位图由一系列二进制位组成,每个位可以被设置为1或0,当我们在处理需要高效存储和操作大量二进制位数据的适合,位图是一个非常有用的工具。
位图操作命令有:
- setbit:设置位图中指定位置的位的值。可以将位设置为 0 或 1。
- getbit:获取位图中指定位置的位的值。
- bitcount:计算位图中置为 1 的位的数量。
- bitop:对多个位图执行逻辑运算(and、or、xor、not)。
- bitfield:执行复杂的位字段操作,允许你在位图上进行位级别的读写操作。
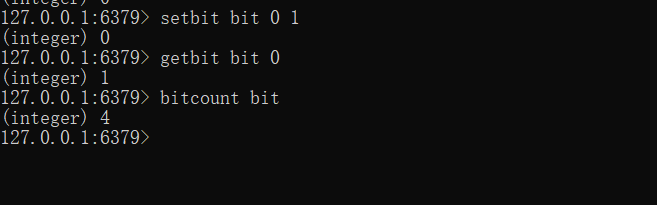
其中,用的最多的是前三个操作,示例如下:
位图的应用十分广泛,包括但不限于以下几方面:
- 统计用户活跃度:可以使用位图追踪用户的登录活动,每个用户对应一个位图,每天的登录状态可以用一个二进制位表示,通过 bitop 命令可以计算多个用户的交集,从而得到活跃用户的统计信息。
- 数据压缩:位图可以高效地存储大量的二进制数据,比如布隆过滤器(bloom filter)就是基于位图实现的一种数据结构,用于快速判断元素是否存在。
- 事件计数:可以使用位图记录每天不同时间段的事件发生情况,比如网站的访问量,每个时间段对应一个位图,每次事件发生时将对应的位设置为 1,通过 bitcount 命令可以计算出每个时间段的事件数量。
- 权限管理:可以使用位图来管理用户的权限,每个用户对应一个位图,每个权限对应一个二进制位,通过 bitop 命令可以进行权限的并集、交集等操作。
redistemplate操作位图
在之前的几篇文章中,我们总结了一个redis工具类,但是那个工具类中,并没有和位图相关的操作,这里添加和位图操作相关的方法:
// value: true为1, false为0
public boolean setbit(string key, int offset, boolean value) {
return redistemplate.opsforvalue().setbit(key, offset, value);
}
public boolean getbit(string key, int offset) {
return redistemplate.opsforvalue().getbit(key, offset);
}
/**
* 统计对应值为1 的数量
* @param key
* @return
*/
public long bitcount(string key) {
if (stringutils.isempty(key)) {
return 0l;
}
return redistemplate.execute((rediscallback<long>) con -> con.bitcount(key.getbytes()));
}
/**
* 统计在字节范围内,对应值为1的数量
* @param key
* @param start
* @param end
* @return
*/
public long bitcount(string key, long start, long end) {
return redistemplate.execute((rediscallback<long>) con -> con.bitcount(key.getbytes(), start, end));
}
添加测试类,用于测试位图操作:
package org.example;
import org.example.util.redisutils;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.springboottest;
@springboottest
public class redisbitmaptest {
@autowired
private redisutils redisutils;
@test
public void testbitmap() {
redisutils.setbit("bit", 0, true);
redisutils.setbit("bit", 1, true);
redisutils.setbit("bit", 3, true);
redisutils.setbit("bit", 7, true);
system.out.println(redisutils.bitcount("bit"));
}
}
执行结果如下:
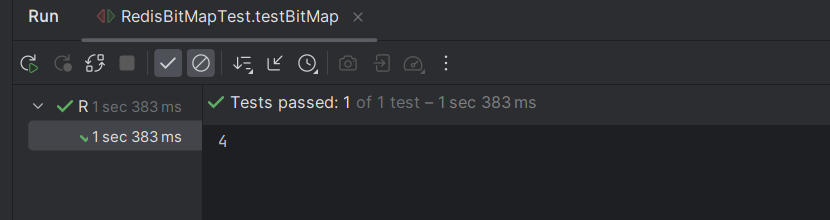
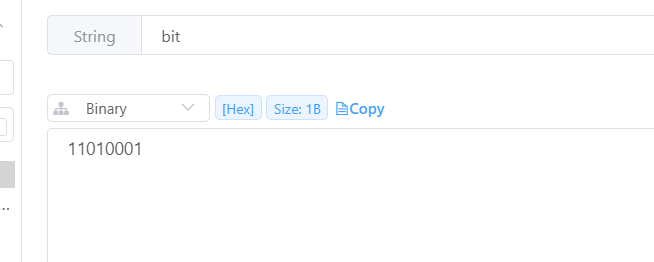
我们通过redis可视化工具,查看bit的值,可以看出其二进制值与我们操作的一致
位图应用之签到
在很多时候,我们遇到用户签到的场景,用户进入应用时,获取用户当天的签到情况,如果没有签到,用户可以签到,一般这种功能,可以通过set数据结构或bitmap来实现,但bitmap和set相比,其占用的空间更小,因此我们选择使用bitmap来实现签到的功能。
signservice:
package org.example.util;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.bitfieldsubcommands;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.redistemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.service;
import java.time.localdate;
import java.util.list;
@service
public class signservice {
@autowired
private redisutils redisutils;
@autowired
private redistemplate<string, object> redistemplate;
/**
* 签到
* @param id
*/
public void sign(integer id) {
localdate now = localdate.now();
string key = buildcachekey(id, now);
int dayofmonth = now.getdayofmonth();
// 签到
redisutils.setbit(key, dayofmonth, true);
}
/**
* 判断是否签到
*/
public boolean issign(integer id) {
localdate now = localdate.now();
string key = buildcachekey(id, now);
int dayofmonth = now.getdayofmonth();
return redisutils.getbit(key, dayofmonth);
}
/**
* 获取当月的签到次数
* @param id
* @return
*/
public long getsigncountofthismonth(integer id) {
localdate now = localdate.now();
string key = buildcachekey(id, now);
int dayofmonth = now.getdayofmonth();
list<long> result = redistemplate.opsforvalue().bitfield(key,
bitfieldsubcommands.create()
.get(bitfieldsubcommands.bitfieldtype.unsigned(dayofmonth)).valueat(1));
if (result == null || result.isempty()) {
return 0l;
}
long num = result.get(0);
if (num == null || num == 0) {
return 0l;
}
string binarystr = long.tostring(num, 2);
long count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < binarystr.length(); i++) {
char ch = binarystr.charat(i);
if (ch == '1') {
count ++;
}
}
return count;
}
/**
* 获取本月连续签到次数
* @param id
* @return
*/
public long getcontinuoussigncountofthismonth(integer id) {
localdate now = localdate.now();
string key = buildcachekey(id, now);
int dayofmonth = now.getdayofmonth();
list<long> result = redistemplate.opsforvalue().bitfield(key,
bitfieldsubcommands.create()
.get(bitfieldsubcommands.bitfieldtype.unsigned(dayofmonth)).valueat(1));
if (result == null || result.isempty()) {
return 0l;
}
long num = result.get(0);
if (num == null || num == 0) {
return 0l;
}
long count = 0;
while (true) {
if ((num & 1) == 0) {
break;
} else {
count ++;
}
num >>>= 1;
}
return count;
}
private string buildcachekey(integer id, localdate localdate) {
int year = localdate.getyear();
int monthvalue = localdate.getmonthvalue();
string key = "sign:" + year + ":" + monthvalue + ":" + id;
return key;
}
}
测试代码如下:
@autowired
private signservice signservice;
@test
public void testsign() {
// 签到
signservice.sign(1);
// 判断是否签到
system.out.println("是否签到:" + signservice.issign(1));
// 获取当月的签到次数
system.out.println("当月的签到次数:" + signservice.getsigncountofthismonth(1));
// 获取当月的连续签到次数
system.out.println("当月连续签到次数:" + signservice.getcontinuoussigncountofthismonth(1));
}
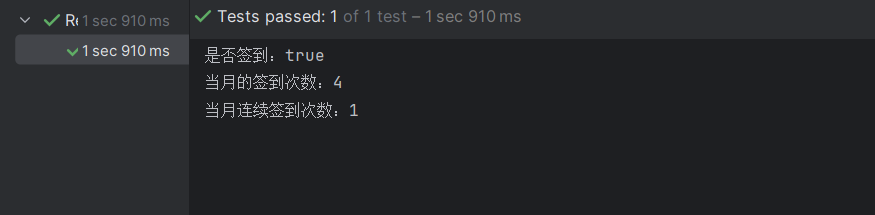
运行结果如下:
到此这篇关于redis应用之签到的使用的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关redis 签到内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论