}@override
public aopproxy createaopproxy(advisedsupport config) throws aopconfigexception {
if (!nativedetector.innativeimage() &&
(config.isoptimize() || config.isproxytargetclass() || hasnousersuppliedproxyinterfaces(config))) {
class<?> targetclass = config.gettargetclass();
if (targetclass == null) {
throw new aopconfigexception("targetsource cannot determine target class: " +
"either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
if (targetclass.isinterface() || proxy.isproxyclass(targetclass) || classutils.islambdaclass(targetclass)) {
return new jdkdynamicaopproxy(config);// 使用jdk创建动态代理
}
return new objenesiscglibaopproxy(config); // 使用cglib创建动态代理
}
else {
return new jdkdynamicaopproxy(config);// 使用jdk创建动态代理
}
}
使用jdk的方式创建动态代理
org.springframework.aop.framework.jdkdynamicaopproxy#getproxy(java.lang.classloader)
@override
public object getproxy(@nullable classloader classloader) {
if (logger.istraceenabled()) {
logger.trace("creating jdk dynamic proxy: " + this.advised.gettargetsource());
}
return proxy.newproxyinstance(classloader, this.proxiedinterfaces, this);
}因为jdk动态代理的最重要的方法是java.lang.reflect.invocationhandler#invoke
重点看该类中的invoke方法
@override
@nullable
public object invoke(object proxy, method method, object[] args) throws throwable {
object oldproxy = null;
boolean setproxycontext = false;
targetsource targetsource = this.advised.targetsource;
object target = null;
try {
if (!this.equalsdefined && aoputils.isequalsmethod(method)) {
// the target does not implement the equals(object) method itself.
return equals(args[0]);
}
else if (!this.hashcodedefined && aoputils.ishashcodemethod(method)) {
// the target does not implement the hashcode() method itself.
return hashcode();
}
else if (method.getdeclaringclass() == decoratingproxy.class) {
// there is only getdecoratedclass() declared -> dispatch to proxy config.
return aopproxyutils.ultimatetargetclass(this.advised);
}
else if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getdeclaringclass().isinterface() &&
method.getdeclaringclass().isassignablefrom(advised.class)) {
// service invocations on proxyconfig with the proxy config...
return aoputils.invokejoinpointusingreflection(this.advised, method, args);
}
object retval;
if (this.advised.exposeproxy) {
// make invocation available if necessary.
oldproxy = aopcontext.setcurrentproxy(proxy);
setproxycontext = true;
}
// get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target,
// in case it comes from a pool.
target = targetsource.gettarget();
class<?> targetclass = (target != null ? target.getclass() : null);
// get the interception chain for this method.
// 获取到所有的通知拦截器
// 0 = {exposeinvocationinterceptor}
// 1 = {aspectjaroundadvice}
// 2 = {methodbeforeadviceinterceptor}
// 3 = {aspectjafteradvice}
// 4 = {afterreturningadviceinterceptor}
// 5 = {aspectjafterthrowingadvice}
list<object> chain = this.advised.getinterceptorsanddynamicinterceptionadvice(method, targetclass);
// check whether we have any advice. if we don't, we can fallback on direct
// reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a methodinvocation.
if (chain.isempty()) {
// we can skip creating a methodinvocation: just invoke the target directly
// note that the final invoker must be an invokerinterceptor so we know it does
// nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying.
// 如果没有拦截器,则直接调用目标方法
object[] argstouse = aopproxyutils.adaptargumentsifnecessary(method, args);
retval = aoputils.invokejoinpointusingreflection(target, method, argstouse);
}
else {
// we need to create a method invocation...
// 创建一个方法调用器,将拦截器链传入
methodinvocation invocation =
new reflectivemethodinvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetclass, chain);
// proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.
// 通过拦截器链进入连接点。
retval = invocation.proceed();
}
// massage return value if necessary.
class<?> returntype = method.getreturntype();
if (retval != null && retval == target &&
returntype != object.class && returntype.isinstance(proxy) &&
!rawtargetaccess.class.isassignablefrom(method.getdeclaringclass())) {
// special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method
// is type-compatible. note that we can't help if the target sets
// a reference to itself in another returned object.
retval = proxy;
}
else if (retval == null && returntype != void.type && returntype.isprimitive()) {
throw new aopinvocationexception(
"null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method);
}
return retval;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetsource.isstatic()) {
// must have come from targetsource.
targetsource.releasetarget(target);
}
if (setproxycontext) {
// restore old proxy.
aopcontext.setcurrentproxy(oldproxy);
}
}
}org.springframework.aop.framework.reflectivemethodinvocation#proceed
/**
* index from 0 of the current interceptor we're invoking.
* -1 until we invoke: then the current interceptor.
*/
// 我们正在调用的拦截器的索引
private int currentinterceptorindex = -1;
@override
@nullable
public object proceed() throws throwable {
// we start with an index of -1 and increment early.
// 也就是说当所有拦截器都执行完成后,执行目标方法
if (this.currentinterceptorindex == this.interceptorsanddynamicmethodmatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokejoinpoint(); // 目标方法的执行
}
// interceptorsanddynamicmethodmatchers表示我们通过构造方法传过来的拦截器
// interceptororinterceptionadvice:渠道的拦截器(或者叫做切面逻辑)
object interceptororinterceptionadvice =
this.interceptorsanddynamicmethodmatchers.get(++this.currentinterceptorindex);
if (interceptororinterceptionadvice instanceof interceptoranddynamicmethodmatcher) {
// evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
interceptoranddynamicmethodmatcher dm =
(interceptoranddynamicmethodmatcher) interceptororinterceptionadvice;
class<?> targetclass = (this.targetclass != null ? this.targetclass : this.method.getdeclaringclass());
if (dm.methodmatcher.matches(this.method, targetclass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// dynamic matching failed.
// skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// it's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: the pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
// 通过不同的拦截器完成切面逻辑
// 也就是说执行该拦截器的切面逻辑
return ((methodinterceptor) interceptororinterceptionadvice).invoke(this);
}
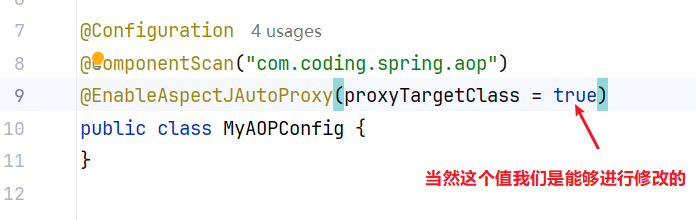
}解下来看看这6个切面的执行逻辑:
// 0 = {exposeinvocationinterceptor}
// 1 = {aspectjaroundadvice}
// 2 = {methodbeforeadviceinterceptor}
// 3 = {aspectjafteradvice}
// 4 = {afterreturningadviceinterceptor}
// 5 = {aspectjafterthrowingadvice}
org.springframework.aop.interceptor.exposeinvocationinterceptor#invoke
@override
@nullable
public object invoke(methodinvocation mi) throws throwable {
methodinvocation oldinvocation = invocation.get();
invocation.set(mi);
try {
return mi.proceed(); // 没有任何执行逻辑,直接调用目标方法
}
finally {
invocation.set(oldinvocation);
}
}org.springframework.aop.aspectj.aspectjaroundadvice#invoke
@override
@nullable
public object invoke(methodinvocation mi) throws throwable {
if (!(mi instanceof proxymethodinvocation)) {
throw new illegalstateexception("methodinvocation is not a spring proxymethodinvocation: " + mi);
}
proxymethodinvocation pmi = (proxymethodinvocation) mi;
proceedingjoinpoint pjp = lazygetproceedingjoinpoint(pmi);
joinpointmatch jpm = getjoinpointmatch(pmi);
return invokeadvicemethod(pjp, jpm, null, null); // 直接调用自定义的逻辑
}org.springframework.aop.framework.adapter.methodbeforeadviceinterceptor#invoke
@override
@nullable
public object invoke(methodinvocation mi) throws throwable {
// 先调用自定的before方法
this.advice.before(mi.getmethod(), mi.getarguments(), mi.getthis());
// 在调用目标方法
return mi.proceed();
}org.springframework.aop.aspectj.aspectjafteradvice#invoke
@override
@nullable
public object invoke(methodinvocation mi) throws throwable {
try {
return mi.proceed(); // 先调用目标方法
}
finally {
// 再调用自定义的after方法
// 这个方法放在了finally块中,不然会执行
invokeadvicemethod(getjoinpointmatch(), null, null);
}
}org.springframework.aop.framework.adapter.afterreturningadviceinterceptor#invoke
@override
@nullable
public object invoke(methodinvocation mi) throws throwable {
// 先执行目标方法
object retval = mi.proceed();
// 没有异常的情况下,再执行自定义的afterreturning逻辑,
this.advice.afterreturning(retval, mi.getmethod(), mi.getarguments(), mi.getthis());
return retval;
}org.springframework.aop.aspectj.aspectjafterthrowingadvice#invoke
@override
@nullable
public object invoke(methodinvocation mi) throws throwable {
try {
// 先执行目标方法
return mi.proceed();
}
catch (throwable ex) {
if (shouldinvokeonthrowing(ex)) {
// 如果出现异常的时候,执行自定义的afterthrowing方法
invokeadvicemethod(getjoinpointmatch(), null, ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}自己最好debug看看这样理解的更加深刻
使用cglib的方式创建动态代理
cglib动态代理主要是enhancer,是创建目标类的子类来完成的动态代理。
重点关注:intercept方法
org.springframework.aop.framework.cglibaopproxy#getproxy(java.lang.classloader)
@override
public object getproxy(@nullable classloader classloader) {
if (logger.istraceenabled()) {
logger.trace("creating cglib proxy: " + this.advised.gettargetsource());
}
try {
class<?> rootclass = this.advised.gettargetclass();
assert.state(rootclass != null, "target class must be available for creating a cglib proxy");
class<?> proxysuperclass = rootclass;
if (rootclass.getname().contains(classutils.cglib_class_separator)) {
proxysuperclass = rootclass.getsuperclass();
class<?>[] additionalinterfaces = rootclass.getinterfaces();
for (class<?> additionalinterface : additionalinterfaces) {
this.advised.addinterface(additionalinterface);
}
}
// validate the class, writing log messages as necessary.
validateclassifnecessary(proxysuperclass, classloader);
// 配置 cglib 增强器...
// configure cglib enhancer...
enhancer enhancer = createenhancer();
if (classloader != null) {
enhancer.setclassloader(classloader);
if (classloader instanceof smartclassloader &&
((smartclassloader) classloader).isclassreloadable(proxysuperclass)) {
enhancer.setusecache(false);
}
}
// 目标代理类 class com.coding.spring.aop.bean.myaopbean
enhancer.setsuperclass(proxysuperclass);
enhancer.setinterfaces(aopproxyutils.completeproxiedinterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setnamingpolicy(springnamingpolicy.instance);
enhancer.setstrategy(new classloaderawaregeneratorstrategy(classloader));
// 0 = dynamicadvisedinterceptor
// 1 = staticunadvisedinterceptor
// 2 = serializablenoop
// 3 = staticdispatcher
// 4 = adviseddispatcher
// 5 = equalsinterceptor
// 6 = hashcodeinterceptor
callback[] callbacks = getcallbacks(rootclass);
class<?>[] types = new class<?>[callbacks.length];
for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getclass();
}
// fixedinterceptormap only populated at this point, after getcallbacks call above
enhancer.setcallbackfilter(new proxycallbackfilter(
this.advised.getconfigurationonlycopy(), this.fixedinterceptormap, this.fixedinterceptoroffset));
enhancer.setcallbacktypes(types);
// 生成代理类并创建代理实例。
// generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.
return createproxyclassandinstance(enhancer, callbacks);
}
catch (codegenerationexception | illegalargumentexception ex) {
throw new aopconfigexception("could not generate cglib subclass of " + this.advised.gettargetclass() +
": common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",
ex);
}
catch (throwable ex) {
// targetsource.gettarget() failed
throw new aopconfigexception("unexpected aop exception", ex);
}
}private callback[] getcallbacks(class<?> rootclass) throws exception {
// parameters used for optimization choices...
boolean exposeproxy = this.advised.isexposeproxy();
boolean isfrozen = this.advised.isfrozen();
boolean isstatic = this.advised.gettargetsource().isstatic();
// choose an "aop" interceptor (used for aop calls).
// aop 回调接口 dynamicadvisedinterceptor
// private static class dynamicadvisedinterceptor implements methodinterceptor, serializable {
callback aopinterceptor = new dynamicadvisedinterceptor(this.advised);
// choose a "straight to target" interceptor. (used for calls that are
// unadvised but can return this). may be required to expose the proxy.
callback targetinterceptor;
if (exposeproxy) {
targetinterceptor = (isstatic ?
new staticunadvisedexposedinterceptor(this.advised.gettargetsource().gettarget()) :
new dynamicunadvisedexposedinterceptor(this.advised.gettargetsource()));
}
else {
targetinterceptor = (isstatic ?
new staticunadvisedinterceptor(this.advised.gettargetsource().gettarget()) :
new dynamicunadvisedinterceptor(this.advised.gettargetsource()));
}
// choose a "direct to target" dispatcher (used for
// unadvised calls to static targets that cannot return this).
callback targetdispatcher = (isstatic ?
new staticdispatcher(this.advised.gettargetsource().gettarget()) : new serializablenoop());
callback[] maincallbacks = new callback[] {
aopinterceptor, // for normal advice
targetinterceptor, // invoke target without considering advice, if optimized
new serializablenoop(), // no override for methods mapped to this
targetdispatcher, this.adviseddispatcher,
new equalsinterceptor(this.advised),
new hashcodeinterceptor(this.advised)
};
callback[] callbacks;
// if the target is a static one and the advice chain is frozen,
// then we can make some optimizations by sending the aop calls
// direct to the target using the fixed chain for that method.
if (isstatic && isfrozen) {
method[] methods = rootclass.getmethods();
callback[] fixedcallbacks = new callback[methods.length];
this.fixedinterceptormap = collectionutils.newhashmap(methods.length);
// todo: small memory optimization here (can skip creation for methods with no advice)
for (int x = 0; x < methods.length; x++) {
method method = methods[x];
list<object> chain = this.advised.getinterceptorsanddynamicinterceptionadvice(method, rootclass);
fixedcallbacks[x] = new fixedchainstatictargetinterceptor(
chain, this.advised.gettargetsource().gettarget(), this.advised.gettargetclass());
this.fixedinterceptormap.put(method, x);
}
// now copy both the callbacks from maincallbacks
// and fixedcallbacks into the callbacks array.
callbacks = new callback[maincallbacks.length + fixedcallbacks.length];
system.arraycopy(maincallbacks, 0, callbacks, 0, maincallbacks.length);
system.arraycopy(fixedcallbacks, 0, callbacks, maincallbacks.length, fixedcallbacks.length);
this.fixedinterceptoroffset = maincallbacks.length;
}
else {
callbacks = maincallbacks;
}
return callbacks;
}// 可以看到methodinterceptor实现了callback接口
public interface methodinterceptor extends callback {
object intercept(object var1, method var2, object[] var3, methodproxy var4) throws throwable;
}/**
* general purpose aop callback. used when the target is dynamic or when the
* proxy is not frozen.
*/
private static class dynamicadvisedinterceptor implements methodinterceptor, serializable {
private final advisedsupport advised;
public dynamicadvisedinterceptor(advisedsupport advised) {
this.advised = advised;
}
// cglibaopproxy.dynamicadvisedinterceptor.intercept
// 最终创建动态代理之后,会调用到这个intercept方法
@override
@nullable
public object intercept(object proxy, method method, object[] args, methodproxy methodproxy) throws throwable {
object oldproxy = null;
boolean setproxycontext = false;
object target = null;
targetsource targetsource = this.advised.gettargetsource();
try {
if (this.advised.exposeproxy) {
// make invocation available if necessary.
oldproxy = aopcontext.setcurrentproxy(proxy);
setproxycontext = true;
}
// get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool...
target = targetsource.gettarget();
class<?> targetclass = (target != null ? target.getclass() : null);
// 0 = {exposeinvocationinterceptor}
// 1 = {aspectjaroundadvice}
// 2 = {methodbeforeadviceinterceptor}
// 3 = {aspectjafteradvice}
// 4 = {afterreturningadviceinterceptor}
// 5 = {aspectjafterthrowingadvice}
// 获取拦截器链
list<object> chain = this.advised.getinterceptorsanddynamicinterceptionadvice(method, targetclass);
object retval;
// check whether we only have one invokerinterceptor: that is,
// no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target.
if (chain.isempty() && cglibmethodinvocation.ismethodproxycompatible(method)) {
// we can skip creating a methodinvocation: just invoke the target directly.
// note that the final invoker must be an invokerinterceptor, so we know
// it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot
// swapping or fancy proxying.
object[] argstouse = aopproxyutils.adaptargumentsifnecessary(method, args);
retval = invokemethod(target, method, argstouse, methodproxy);
}
else {
// we need to create a method invocation...
// 创建 cglibmethodinvocation 进行proceed()方法调用
retval = new cglibmethodinvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetclass, chain, methodproxy).proceed();
}
retval = processreturntype(proxy, target, method, retval);
return retval;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetsource.isstatic()) {
targetsource.releasetarget(target);
}
if (setproxycontext) {
// restore old proxy.
aopcontext.setcurrentproxy(oldproxy);
}
}
}
@override
public boolean equals(@nullable object other) {
return (this == other ||
(other instanceof dynamicadvisedinterceptor &&
this.advised.equals(((dynamicadvisedinterceptor) other).advised)));
}
/**
* cglib uses this to drive proxy creation.
*/
@override
public int hashcode() {
return this.advised.hashcode();
}
}org.springframework.aop.framework.cglibaopproxy.cglibmethodinvocation#proceed
@override
@nullable
public object proceed() throws throwable {
try {
// 调用 reflectivemethodinvocation.proceed
return super.proceed();
}
catch (runtimeexception ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (exception ex) {
if (reflectionutils.declaresexception(getmethod(), ex.getclass()) ||
kotlindetector.iskotlintype(getmethod().getdeclaringclass())) {
// propagate original exception if declared on the target method
// (with callers expecting it). always propagate it for kotlin code
// since checked exceptions do not have to be explicitly declared there.
throw ex;
}
else {
// checked exception thrown in the interceptor but not declared on the
// target method signature -> apply an undeclaredthrowableexception,
// aligned with standard jdk dynamic proxy behavior.
throw new undeclaredthrowableexception(ex);
}
}
}org.springframework.aop.framework.objenesiscglibaopproxy#createproxyclassandinstance
@override
protected object createproxyclassandinstance(enhancer enhancer, callback[] callbacks) {
class<?> proxyclass = enhancer.createclass();
object proxyinstance = null;
if (objenesis.isworthtrying()) {
try {
// 创建代理类实例
proxyinstance = objenesis.newinstance(proxyclass, enhancer.getusecache());
}
catch (throwable ex) {
logger.debug("unable to instantiate proxy using objenesis, " +
"falling back to regular proxy construction", ex);
}
}
if (proxyinstance == null) {
// regular instantiation via default constructor...
try {
constructor<?> ctor = (this.constructorargs != null ?
proxyclass.getdeclaredconstructor(this.constructorargtypes) :
proxyclass.getdeclaredconstructor());
reflectionutils.makeaccessible(ctor);
proxyinstance = (this.constructorargs != null ?
ctor.newinstance(this.constructorargs) : ctor.newinstance());
}
catch (throwable ex) {
throw new aopconfigexception("unable to instantiate proxy using objenesis, " +
"and regular proxy instantiation via default constructor fails as well", ex);
}
}
// 设置 callback 回调接口
((factory) proxyinstance).setcallbacks(callbacks);
return proxyinstance;
}org.springframework.aop.framework.reflectivemethodinvocation#proceed
@override
@nullable
public object proceed() throws throwable {
// we start with an index of -1 and increment early.
// 所有拦截器都执行完成后,执行目标方法
if (this.currentinterceptorindex == this.interceptorsanddynamicmethodmatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokejoinpoint();
}
object interceptororinterceptionadvice =
this.interceptorsanddynamicmethodmatchers.get(++this.currentinterceptorindex);
if (interceptororinterceptionadvice instanceof interceptoranddynamicmethodmatcher) {
// evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
interceptoranddynamicmethodmatcher dm =
(interceptoranddynamicmethodmatcher) interceptororinterceptionadvice;
class<?> targetclass = (this.targetclass != null ? this.targetclass : this.method.getdeclaringclass());
if (dm.methodmatcher.matches(this.method, targetclass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// dynamic matching failed.
// skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// it's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: the pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
// 通过不同的拦截器完成切面逻辑
// 看到这里就和jdk动态代理的逻辑是一样的了
return ((methodinterceptor) interceptororinterceptionadvice).invoke(this);
}
}后面的执行逻辑就和上面jdk动态代理的执行逻辑一样了。
到此这篇关于spring aop底层源码执行逻辑剖析的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关spring aop底层源码内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论