前言
ajax (asynchronous javascript and xml) 封装是为了简化重复的异步请求代码,提高开发效率和代码复用性。下面我将介绍几种常见的 ajax 封装方式。
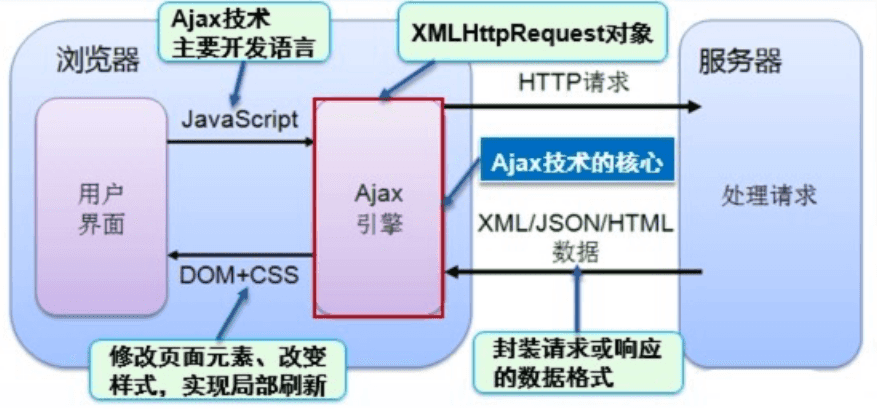
方法1. 基于原生 xmlhttprequest 的封装
xmlhttprequest。其主要特点如下:
- 实现动态不刷新,通过异步⽅式,提升⽤户体验,优化了浏览器和服务器之间的传输。
- 把⼀部分原本由服务器负担的⼯作转移到客户端,利⽤客户端闲置的资源进⾏处理,减轻服务器和带宽的负担,节约空间和成本。
- ⽆刷新更新⻚⾯,⽤户不⽤再像以前⼀样在服务器处理数据时,只能在死板的⽩屏前焦急的等待。ajax使⽤xmlhttprequest对象发送请求并得到服务器响应,在不需要重新载⼊整个⻚⾯的情况下,就可以通过dom及时将更新的内容显示在⻚⾯上。
/**
* 基于原生xhr的ajax封装
* @param {object} options 配置对象
* @param {string} options.url 请求地址
* @param {string} [options.method='get'] 请求方法
* @param {object} [options.data=null] 请求数据
* @param {object} [options.headers={}] 请求头
* @param {function} [options.success] 成功回调
* @param {function} [options.error] 失败回调
*/
function ajax(options) {
const xhr = new xmlhttprequest();
const method = options.method || 'get';
let url = options.url;
let data = options.data || null;
// 处理get请求的查询参数
if (method === 'get' && data) {
const params = new urlsearchparams();
for (const key in data) {
params.append(key, data[key]);
}
url += '?' + params.tostring();
data = null;
}
xhr.open(method, url, true);
// 设置请求头
if (options.headers) {
for (const key in options.headers) {
xhr.setrequestheader(key, options.headers[key]);
}
}
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (xhr.readystate === 4) {
if (xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) {
let response = xhr.responsetext;
try {
response = json.parse(response);
} catch (e) {}
options.success && options.success(response);
} else {
options.error && options.error(xhr.status, xhr.statustext);
}
}
};
xhr.onerror = function() {
options.error && options.error(-1, 'network error');
};
// 发送请求
if (data && typeof data === 'object') {
xhr.setrequestheader('content-type', 'application/json');
xhr.send(json.stringify(data));
} else {
xhr.send(data);
}
}
// 使用示例
ajax({
url: '/api/user',
method: 'post',
data: { name: 'john', age: 30 },
headers: {
'authorization': 'bearer token123'
},
success: function(response) {
console.log('success:', response);
},
error: function(status, statustext) {
console.error('error:', status, statustext);
}
});
方法2. 基于 fetch api 的封装
/**
* 基于fetch api的ajax封装
* @param {string} url 请求地址
* @param {object} [options={}] 请求配置
* @returns {promise} 返回promise对象
*/
function fetchajax(url, options = {}) {
const defaultoptions = {
method: 'get',
headers: {
'content-type': 'application/json'
},
credentials: 'same-origin', // 携带cookie
...options
};
// 处理get请求的查询参数
if (defaultoptions.method === 'get' && defaultoptions.body) {
const params = new urlsearchparams();
for (const key in defaultoptions.body) {
params.append(key, defaultoptions.body[key]);
}
url += '?' + params.tostring();
delete defaultoptions.body;
}
// 处理非get请求的body数据
if (defaultoptions.body && typeof defaultoptions.body === 'object') {
defaultoptions.body = json.stringify(defaultoptions.body);
}
return fetch(url, defaultoptions)
.then(async response => {
const data = await response.json().catch(() => ({}));
if (!response.ok) {
const error = new error(response.statustext);
error.response = response;
error.data = data;
throw error;
}
return data;
});
}
// 使用示例
fetchajax('/api/user', {
method: 'post',
body: { name: 'john', age: 30 },
headers: {
'authorization': 'bearer token123'
}
})
.then(data => console.log('success:', data))
.catch(err => console.error('error:', err));
方法 3. 基于 axios 风格的封装
class ajax {
constructor(baseurl = '', timeout = 10000) {
this.baseurl = baseurl;
this.timeout = timeout;
this.interceptors = {
request: [],
response: []
};
}
request(config) {
// 处理请求拦截器
let chain = [this._dispatchrequest, undefined];
this.interceptors.request.foreach(interceptor => {
chain.unshift(interceptor.fulfilled, interceptor.rejected);
});
this.interceptors.response.foreach(interceptor => {
chain.push(interceptor.fulfilled, interceptor.rejected);
});
let promise = promise.resolve(config);
while (chain.length) {
promise = promise.then(chain.shift(), chain.shift());
}
return promise;
}
_dispatchrequest(config) {
return new promise((resolve, reject) => {
const xhr = new xmlhttprequest();
let url = config.baseurl ? config.baseurl + config.url : config.url;
let data = config.data;
// 处理get请求参数
if (config.method === 'get' && data) {
const params = new urlsearchparams();
for (const key in data) {
params.append(key, data[key]);
}
url += '?' + params.tostring();
data = null;
}
xhr.timeout = config.timeout || 10000;
xhr.open(config.method, url, true);
// 设置请求头
if (config.headers) {
for (const key in config.headers) {
xhr.setrequestheader(key, config.headers[key]);
}
}
xhr.onload = function() {
if (xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) {
let response = xhr.responsetext;
try {
response = json.parse(response);
} catch (e) {}
resolve({
data: response,
status: xhr.status,
statustext: xhr.statustext,
headers: xhr.getallresponseheaders()
});
} else {
reject(new error(`request failed with status code ${xhr.status}`));
}
};
xhr.onerror = function() {
reject(new error('network error'));
};
xhr.ontimeout = function() {
reject(new error('timeout'));
};
// 发送请求
if (data && typeof data === 'object') {
xhr.setrequestheader('content-type', 'application/json');
xhr.send(json.stringify(data));
} else {
xhr.send(data);
}
});
}
get(url, config = {}) {
return this.request({
...config,
method: 'get',
url
});
}
post(url, data, config = {}) {
return this.request({
...config,
method: 'post',
url,
data
});
}
// 添加拦截器
userequestinterceptor(fulfilled, rejected) {
this.interceptors.request.push({ fulfilled, rejected });
return this.interceptors.request.length - 1;
}
useresponseinterceptor(fulfilled, rejected) {
this.interceptors.response.push({ fulfilled, rejected });
return this.interceptors.response.length - 1;
}
// 移除拦截器
ejectrequestinterceptor(id) {
if (this.interceptors.request[id]) {
this.interceptors.request.splice(id, 1);
}
}
ejectresponseinterceptor(id) {
if (this.interceptors.response[id]) {
this.interceptors.response.splice(id, 1);
}
}
}
// 使用示例
const api = new ajax('https://api.example.com');
// 添加请求拦截器
api.userequestinterceptor(config => {
config.headers = config.headers || {};
config.headers['authorization'] = 'bearer token123';
return config;
});
// 添加响应拦截器
api.useresponseinterceptor(response => {
console.log('response:', response);
return response.data;
}, error => {
console.error('error:', error);
return promise.reject(error);
});
// 发起请求
api.get('/user/123')
.then(data => console.log('user data:', data))
.catch(err => console.error('error:', err));
api.post('/user', { name: 'john', age: 30 })
.then(data => console.log('created user:', data))
.catch(err => console.error('error:', err));
4. 封装要点总结
统一接口:提供一致的调用方式,如get(), post()等方法
参数处理:
get请求自动拼接查询参数
post请求自动处理content-type
拦截器机制:支持请求/响应拦截
错误处理:统一错误处理逻辑
promise支持:返回promise便于链式调用
超时处理:设置合理的请求超时时间
扩展性:支持自定义配置和拦截器
5. 实际项目中的增强功能
1.自动重试机制:
function withretry(fn, retries = 3, delay = 1000) {
return function(...args) {
return new promise((resolve, reject) => {
function attempt(retrycount) {
fn(...args)
.then(resolve)
.catch(err => {
if (retrycount < retries) {
settimeout(() => attempt(retrycount + 1), delay);
} else {
reject(err);
}
});
}
attempt(0);
});
};
}
// 使用示例
const ajaxwithretry = withretry(ajax, 3, 1000);
2.请求取消功能:
function createcanceltoken() {
let cancel;
const token = new promise((resolve, reject) => {
cancel = reject;
});
return { token, cancel };
}
// 在请求中检查取消token
function ajaxwithcancel(options) {
const { token, cancel } = createcanceltoken();
const xhr = new xmlhttprequest();
const promise = new promise((resolve, reject) => {
// ...正常请求逻辑
// 检查取消
token.catch(err => {
xhr.abort();
reject(err);
});
});
return { promise, cancel };
}
3.请求缓存:
const cache = new map();
function cachedajax(options) {
const cachekey = json.stringify(options);
if (cache.has(cachekey)) {
return promise.resolve(cache.get(cachekey));
}
return ajax(options).then(response => {
cache.set(cachekey, response);
return response;
});
}
根据项目需求选择合适的封装方式,小型项目可使用简单封装,大型项目建议使用成熟的库如axios。
到此这篇关于ajax常见的几种封装方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关ajax封装方法内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论