文章目录
- 1. [链表的回文结构](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d281619e4b3e4a60a2cc66ea32855bfa?tpid=49&&tqid=29370&rp=1&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/2016test/question-ranking)
- 2. [相交链表](https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/description/)
- 3. 链表中倒数第k个结点
- 4. [环形链表](https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/description/)
- 5. [环形链表 ii](https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/)
- 6. [随机链表的复制](https://leetcode.cn/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/description/)
1. 链表的回文结构

因为单链表不能从后往前找节点,所以我们先找到中间节点,然后逆置,最后进行比较。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef struct listnode
{
int val;
struct listnode* next;
}listnode;
struct listnode* middlenode(struct listnode* head)
{
listnode* slow, * fast;
slow = fast = head;
while (fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
struct listnode* reverselist(struct listnode* head)
{
if (null == head)
{
return head;
}
listnode* n1, * n2, * n3;
n1 = null, n2 = head, n3 = head->next;
while (n2)
{
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if (n3)
{
n3 = n3->next;
}
}
return n1;
}
bool chkpalindrome(listnode* a)
{
listnode* mid = middlenode(a);
listnode* rmid = reverselist(mid);
while (a && rmid)
{
if (a->val != rmid->val)
{
return false;
}
a = a->next;
rmid = rmid->next;
}
return true;
}
2. 相交链表

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct listnode
{
int val;
struct listnode* next;
};
struct listnode* getintersectionnode(struct listnode* heada, struct listnode* headb)
{
struct listnode* cura = heada;
struct listnode* curb = headb;
int lena = 0;
while (cura->next)
{
++lena;
cura = cura->next;
}
int lenb = 0;
while (curb->next)
{
++lenb;
curb = curb->next;
}
//不相交
if (cura != curb)
{
return null;
}
int gap = abs(lena - lenb);
//因为我们不知道a长还是b长,所以我们要用假设法,先假设a长,如果不对,再调换一下就行
struct listnode* longlist = heada;
struct listnode* shortlist = headb;
if (lenb > lena)
{
longlist = headb;
shortlist = heada;
}
//让长的先走gap步
while (gap--)
{
longlist = longlist->next;
}
//再同时走,找交点
while (longlist != shortlist)
{
longlist = longlist->next;
shortlist = shortlist->next;
}
return longlist;
}
3. 链表中倒数第k个结点
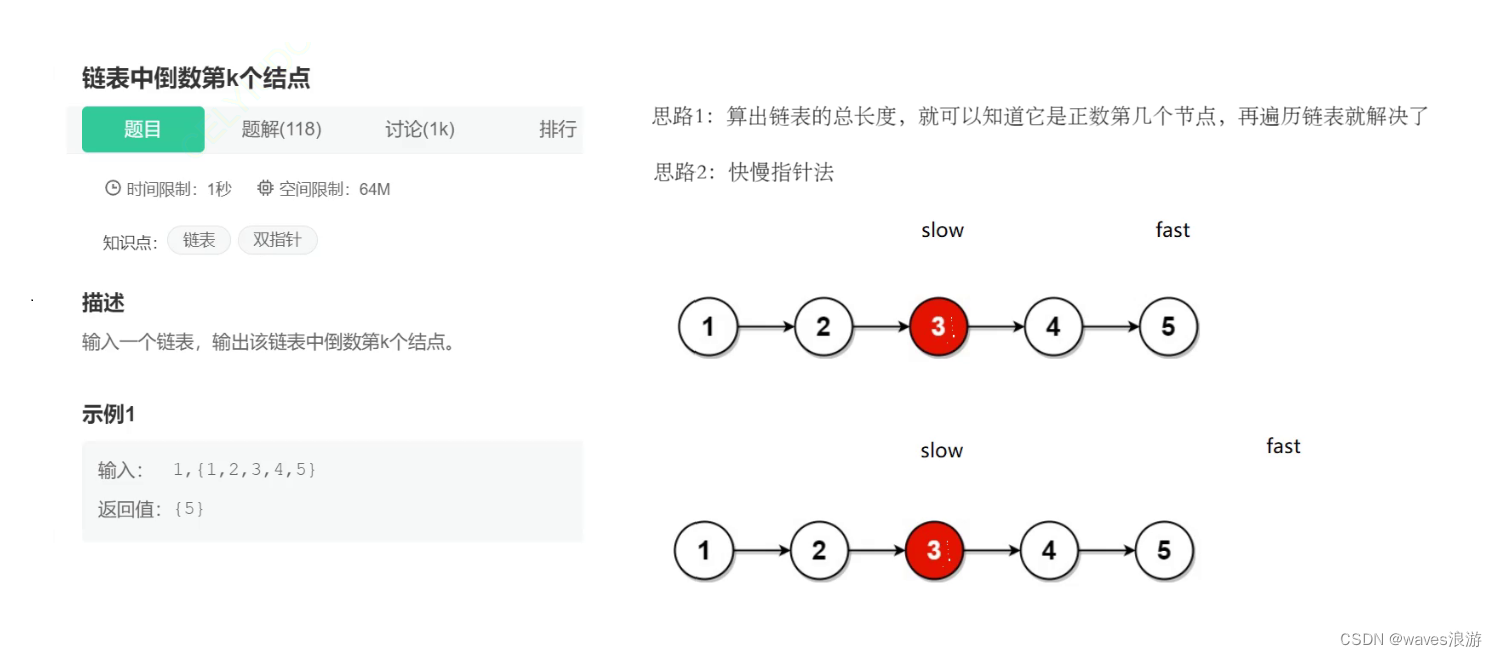
思路2:
#include <stdio.h>
struct listnode
{
int val;
struct listnoe* next;
};
struct listnode* findkthtotail(struct listnode* plisthead, int k)
{
struct listnode* slow = plisthead, * fast = plisthead;
//fast先走k步
while (k--)
{
//k还没有减到0,链表已经空了,说明k大于链表的长度
if (null == fast)
{
return null;
}
fast = fast->next;
}
//slow和fast同时走,fast走到空,slow就是倒数第k个
while (fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
4. 环形链表
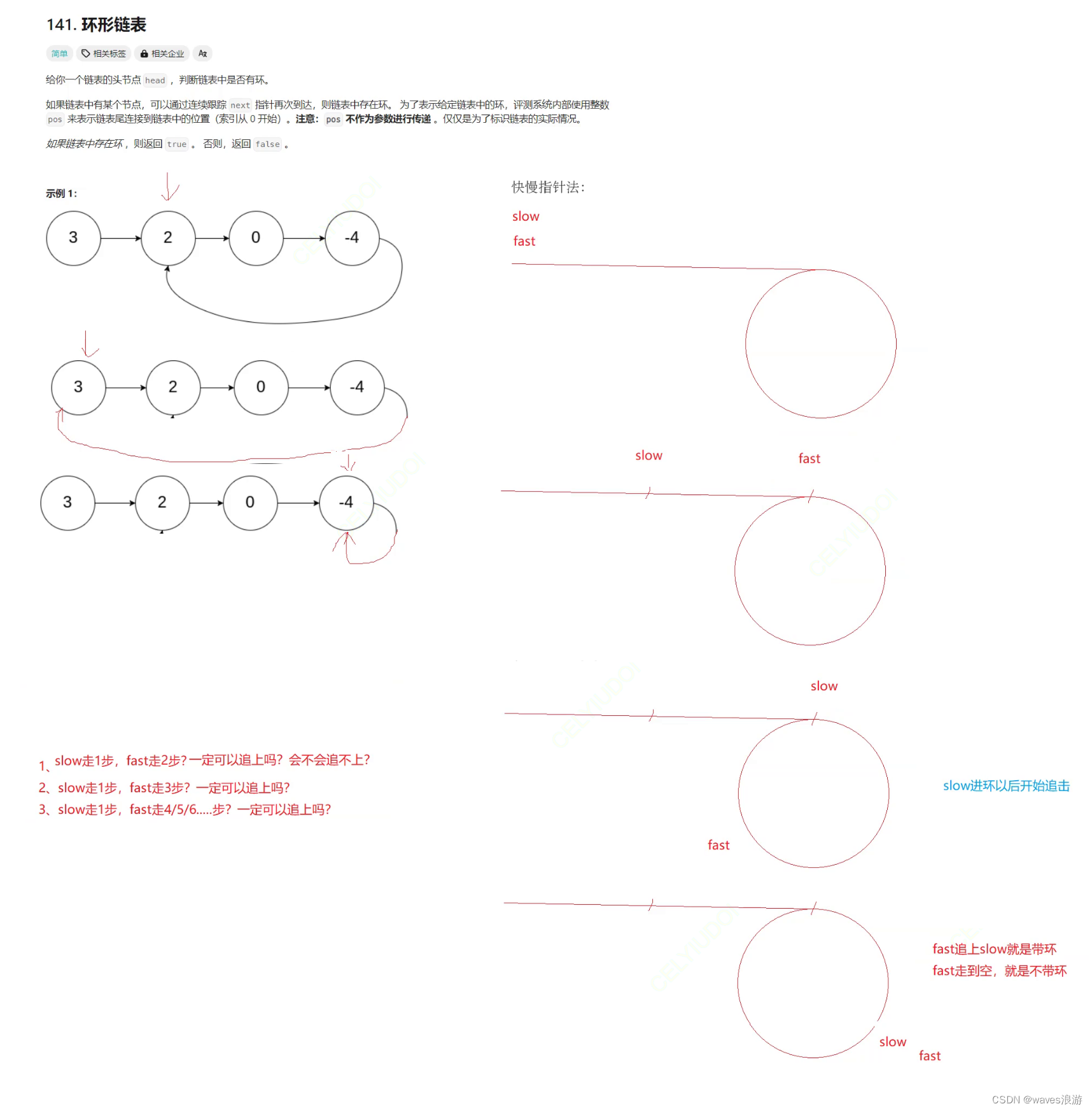

#include <stdbool.h>
struct listnode
{
int val;
struct listnode* next;
};
bool hascycle(struct listnode* head)
{
struct listnode* slow = head, * fast = head;
while (fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
5. 环形链表 ii
找入环点:
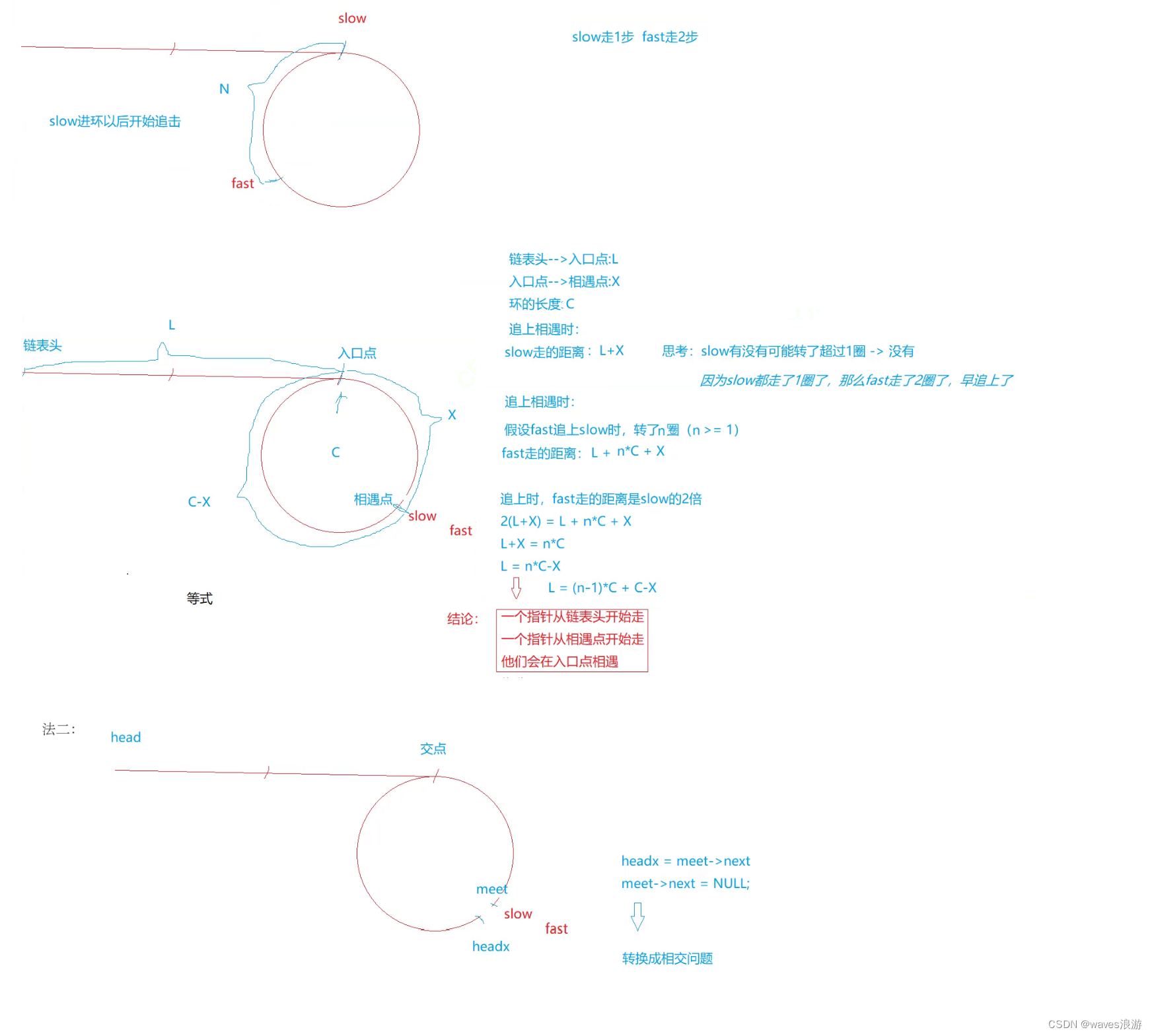
法一:
#include <stdio.h>
struct listnode
{
int val;
struct listnode* next;
};
struct listnode* detectcycle(struct listnode* head)
{
struct listnode* slow = head, * fast = head;
while (fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast)
{
struct listnode* meet = slow;
while (meet != head)
{
meet = meet->next;
head = head->next;
}
return meet;
}
}
return null;
}
法二:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct listnode
{
int val;
struct listnode* next;
};
struct listnode* getintersectionnode(struct listnode* heada, struct listnode* headb)
{
struct listnode* cura = heada;
struct listnode* curb = headb;
int lena = 0;
while (cura->next)
{
++lena;
cura = cura->next;
}
int lenb = 0;
while (curb->next)
{
++lenb;
curb = curb->next;
}
//不相交
if (cura != curb)
{
return null;
}
int gap = abs(lena - lenb);
struct listnode* longlist = heada;
struct listnode* shortlist = headb;
if (lenb > lena)
{
longlist = headb;
shortlist = heada;
}
//让长的先走gap步
while (gap--)
{
longlist = longlist->next;
}
//再同时走,找交点
while (longlist != shortlist)
{
longlist = longlist->next;
shortlist = shortlist->next;
}
return longlist;
}
struct listnode* detectcycle(struct listnode* head)
{
struct listnode* slow = head, * fast = head;
while (fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast)
{
struct listnode* meet = slow;
struct listnode* headx = meet->next;
meet->next = null;
return getintersectionnode(head, headx);
}
}
return null;
}
6. 随机链表的复制
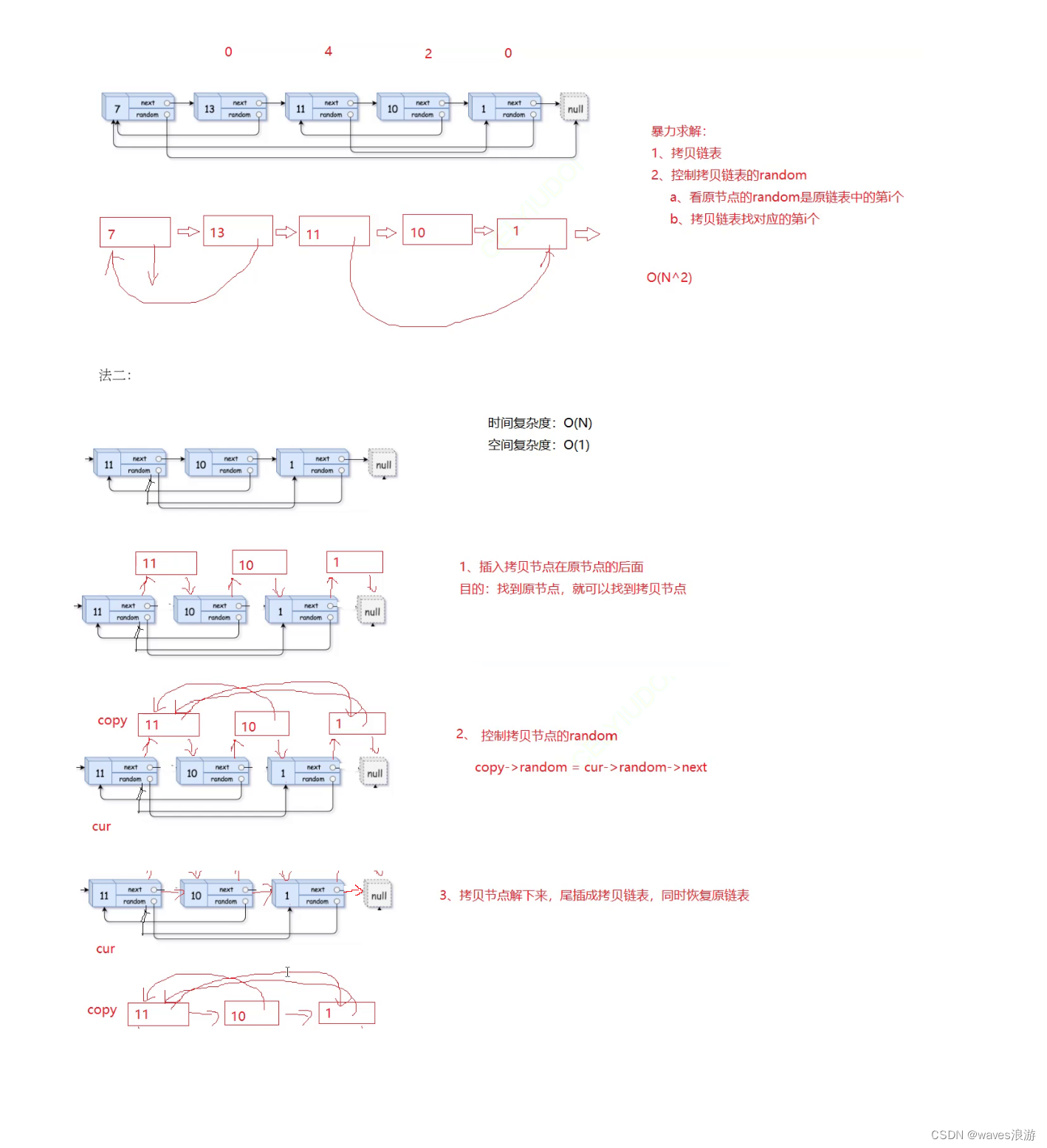
写代码的时候建议一边画细图,一边写:

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node
{
int val;
struct node *next;
struct node *random;
};
struct node* copyrandomlist(struct node* head)
{
struct node* cur = head;
//拷贝节点插入原节点的后面
while (cur)
{
struct node* copy = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
copy->val = cur->val;
//插入
copy->next = cur->next;
cur->next = copy;
//迭代
cur = cur->next->next;
}
//控制拷贝节点的random
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
struct node* copy = cur->next;
if (null == cur->random)
{
copy->random = null;
}
else
{
copy->random = cur->random->next;
}
//迭代
cur = cur->next->next;
}
//把copy节点解下来,链接成新链表
struct node* copyhead = null, * tail = null;
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
struct node* copy = cur->next;
struct node* next = copy->next;
//尾插
if (null == tail)
{
copyhead = tail = copy;
}
else
{
tail->next = copy;
tail = tail->next;
}
cur->next = next;
cur = next;
}
return copyhead;
}




发表评论