概述
解释器模式(interpreter pattern)是一种行为型设计模式,它定义了一种语言的文法表示,并提供一个解释器来解释该语言中的句子。
这种模式主要用于处理特定类型的问题,特别是那些可以被表示为语言句子的领域。
一、解释器模式的核心概念
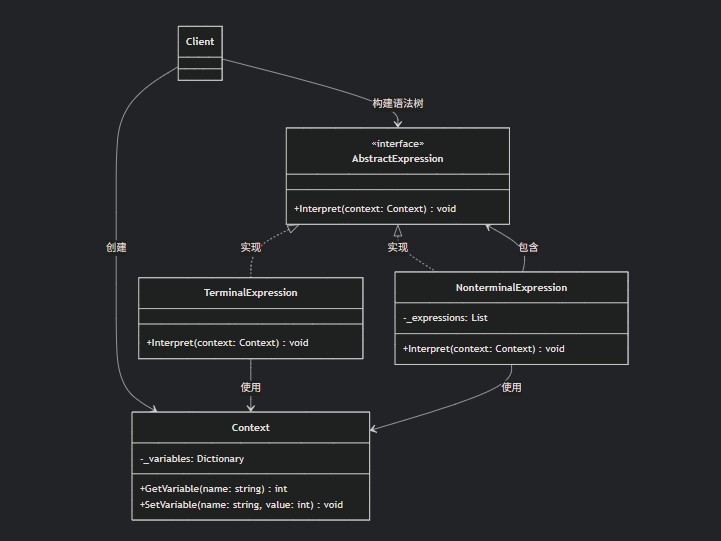
1. 解释器模式的主要角色
abstractexpression(抽象表达式) :
- 声明一个抽象的解释操作接口
terminalexpression(终结符表达式) :
- 实现与文法中的终结符相关联的解释操作
- 句子中的每个终结符都需要一个实例
nonterminalexpression(非终结符表达式) :
- 文法中的每条规则都需要一个非终结符表达式类
- 包含对其他表达式的引用(可能是终结符或非终结符)
context(上下文) :
- 包含解释器之外的全局信息
client(客户端) :
- 构建(或被给定)表示该语言中特定句子的抽象语法树
- 调用解释操作
2. 解释器模式的 uml 类图
二、解释器模式的实现方式
1. 基础实现(布尔表达式解释器)
// 上下文 - 存储变量值
public class context
{
private readonly dictionary<string, bool> _variables = new();
public bool getvariable(string name) => _variables.trygetvalue(name, out var value) ? value : false;
public void setvariable(string name, bool value) => _variables[name] = value;
}
// 抽象表达式
public interface iexpression
{
bool interpret(context context);
}
// 终结符表达式 - 变量
public class variableexpression : iexpression
{
private readonly string _name;
public variableexpression(string name) => _name = name;
public bool interpret(context context) => context.getvariable(_name);
}
// 非终结符表达式 - and
public class andexpression : iexpression
{
private readonly iexpression _left;
private readonly iexpression _right;
public andexpression(iexpression left, iexpression right)
{
_left = left;
_right = right;
}
public bool interpret(context context) => _left.interpret(context) && _right.interpret(context);
}
// 非终结符表达式 - or
public class orexpression : iexpression
{
private readonly iexpression _left;
private readonly iexpression _right;
public orexpression(iexpression left, iexpression right)
{
_left = left;
_right = right;
}
public bool interpret(context context) => _left.interpret(context) || _right.interpret(context);
}
// 非终结符表达式 - not
public class notexpression : iexpression
{
private readonly iexpression _expression;
public notexpression(iexpression expression) => _expression = expression;
public bool interpret(context context) => !_expression.interpret(context);
}
// 客户端代码
class program
{
static void main()
{
// 创建上下文并设置变量
var context = new context();
context.setvariable("a", true);
context.setvariable("b", false);
context.setvariable("c", true);
// 构建表达式: (a and b) or (not c)
var expression = new orexpression(
new andexpression(
new variableexpression("a"),
new variableexpression("b")),
new notexpression(
new variableexpression("c")));
// 解释执行
bool result = expression.interpret(context);
console.writeline($"表达式结果为: {result}"); // 输出 false
}
}
2. 数学表达式解释器(四则运算)
// 上下文 - 存储变量值
public class mathcontext
{
private readonly dictionary<string, int> _variables = new();
public int getvariable(string name) => _variables.trygetvalue(name, out var value) ? value : 0;
public void setvariable(string name, int value) => _variables[name] = value;
}
// 抽象表达式
public interface imathexpression
{
int interpret(mathcontext context);
}
// 终结符表达式 - 数字
public class numberexpression : imathexpression
{
private readonly int _number;
public numberexpression(int number) => _number = number;
public int interpret(mathcontext context) => _number;
}
// 终结符表达式 - 变量
public class variablemathexpression : imathexpression
{
private readonly string _name;
public variablemathexpression(string name) => _name = name;
public int interpret(mathcontext context) => context.getvariable(_name);
}
// 非终结符表达式 - 加法
public class addexpression : imathexpression
{
private readonly imathexpression _left;
private readonly imathexpression _right;
public addexpression(imathexpression left, imathexpression right)
{
_left = left;
_right = right;
}
public int interpret(mathcontext context) => _left.interpret(context) + _right.interpret(context);
}
// 非终结符表达式 - 减法
public class subtractexpression : imathexpression
{
private readonly imathexpression _left;
private readonly imathexpression _right;
public subtractexpression(imathexpression left, imathexpression right)
{
_left = left;
_right = right;
}
public int interpret(mathcontext context) => _left.interpret(context) - _right.interpret(context);
}
// 使用示例
var context = new mathcontext();
context.setvariable("x", 10);
context.setvariable("y", 5);
// 构建表达式: (x + 5) - (y - 2)
var expression = new subtractexpression(
new addexpression(
new variablemathexpression("x"),
new numberexpression(5)),
new subtractexpression(
new variablemathexpression("y"),
new numberexpression(2)));
int result = expression.interpret(context); // 结果为 12
三、解释器模式的特点
1. 优点
- 易于扩展语法:新增表达式类即可扩展语言
- 易于实现简单语言:对于简单文法实现直观
- 分离语法分析:将语法分析与表达式执行分离
- 灵活性强:可以动态改变解释方式
2. 缺点
- 复杂度高:对于复杂文法,类数量会急剧增加
- 效率较低:解释器模式通常比编译器效率低
- 难以维护复杂文法:文法规则过多时代码难以维护
- 应用场景有限:仅适用于特定领域问题
四、解释器模式的使用场景
1. 典型应用场景
领域特定语言(dsl) :
- 正则表达式解释器
- sql条件解释器
- 业务规则引擎
数学表达式处理:
- 科学计算器
- 公式编辑器
- 财务计算系统
配置文件解析:
- 自定义配置语法
- 过滤条件解析
编译器/解释器:
- 简单编程语言解释器
- 模板引擎
游戏开发:
- 游戏ai行为脚本
- 技能效果描述语言
2. 具体案例
案例1:正则表达式解释器(简化版)
// 抽象表达式
public interface iregexexpression
{
bool interpret(string input);
}
// 终结符表达式 - 字符匹配
public class charexpression : iregexexpression
{
private readonly char _char;
public charexpression(char c) => _char = c;
public bool interpret(string input) => input.length > 0 && input[0] == _char;
}
// 非终结符表达式 - 序列
public class sequenceexpression : iregexexpression
{
private readonly list<iregexexpression> _expressions;
public sequenceexpression(params iregexexpression[] expressions)
=> _expressions = new list<iregexexpression>(expressions);
public bool interpret(string input)
{
string remaining = input;
foreach (var expr in _expressions)
{
if (!expr.interpret(remaining)) return false;
remaining = remaining.substring(1);
}
return true;
}
}
// 非终结符表达式 - 或
public class orexpression : iregexexpression
{
private readonly iregexexpression _left;
private readonly iregexexpression _right;
public orexpression(iregexexpression left, iregexexpression right)
{
_left = left;
_right = right;
}
public bool interpret(string input) => _left.interpret(input) || _right.interpret(input);
}
// 使用
var regex = new sequenceexpression(
new charexpression('a'),
new orexpression(
new charexpression('b'),
new charexpression('c')));
bool match1 = regex.interpret("ab"); // true
bool match2 = regex.interpret("ac"); // true
bool match2 = regex.interpret("ad"); // false
案例2:业务规则引擎
// 业务规则上下文
public class businesscontext
{
public dictionary<string, object> data { get; } = new();
}
// 条件表达式
public class conditionexpression
{
private readonly string _field;
private readonly object _value;
private readonly string _operator;
public conditionexpression(string field, string op, object value)
{
_field = field;
_operator = op;
_value = value;
}
public bool interpret(businesscontext context)
{
if (!context.data.trygetvalue(_field, out var fieldvalue)) return false;
return _operator switch
{
"==" => equals(fieldvalue, _value),
">" => comparer.default.compare(fieldvalue, _value) > 0,
"<" => comparer.default.compare(fieldvalue, _value) < 0,
_ => false
};
}
}
// 规则集
public class ruleset
{
private readonly list<conditionexpression> _conditions = new();
public void addcondition(conditionexpression condition) => _conditions.add(condition);
public bool evaluate(businesscontext context)
{
return _conditions.all(c => c.interpret(context));
}
}
// 使用
var context = new businesscontext();
context.data["age"] = 25;
context.data["salary"] = 50000;
context.data["isemployed"] = true;
var rule = new ruleset();
rule.addcondition(new conditionexpression("age", ">", 18));
rule.addcondition(new conditionexpression("salary", ">", 40000));
rule.addcondition(new conditionexpression("isemployed", "==", true));
bool eligible = rule.evaluate(context); // true
五、解释器模式的进阶话题
1. 语法树构建
通常需要配合解析器将输入文本转换为抽象语法树(ast):
public class parser
{
public iexpression parse(string input)
{
// 简单实现 - 实际需要更复杂的词法/语法分析
if (input.contains("and"))
{
var parts = input.split(new[] {" and "}, stringsplitoptions.none);
return new andexpression(parse(parts[0]), parse(parts[1]));
}
else if (input.contains("or"))
{
var parts = input.split(new[] {" or "}, stringsplitoptions.none);
return new orexpression(parse(parts[0]), parse(parts[1]));
}
else
{
return new variableexpression(input.trim());
}
}
}
// 使用
var parser = new parser();
var expression = parser.parse("a and b or c");
2. 使用访问者模式遍历语法树
public interface iexpressionvisitor
{
void visit(variableexpression exp);
void visit(andexpression exp);
void visit(orexpression exp);
}
public class printvisitor : iexpressionvisitor
{
public void visit(variableexpression exp) => console.write(exp.name);
public void visit(andexpression exp)
{
console.write("(");
exp.left.accept(this);
console.write(" and ");
exp.right.accept(this);
console.write(")");
}
public void visit(orexpression exp)
{
console.write("(");
exp.left.accept(this);
console.write(" or ");
exp.right.accept(this);
console.write(")");
}
}
// 在表达式接口中添加accept方法
public interface iexpression
{
bool interpret(context context);
void accept(iexpressionvisitor visitor);
}
3. 解释器模式与编译器技术的区别
| 特性 | 解释器模式 | 编译器 |
|---|---|---|
| 执行方式 | 直接执行语法树 | 生成中间代码/机器码 |
| 效率 | 较低(每次解释) | 较高(预先编译) |
| 灵活性 | 高(可动态修改) | 低(编译后固定) |
| 实现复杂度 | 相对简单 | 复杂 |
| 适用场景 | 简单dsl、动态需求 | 通用编程语言 |
六、解释器模式的最佳实践
控制文法复杂度:
- 解释器模式适合相对简单的文法(bnf范式不超过一页)
- 复杂文法考虑使用解析器生成器(如antlr)
共享终结符:
- 终结符表达式通常是无状态的,可以共享实例
分离解析与解释:
- 使用单独解析器构建语法树
- 保持解释器专注于执行
考虑性能优化:
- 缓存解释结果
- 预编译常用表达式
合理使用组合:
- 与访问者模式结合遍历语法树
- 与享元模式共享终结符
七、解释器模式与其他模式的关系
与组合模式:
- 抽象语法树就是组合模式的应用
- 非终结符表达式是组合节点,终结符表达式是叶节点
与访问者模式:
- 访问者模式可用于在语法树上执行多种操作
- 分离解释逻辑与语法树结构
与享元模式:
- 共享终结符表达式实例
- 减少内存使用
与策略模式:
- 解释器模式可以看作是在语法树上应用的策略模式
八、现代替代方案
对于复杂语言处理,现代开发中更常用:
解析器生成器:
- antlr
- yacc/lex
表达式树:
- c#的
expression<t> - 动态构建和执行表达式
脚本引擎:
- roslyn脚本api
- lua、python等嵌入式脚本
总结一下:
解释器模式在c#中适用于:
- 特定领域语言:需要为特定领域定义简单语言
- 灵活规则系统:业务规则需要动态配置
- 数学表达式:需要解释执行公式
关键优势:
✅ 易于实现简单语言的解释执行
✅ 灵活扩展语法规则
✅ 分离语法定义与执行
适用限制:
❌ 不适合复杂文法(类爆炸问题)
❌ 性能不如编译执行
❌ 维护成本随文法复杂度增加
在实际开发中,应权衡需求复杂度,对于简单dsl可以使用解释器模式快速实现,对于复杂语言处理建议使用专业解析工具。
九、在uniry中的应用
示例1:简单数学表达式解释器
using unityengine;
using system.collections.generic;
// 抽象表达式
public abstract class expression
{
public abstract int interpret(dictionary<string, int> context);
}
// 终结符表达式 - 变量
public class variableexpression : expression
{
private string name;
public variableexpression(string name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public override int interpret(dictionary<string, int> context)
{
// 从上下文中获取变量值
if (context.containskey(name))
{
return context[name];
}
throw new system.exception($"变量 {name} 未定义");
}
}
// 终结符表达式 - 常量
public class constantexpression : expression
{
private int value;
public constantexpression(int value)
{
this.value = value;
}
public override int interpret(dictionary<string, int> context)
{
return value;
}
}
// 非终结符表达式 - 加法
public class addexpression : expression
{
private expression left;
private expression right;
public addexpression(expression left, expression right)
{
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
public override int interpret(dictionary<string, int> context)
{
return left.interpret(context) + right.interpret(context);
}
}
// 非终结符表达式 - 减法
public class subtractexpression : expression
{
private expression left;
private expression right;
public subtractexpression(expression left, expression right)
{
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
public override int interpret(dictionary<string, int> context)
{
return left.interpret(context) - right.interpret(context);
}
}
// 非终结符表达式 - 乘法
public class multiplyexpression : expression
{
private expression left;
private expression right;
public multiplyexpression(expression left, expression right)
{
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
public override int interpret(dictionary<string, int> context)
{
return left.interpret(context) * right.interpret(context);
}
}
// 表达式解析器
public class expressionparser
{
private dictionary<string, int> variables = new dictionary<string, int>();
// 解析表达式字符串
public expression parse(string expression)
{
// 这里简化处理,实际应用中需要更复杂的解析逻辑
if (expression.contains("+"))
{
string[] parts = expression.split('+');
return new addexpression(parse(parts[0]), parse(parts[1]));
}
else if (expression.contains("-"))
{
string[] parts = expression.split('-');
return new subtractexpression(parse(parts[0]), parse(parts[1]));
}
else if (expression.contains("*"))
{
string[] parts = expression.split('*');
return new multiplyexpression(parse(parts[0]), parse(parts[1]));
}
else if (int.tryparse(expression, out int value))
{
return new constantexpression(value);
}
else
{
return new variableexpression(expression);
}
}
// 设置变量值
public void setvariable(string name, int value)
{
variables[name] = value;
}
// 获取当前变量表
public dictionary<string, int> getcontext()
{
return variables;
}
}
// 测试代码
public class mathinterpretertest : monobehaviour
{
void start()
{
expressionparser parser = new expressionparser();
// 设置变量
parser.setvariable("x", 10);
parser.setvariable("y", 5);
// 解析并计算表达式
testexpression(parser, "x+y"); // 10 + 5 = 15
testexpression(parser, "x-y"); // 10 - 5 = 5
testexpression(parser, "x*y"); // 10 * 5 = 50
testexpression(parser, "x+y*2"); // 10 + (5 * 2) = 20
}
void testexpression(expressionparser parser, string expression)
{
expression exp = parser.parse(expression);
int result = exp.interpret(parser.getcontext());
debug.log($"{expression} = {result}");
}
}
示例2:简单ai行为脚本解释器
using unityengine;
using system.collections.generic;
// 抽象行为表达式
public abstract class aiactionexpression
{
public abstract void interpret(aicontext context);
}
// 移动行为
public class moveaction : aiactionexpression
{
private string direction;
private float distance;
public moveaction(string direction, float distance)
{
this.direction = direction.tolower();
this.distance = distance;
}
public override void interpret(aicontext context)
{
vector3 movevector = vector3.zero;
switch (direction)
{
case "forward":
movevector = context.aitransform.forward * distance;
break;
case "back":
movevector = -context.aitransform.forward * distance;
break;
case "left":
movevector = -context.aitransform.right * distance;
break;
case "right":
movevector = context.aitransform.right * distance;
break;
case "up":
movevector = context.aitransform.up * distance;
break;
case "down":
movevector = -context.aitransform.up * distance;
break;
}
context.aitransform.position += movevector;
debug.log($"ai移动: {direction} {distance}米");
}
}
// 等待行为
public class waitaction : aiactionexpression
{
private float seconds;
public waitaction(float seconds)
{
this.seconds = seconds;
}
public override void interpret(aicontext context)
{
debug.log($"ai等待: {seconds}秒");
// 实际游戏中可以使用协程实现等待
}
}
// 攻击行为
public class attackaction : aiactionexpression
{
private string target;
public attackaction(string target)
{
this.target = target;
}
public override void interpret(aicontext context)
{
debug.log($"ai攻击: {target}");
// 实际游戏中这里会实现攻击逻辑
}
}
// ai行为序列
public class actionsequence : aiactionexpression
{
private list<aiactionexpression> actions = new list<aiactionexpression>();
public void addaction(aiactionexpression action)
{
actions.add(action);
}
public override void interpret(aicontext context)
{
foreach (var action in actions)
{
action.interpret(context);
}
}
}
// ai上下文
public class aicontext
{
public transform aitransform { get; set; }
public dictionary<string, object> variables { get; } = new dictionary<string, object>();
}
// ai脚本解析器
public class aiscriptparser
{
public aiactionexpression parse(string script)
{
actionsequence sequence = new actionsequence();
// 分割脚本为多行
string[] lines = script.split(new[] { '\n', ';' }, system.stringsplitoptions.removeemptyentries);
foreach (string line in lines)
{
string trimmedline = line.trim();
if (string.isnullorempty(trimmedline)) continue;
// 分割命令和参数
string[] parts = trimmedline.split(new[] { ' ' }, system.stringsplitoptions.removeemptyentries);
if (parts.length == 0) continue;
string command = parts[0].tolower();
switch (command)
{
case "move":
if (parts.length >= 3)
{
string direction = parts[1];
if (float.tryparse(parts[2], out float distance))
{
sequence.addaction(new moveaction(direction, distance));
}
}
break;
case "wait":
if (parts.length >= 2 && float.tryparse(parts[1], out float seconds))
{
sequence.addaction(new waitaction(seconds));
}
break;
case "attack":
if (parts.length >= 2)
{
sequence.addaction(new attackaction(parts[1]));
}
break;
}
}
return sequence;
}
}
// ai控制器
public class aicontroller : monobehaviour
{
public string aiscript = @"
move forward 5
wait 2
attack player
move back 3
wait 1
";
private aicontext context;
private aiactionexpression behavior;
void start()
{
context = new aicontext { aitransform = transform };
aiscriptparser parser = new aiscriptparser();
behavior = parser.parse(aiscript);
// 执行ai脚本
behavior.interpret(context);
}
}
示例3:对话条件解释器
using unityengine;
using system.collections.generic;
// 抽象条件表达式
public abstract class conditionexpression
{
public abstract bool interpret(dialoguecontext context);
}
// 变量条件
public class variablecondition : conditionexpression
{
private string variablename;
private int expectedvalue;
private string comparison; // "==", ">", "<", etc.
public variablecondition(string variablename, string comparison, int expectedvalue)
{
this.variablename = variablename;
this.comparison = comparison;
this.expectedvalue = expectedvalue;
}
public override bool interpret(dialoguecontext context)
{
if (!context.variables.containskey(variablename))
{
debug.logwarning($"变量 {variablename} 未定义");
return false;
}
int actualvalue = context.variables[variablename];
switch (comparison)
{
case "==": return actualvalue == expectedvalue;
case "!=": return actualvalue != expectedvalue;
case ">": return actualvalue > expectedvalue;
case "<": return actualvalue < expectedvalue;
case ">=": return actualvalue >= expectedvalue;
case "<=": return actualvalue <= expectedvalue;
default:
debug.logwarning($"未知比较运算符: {comparison}");
return false;
}
}
}
// 逻辑与条件
public class andcondition : conditionexpression
{
private conditionexpression left;
private conditionexpression right;
public andcondition(conditionexpression left, conditionexpression right)
{
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
public override bool interpret(dialoguecontext context)
{
return left.interpret(context) && right.interpret(context);
}
}
// 逻辑或条件
public class orcondition : conditionexpression
{
private conditionexpression left;
private conditionexpression right;
public orcondition(conditionexpression left, conditionexpression right)
{
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
public override bool interpret(dialoguecontext context)
{
return left.interpret(context) || right.interpret(context);
}
}
// 非条件
public class notcondition : conditionexpression
{
private conditionexpression condition;
public notcondition(conditionexpression condition)
{
this.condition = condition;
}
public override bool interpret(dialoguecontext context)
{
return !condition.interpret(context);
}
}
// 对话上下文
public class dialoguecontext
{
public dictionary<string, int> variables { get; } = new dictionary<string, int>();
}
// 条件解析器
public class conditionparser
{
public conditionexpression parse(string conditionstr)
{
// 这里简化处理,实际应用中需要更复杂的解析逻辑
if (conditionstr.contains("&&"))
{
string[] parts = conditionstr.split(new[] { "&&" }, system.stringsplitoptions.removeemptyentries);
return new andcondition(parse(parts[0]), parse(parts[1]));
}
else if (conditionstr.contains("||"))
{
string[] parts = conditionstr.split(new[] { "||" }, system.stringsplitoptions.removeemptyentries);
return new orcondition(parse(parts[0]), parse(parts[1]));
}
else if (conditionstr.startswith("!"))
{
return new notcondition(parse(conditionstr.substring(1)));
}
else
{
// 解析变量条件 如: "health > 50"
string[] parts = conditionstr.split(new[] { ' ' }, system.stringsplitoptions.removeemptyentries);
if (parts.length == 3)
{
string varname = parts[0];
string op = parts[1];
if (int.tryparse(parts[2], out int value))
{
return new variablecondition(varname, op, value);
}
}
}
throw new system.exception($"无法解析条件: {conditionstr}");
}
}
// 对话选项
public class dialogueoption
{
public string text { get; }
public conditionexpression condition { get; }
public dialogueoption(string text, conditionexpression condition = null)
{
text = text;
condition = condition;
}
public bool isavailable(dialoguecontext context)
{
return condition == null || condition.interpret(context);
}
}
// 测试代码
public class dialogueconditiontest : monobehaviour
{
void start()
{
dialoguecontext context = new dialoguecontext();
context.variables["health"] = 75;
context.variables["haskey"] = 1;
context.variables["karma"] = -10;
conditionparser parser = new conditionparser();
testcondition(parser, context, "health > 50"); // true
testcondition(parser, context, "haskey == 1"); // true
testcondition(parser, context, "karma >= 0"); // false
testcondition(parser, context, "health > 50 && haskey == 1"); // true
testcondition(parser, context, "health > 50 || karma >= 0"); // true
testcondition(parser, context, "!haskey == 1"); // false
// 创建对话选项
dialogueoption option1 = new dialogueoption("攻击敌人", parser.parse("health > 50"));
dialogueoption option2 = new dialogueoption("和平解决", parser.parse("karma >= 0"));
dialogueoption option3 = new dialogueoption("逃跑", null); // 无条件
debug.log($"选项1可用: {option1.isavailable(context)}"); // true
debug.log($"选项2可用: {option2.isavailable(context)}"); // false
debug.log($"选项3可用: {option3.isavailable(context)}"); // true
}
void testcondition(conditionparser parser, dialoguecontext context, string conditionstr)
{
conditionexpression condition = parser.parse(conditionstr);
bool result = condition.interpret(context);
debug.log($"{conditionstr} = {result}");
}
}
在unity中的实现建议
- 结合scriptableobject:可以将表达式配置为scriptableobject,便于在编辑器中设置
- 使用解析器生成器:对于复杂文法,考虑使用antlr等解析器生成器
- 限制文法复杂度:保持解释的语言简单,避免过度设计
- 缓存解析结果:对于频繁使用的表达式,可以缓存解析结果提高性能
- 与事件系统结合:将解释结果转换为游戏事件,降低耦合度
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持代码网。







发表评论