前言
python通过ctypes模块可以方便地调用c/c++编写的动态库(windows下为dll,linux下为so文件)。这种方式允许python与底层系统进行高效交互,广泛用于硬件控制、高性能计算等场景。
基本原理
- 动态库加载:使用
ctypes.cdll(加载c库)或ctypes.windll(加载windows特定的stdcall调用约定的dll)加载动态库文件 - 函数参数与返回值类型声明:明确指定c函数的参数类型和返回值类型,确保数据传递正确
- 数据类型映射:将python数据类型转换为c兼容的数据类型(如整数、字符串、结构体等)
实践案例
1. 简单c函数调用示例
c代码(保存为example.c):
// example.c
#include <stdio.h>
// 简单加法函数
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
// 字符串处理函数
void reverse_string(char* str) {
int len = 0;
while (str[len] != '\0') len++;
for (int i = 0; i < len/2; i++) {
char temp = str[i];
str[i] = str[len - i - 1];
str[len - i - 1] = temp;
}
}
编译为动态库:
# linux/macos gcc -shared -o example.so -fpic example.c # windows (mingw) gcc -shared -o example.dll example.c
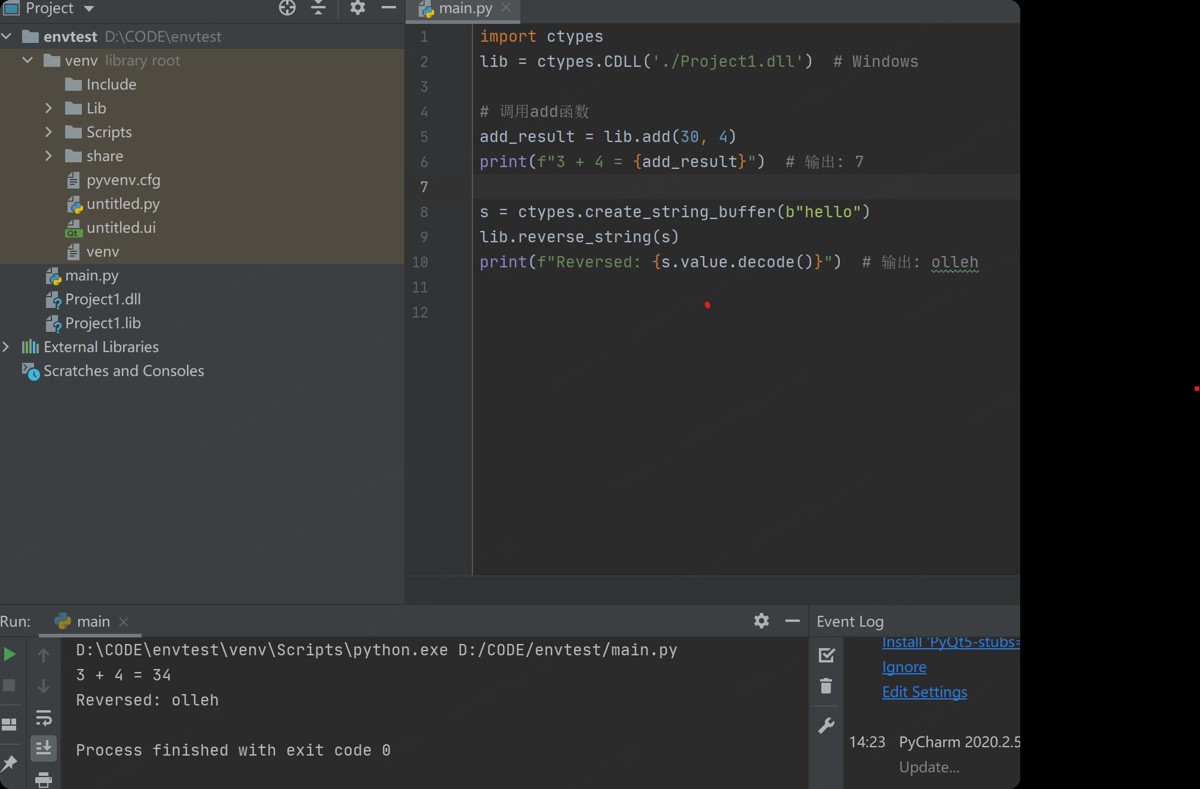
python调用代码:
import ctypes
# 加载动态库
lib = ctypes.cdll('./example.so') # linux/macos
# lib = ctypes.cdll('./example.dll') # windows
# 调用add函数
add_result = lib.add(3, 4)
print(f"3 + 4 = {add_result}") # 输出: 7
# 调用reverse_string函数
# 注意:需要传递可变的字节数组
s = ctypes.create_string_buffer(b"hello")
lib.reverse_string(s)
print(f"reversed: {s.value.decode()}") # 输出: olleh
2. 传递和返回结构体
c代码(保存为struct_example.c):
#include <stdio.h>
// 定义结构体
typedef struct {
int x;
int y;
} point;
// 结构体加法函数
point add_points(point a, point b) {
point result;
result.x = a.x + b.x;
result.y = a.y + b.y;
return result;
}
// 修改结构体内容
void scale_point(point* p, int factor) {
p->x *= factor;
p->y *= factor;
}
编译为动态库:
gcc -shared -o struct_example.so -fpic struct_example.c
python调用代码:
import ctypes
# 加载动态库
lib = ctypes.cdll('./struct_example.so')
# 定义point结构体
class point(ctypes.structure):
_fields_ = [
("x", ctypes.c_int),
("y", ctypes.c_int)
]
# 设置函数参数和返回值类型
lib.add_points.argtypes = [point, point]
lib.add_points.restype = point
lib.scale_point.argtypes = [ctypes.pointer(point), ctypes.c_int]
lib.scale_point.restype = none
# 调用add_points函数
p1 = point(1, 2)
p2 = point(3, 4)
result = lib.add_points(p1, p2)
print(f"({p1.x}, {p1.y}) + ({p2.x}, {p2.y}) = ({result.x}, {result.y})")
# 输出: (1, 2) + (3, 4) = (4, 6)
# 调用scale_point函数
p = point(5, 6)
lib.scale_point(ctypes.byref(p), 2)
print(f"缩放后的点: ({p.x}, {p.y})")
# 输出: 缩放后的点: (10, 12)
3. 处理数组和指针
c代码(保存为array_example.c):
#include <stdio.h>
// 计算数组元素之和
int sum_array(int* arr, int size) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
}
return sum;
}
// 修改数组内容
void multiply_array(int* arr, int size, int factor) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
arr[i] *= factor;
}
}
编译为动态库:
gcc -shared -o array_example.so -fpic array_example.c
python调用代码:
import ctypes
# 加载动态库
lib = ctypes.cdll('./array_example.so')
# 创建c整数数组类型
intarray5 = ctypes.c_int * 5 # 定义长度为5的整数数组
# 设置函数参数类型
lib.sum_array.argtypes = [ctypes.pointer(ctypes.c_int), ctypes.c_int]
lib.sum_array.restype = ctypes.c_int
lib.multiply_array.argtypes = [ctypes.pointer(ctypes.c_int), ctypes.c_int, ctypes.c_int]
lib.multiply_array.restype = none
# 调用sum_array函数
arr = intarray5(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
sum_result = lib.sum_array(arr, 5)
print(f"数组和: {sum_result}") # 输出: 15
# 调用multiply_array函数
lib.multiply_array(arr, 5, 10)
print(f"修改后的数组: {[arr[i] for i in range(5)]}")
# 输出: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
4. 调用c++类和函数(需要extern “c”)
c++代码(保存为cpp_example.cpp):
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// c++类
class calculator {
public:
int add(int a, int b) { return a + b; }
int subtract(int a, int b) { return a - b; }
};
// 封装c++类的c接口
extern "c" {
// 创建对象
calculator* calculator_new() { return new calculator(); }
// 释放对象
void calculator_delete(calculator* calc) { delete calc; }
// 调用成员函数
int calculator_add(calculator* calc, int a, int b) { return calc->add(a, b); }
int calculator_subtract(calculator* calc, int a, int b) { return calc->subtract(a, b); }
}
编译为动态库:
g++ -shared -o cpp_example.so -fpic cpp_example.cpp
python调用代码:
import ctypes
# 加载动态库
lib = ctypes.cdll('./cpp_example.so')
# 定义函数参数和返回值类型
lib.calculator_new.restype = ctypes.c_void_p
lib.calculator_delete.argtypes = [ctypes.c_void_p]
lib.calculator_add.argtypes = [ctypes.c_void_p, ctypes.c_int, ctypes.c_int]
lib.calculator_add.restype = ctypes.c_int
lib.calculator_subtract.argtypes = [ctypes.c_void_p, ctypes.c_int, ctypes.c_int]
lib.calculator_subtract.restype = ctypes.c_int
# 创建calculator对象
calc_ptr = lib.calculator_new()
# 调用成员函数
result_add = lib.calculator_add(calc_ptr, 10, 5)
result_sub = lib.calculator_subtract(calc_ptr, 10, 5)
print(f"10 + 5 = {result_add}") # 输出: 15
print(f"10 - 5 = {result_sub}") # 输出: 5
# 释放对象
lib.calculator_delete(calc_ptr)
常见问题与解决方案
找不到动态库文件
- 确保动态库文件在正确路径下
- 使用绝对路径加载库:
ctypes.cdll('/path/to/library.so')
参数类型不匹配
- 始终显式设置
argtypes和restype - 对于字符串,使用
ctypes.create_string_buffer()创建可变字节数组
- 始终显式设置
处理c++类
- 必须使用
extern "c"封装c++接口 - 通过指针管理对象生命周期(创建和销毁)
- 必须使用
内存管理问题
- 手动管理动态分配的内存(如使用
delete释放c++对象) - 避免返回指向局部变量的指针
- 手动管理动态分配的内存(如使用
通过ctypes调用c/c++动态库是python与底层系统交互的强大方式,能够在保持python灵活性的同时获得c/c++的高性能。
总结
到此这篇关于python调用c/c++动态库的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python调用c/c++动态库内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论