1、having关键字概览
1.1、作用
- 对查询的数据进行筛选
1.2、having关键字产生的原因
- 使用where对查询的数据进行筛选时,where子句中无法使用聚合函数,所以引出having关键字
1.3、having使用语法
- having单独使用(不与group by一起使用,在oracle中会报错),单独使用时,大部分场合与where相同
- having与group by一起使用,这是having关键字产生的初衷,对分组之后的数据再进行筛选
1.4、having与where的区别
- 一般情况下,where用于过滤数据行,而having用于过滤分组(能用where的地方,不要使用having)
- where中不能出现聚合函数,而having可以使用聚合函数作为条件
- where在数据分组前进行过滤,而having在数据分组后进行过滤(因此where效率一般比having高);where是数据从磁盘读入内存时筛选,而having是在内存中筛选
- where是对数据库文件过滤(过滤条件是表中的字段),而having是对select中查询的字段进行过滤
- where子句中不能使用字段别名,而having子句中可以使用字段别名
- 多表关联查询时,where先筛选再联接,having先联接再筛选
2、having案例
初始化表(以student表为例):
create table if not exists student ( id int null, name varchar(50) null, age int null, sex varchar(2) null, score double null ) comment '学生表'; insert into student (id, name, age, sex, score) values (1, '张三', 18, '男', 70); insert into student (id, name, age, sex, score) values (2, '李四', 17, '男', 60); insert into student (id, name, age, sex, score) values (3, '王五', 19, '男', 80); insert into student (id, name, age, sex, score) values (4, '赵六', 16, '男', 90); insert into student (id, name, age, sex, score) values (5, '七七', 16, '女', 95); insert into student (id, name, age, sex, score) values (6, '九九', 17, '女', 85); insert into student (id, name, age, sex, score) values (7, '十一', 18, '女', 80); insert into student (id, name, age, sex, score) values (8, '小明', 19, '男', 90); insert into student (id, name, age, sex, score) values (9, '小军', 17, '男', 55); insert into student (id, name, age, sex, score) values (10, '小雷', 19, '女', 60);
2.1、having单独使用
案例1:查询学生表中,成绩在80分以上的数据
select * from student having score >= 80
等同于:
select * from student where score >= 80
having使用的错误:
select
id
,name
,age
from student
having score >= 80 -- 报错,score筛选条件没有出现在select中
where使用的错误:
select
id
,name
,age
,score as fenshu
from student
where fenshu >= 80 -- 报错,where子句中不能使用字段别名2.2、having与group by一起使用
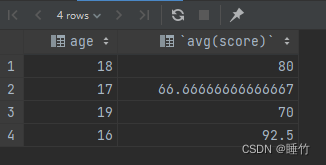
案例2:求各个年龄段的平均分和年龄
select age,avg(score) from student group by age
如下:
案例3:求学生平均分大于80分的年龄段及平均分
- 这里只能使用having,对平均分进行筛选,使用where会报错
select
age
,avg(score)
from student
group by age
having avg(score) > 80
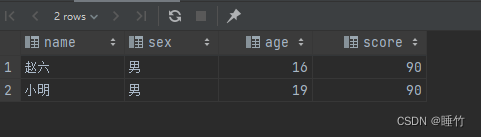
-- 结果为16岁案例4:查询学生年龄平均分大于80分中,男生的信息(姓名,男生的分数)
select
name
,sex
,age
,score
from student
where sex = '男'
group by name,sex,age,score
having avg(score) > 80
结果:
总结
到此这篇关于mysql中having关键字详解以及与where区别的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关mysql having关键字与where区别内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!




发表评论