项目场景
解析电子病历cda文档,由于cda文档是xml 格式的,有些节点的属性值需要修改。
问题描述
在使用python 解析xml时,百度了很多方面的资料,其实都不尽人意,要么示例不够详细,要么示例本身就是坑,总结一下,主要遇到的是这几个方面的问题
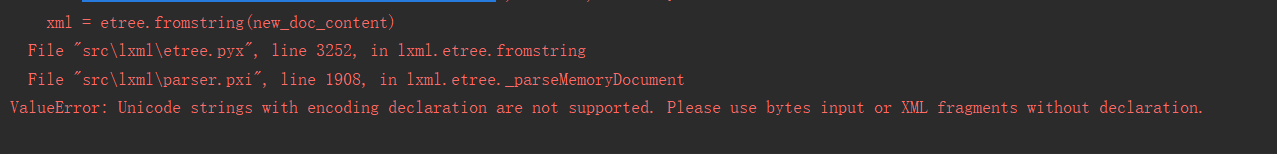
1.使用etree.fromstring(new_doc_content)报错
valueerror: unicode strings with encoding declaration are not supported. please use bytes input or xml fragments without declaration.
2.xpath无法获取值、返回值为[]或者{}的问题
原因分析
1.由于数据是从数据库查询出来得到的,所以etree.fromstring(new_doc_content)需要传 byte string
2.由于cda文档含有字符声明,以及命名空间的,在使用常规的xpath语法取不到数据,或者有些text能取到,其他节点或者属性值取不到。那么在含有命名空间的xml数据里,xpath需要将命名空间也带上才能正常取到,其实问题就出在命名空间这里,从网上百度出来的资料,有些命名空间写成了
ns = {"d" : "http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9"}
url = root.xpath("//d:loc", namespaces=ns)
正是这里把我带入了误区,使用这个方式反复调试,始终是取不到数据,从其他地方查到的资料很多也是类似的这种写法,同时也忽略掉了一些不一样的点。
例如这样的写法:
url = root.xpath("//d:loc", namespaces={'d' : 'http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9'})`咋一看只是namespaces的值事先定义好了而已,没有往其他方向想。
后来通过foo_tree = etree.elementtree(xml) 然后通过遍历foo_tree.getroot()修改属性内容,虽然说能解决,但是还是想通过xpath来查询定位,因为之前爬虫用过xpath,知道它的便利之处,回过头来还是要去解决xpath这个问题。
猛回头,发现namespaces字典定义的区别,单引号 和双引号这里有所不同。那就是试试把,将双引号改成了单引号。
啪,完美,它起作用了,能找到节点了。
解决方案
1.将str转换成byte string
etree.fromstring(new_doc_content.encode('utf-8'))2.将namespaces定义的字典中的双引号换成单引号
url = root.xpath("//d:loc", namespaces={'d' : 'http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9'})`示例xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <clinicaldocument xmlns="urn:hl7-org:v3" xmlns:mif="urn:hl7-org:v3/mif" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/xmlschema-instance" xsi:schemalocation="urn:hl7-org:v3 ..\sdschemas\sda.xsd"> <realmcode code="cn"/> <typeid root="2.16.840.1.113883.1.3" extension="pocd_mt000040"/> <templateid root="2.16.156.10011.2.1.1.33"/> <id root="2.16.156.10011.1.1" extension="545ed988-5235-45f1-bbfd-9326d74faa43"/> <code code="00000" codesystem="545ed988-5235-45f1-bbfd-9326d74faa43" codesystemname="卫生信息共享文档规范编码体系"/> <title>测试</title> <effectivetime value="20220407090145"/> <confidentialitycode code="n" codesystem="2.16.840.1.113883.5.25" codesystemname="confidentiality" displayname="正常访问保密级别"/> <languagecode code="zh-cn"/> <setid/> <versionnumber/> <recordtarget typecode="rct" contextcontrolcode="op"> <patientrole classcode="pat"> <id root="2.16.156.10011.1.11" extension="00000000"/> <id root="2.16.156.10011.1.12" extension="00000000"/> <id root="2.16.156.10011.1.24" extension="-"/> <patient classcode="psn" determinercode="instance"> <name>xxx</name> <administrativegendercode code="1" displayname="男性" codesystem="2.16.156.10011.2.3.3.4" codesystemname="生理性别代码表(gb/t 2261.1)"/> <age value="0" unit="岁"/> </patient> </patientrole> </recordtarget> </clinicaldocument>
示例python
xml = etree.fromstring(new_doc_content.encode('utf-8'))
# 示例的默认命名空间是urn:hl7-org:v3,使用xpath需要将命名空间带上
effective_time = xml.xpath("//x:effectivetime[@*]", namespaces={'x': 'urn:hl7-org:v3'})
extension = xml.xpath('//x:recordtarget//x:patientrole/x:id[@extension]',
namespaces={'x': 'urn:hl7-org:v3'})
print(effective_time)
print(extension)
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持代码网。



发表评论