一、简介
前面我详细介绍了关于机器学习的归一化和反归一化以及表格数据在机器学习中的输入格式问题:
【python机器学习系列】一文彻底搞懂机器学习中表格数据的输入形式(理论+源码)
本文将介绍机器系学习中的k折交叉验证的使用方法。
交叉验证(cross-validation)是一种在机器学习中常用的模型评估技术,用于估计模型在未知数据上的性能。它通过将数据集划分为训练集和验证集,并多次重复这个过程来评估模型的性能。
k折交叉验证是将数据分为k份,选取其中的k-1份为训练数据,剩余的一份为测试数据。k份数据循环做测试集进行测试。此原理适用于数据量小的数据。
使用交叉验证,可以实现:
-
寻找单个模型最好的效果时候的数据集划分以及参数
-
比较多个模型,选择最佳模型
二、实现
准备数据
import pandas as pd
# 准备数据
data = pd.read_csv(r'g:\数据杂坛\\uci heart disease dataset.csv')
df = pd.dataframe(data)
# 目标变量和特征变量
target = 'target'
features = df.columns.drop(target)
x = df[features].values
y = df[target].values方法1
from sklearn.tree import decisiontreeclassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import kfold
kf = kfold(n_splits = 5, shuffle=true, random_state=0)
score=0
for train_index, test_index in kf.split(y):
x_train, x_test = x[train_index], x[test_index]
y_train, y_test = y[train_index], y[test_index]
clt = decisiontreeclassifier(max_depth=5, random_state=0).fit(x_train, y_train)
curr_score = clt.score(x_test, y_test)
print("准确率为:", curr_score)
score = score + curr_score
avg_score = score / 5
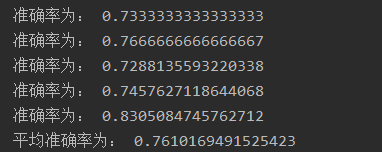
print("平均准确率为:", avg_score)n_splits = 5,表示进行5折交叉验证,分别计算每一次的准确率,最后求得平均准确率。使用kfold.split()实现,效果如下:
方法2
from sklearn.tree import decisiontreeclassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import kfold
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
kf = kfold(n_splits=5, shuffle=true, random_state=0)
model1 = decisiontreeclassifier(max_depth=5, random_state=0)
scores_model1 = cross_val_score(model1, x, y, cv=kf)
print("准确率为:", scores_model1)
print("平均准确率为:", scores_model1.mean())直接使用sklearn中的cross_val_score()函数实现,效果和第一种方法一样,结果如下:

三、应用场景
方法1 选择模型效果最好的数据集划分
from sklearn.tree import decisiontreeclassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import kfold
kf = kfold(n_splits = 5, shuffle=true, random_state=0)
score=0
best_score = -float('inf') # 初始化为正无穷大
best_train_index = none
best_test_index = none
for train_index, test_index in kf.split(y):
x_train, x_test = x[train_index], x[test_index]
y_train, y_test = y[train_index], y[test_index]
clt = decisiontreeclassifier(max_depth=5, random_state=0).fit(x_train, y_train)
curr_score = clt.score(x_test, y_test)
print("准确率为:", curr_score)
score = score + curr_score
# 如果当前数据集划分的性能更好,则更新最佳数据集划分
if curr_score > best_score:
best_score = curr_score
best_train_index = train_index
best_test_index = test_index
avg_score = score / 5
print("平均准确率为:", avg_score)
print("best train indices:", best_train_index)
print("best test indices:", best_test_index)
x_train, x_test = x[best_train_index], x[best_test_index]
y_train, y_test = y[best_train_index], y[best_test_index]kfold的split方法会生成交叉验证的训练集和测试集索引,然后你可以使用这些索引将数据集划分为相应的训练集和测试集。通过在每个数据集划分上训练模型并评估性能,你可以选择具有最佳性能的数据集划分。最后,你可以打印最佳数据集划分的索引,以便进一步分析和使用。
方法2 用于比较不同模型的评分,选择最优模型
from sklearn.linear_model import logisticregression
kf = kfold(n_splits=5, shuffle=true, random_state=0)
model1 = decisiontreeclassifier(max_depth=5, random_state=0)
model2 = logisticregression()
scores_model1 = cross_val_score(model1, x, y, cv=kf)
scores_model2 = cross_val_score(model2, x, y, cv=kf)
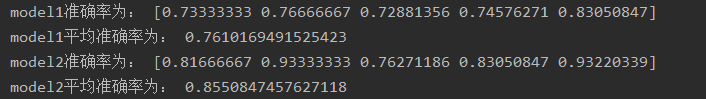
print("model1准确率为:", scores_model1)
print("model1平均准确率为:", scores_model1.mean())
print("model2准确率为:", scores_model2)
print("model2平均准确率为:", scores_model2.mean())通过比较不同模型的评分,你可以选择最佳模型,评分较高的模型通常具有更好的性能。
好了,本篇内容就到这里,需要数据集和源码的小伙伴可以关注我领取!


发表评论