安装
pip install psycopg2-binary
连接数据库
使用连接参数直接连接
import psycopg2
# 基本连接参数
conn_params = {
"dbname": "test",
"user": "postgres",
"password": "password",
"host": "localhost",
"port": "5432"
}
try:
conn = psycopg2.connect(**conn_params)
print("数据库连接成功")
# 执行数据库操作...
except psycopg2.error as e:
print(f"连接数据库失败: {e}")
finally:
if 'conn' in locals():
conn.close()
使用连接字符串 (dsn)
import psycopg2
# 连接字符串格式
dsn = "dbname=test user=postgres password=password host=localhost port=5432"
try:
conn = psycopg2.connect(dsn)
print("数据库连接成功")
# 执行数据库操作...
except psycopg2.error as e:
print(f"连接数据库失败: {e}")
finally:
if 'conn' in locals():
conn.close()
创建表
import psycopg2
conn = psycopg2.connect(host='127.0.0.1',
port='5432',
dbname="test",
user="postgres",
password="password")
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("""
create table students (
id serial primary key,
name varchar(100) not null,
class varchar(50) not null,
math_score numeric(5, 2) check (math_score >= 0 and math_score <= 100),
english_score numeric(5, 2) check (english_score >= 0 and english_score <= 100),
science_score numeric(5, 2) check (science_score >= 0 and science_score <= 100),
history_score numeric(5, 2) check (history_score >= 0 and history_score <= 100),
created_at timestamp default current_timestamp,
updated_at timestamp default current_timestamp
)
""")
conn.commit()
插入随机数据
import psycopg2
import random
from faker import faker
conn = psycopg2.connect(host='127.0.0.1',
port='5432',
dbname="test",
user="postgres",
password="password")
cursor = conn.cursor()
fake = faker('zh_cn')
# 准备随机数据
classes = ['一年一班', '一年二班', '二年一班', '二年二班', '三年一班', '三年二班']
students = []
count = 10
for _ in range(count):
name = fake.name()
class_name = random.choice(classes)
math = round(random.uniform(50, 100), 1)
english = round(random.uniform(50, 100), 1)
science = round(random.uniform(50, 100), 1)
history = round(random.uniform(50, 100), 1)
students.append((name, class_name, math, english, science, history))
# 插入数据
cursor.executemany("""
insert into students
(name, class, math_score, english_score, science_score, history_score)
values (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)
""", students)
conn.commit()
print(f"成功插入 {count} 条随机学生数据")
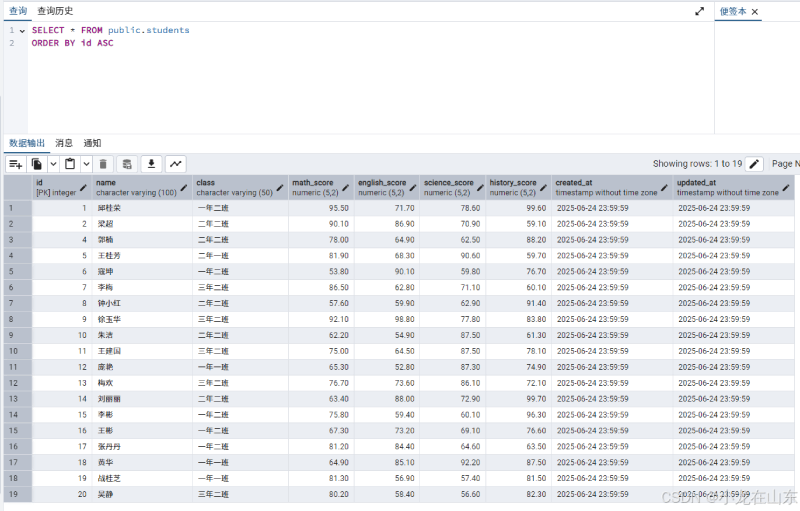
查询数据
def get_students_as_dict(dbname, user, password, host='localhost', port=5432):
"""以字典形式返回学生数据"""
try:
conn = psycopg2.connect(host=host,
port=port,
dbname=dbname,
user=user,
password=password)
# 使用dictcursor可以返回字典形式的结果
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor_factory=psycopg2.extras.dictcursor)
cursor.execute("""
select id, name, class,
math_score, english_score,
science_score, history_score
from students
limit 3
""")
print("\n字典形式的学生数据:")
for row in cursor:
# 可以直接通过列名访问
print(dict(row))
except psycopg2.error as e:
print(f"查询数据时出错: {e}")
finally:
if conn:
conn.close()
更改数据
import psycopg2
def update_student_score(dbname, user, password, student_id, subject, new_score, host='localhost', port=5432):
"""
更新指定学生的单科成绩
参数:
student_id: 学生id
subject: 科目名称 ('math_score', 'english_score', 'science_score', 'history_score')
new_score: 新成绩 (0-100)
"""
try:
conn = psycopg2.connect(
dbname=dbname,
user=user,
password=password,
host=host,
port=port
)
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 验证科目名称
valid_subjects = ['math_score', 'english_score', 'science_score', 'history_score']
if subject not in valid_subjects:
raise valueerror(f"无效科目名称,必须是: {', '.join(valid_subjects)}")
# 执行更新
cursor.execute(f"""
update students
set {subject} = %s
where id = %s
returning id, name, {subject}
""", (new_score, student_id))
updated_row = cursor.fetchone()
if updated_row:
conn.commit()
print(f"成功更新学生 {updated_row[1]} (id: {updated_row[0]}) 的{subject.replace('_', '')}为 {updated_row[2]}")
else:
print(f"未找到id为 {student_id} 的学生")
except psycopg2.error as e:
print(f"更新数据时出错: {e}")
conn.rollback()
except valueerror as e:
print(f"参数错误: {e}")
finally:
if conn:
conn.close()
# 使用示例
update_student_score(
dbname='test',
user='postgres',
password='password',
student_id=1, # 要更新的学生id
subject='math_score', # 要更新的科目
new_score=95.5, # 新成绩
host='localhost'
)
删除数据
import psycopg2
def delete_student_by_id(dbname, user, password, student_id, host='localhost', port=5432):
"""根据学生id删除记录"""
try:
conn = psycopg2.connect(
dbname=dbname,
user=user,
password=password,
host=host,
port=port
)
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 先查询学生是否存在
cursor.execute("""
select name, class from students where id = %s
""", (student_id,))
student = cursor.fetchone()
if not student:
print(f"未找到id为 {student_id} 的学生")
return
# 确认删除
confirm = input(f"确定要删除学生 {student[0]} (班级: {student[1]}) 吗? (y/n): ")
if confirm.lower() != 'y':
print("删除操作已取消")
return
# 执行删除
cursor.execute("""
delete from students
where id = %s
returning id, name, class
""", (student_id,))
deleted_student = cursor.fetchone()
if deleted_student:
conn.commit()
print(f"已删除学生: id {deleted_student[0]}, 姓名: {deleted_student[1]}, 班级: {deleted_student[2]}")
else:
print("删除失败,未找到该学生")
except psycopg2.error as e:
print(f"删除数据时出错: {e}")
conn.rollback()
finally:
if conn:
conn.close()
# 使用示例
delete_student_by_id(
dbname='test',
user='postgres',
password='password',
student_id=3, # 要删除的学生id
host='localhost'
)
到此这篇关于python使用psycopg2操作postgresql数据库的完全指南的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python psycopg2操作postgresql内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论