duckx是一个用于创建和编辑 microsoft word (.docx) 文件的 c++ 库。
一、基本用法
1. 读取文档
#include <iostream>
#include "duckx.hpp"
int main() {
duckx::document doc("foo.docx");
doc.open();
for (auto p = doc.paragraphs(); p.has_next(); p.next()) {
for (auto r = p.runs(); r.has_next(); r.next()) {
std::cout << r.get_text() << std::endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
运行结果如下:
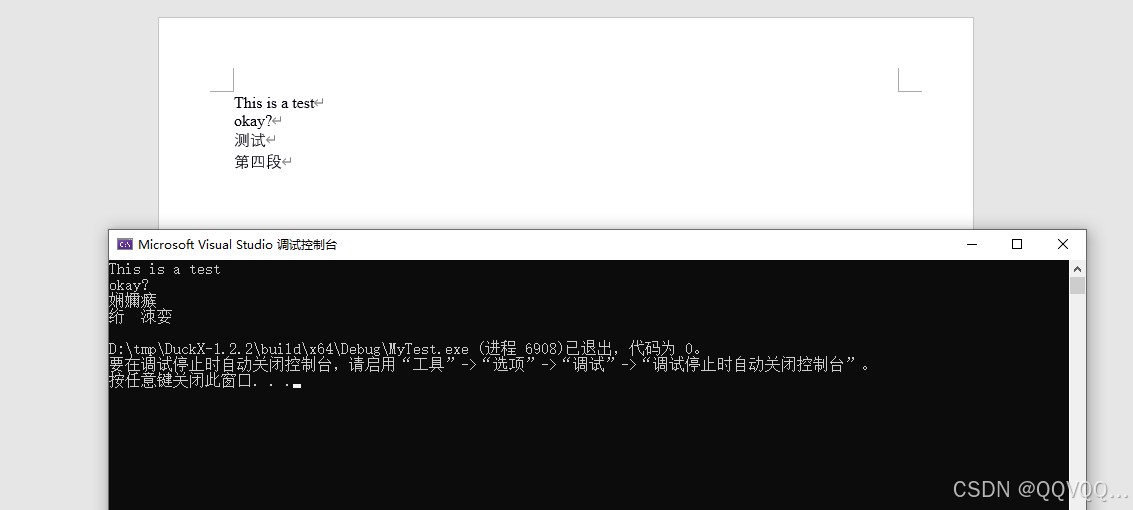
中文乱码的原因时由于将utf-8字符串使用gbk编码显示了,更改编码方案即可。
3. 添加段落
#include "duckx.hpp"
#include <iostream>
int main() {
// 加载文档
duckx::document doc("foo.docx");
doc.open();
// 遍历段落
duckx::paragraph& paragraph = doc.paragraphs();
while (paragraph.has_next()) {
// 如果需要在某段之后插入段落
if (paragraph.runs().get_text() == "aaa") {
paragraph.insert_paragraph_after("this is a new paragraph.");
}
// 移动到下一个段落
paragraph.next();
}
// 保存修改后的文档
doc.save();
return 0;
}
原始文件如下:

修改文件如下:

4. 添加片段
#include "duckx.hpp"
#include <iostream>
int main() {
// 加载文档
duckx::document doc("foo.docx");
doc.open();
// 遍历段落
duckx::paragraph& paragraph = doc.paragraphs();
while (paragraph.has_next()) {
// 在某段中追加运行文本
if (paragraph.runs().get_text() == "aaa") {
paragraph.add_run(" added new text here.");
}
// 移动到下一个段落
paragraph.next();
}
// 保存修改后的文档
doc.save();
return 0;
}

3. 编辑表格
#include "duckx.hpp"
#include <iostream>
int main() {
// 加载文档
duckx::document doc("table.docx");
doc.open();
// 遍历表格
duckx::table& table = doc.tables();
while (table.has_next()) {
duckx::tablerow& row = table.rows();
while (row.has_next()) {
duckx::tablecell& cell = row.cells();
while (cell.has_next()) {
// 在单元格内新增段落
duckx::paragraph& paragraph = cell.paragraphs();
if (paragraph.runs().get_text() == "") {
paragraph.add_run("2024");
}
cell.next();
}
row.next();
}
table.next();
}
// 保存修改后的文档
doc.save();
return 0;
}
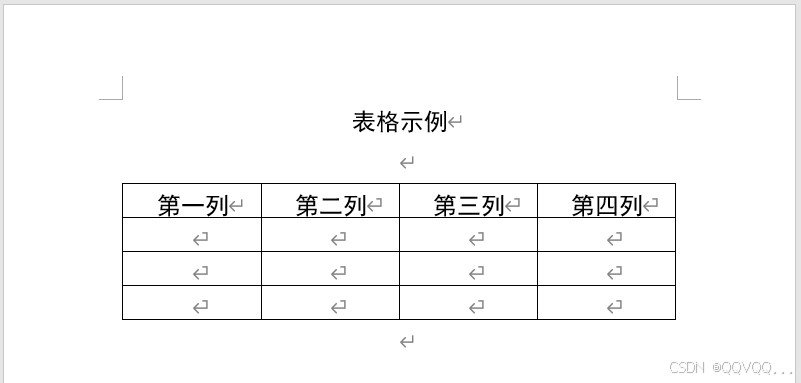
原始文档如下:
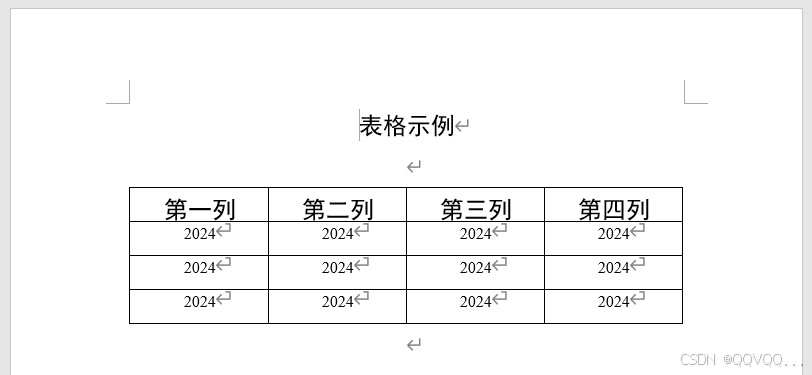
修改文档如下:
二、进阶用法
1. 文本替换
#include "duckx.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <string>
void replace(const std::string & path, const std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string>& replacements) {
// 打开文档
duckx::document doc(path);
doc.open();
// 遍历段落
for (auto p = doc.paragraphs(); p.has_next(); p.next()) {
// 遍历运行文本
for (auto r = p.runs(); r.has_next(); r.next()) {
// 获取当前运行文本内容
std::string text = r.get_text();
// 检查键值对中的键是否存在于当前文本中
for (const auto& [key, value] : replacements) {
// 如果找到匹配键,进行替换
size_t pos = text.find(key);
if (pos != std::string::npos) {
text.replace(pos, key.length(), value);
r.set_text(text);
}
}
}
}
// 保存修改后的文档
doc.save();
}
int main() {
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> replacements = {
{"{name}", "john doe"},
{"{date}", "2024-11-29"},
{"{city}", "new york"}
};
replace("foo.docx", replacements);
std::cout << "replacements complete. saved to foo.docx." << std::endl;
return 0;
}


进阶版:可同时替换普通文本和表格中的文本
#include "duckx.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <string>
void replace(const std::string& path, const std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string>& replacements) {
// 打开文档
duckx::document doc(path);
doc.open();
// 遍历段落
for (auto p = doc.paragraphs(); p.has_next(); p.next()) {
// 遍历运行文本
for (auto r = p.runs(); r.has_next(); r.next()) {
// 获取当前运行文本内容
std::string text = r.get_text();
// 检查键值对中的键是否存在于当前文本中
for (const auto& [key, value] : replacements) {
// 如果找到匹配键,进行替换
size_t pos = text.find(key);
if (pos != std::string::npos) {
text.replace(pos, key.length(), value);
r.set_text(text);
}
}
}
}
// 遍历表格
for (auto t = doc.tables(); t.has_next(); t.next()) {
// 遍历表格行
for (auto r = t.rows(); r.has_next(); r.next()) {
// 遍历表格单元格
for (auto c = r.cells(); c.has_next(); c.next()) {
// 遍历单元格中的段落
for (auto p = c.paragraphs(); p.has_next(); p.next()) {
// 遍历单元格段落中的运行文本
for (auto r = p.runs(); r.has_next(); r.next()) {
// 获取当前运行文本内容
std::string text = r.get_text();
// 检查键值对中的键是否存在于当前文本中
for (const auto& [key, value] : replacements) {
// 如果找到匹配键,进行替换
size_t pos = text.find(key);
if (pos != std::string::npos) {
text.replace(pos, key.length(), value);
r.set_text(text);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
// 保存修改后的文档
doc.save();
}
int main() {
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> replacements = {
{"{name}", "john doe"},
{"{date}", "2024-11-29"},
{"{city}", "new york"}
};
replace("foo.docx", replacements);
std::cout << "replacements complete. saved to foo.docx." << std::endl;
return 0;
}
2. 合并文档
只能合并文本
#include "duckx.hpp"
#include <iostream>
int main() {
// 加载第一个文档
duckx::document doc1("document1.docx");
doc1.open();
// 加载第二个文档
duckx::document doc2("document2.docx");
doc2.open();
// 将第二个文档的段落添加到第一个文档
duckx::paragraph ¶graph2 = doc2.paragraphs();
while (paragraph2.has_next()) {
// 获取第二个文档中的段落
std::string text = paragraph2.runs().get_text();
// 在第一个文档中插入段落
doc1.paragraphs().insert_paragraph_after(text);
paragraph2.next();
}
// 将第二个文档的表格添加到第一个文档
duckx::table &table2 = doc2.tables();
while (table2.has_next()) {
duckx::tablerow &row2 = table2.rows();
while (row2.has_next()) {
duckx::tablecell &cell2 = row2.cells();
while (cell2.has_next()) {
// 获取第二个文档中的单元格
std::string celltext = cell2.paragraphs().runs().get_text();
// 在第一个文档中插入单元格
doc1.tables().rows().cells().add_run(celltext);
cell2.next();
}
row2.next();
}
table2.next();
}
// 保存合并后的文档
doc1.save();
std::cout << "documents merged and saved to document1.docx." << std::endl;
return 0;
}
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持代码网。





发表评论