引言
在数据科学和机器学习的工作中,jupyter notebook 已成为不可或缺的工具。它提供了一个交互式的环境,允许我们在文档中同时编写代码、展示图表以及添加文本说明。不过,许多时候我们希望自动化生成 notebook 文件,并将其导出为 html 或其他格式,这篇文章将带你通过 python 来实现这一目标。效果如下图所示
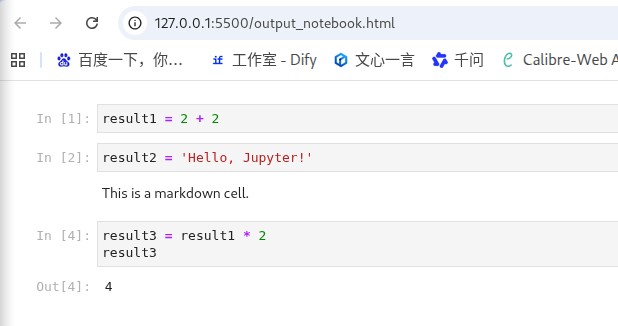
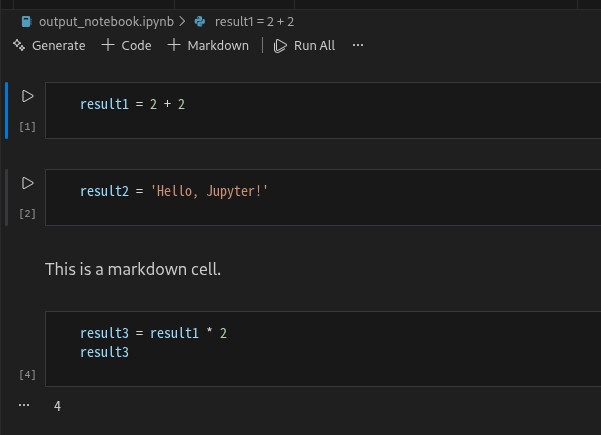
1. 背景
有时候,我们可能需要根据特定的需求自动生成包含代码单元格、markdown 单元格和输出的 jupyter notebook 文件,并将其导出为 .html 或 .ipynb 格式。为了完成这一任务,我们将使用 nbformat 和 nbconvert 这两个 python 库。
本文将为大家展示如何使用这两个库实现以下功能:
- 创建新的 jupyter notebook。
- 添加代码和 markdown 单元格。
- 为代码单元格添加执行计数。
- 将 notebook 导出为 html 文件。
- 保存为
.ipynb文件。
2. 安装必要的依赖
在开始之前,你需要安装以下两个库:nbformat 和 nbconvert。你可以使用 pip 命令进行安装:
pip install nbformat nbconvert
3. 创建并修改 notebook
接下来,我们将编写 python 代码来生成一个 jupyter notebook,并为其添加代码单元格、markdown 单元格以及带有执行结果的代码单元格。
import nbformat
from nbconvert import htmlexporter
# 创建一个新的jupyter notebook
notebook = nbformat.v4.new_notebook()
# 添加代码单元格
code1 = "result1 = 2 + 2"
notebook.cells.append(nbformat.v4.new_code_cell(code1))
code2 = "result2 = 'hello, jupyter!'"
notebook.cells.append(nbformat.v4.new_code_cell(code2))
# 添加markdown单元格
markdown_text = "this is a markdown cell."
notebook.cells.append(nbformat.v4.new_markdown_cell(markdown_text))
# 添加带有输出的代码单元格
code3 = "result3 = result1 * 2\nresult3"
notebook.cells.append(nbformat.v4.new_code_cell(code3))
notebook.cells[-1].outputs.append(nbformat.v4.new_output(
output_type='execute_result',
data={'text/plain': '4'},
))
# 为每个代码单元格添加执行计数
for i, cell in enumerate(notebook.cells):
if cell.cell_type == 'code':
cell['execution_count'] = i + 1
代码解释:
- 创建一个新的 notebook:使用
nbformat.v4.new_notebook()创建一个空的 notebook 对象。 - 添加代码单元格:我们通过
nbformat.v4.new_code_cell()向 notebook 中添加代码单元格。例如,第一个代码单元格执行了简单的加法运算result1 = 2 + 2。 - 添加 markdown 单元格:使用
nbformat.v4.new_markdown_cell()向 notebook 中添加 markdown 单元格。markdown 允许你在文档中插入文本、图片、数学公式等。 - 添加带有输出的代码单元格:最后,我们添加一个带有输出的代码单元格,这个单元格计算
result1 * 2,并返回结果4。
4. 导出为 html 文件
接下来,我们将使用 htmlexporter 将 notebook 转换为 html 格式,并确保插入类似 in [1]: 的执行计数。
# 将notebook导出为html
html_exporter = htmlexporter()
(body, _) = html_exporter.from_notebook_node(notebook)
# 插入带有执行计数的in [1]:等
lines = []
for line in body.split('\n'):
if line.startswith('in '):
lines.append(f'in [{line[4:]}')
else:
lines.append(line)
# 将html输出保存为文件
output_file_path_html = "output_notebook.html"
with open(output_file_path_html, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write('\n'.join(lines))
print(f"jupyter notebook html saved to {output_file_path_html}")
代码解释:
htmlexporter:我们通过htmlexporter将 notebook 对象转换为 html 格式。from_notebook_node()方法会返回 html 内容。- 插入执行计数:接着,我们遍历生成的 html 内容,将每个包含
in的行转化为in [1]:这样的格式,以保证代码单元格的执行计数能够正确显示。 - 保存为 html 文件:最后,我们将处理过的 html 内容保存到
output_notebook.html文件中。
5. 将 notebook 保存为.ipynb文件
除了导出为 html 格式,我们还需要将 notebook 保存为 .ipynb 格式,这样可以方便地在 jupyter notebook 中打开。
# 将notebook保存为.ipynb文件
output_file_path_ipynb = "output_notebook.ipynb"
nbformat.write(notebook, output_file_path_ipynb)
print(f"jupyter notebook .ipynb saved to {output_file_path_ipynb}")
代码解释:
nbformat.write():这行代码将 notebook 对象保存为.ipynb格式的文件。
6. 完整代码
将上述所有代码整合在一起,形成完整的 python 脚本:
import nbformat
from nbconvert import htmlexporter
# 创建一个新的jupyter notebook
notebook = nbformat.v4.new_notebook()
# 添加代码单元格
code1 = "result1 = 2 + 2"
notebook.cells.append(nbformat.v4.new_code_cell(code1))
code2 = "result2 = 'hello, jupyter!'"
notebook.cells.append(nbformat.v4.new_code_cell(code2))
# 添加markdown单元格
markdown_text = "this is a markdown cell."
notebook.cells.append(nbformat.v4.new_markdown_cell(markdown_text))
# 添加带有输出的代码单元格
code3 = "result3 = result1 * 2\nresult3"
notebook.cells.append(nbformat.v4.new_code_cell(code3))
notebook.cells[-1].outputs.append(nbformat.v4.new_output(
output_type='execute_result',
data={'text/plain': '4'},
))
# 为每个代码单元格添加执行计数
for i, cell in enumerate(notebook.cells):
if cell.cell_type == 'code':
cell['execution_count'] = i + 1
# 将notebook导出为html
html_exporter = htmlexporter()
(body, _) = html_exporter.from_notebook_node(notebook)
# 插入带有执行计数的in [1]:等
lines = []
for line in body.split('\n'):
if line.startswith('in '):
lines.append(f'in [{line[4:]}')
else:
lines.append(line)
# 将html输出保存为文件
output_file_path_html = "output_notebook.html"
with open(output_file_path_html, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write('\n'.join(lines))
print(f"jupyter notebook html saved to {output_file_path_html}")
# 将notebook保存为.ipynb文件
output_file_path_ipynb = "output_notebook.ipynb"
nbformat.write(notebook, output_file_path_ipynb)
print(f"jupyter notebook .ipynb saved to {output_file_path_ipynb}")
7. 总结
通过本文的介绍,我们已经学会了如何使用 python 创建和导出 jupyter notebook 文件。无论是将其保存为 .ipynb 格式以供后续使用,还是将其导出为 .html 格式进行展示,我们都可以通过简单的 python 脚本来实现这一切。
以上就是使用python创建和导出jupyter notebook的完整教程的详细内容,更多关于python创建和导出jupyter notebook的资料请关注代码网其它相关文章!







发表评论