mysql字段值如何区分大小写
注意:设置的是字段值区分大小写
1. 查询时指定大小写敏感,加关键字‘binary’
(1)删表,建表,新增数据
drop table binary_test;
create table binary_test (
`id` int unsigned primary key not null auto_increment,
`name` varchar(255) not null
) engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
insert into binary_test (name) values ('qwerty');
insert into binary_test (name) values ('qwerty');
(2)测试数据
①查询小写字母
select * from binary_test where name ='qwerty';

②查询大写字母
select * from binary_test where binary name ='qwerty';
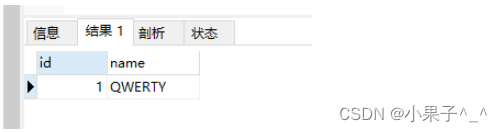
2. 定义表结构时指定字段大小写敏感 关键字“binary”指定guid字段大小写敏感
drop table binary_test;
create table binary_test (
`id` int unsigned primary key not null auto_increment,
`name` varchar(255) binary not null
) engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
insert into binary_test (name) values ('qwerty');
insert into binary_test (name) values ('qwerty');
注意 name字段使用binary修饰了。
select * from binary_test where name ='qwerty';

3. 修改排序规则(collation)
show variables like ‘collation_database';
collation以 “_ci"结尾的不区分大小写(ci——case ignore),以”_bin"或者"_cs"结尾的区分大小写
将collation改为 utf8_bin(大小写敏感的)
可以为库、表、列指定collation。
优先级为 列>表>库
create database sys_usercollate utf8_bin; alter table sys_userdefault character set=utf8 collate=utf8_bin; alter table sys_user modify column username varchar(255) character set utf8 collate utf8_bin not null
alter table sys_user modify column username varchar(255) binary
mysql查询区分大小写
在mysql中,可以利用select查询语句配合binary关键字来区分大小写,select语句用于查询数据,binary关键字用于区分大小写,语法为“select * from 表名 where binary 字段=字段值”。
select count(*) from ct_brand_info where binary brand_abbr = 'na'
在sql语句中,binary关键字用于进行二进制比较。当你使用binary关键字时,数据库会以二进制方式比较所有的字符串,包括大小写。
在你的示例中,select count(*) from ct_brand_info where binary brand_abbr =
'na’的目的是计算在ct_brand_info表中,brand_abbr列中等于’na’的记录数。
使用binary的关键字在这里有两方面的影响
1.大小写敏感性:binary使比较区分大小写。这意味着它不仅会匹配完全等于’na’的字符串,还会匹配等于’na’或’na’等其他大小写组合的字符串。
2.二进制比较:binary将字符串转换为二进制格式进行比较。这使得比较更精确,因为它考虑了每个字符的二进制表示。
总结起来,binary关键字在你的sql查询中的作用是使字符串比较区分大小写并使用二进制格式进行比较。
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持代码网。




发表评论