nosql数据库之中最具代表性的,当属键值对数据库类别下的redis,以及文档型数据库的mongodb,本节我们重点关注这两个产品在springboot下的整合及使用
最近很忙,好不容易才抽出了时间,咱们接
上次我们主要讲了如何通过springboot快速集成mybatis/mybatis-plus,以实现业务交互中的数据持久化,而这一切都是基于关系型数据库(sql)实现的
本节我们来把关注点转向nosql
nosql的概念:
nosql,泛指非关系型的数据库。随着互联网web2.0网站的兴起,传统的关系数据库在处理web2.0网站,特别是超大规模和高并发的sns类型的web2.0纯动态网站已经显得力不从心,出现了很多难以克服的问题,而非关系型的数据库则由于其本身的特点得到了非常迅速的发展。nosql数据库的产生就是为了解决大规模数据集合多重数据种类带来的挑战,特别是大数据应用难题。(——来自百度百科)
得益于其直接基于内存的存储方式,nosql的访问速度可以用“飞快”两个字来形容
在生产环境中,nosql常常配合传统关系型数据库来使用,比如构建一层数据缓存来极大的提升数据的读取速度
nosql在日常业务的驱动之下,逐渐发展出几个主要的类别:键值对数据库、文档型数据库、列存储数据库以及图形化数据库
这4类nosql数据库之中最具代表性的,当属键值对数据库类别下的redis,以及文档型数据库的mongodb,本节我们重点关注这两个产品在springboot下的整合及使用
照惯例先上项目结构:
一、先看redis的使用:
1. 在pom.xml中添加redis相关依赖项
<!-- 引入redis依赖(基于lettuce) -->
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactid>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.apache.commons</groupid>
<artifactid>commons-pool2</artifactid>
</dependency>2. 在application.properties中添加redis的相关配置
# redis相关设置 spring.redis.database=0 spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1 spring.redis.port=6379 spring.redis.password= # redis默认基于lettuce内核 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active=8 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-idle=8 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-wait=-1ms spring.redis.lettuce.pool.min-idle=0
这里关于lettuce内核有必要给大家解释一下:
在springboot2.x版本之前,其集成的默认redis库是jedis,而在2.x版本之后才改为默认基于lettuce
jedis默认和redis直连,为非线程安全模型,并发环境下需要池化使用
而lettuce则是线程安全的,并发环境下可以通过一个实例搞定
当然,你也可以在springboot2.x环境下依然使用jedis,只需要把spring.redis.lettuce 相关配置替换为spring.redis.jedis 即可
更多内容大家感兴趣可以从网上查阅相关资料,这里推荐一篇:https://blog.csdn.net/kenkao/article/details/127085687
3. 新建 service/redisservice 接口及其实现类 service/impl/redisserviceimpl
package com.example.hellospringboot.service;
public interface redisservice {
void set(string key, string val);
string get(string key);
}package com.example.hellospringboot.service.impl;
import com.example.hellospringboot.service.redisservice;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.stringredistemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.valueoperations;
import org.springframework.stereotype.service;
@service
public class redisserviceimpl implements redisservice {
@autowired
stringredistemplate redis;
public void set(string key, string val){
valueoperations<string,string> ops = redis.opsforvalue();
ops.set(key, val);
}
public string get(string key){
valueoperations<string,string> ops = redis.opsforvalue();
return ops.get(key);
}
}我们在service中自动装载一个stringredistemplate实例,而后通过其创建operation对象,进行可以进行各种redis读写操作
4. 新建 controller/rediscontroller
package com.example.hellospringboot.controller;
import com.example.hellospringboot.service.redisservice;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.getmapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.postmapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.requestmapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.restcontroller;
import javax.servlet.http.httpsession;
@restcontroller
@requestmapping("/redis")
public class rediscontroller {
@autowired
redisservice service;
@postmapping("/set")
public void set(string key, string val){
service.set(key, val);
}
@getmapping("/get")
public string get(string key){
return service.get(key);
}
}5. 通过postman进行结果验证
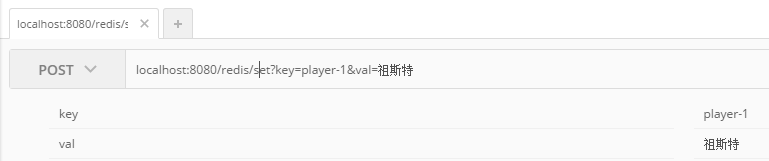
通过rdm查看写入redis的数据:

之后是读操作:
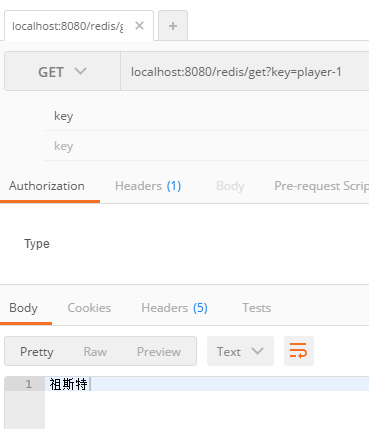
至此我们便完成了springboot中集成redis的操作
二、mongodb的使用
1. 首先还是先添加mongodb相关依赖项
<!-- 引入mongodb依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactid>
</dependency>2. 然后是添加mongodb相关配置
# mongodb相关设置 spring.data.mongodb.authentication-database=admin spring.data.mongodb.database=local spring.data.mongodb.host=127.0.0.1 spring.data.mongodb.port=27017 #spring.data.mongodb.username=admin #spring.data.mongodb.password=admin
各注释项内容依次是:身份验证库、目标数据库、主机地址、端口以及用户名和口令
由于我没有设置用户名和口令,所以直接注释掉这两项
3. 新建 repository/personrepository
package com.example.hellospringboot.repository;
import com.example.hellospringboot.model.person;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.mongorepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.repository;
@repository
public interface personrepository extends mongorepository<person, integer> {
person findbynameis(string name);
person findbyidis(int id);
person findbyidandname(int id, string name);
person findbyidorname(int id, string name);
}这里出现了非常神奇的一幕:
我们仅需要提供一个接口,而不用提供具体实现!
仅凭方法的命名规范,spring.data.mongodb就能自行分析开发者的意图,进行补全内部的业务逻辑!
而同样具备这种智能化能力的还有spring.jpa,后者也是一种非常便捷高效数据库驱动,与mybatis属于同类产品
顺便也给大家提供一份方法命名规范清单,请各位在方法命名时务必遵循以下规则:
| 关键字 | 方法命名 | sql where字句 |
| and | findbynameandpwd | where name= ? and pwd =? |
| or | findbynameorsex | where name= ? or sex=? |
| is,equals | findbyid,findbyidequals | where id= ? |
| between | findbyidbetween | where id between ? and ? |
| lessthan | findbyidlessthan | where id < ? |
| lessthanequal | findbyidlessthanequal | where id <= ? |
| greaterthan | findbyidgreaterthan | where id > ? |
| greaterthanequal | findbyidgreaterthanequal | where id > = ? |
| after | findbyidafter | where id > ? |
| before | findbyidbefore | where id < ? |
| isnull | findbynameisnull | where name is null |
| isnotnull,notnull | findbynamenotnull | where name is not null |
| like | findbynamelike | where name like ? |
| notlike | findbynamenotlike | where name not like ? |
startingwith | findbynamestartingwith | where name like '?%' |
| endingwith | findbynameendingwith | where name like '%?' |
| containing | findbynamecontaining | where name like '%?%' |
| orderby | findbyidorderbyxdesc | where id=? order by x desc |
| not | findbynamenot | where name <> ? |
| in | findbyidin(collection<?> c) | where id in (?) |
| notin | findbyidnotin(collection<?> c) | where id not in (?) |
| true | findbyaaatue | where aaa = true |
| false | findbyaaafalse | where aaa = false |
| ignorecase | findbynameignorecase | where upper(name)=upper(?) |
4. service接口定义及实现
package com.example.hellospringboot.service;
import com.example.hellospringboot.model.person;
public interface mongoservice {
public void insert(person person);
public person findbyname(string name);
public person findbyid(int id);
public person findbyidandname(int id, string name);
public person findbyidorname(int id, string name);
}package com.example.hellospringboot.service.impl;
import com.example.hellospringboot.model.person;
import com.example.hellospringboot.repository.personrepository;
import com.example.hellospringboot.service.mongoservice;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.service;
@service
public class mongoserviceimpl implements mongoservice {
@autowired
personrepository repository;
public void insert(person person){
repository.insert(person);
}
public person findbyname(string name){
return repository.findbynameis(name);
}
public person findbyid(int id){
return repository.findbyidis(id);
}
public person findbyidandname(int id, string name){
return repository.findbyidandname(id, name);
}
public person findbyidorname(int id, string name){
return repository.findbyidorname(id, name);
}
}
5. controller实现
package com.example.hellospringboot.controller;
import com.example.hellospringboot.model.person;
import com.example.hellospringboot.service.mongoservice;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.getmapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.postmapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.requestmapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.restcontroller;
@restcontroller
@requestmapping("/mongo")
public class mongocontroller {
@autowired
mongoservice service;
@postmapping("/insert")
public void insert(person person){
service.insert(person);
}
@getmapping("/findbyname")
public person findbyname(string name){
return service.findbyname(name);
}
@getmapping("/findbyid")
public person findbyid(int id){
return service.findbyid(id);
}
@getmapping("/findbyidandname")
public person findbyidandname(int id, string name){
return service.findbyidandname(id, name);
}
@getmapping("/findbyidorname")
public person findbyidorname(int id, string name) {
return service.findbyidorname(id, name);
}
}service及controller的实现不再做过多赘述,还是老一套
6. postman验证结果
向mongodb中写入一条数据
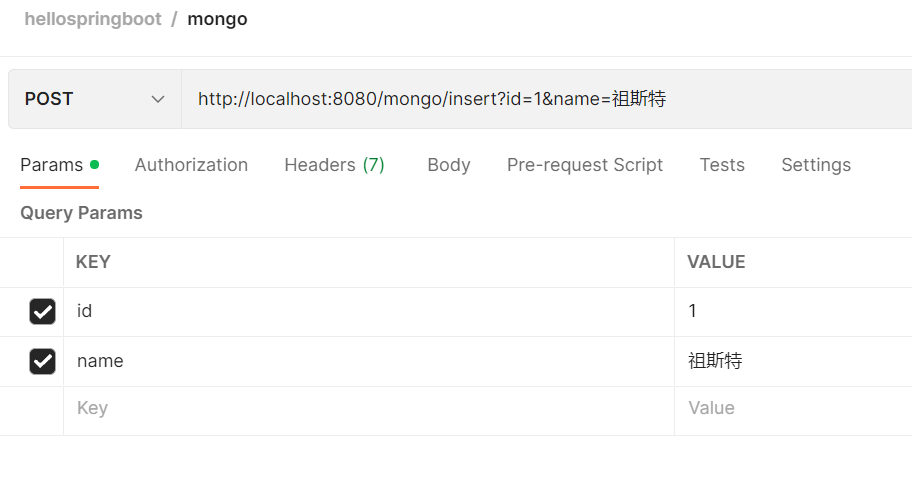
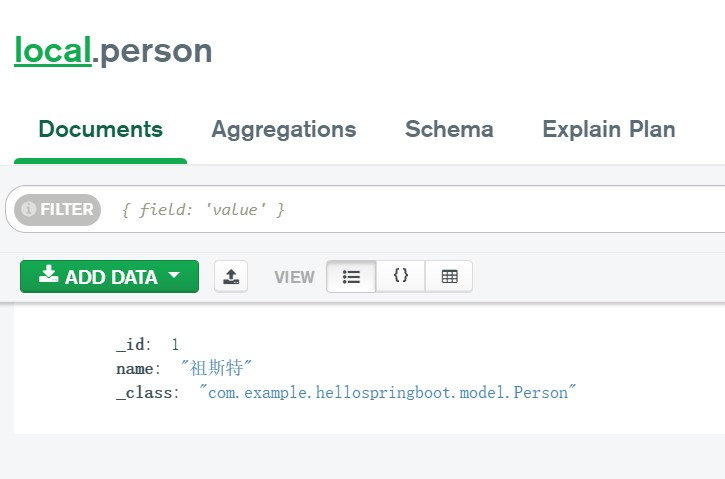
之后是几种读取操作:
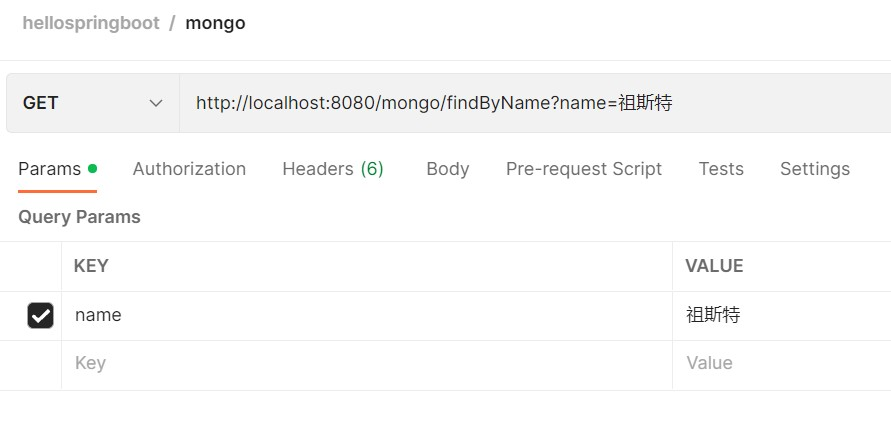
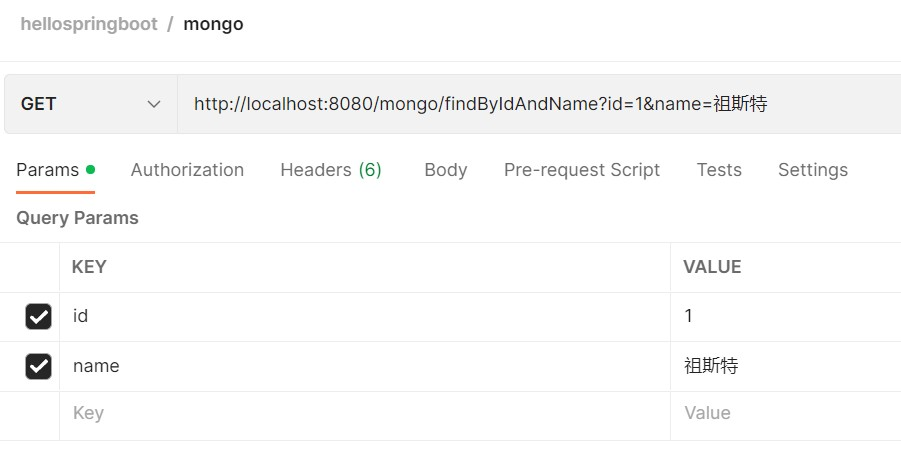
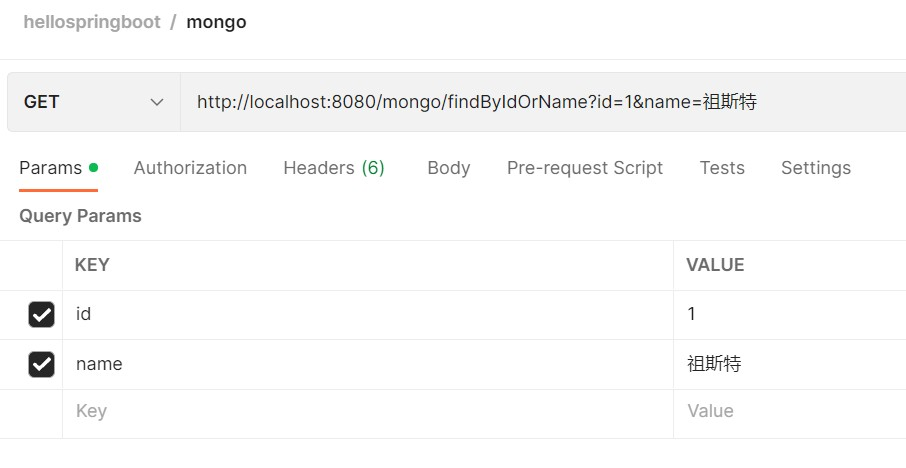
不论是与或操作,我们都可以得到正确的结果
到这里,mongodb的集成就完成了
三、基于redis实现session配置共享
这部分纯属附送内容 ^ ^
前边我们已经完成了对redis的集成操作,而基于redis我们可以非常便捷的实现服务端session配置的跨节点共享
服务端session默认存储在本地,而当我们需要多台服务器共享一套session配置时,本地化session便不再满足我们的要求
而基于springsession,我们可以完全透明化的替换掉默认的session容器,直接改为基于redis存储
1. 添加相关依赖
<!-- 引入spring session无缝替换原有的session系统 -->
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.session</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-session-data-redis</artifactid>
</dependency>2. 新增两个rediscontroller方法
@postmapping("/setsession")
public void setsession(string key, string val, httpsession session){
session.setattribute(key, val);
}
@getmapping("/getsession")
public object getsession(string key, httpsession session){
return session.getattribute(key);
}就完事儿了?对!就完事儿了 ^ ^,超级简单是吧?
到此,我们就完成了springboot对于redis以及mongodb的集成和使用
非常感慨于springboot框架设计的智能化及人性化,就像身边有一哥们说的:这年头,框架都能直接听懂人话了!哈哈
到此这篇关于springboot整合redis及mongodb的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关springboot整合redis内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!



发表评论