一、where子句语法格式详解
1.1 基础语法结构
where子句是select语句中的筛选条件部分,用于从表中提取满足特定条件的记录。
sql select 列名1, 列名2, ... from 表名 where 条件表达式;
1.2 完整的select语句结构
sql
select
[all | distinct | distinctrow]
select_expr [, select_expr ...]
from
table_references
[where where_condition] -- where子句位置
[group by {col_name | expr | position}]
[having where_condition]
[order by {col_name | expr | position} [asc | desc]]
[limit {[offset,] row_count | row_count offset offset}];
1.3 运算符优先级表
优先级 运算符 描述 1 =, <>, !=, <, <=, >, >= 比较运算符 2 between, like, in, is null 特殊比较 3 not 逻辑非 4 and 逻辑与 5 or 逻辑或
二、带in关键字的查询:多值匹配
2.1 基本语法格式
sql select 列名 from 表名 where 列名 in (值1, 值2, 值3, ...);
2.2 实际应用示例
sql
-- 示例表:员工表(employees)
create table employees (
id int primary key,
name varchar(50),
department varchar(30),
salary decimal(10,2),
hire_date date
);
-- 插入示例数据
insert into employees values
(1, '张三', '技术部', 8500, '2022-03-15'),
(2, '李四', '销售部', 7500, '2021-08-22'),
(3, '王五', '技术部', 9200, '2020-11-05'),
(4, '赵六', '市场部', 6800, '2023-01-30'),
(5, '孙七', '人事部', 6500, '2022-06-18'),
(6, '周八', '技术部', 8800, '2021-09-10');
示例1:查询指定部门的员工
sql
-- 查询属于技术部或销售部的员工
select
id as '员工编号',
name as '姓名',
department as '部门',
salary as '薪资'
from employees
where department in ('技术部', '销售部');
查询结果:
text
员工编号 姓名 部门 薪资
1 张三 技术部 8500.00
2 李四 销售部 7500.00
3 王五 技术部 9200.00
6 周八 技术部 8800.00
示例2:in子查询的运用
sql
-- 查询薪资高于平均薪资的员工
select
name as '姓名',
salary as '薪资'
from employees
where salary in (
select salary
from employees
where salary > (select avg(salary) from employees)
);
2.3 not in的用法
sql
-- 查询不在某些部门的员工
select
name as '姓名',
department as '部门'
from employees
where department not in ('人事部', '市场部');
三、带between and的范围查询
3.1 基础语法格式
sql select 列名 from 表名 where 列名 between 值1 and 值2; -- 等价于:where 列名 >= 值1 and 列名 <= 值2
3.2 实际应用示例
sql
-- 示例表:学生成绩表(scores)
create table scores (
student_id int,
student_name varchar(50),
subject varchar(20),
score int,
exam_date date
);
insert into scores values
(101, '张三', '数学', 85, '2023-06-15'),
(102, '李四', '数学', 92, '2023-06-15'),
(103, '王五', '数学', 78, '2023-06-15'),
(104, '赵六', '数学', 65, '2023-06-15'),
(105, '孙七', '数学', 88, '2023-06-15');
示例1:查询分数在某个区间的学生
sql
-- 查询数学成绩在80-90分之间的学生
select
student_id as '学号',
student_name as '姓名',
score as '数学成绩'
from scores
where subject = '数学'
and score between 80 and 90;
查询结果:
text
学号 姓名 数学成绩
101 张三 85
105 孙七 88
示例2:日期范围查询
sql
-- 查询2023年上半年入职的员工
select
name as '姓名',
department as '部门',
hire_date as '入职日期'
from employees
where hire_date between '2023-01-01' and '2023-06-30';
示例3:not between的用法
sql
-- 查询薪资不在8000-9000范围内的员工
select
name as '姓名',
salary as '薪资'
from employees
where salary not between 8000 and 9000;
3.3 注意事项
sql -- between包含边界值 where score between 80 and 90 -- 包含80和90 -- 对于日期,注意时间部分 where date_column between '2023-01-01' and '2023-01-31' -- 等价于:'2023-01-01 00:00:00' 到 '2023-01-31 23:59:59'
四、带like关键字的模糊查询
4.1 通配符说明
通配符 描述 示例 % 匹配任意多个字符(0个或多个) 张% 匹配"张三"、"张" _ 匹配单个字符 _三 匹配"张三"、"李三" [charlist] 匹配字符列表中的任意一个 [张李]三 匹配"张三"、"李三" [^charlist] 匹配不在字符列表中的任意一个 [^张李]三 匹配"王三"、"赵三"
4.2 实际应用示例
sql
-- 示例表:图书表(books)
create table books (
book_id int,
book_name varchar(100),
author varchar(50),
price decimal(8,2),
publish_date date
);
insert into books values
(1, 'mysql数据库实战', '张三', 59.80, '2023-01-15'),
(2, 'python编程从入门到精通', '李四', 79.90, '2022-11-20'),
(3, 'java核心技术', '王五', 89.90, '2023-03-10'),
(4, 'web前端开发实战', '李四', 69.90, '2022-09-05'),
(5, 'mysql优化指南', '赵六', 49.90, '2023-05-20');
示例1:%通配符使用
sql
-- 查询书名包含"mysql"的图书
select
book_name as '书名',
author as '作者',
price as '价格'
from books
where book_name like '%mysql%';
-- 查询以"实战"结尾的图书
select book_name
from books
where book_name like '%实战';
-- 查询以"python"开头的图书
select book_name
from books
where book_name like 'python%';
示例2:_通配符使用
sql
-- 查询作者姓"李"且名字为两个字的图书
select
book_name as '书名',
author as '作者'
from books
where author like '李_';
-- 查询书名第三个字是"编"的图书
select book_name
from books
where book_name like '__编%';
示例3:组合使用通配符
sql
-- 查询书名以"实战"结尾且长度至少为4个字的图书
select book_name
from books
where book_name like '%实战'
and length(book_name) >= 4;
-- 查询作者不是"张"、"李"、"王"开头的图书
select book_name, author
from books
where author not like '[张李王]%';
示例4:escape转义字符
sql
-- 当需要查询包含%或_本身时
select column_name
from table_name
where column_name like '%\%%' escape '\'; -- 查找包含%的内容
select column_name
from table_name
where column_name like '%\_%' escape '\'; -- 查找包含_的内容
五、用is null关键字查询空值
5.1 null值特性说明
null表示"未知"或"不存在"
null与任何值比较都返回null(包括null本身)
不能使用 = null 判断,必须使用 is null
5.2 实际应用示例
sql
-- 示例表:客户表(customers)
create table customers (
customer_id int,
customer_name varchar(50),
phone varchar(20),
email varchar(100),
address varchar(200),
register_date date
);
insert into customers values
(1, '张三', '13800138001', 'zhangsan@email.com', '北京市朝阳区', '2023-01-15'),
(2, '李四', null, 'lisi@email.com', null, '2023-02-20'),
(3, '王五', '13900139002', null, '上海市浦东新区', '2023-03-10'),
(4, '赵六', null, null, null, '2023-04-05'),
(5, '孙七', '13700137003', 'sunqi@email.com', '广州市天河区', '2023-05-12');
示例1:查询空值
sql
-- 查询没有电话号码的客户
select
customer_name as '客户姓名',
phone as '联系电话',
email as '电子邮箱'
from customers
where phone is null;
查询结果:
text
客户姓名 联系电话 电子邮箱
李四 null lisi@email.com
赵六 null null
示例2:查询非空值
sql
-- 查询有电子邮箱的客户
select
customer_name as '客户姓名',
email as '电子邮箱'
from customers
where email is not null;
示例3:多列空值判断
sql
-- 查询既没有电话也没有地址的客户
select
customer_name as '客户姓名',
register_date as '注册日期'
from customers
where phone is null
and address is null;
5.3 空值处理函数
sql
-- 使用ifnull处理空值显示
select
customer_name as '姓名',
ifnull(phone, '未登记') as '联系电话',
ifnull(address, '地址不详') as '联系地址'
from customers;
-- 使用coalesce返回第一个非空值
select
customer_name,
coalesce(email, phone, address, '无联系方式') as '主要联系方式'
from customers;
六、带and的多条件查询
6.1 基础语法格式
sql select 列名 from 表名 where 条件1 and 条件2 and 条件3 ...;
6.2 实际应用示例
sql
-- 示例表:订单表(orders)
create table orders (
order_id int,
customer_id int,
product_name varchar(100),
quantity int,
unit_price decimal(10,2),
order_date date,
status varchar(20)
);
insert into orders values
(1001, 1, '笔记本电脑', 1, 6999.00, '2023-10-15', '已完成'),
(1002, 2, '智能手机', 2, 2999.00, '2023-10-16', '待发货'),
(1003, 1, '平板电脑', 1, 3999.00, '2023-10-17', '已取消'),
(1004, 3, '无线耳机', 3, 399.00, '2023-10-18', '已完成'),
(1005, 2, '智能手表', 1, 1299.00, '2023-10-19', '待付款'),
(1006, 4, '显示器', 2, 1599.00, '2023-10-20', '待发货');
示例1:多条件组合查询
sql
-- 查询2023年10月订单金额超过5000元且状态为"已完成"的订单
select
order_id as '订单编号',
product_name as '产品名称',
quantity as '数量',
unit_price as '单价',
(quantity * unit_price) as '总金额',
order_date as '订单日期',
status as '订单状态'
from orders
where order_date between '2023-10-01' and '2023-10-31'
and (quantity * unit_price) > 5000
and status = '已完成';
查询结果:
text
订单编号 产品名称 数量 单价 总金额 订单日期 订单状态
1001 笔记本电脑 1 6999.00 6999.00 2023-10-15 已完成
示例2:复杂条件组合
sql
-- 查询数量大于1且单价在1000-5000元之间的订单
select
order_id,
product_name,
quantity,
unit_price,
status
from orders
where quantity > 1
and unit_price between 1000 and 5000
and status in ('待发货', '已完成');
示例3:结合like和and
sql
-- 查询产品名称包含"电脑"且状态不是"已取消"的订单
select
order_id as '订单号',
product_name as '产品',
status as '状态'
from orders
where product_name like '%电脑%'
and status != '已取消';
6.3 注意事项
sql -- 条件执行的优先级 where 条件1 or 条件2 and 条件3 -- 等价于:where 条件1 or (条件2 and 条件3) -- 建议使用括号明确优先级 where (条件1 or 条件2) and 条件3
七、带or的多条件查询
7.1 基础语法格式
sql select 列名 from 表名 where 条件1 or 条件2 or 条件3 ...;
7.2 实际应用示例
sql
-- 示例表:员工考勤表(attendance)
create table attendance (
record_id int,
employee_id int,
employee_name varchar(50),
department varchar(30),
attendance_date date,
status varchar(20)
);
insert into attendance values
(1, 101, '张三', '技术部', '2023-10-23', '正常'),
(2, 102, '李四', '销售部', '2023-10-23', '迟到'),
(3, 103, '王五', '技术部', '2023-10-23', '请假'),
(4, 104, '赵六', '市场部', '2023-10-23', '正常'),
(5, 105, '孙七', '人事部', '2023-10-23', '早退'),
(6, 101, '张三', '技术部', '2023-10-24', '请假'),
(7, 102, '李四', '销售部', '2023-10-24', '正常');
示例1:简单or条件查询
sql
-- 查询状态为"请假"或"迟到"的员工
select
attendance_date as '考勤日期',
employee_name as '员工姓名',
department as '部门',
status as '考勤状态'
from attendance
where status = '请假' or status = '迟到';
查询结果:
text
考勤日期 员工姓名 部门 考勤状态
2023-10-23 李四 销售部 迟到
2023-10-23 王五 技术部 请假
2023-10-24 张三 技术部 请假
示例2:or与in的等价转换
sql
-- 以下两种写法等价:
select * from attendance
where status = '请假' or status = '迟到' or status = '早退';
select * from attendance
where status in ('请假', '迟到', '早退');
示例3:多列or条件查询
sql
-- 查询部门为"技术部"或状态为"正常"的记录
select
attendance_date as '日期',
employee_name as '姓名',
department as '部门',
status as '状态'
from attendance
where department = '技术部' or status = '正常';
7.3 and与or的组合使用
示例1:复杂条件组合
sql
-- 查询(技术部且请假)或(销售部且迟到)的员工
select
employee_name as '姓名',
department as '部门',
status as '状态',
attendance_date as '日期'
from attendance
where (department = '技术部' and status = '请假')
or (department = '销售部' and status = '迟到');
示例2:多层条件嵌套
sql
-- 查询(状态为正常)或(部门为技术部且状态不为早退)的记录
select *
from attendance
where status = '正常'
or (department = '技术部' and status != '早退');
7.4 性能优化建议
sql -- 不推荐的写法(or导致索引失效) select * from orders where customer_id = 1 or product_name like '%电脑%'; -- 推荐的改写方式(使用union) select * from orders where customer_id = 1 union select * from orders where product_name like '%电脑%';
八、综合实战案例
8.1 复杂查询综合应用
sql
-- 创建一个综合示例表
create table sales (
sale_id int primary key,
product_id int,
product_name varchar(100),
category varchar(50),
sale_date date,
quantity int,
unit_price decimal(10,2),
salesperson varchar(50),
region varchar(50)
);
-- 综合查询示例
select
product_name as '产品名称',
category as '产品类别',
sum(quantity) as '总销量',
sum(quantity * unit_price) as '总销售额',
avg(unit_price) as '平均单价'
from sales
where sale_date between '2023-01-01' and '2023-12-31'
and category in ('电子产品', '办公用品')
and (region = '华东' or region = '华南')
and quantity > 0
and salesperson is not null
group by product_name, category
having sum(quantity * unit_price) > 10000
order by sum(quantity * unit_price) desc;
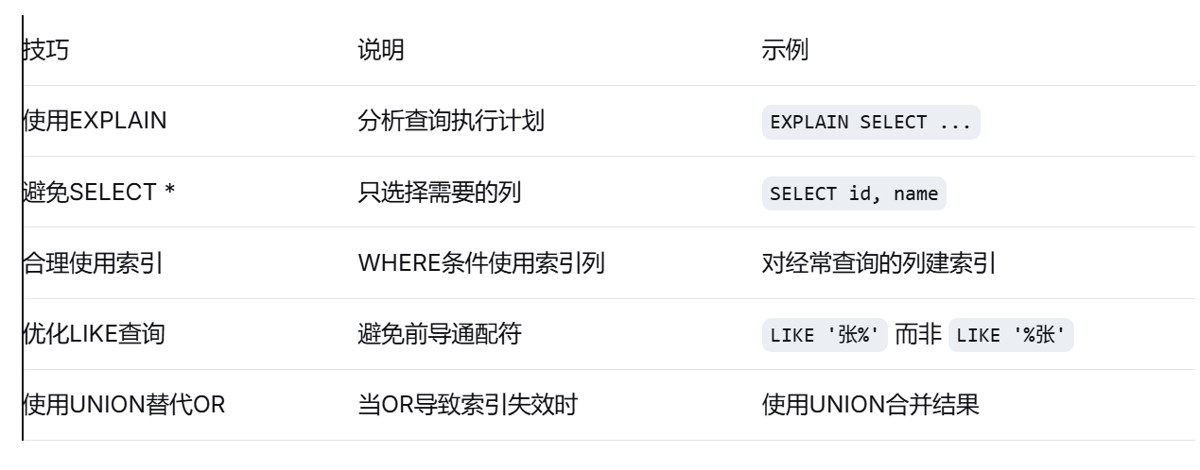
8.2 查询优化技巧总结
到此这篇关于mysql where子句实践指南(精准过滤数据的艺术)的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关mysql where字句内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论