目录
一.顺序表经典面试题
1.移除元素
oj链接力扣
题目描述:

代码:
int removeelement(int* nums, int numssize, int val){
int arr[101];
int i=0;//循环变量,以遍历数组
int dst=0;//当前原数组被覆盖的值的数量
for(i=0;i<numssize;i++)
{
if(nums[i]!=val)//判断是否数值等于val
{
nums[dst]=nums[i];//将不相等的元素赋值给原数组
dst++;
}
}
return dst;
}
2.删除有序数组中的重复项
oj链接力扣
题目描述: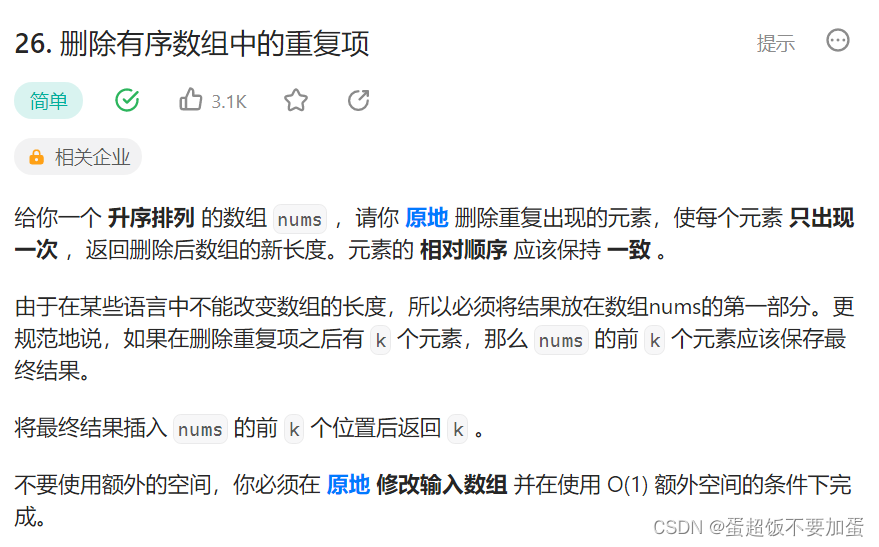
代码;
int seach(int* nums, int numssize,int x)//查找函数
{
int i=0;
for(i=0;i<numssize;i++)
{
if(nums[i]==x)
return i;//出现过则返回该元素在数组中下标
}
return -1;//没有出现过则返回-1
}
int removeduplicates(int* nums, int numssize){
int i=0;
int dst=1;
for(i=1;i<numssize;i++)
{
int ret=seach(nums,i,nums[i]);//调用查找函数判断是否是重复元素
if(ret==-1)//返回-1说明不是重复元素
{
nums[dst]=nums[i];赋值给原数组
dst++;
}
}
return dst;
}
3.合并两个有序数组
oj链接力扣
题目描述:
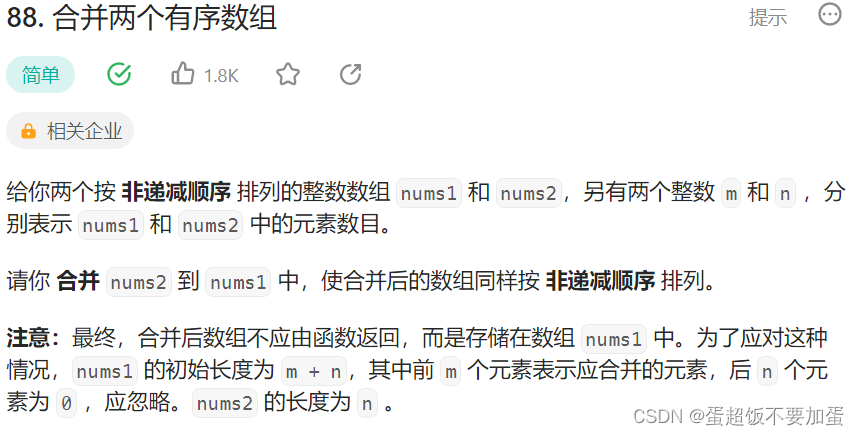
代码:
void merge(int* nums1, int nums1size, int m, int* nums2, int nums2size, int n){
int ret1=m-1;//数组1的下标,从末尾开始遍历
int ret2=n-1;//数组2的下标,从末尾开始遍历
int j=m+n-1;//总空间的下标,从末尾开始
while(ret1>=0&&ret2>=0)//一个数组遍历完则结束
{
if(nums1[ret1]>nums2[ret2])//比较大的元素从总空间最后面依次赋值
{
nums1[j]=nums1[ret1];
ret1--;
j--;
}
else if(nums1[ret1]==nums2[ret2])
{
nums1[j]=nums2[ret2];
ret2--;
j--;
}
else
{
nums1[j]=nums2[ret2];
ret2--;
j--;
}
}
while(ret2>=0)//数组2没有遍历完,将剩余的元素赋值给总空间
{
nums1[j]=nums2[ret2];
ret2--;
j--;
}
}
二.链表经典面试题
1.移除链表元素
oj链接力扣
题目描述:
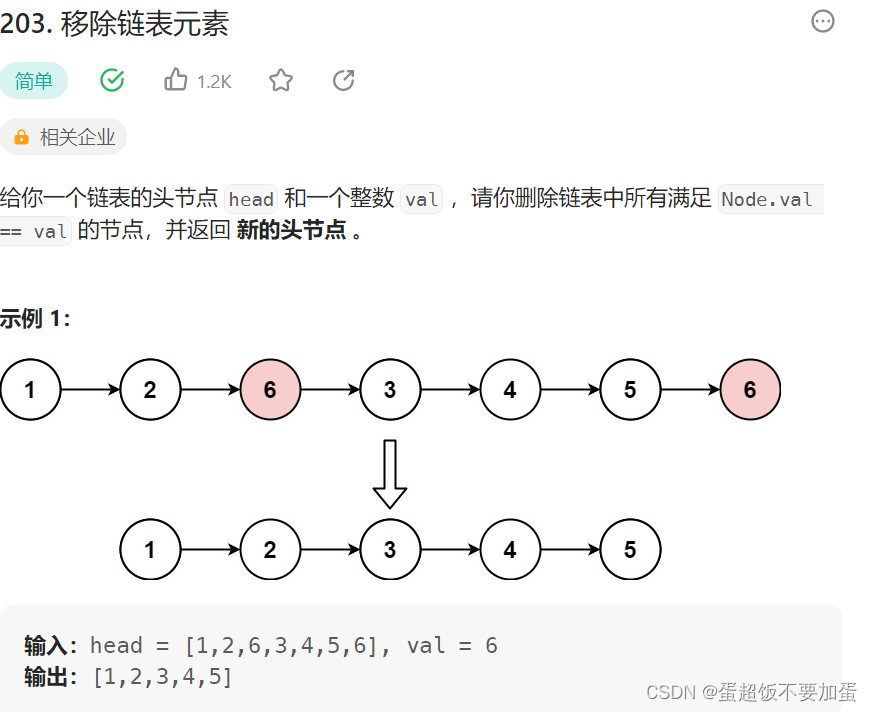
代码:
/**
* definition for singly-linked list.
* struct listnode {
* int val;
* struct listnode *next;
* };
*/
struct listnode* removeelements(struct listnode* head, int val)
{
struct listnode* cur=head;//定义遍历指针
struct listnode* guard,*tail;//定义带头节点的新链表
guard=tail=(struct listnode*)malloc(sizeof(struct listnode));//开辟头结点
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val!=val)//如果不是要删除的值,则尾插到新链表
{
tail->next=cur;
tail=tail->next;
cur=cur->next;
}
else//是则删除
{
struct listnode *next=cur->next;
free(cur);
cur=next;
}
}
tail->next=null;//将尾及诶点的next置空
struct listnode *newnode=guard->next;//将头指针指向第一个节点
free(guard);//删除头结点
return newnode;
}
2.反转一个单链表
oj链接力扣
题目描述:
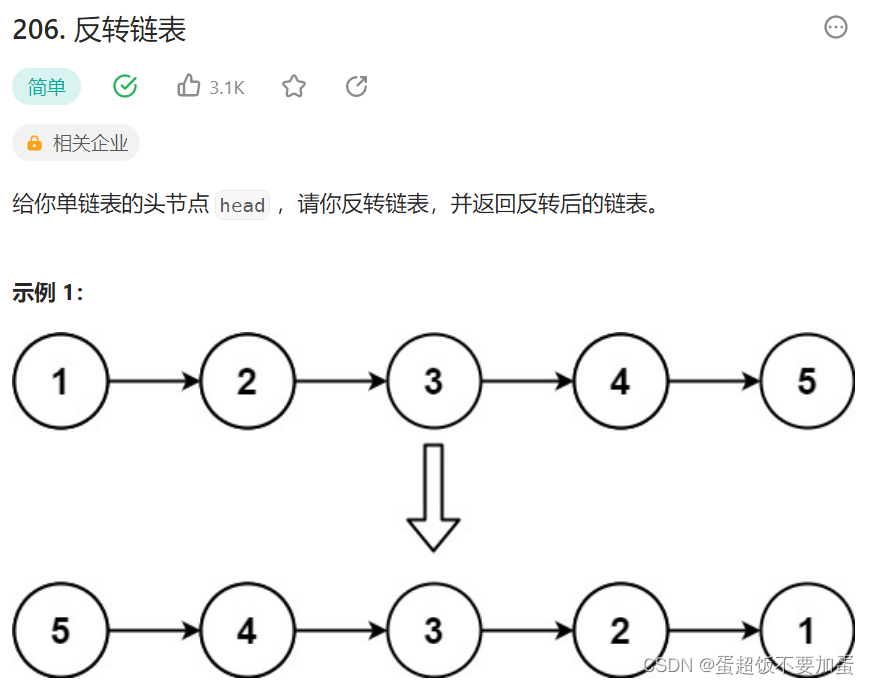
代码:
/**
* definition for singly-linked list.
* struct listnode {
* int val;
* struct listnode *next;
* };
*/
struct listnode* reverselist(struct listnode* head){
struct listnode* newnode=null;//新建一个空链表
struct listnode* cur=head;//新建两个遍历指针
struct listnode* next=head;
if(cur==null)//原链表为空则返回空
return head;
else
{
while(cur)//遍历原链表的节点,将每个节点头插到新链表
{
next=next->next;
cur->next=newnode;
newnode=cur;
cur=next;
}
}
return newnode;
}
3.链表的中间节点
oj链接力扣
题目描述:

代码:
思路1:
struct listnode* middlenode(struct listnode* head){
struct listnode* cur=head;//定义一个遍历指针
int num=0;//用来统计链表节点的数量
while(cur)//遍历统计数量
{
num++;
cur=cur->next;
}
cur=head;
int i=0;
for(i=0;i<num/2;i++)//让指针走到中间节点
{
cur=cur->next;
}
return cur;
}
思路2:
struct listnode* middlenode(struct listnode* head){
struct listnode*low=head;//定义快慢指针
struct listnode*fast=head;
if(head==null)//原链表为空则返回空
return null;
while(fast&&fast->next)//节点数量为奇数和偶数的两种结束条件
{
low=low->next;//慢指针一次走一步
fast=fast->next->next;//快指针一次走两步
}
return low;
}
4.链表中倒数第k个节点
题目描述:
代码:
思路1:
struct listnode* findkthtotail(struct listnode* plisthead, int k ) {
int i=0;
struct listnode*cur=plisthead;//遍历指针统计节点数量
int n=0;
while(cur)
{
n++;
cur=cur->next;
}
cur=plisthead;
if(k>0&&k<=n)//判断k的合法性,合法则让遍历指针走n-k步
{
for(i=0;i<n-k;i++)//让遍历指针走n-k步
{
cur=cur->next;
}
return cur;
}
else//不合法返回空
{
return null;
}
}
思路2:
struct listnode* findkthtotail(struct listnode* plisthead, int k ) {
if(plisthead==null)//判断链表是否为空,为空则返回为空
return null;
struct listnode*cur=plisthead;//定义三个遍历指针
struct listnode*p1=plisthead;
struct listnode*p2=plisthead;
int num=0;//记录节点数量
while(cur)//遍历统计节点数量
{
num++;
cur=cur->next;
}
if(k<=0||k>num)//判断k的合法性
return null;
k=k-1;
while(k--)//让p1先走k-1步
{
p1=p1->next;
}
while(p1->next)//之后两个指针一起走
{
p1=p1->next;
p2=p2->next;
}
return p2;
}
5.合并两个有序链表
oj链接力扣
题目描述:
代码:
struct listnode* mergetwolists(struct listnode* list1, struct listnode* list2){
struct listnode *cur1=list1;//两个指针分别指向两个链表
struct listnode *cur2=list2;
struct listnode *guard,*tail;//新建一个带头结点的单链表
guard=tail=(struct listnode*)malloc(sizeof(struct listnode));//开辟头结点
while(cur1&&cur2)//遍历两个链表,当有一个链表遍历完则结束
{
if(cur1->val<cur2->val)//节点的值比较,较小的值尾插到新链表
{
tail->next=cur1;
tail=tail->next;
cur1=cur1->next;
}
else
{
tail->next=cur2;
tail=tail->next;
cur2=cur2->next;
}
}
//检查哪个链表没有遍历完,没有遍历完的链表的节点则尾插到新链表中
if(cur1==null)
{
while(cur2)
{
tail->next=cur2;
tail=tail->next;
cur2=cur2->next;
}
tail->next=null;
}
else if(cur2==null)
{
while(cur1)
{
tail->next=cur1;
tail=tail->next;
cur1=cur1->next;
}
tail->next=null;
}
else{
return null;
}
struct listnode*newnode=guard->next;//头指针指向第一个节点
free(guard);//删除头结点
return newnode;
}6.链表分割
oj链接链表分割_牛客题霸_牛客网
题目描述:
代码:
listnode* partition(listnode* phead, int x) {
// write code here
if(phead==null)//判断原链表是否为空
return null;
listnode* cur=phead;//定义遍历指针
listnode* guard1,*tail1,*guard2,*tail2;//定义两个新链表
//开辟头结点
guard1=tail1=(listnode*)malloc(sizeof(listnode));
guard1->next=null;
guard2=tail2=(listnode*)malloc(sizeof(listnode));
guard2->next=null;
//遍历原链表,值小于x的节点尾插到一个新链表中,大于x的节点尾插到另一个新链表中
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val<x)
{
tail1->next=cur;
tail1=tail1->next;
cur=cur->next;
}
else
{
tail2->next=cur;
tail2=tail2->next;
cur=cur->next;
}
}
tail1->next=guard2->next;//两个新链表链接在一起
tail2->next=null;//链表的最后一个节点next置空
listnode* newnode1=guard1->next;//头指针指向第一个节点
listnode* newnode2=guard2->next;
//删除头结点
free(guard1);
free(guard2);
return newnode1;
}
}
7.链表的回文结构
oj链接链表的回文结构_牛客题霸_牛客网
题目描述:
代码:
//返回中间节点
struct listnode* middlenode(struct listnode* head){
struct listnode* cur=head;
int num=0;
while(cur)
{
num++;
cur=cur->next;
}
cur=head;
int i=0;
for(i=0;i<num/2;i++)
{
cur=cur->next;
}
return cur;
}
//反转链表
struct listnode* reverselist(struct listnode* head){
struct listnode* newnode=null;
struct listnode* cur=head;
struct listnode* next=head;
if(cur==null)
return head;
else
{
while(cur)
{
next=next->next;
cur->next=newnode;
newnode=cur;
cur=next;
}
}
return newnode;
}
bool chkpalindrome(listnode* a) {
// write code here
listnode *mid=middlenode(a);//返回原链表的中间节点
listnode *rhead=reverselist(mid);//翻转原链表的后半部分
while(a&&rhead)//遍历两个链表,比较节点的值
{
if(a->val!=rhead->val)
return false;
a=a->next;
rhead=rhead->next;
}
return true;
}
}
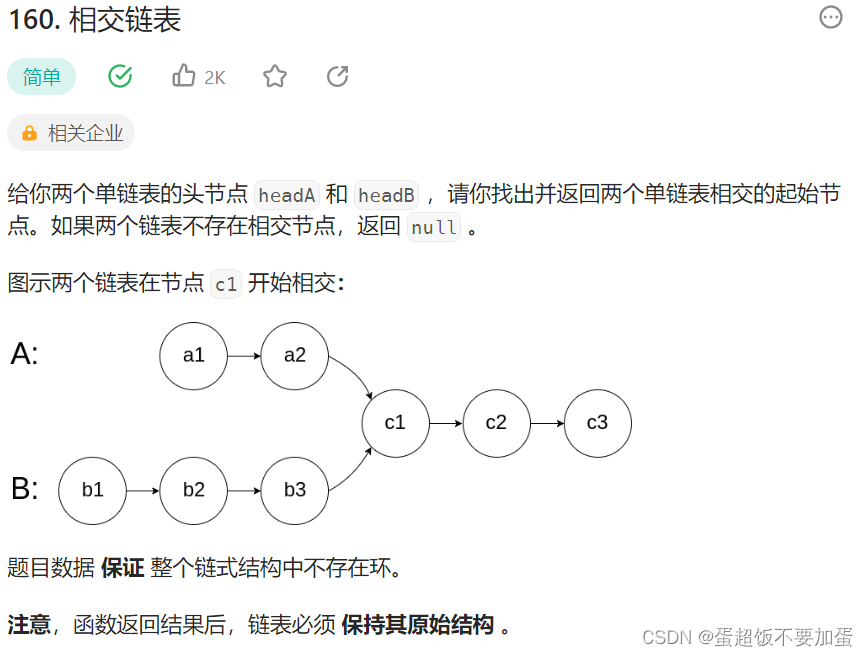
8.相交链表
oj链接力扣
题目描述:
代码:
struct listnode *getintersectionnode(struct listnode *heada, struct listnode *headb) {
//定义两个遍历指针
struct listnode *cur1=heada;
struct listnode *cur2=headb;
//分别统计两个链表节点数量
int num1=0;
int num2=0;
//遍历统计两个链表节点数量
while(cur1)
{
num1++;
cur1=cur1->next;
}
while(cur2)
{
num2++;
cur2=cur2->next;
}
cur1=heada;
cur2=headb;
//让节点数量多的链表遍历指针先走差值的步数
if(num1>num2)
{
int k=num1-num2;
while(k--)
cur1=cur1->next;
}
else if(num1<num2)
{
int k=num2-num1;
while(k--)
cur2=cur2->next;
}
//两个链表一起遍历
while(cur1)
{
//两个链表的节点相比较,相同则返回
if(cur1==cur2)
return cur1;
if(cur1->next==cur2->next)
return cur1->next;
//不同则继续遍历
else
{
cur1=cur1->next;
cur2=cur2->next;
}
}
return null;
}
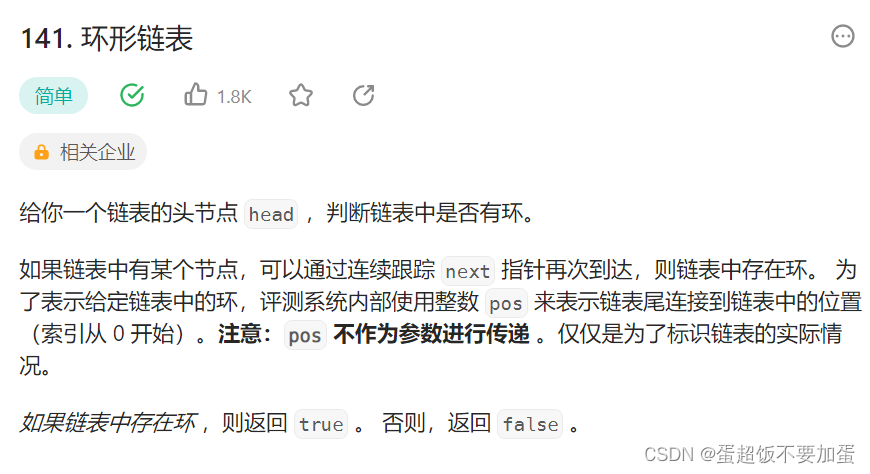
9.环形链表
oj链接力扣
题目描述:
代码:
bool hascycle(struct listnode *head)
{
if(head==null)//判断原链表是否为空,为空则返回空
return false;
//定义两个快慢指针
struct listnode* low=head;
struct listnode* fast=head;
low=low->next;//慢指针每次走一步
fast=fast->next->next;//快指针每次走两步
while(low!=fast&&fast!=null)//两个指针一直走,直到相遇或者为空结束
{
low=low->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
}
if(low==fast)//相遇则返回真
return true;
if(fast==null)//为空则返回假
return false;
}
10.环形链表||
oj链接力扣
题目描述:
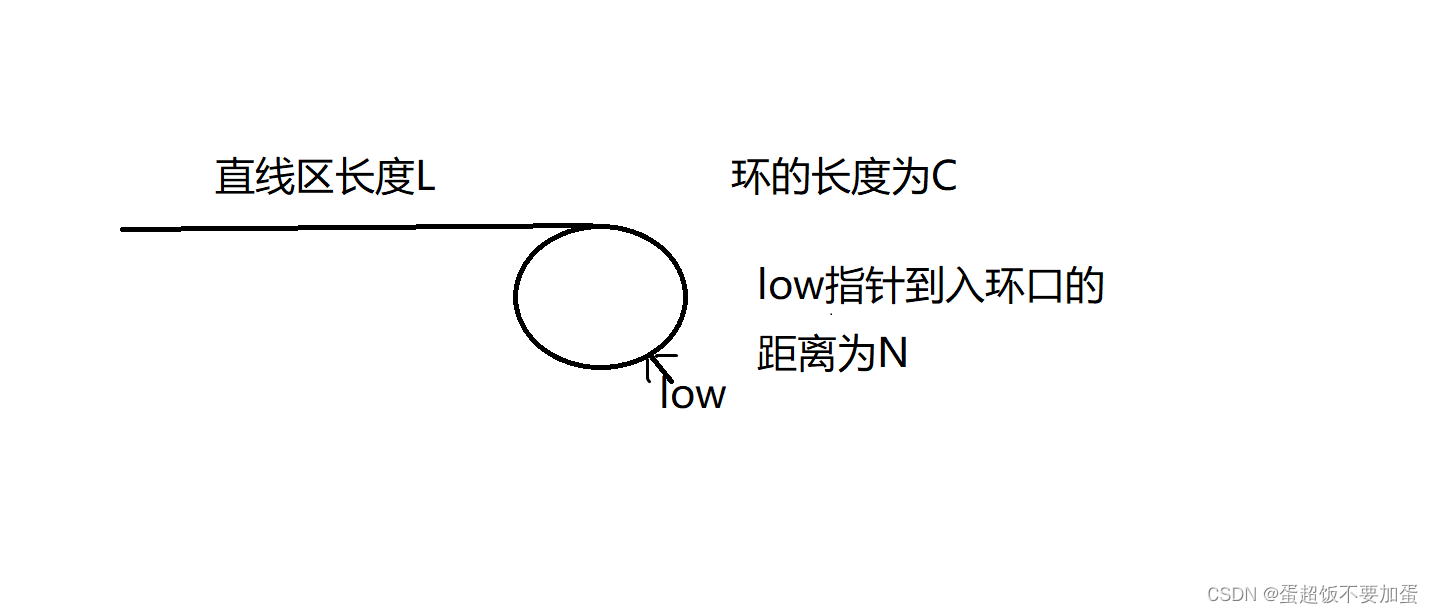
证明:假设直线区长度为l,环的长度为c,快慢指针相遇点至入环口的距离为n,第9题的快指针走的路程是慢指针的两倍
慢指针走的路程:l+n
快指针走的路程:假设快指针已经在环走了k圈,则路程为l+kc+n
则由(l+n)*2=l+kc+n,化解得l=kc-n=(k-1)c+c-n,(k-1)c可以认为指针走了k圈又回到原点,故得证l=c-n
代码:
struct listnode *detectcycle(struct listnode *head) {
if(head==null||head->next==null)//判断链表是否为空或者只有一个节点
return null;
//定义两个快慢指针
struct listnode *low=head;
struct listnode *fast=head;
while(fast&&fast->next)//快慢指针遍历
{
low=low->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
//如果快慢指针相遇则让一个指针从头开始走,另一个指针从相遇点开始走
if(low==fast)
{
struct listnode *meet=low;
while(head!=meet)
{
head=head->next;
meet=meet->next;
}
return meet;
}
}
//上面的循环结束到这里说明链表没有环,返回空
return null;
}好啦,顺序表和链表经典面试题就先学习到这里,如果文章对您有帮助,欢迎一键三连~
最后附上寄语:种一棵树最好的时间是十年前,其次是现在





发表评论