framework 中 reboot 流程
reboot 在 android 系统中主要通过物理按键或ui菜单进行触发,最终由 powermanager 执行 reboot 流程。下图描述了 reboot 执行时,framework 中相关线程的状态,最终将 reboot 相关信息设置到属性 sys.powerctl 中。framework 中的具体流程本文不再描述。
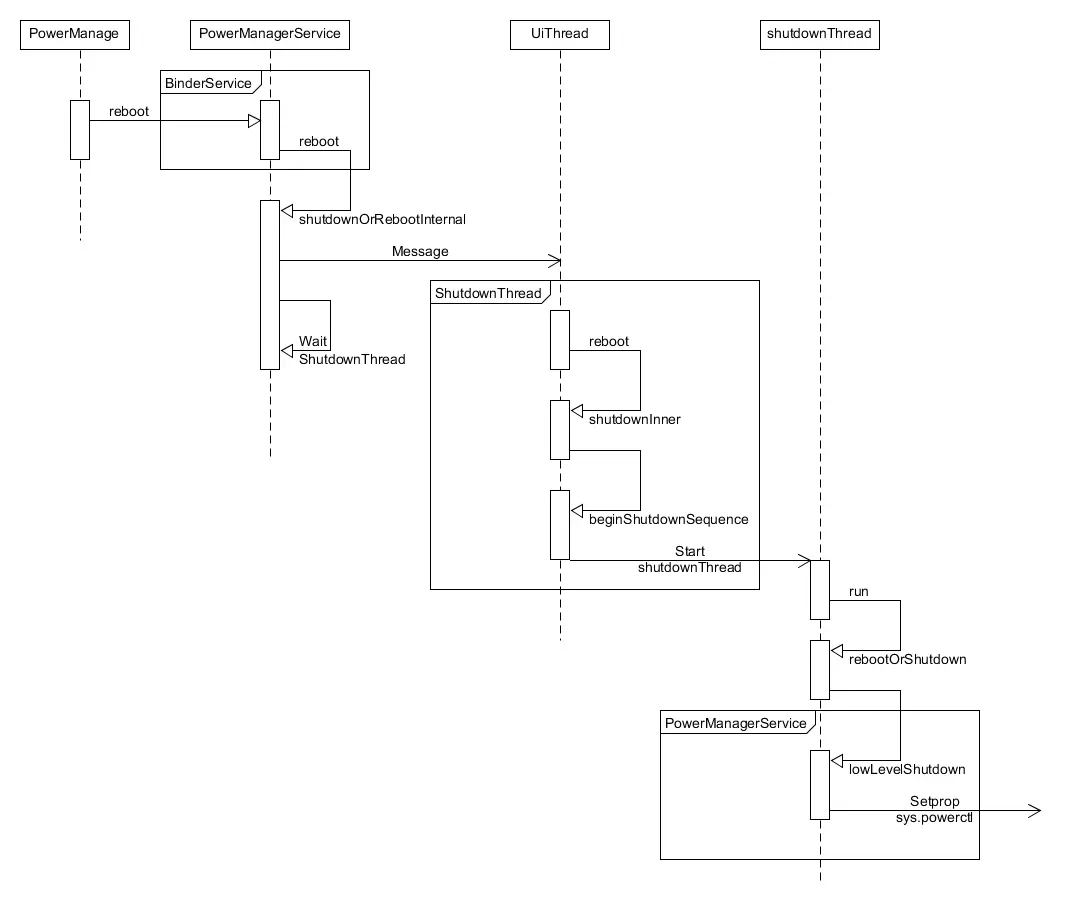
init 中 reboot 流程
android framework 处理完 reboot 流程后,更新了属性 sys.powerctl。init 正是依靠该属性来执行底层 reboot 动作。init 对 reboot 的处理主要为以下几个方面:
1,进程监控属性 sys.powerctl 的改变
/system/core/init/init.cpp
void propertychanged(const std::string& name, const std::string& value) {
// if the property is sys.powerctl, we bypass the event queue and immediately handle it.
// this is to ensure that init will always and immediately shutdown/reboot, regardless of
// if there are other pending events to process or if init is waiting on an exec service or
// waiting on a property.
// in non-thermal-shutdown case, 'shutdown' trigger will be fired to let device specific
// commands to be executed.
// sys.powerctl 做为特殊属性来处理,直接触发 shutdown/reboot 流程。
if (name == "sys.powerctl") {
trigger_shutdown(value);
}
if (property_triggers_enabled) {
actionmanager::getinstance().queuepropertychange(name, value);
wakemaininitthread();
}
prop_waiter_state.checkandresetwait(name, value);
}2,handlepowerctlmessage()对属性 sys.powerctl 进行解析
真正 shutdown/reboot 的流程在 handlepowerctlmessage(),对属性 sys.powerctl 进行解析,并存储相关信息。
/system/core/init/reboot.cpp
void handlepowerctlmessage(const std::string& command) {
unsigned int cmd = 0;
std::vector<std::string> cmd_params = split(command, ",");
std::string reboot_target = "";
bool run_fsck = false;
bool command_invalid = false;
bool userspace_reboot = false;
// 解析 shutdown 参数
if (cmd_params[0] == "shutdown") {
cmd = android_rb_poweroff;
if (cmd_params.size() >= 2) {
if (cmd_params[1] == "userrequested") { // shutdown,userrequested
// the shutdown reason is powermanager.shutdown_user_requested.
// run fsck once the file system is remounted in read-only mode.
run_fsck = true;
} else if (cmd_params[1] == "thermal") { // shutdown,thermal
// turn off sources of heat immediately.
turnoffbacklight();
// run_fsck is false to avoid delay
cmd = android_rb_thermoff;
}
}
// 解析 reboot 参数
} else if (cmd_params[0] == "reboot") {
cmd = android_rb_restart2;
if (cmd_params.size() >= 2) {
reboot_target = cmd_params[1];
if (reboot_target == "userspace") { // reboot,userspace
log(info) << "userspace reboot requested";
userspace_reboot = true;
}
// adb reboot fastboot should boot into bootloader for devices not
// supporting logical partitions.
if (reboot_target == "fastboot" &&
!android::base::getboolproperty("ro.boot.dynamic_partitions", false)) {
reboot_target = "bootloader"; // 在非动态分区的系统上,reboot后进入bootloader
}
// when rebooting to the bootloader notify the bootloader writing
// also the bcb.
if (reboot_target == "bootloader") { // reboot,bootloader
std::string err;
if (!write_reboot_bootloader(&err)) { // 更新bcb
log(error) << "reboot-bootloader: error writing "
"bootloader_message: "
<< err;
}
} else if (reboot_target == "recovery") { // reboot,recovery
bootloader_message boot = {};
if (std::string err; !read_bootloader_message(&boot, &err)) {
log(error) << "failed to read bootloader message: " << err;
}
// update the boot command field if it's empty, and preserve
// the other arguments in the bootloader message.
if (!commandispresent(&boot)) { // 更新bcb
strlcpy(boot.command, "boot-recovery", sizeof(boot.command));
if (std::string err; !write_bootloader_message(boot, &err)) {
log(error) << "failed to set bootloader message: " << err;
return;
}
}
} else if (reboot_target == "sideload" || reboot_target == "sideload-auto-reboot" ||
reboot_target == "fastboot") { // reboot,fastboot
std::string arg = reboot_target == "sideload-auto-reboot" ? "sideload_auto_reboot"
: reboot_target;
const std::vector<std::string> options = {
"--" + arg,
};
std::string err;
if (!write_bootloader_message(options, &err)) { // 更新bcb
log(error) << "failed to set bootloader message: " << err;
return;
}
reboot_target = "recovery"; // reboot后进入recovery
}
// if there are additional parameter, pass them along
for (size_t i = 2; (cmd_params.size() > i) && cmd_params[i].size(); ++i) {
reboot_target += "," + cmd_params[i];
}
}
} else {
command_invalid = true;
}
if (command_invalid) {
log(error) << "powerctl: unrecognized command '" << command << "'";
return;
}
// we do not want to process any messages (queue'ing triggers, shutdown messages, control
// messages, etc) from properties during reboot.
stopsendingmessages(); // 停止所有的属性处理
if (userspace_reboot) { // reboot,userspace 执行用户空间重启,并不重启整个系统
handleuserspacereboot();
return;
}
log(info) << "clear action queue and start shutdown trigger";
actionmanager::getinstance().clearqueue(); // 清空init action队列
// queue shutdown trigger first
actionmanager::getinstance().queueeventtrigger("shutdown"); // 执行init中的shutdown action
// queue built-in shutdown_done
auto shutdown_handler = [cmd, command, reboot_target, run_fsck](const builtinarguments&) {
doreboot(cmd, command, reboot_target, run_fsck); // 执行 shutdown/reboot 动作
return result<void>{};
};
actionmanager::getinstance().queuebuiltinaction(shutdown_handler, "shutdown_done");
entershutdown(); // 清理相关资源
}3,doreboot() 执行 shutdown/reboot 动作
/system/core/init/reboot.cpp
static void doreboot(unsigned int cmd, const std::string& reason, const std::string& reboot_target,
bool run_fsck) {
timer t;
log(info) << "reboot start, reason: " << reason << ", reboot_target: " << reboot_target;
bool is_thermal_shutdown = cmd == android_rb_thermoff;
// 配置shutdown timeout时间,缺省是6秒
auto shutdown_timeout = 0ms;
if (!shutdown_zero_timeout) {
constexpr unsigned int shutdown_timeout_default = 6;
constexpr unsigned int max_thermal_shutdown_timeout = 3;
auto shutdown_timeout_final = android::base::getuintproperty("ro.build.shutdown_timeout",
shutdown_timeout_default);
if (is_thermal_shutdown && shutdown_timeout_final > max_thermal_shutdown_timeout) {
shutdown_timeout_final = max_thermal_shutdown_timeout;
}
shutdown_timeout = std::chrono::seconds(shutdown_timeout_final);
}
......
// start a thread to monitor init shutdown process
// 启动一个reboot监控线程
log(info) << "create reboot monitor thread.";
bool reboot_monitor_run = true;
std::thread reboot_monitor_thread(&rebootmonitorthread, cmd, reboot_target, &reboot_semaphore,
shutdown_timeout, &reboot_monitor_run);
reboot_monitor_thread.detach();
......
// 保存reboot原因到属性中
std::vector<std::string> reasons = split(reason, ",");
if (reasons.size() >= 2 && reasons[0] == "reboot" &&
(reasons[1] == "recovery" || reasons[1] == "bootloader" || reasons[1] == "cold" ||
reasons[1] == "hard" || reasons[1] == "warm")) {
skip = strlen("reboot,");
}
persistrebootreason(reason.c_str() + skip, true);
......
// 安全关闭watchdogd
const std::set<std::string> to_starts{"watchdogd"};
std::set<std::string> stop_first;
for (const auto& s : servicelist::getinstance()) {
......
}
// remaining operations (specifically fsck) may take a substantial duration
if (cmd == android_rb_poweroff || is_thermal_shutdown) {
turnoffbacklight(); // 先关背光
}
// 显示shutdown animation
service* boot_anim = servicelist::getinstance().findservice("bootanim");
service* surface_flinger = servicelist::getinstance().findservice("surfaceflinger");
if (boot_anim != nullptr && surface_flinger != nullptr && surface_flinger->isrunning()) {
......
}
// optional shutdown step
// 1. terminate all services except shutdown critical ones. wait for delay to finish
if (shutdown_timeout > 0ms) { // 使用sigterm终止所有非关键服务
stopservicesandlogviolations(stop_first, shutdown_timeout / 2, true /* sigterm */);
}
// send sigkill to ones that didn't terminate cleanly.
stopservicesandlogviolations(stop_first, 0ms, false /* sigkill */); // 使用sigkill终止所有非关键服务
subcontextterminate();
// reap subcontext pids.
reapanyoutstandingchildren();
// 3. send volume abort_fuse and volume shutdown to vold
service* vold_service = servicelist::getinstance().findservice("vold");
if (vold_service != nullptr && vold_service->isrunning()) {
// manually abort fuse connections, since the fuse daemon is already dead
// at this point, and unmounting it might hang.
callvdc("volume", "abort_fuse");
callvdc("volume", "shutdown");
vold_service->stop(); // 关闭vold服务
} else {
log(info) << "vold not running, skipping vold shutdown";
}
// logcat stopped here
stopservices(kdebuggingservices, 0ms, false /* sigkill */);
// 4. sync, try umount, and optionally run fsck for user shutdown
{
timer sync_timer;
log(info) << "sync() before umount...";
sync(); // 同步文件系统
log(info) << "sync() before umount took" << sync_timer;
}
// 5. drop caches and disable zram backing device, if exist
killzrambackingdevice(); // kill zram服务
log(info) << "ready to unmount apexes. so far shutdown sequence took " << t;
// 6. unmount active apexes, otherwise they might prevent clean unmount of /data.
if (auto ret = unmountallapexes(); !ret.ok()) {
log(error) << ret.error();
}
umountstat stat = // unmount
tryumountandfsck(cmd, run_fsck, shutdown_timeout - t.duration(), &reboot_semaphore);
// follow what linux shutdown is doing: one more sync with little bit delay
{
timer sync_timer;
log(info) << "sync() after umount...";
sync(); // 再次同步文件系统
log(info) << "sync() after umount took" << sync_timer;
}
if (!is_thermal_shutdown) std::this_thread::sleep_for(100ms);
logshutdowntime(stat, &t);
// send signal to terminate reboot monitor thread.
reboot_monitor_run = false;
sem_post(&reboot_semaphore);
// reboot regardless of umount status. if umount fails, fsck after reboot will fix it.
rebootsystem(cmd, reboot_target); // 执行系统reboot
abort();
}4,通过rebootsystem() 执行系统 reboot 调用
/system/core/init/reboot_utils.cpp
void __attribute__((noreturn)) rebootsystem(unsigned int cmd, const std::string& reboottarget) {
log(info) << "reboot ending, jumping to kernel";
if (!isrebootcapable()) {
// on systems where init does not have the capability of rebooting the
// device, just exit cleanly.
exit(0);
}
switch (cmd) {
case android_rb_poweroff: // 执行关机
reboot(rb_power_off);
break;
case android_rb_restart2: // 执行重启
syscall(__nr_reboot, linux_reboot_magic1, linux_reboot_magic2,
linux_reboot_cmd_restart2, reboottarget.c_str());
break;
case android_rb_thermoff: // 过热保护,根据属性来执行关机或重起
if (android::base::getboolproperty("ro.thermal_warmreset", false)) {
log(info) << "try to trigger a warm reset for thermal shutdown";
static constexpr const char kthermalshutdowntarget[] = "shutdown,thermal";
syscall(__nr_reboot, linux_reboot_magic1, linux_reboot_magic2,
linux_reboot_cmd_restart2, kthermalshutdowntarget);
} else {
reboot(rb_power_off);
}
break;
}
// in normal case, reboot should not return.
plog(error) << "reboot call returned";
abort();
}属性 sys.powerctl 的值决定了shutdown/reboot的行为,其格式为:[mode],[reason]。mode 为 reboot 或 shutdown,常见reason如下:
| shutdown,[reason] | userrequested | thermal | <null> |
|---|---|---|---|
| 用户请求关机,需要运行fsck检查 | 温度异常引起的关机 | 执行基本关机流程 |
| reboot,[reason] | userspace | fastboot | bootloader | recovery | sideload | sideload-auto-reboot | cold / warm / hard / <null> |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 用户空间软重启,用于更新应用 | 重启到fastboot模式。不支持逻辑分区时,重启到bootloader模式。写入bcb | 重启到bootloader模式。写入bcb | 重启进入recvoery。写入bcb | 重启进入recovery,执行sideload,用于本地升级系统。写入bcb | sideload完成后自动重启。写入bcb | 执行基本重启流程 |
内核中 reboot 流程
内核中的入口
android native 中最终执行了 reboot 系统调用,对应在内核中的入口为:
/kernel/reboot.c
syscall_define4(reboot, int, magic1, int, magic2, unsigned int, cmd,
void __user *, arg)
{
......
mutex_lock(&system_transition_mutex);
switch (cmd) {
case linux_reboot_cmd_restart:
kernel_restart(null);
break;
........
case linux_reboot_cmd_power_off: // 关机
kernel_power_off();
do_exit(0);
break;
case linux_reboot_cmd_restart2: // 重启
ret = strncpy_from_user(&buffer[0], arg, sizeof(buffer) - 1);
if (ret < 0) {
ret = -efault;
break;
}
buffer[sizeof(buffer) - 1] = '\0';
kernel_restart(buffer);
break;
........
}kernel_restart() 完成重启
内核通过 kernel_power_off() 完成关机动作,通过 kernel_restart() 完成重启动作。
/kernel/reboot.c
void kernel_restart(char *cmd)
{
kernel_restart_prepare(cmd); // 执行重启的准备工作:调用reboot通知队列,关闭usermodehelper,关闭所有设备
migrate_to_reboot_cpu(); // 迁移所有任务到cpu0上
syscore_shutdown(); // 关闭syscore设备
if (!cmd)
pr_emerg("restarting system\n");
else
pr_emerg("restarting system with command '%s'\n", cmd);
kmsg_dump(kmsg_dump_shutdown);
machine_restart(cmd); // 调用machine_restart()
}
export_symbol_gpl(kernel_restart);
......
void kernel_power_off(void)
{
kernel_shutdown_prepare(system_power_off); // 执行重启的准备工作:调用reboot通知队列,关闭usermodehelper,关闭所有设备
if (pm_power_off_prepare)
pm_power_off_prepare();
migrate_to_reboot_cpu(); // 迁移所有任务到cpu0上
syscore_shutdown(); // 关闭syscore设备
pr_emerg("power down\n");
kmsg_dump(kmsg_dump_shutdown);
machine_power_off(); // 调用machine_power_off()
}
export_symbol_gpl(kernel_power_off);reboot 和 power off 的大致流程
reboot 和 power off 的大致流程是一样的,主要区别在调用reboot通知队列的传参不同和machine执行函数不同。这里简单看一下 arm64 的 machine_restart() 函数。
/arch/arm64/kernel/process.c
void machine_restart(char *cmd)
{
/* disable interrupts first */
local_irq_disable(); // 关闭中断
smp_send_stop(); // 停止当前处理器外的所有处理器
/*
* updatecapsule() depends on the system being reset via
* resetsystem().
*/
if (efi_enabled(efi_runtime_services))
efi_reboot(reboot_mode, null); // efi系统时
/* now call the architecture specific reboot code. */
do_kernel_restart(cmd); // 调用restart处理队列
/*
* whoops - the architecture was unable to reboot.
*/
printk("reboot failed -- system halted\n");
while (1);
}
/kernel/reboot.c
/**
* do_kernel_restart - execute kernel restart handler call chain
*
* calls functions registered with register_restart_handler.
*
* expected to be called from machine_restart as last step of the restart
* sequence.
*
* restarts the system immediately if a restart handler function has been
* registered. otherwise does nothing.
*/
void do_kernel_restart(char *cmd)
{
atomic_notifier_call_chain(&restart_handler_list, reboot_mode, cmd);
}内核中的 reboot 流程比较简单,核心就是处理内核、芯片、外设的状态,然后进行重启。
reboot 后的流程
重启后,硬件相当于重新上电,最先进入 bootloader,bootloader 会根据 reboot reason 进入到不同的系统状态。通常来说,bootloader 会分为多级,每家芯片原厂的实现都会有些区别,这里不去分析客制化的代码,只看一下 android 在 u-boot 中对 reboot 的处理。
/u-boot/common/android_bootloader.c
int android_bootloader_boot_flow(const char* iface_str,
const char* dev_str,
struct blk_desc *dev_desc,
const struct disk_partition *misc_part_info,
const char *slot,
bool verify,
unsigned long kernel_address,
struct blk_desc *persistant_dev_desc)
{
......
/* determine the boot mode and clear its value for the next boot if
* needed.
*/
// 根据misc分区信息获取启动模式
mode = android_bootloader_load_and_clear_mode(dev_desc, misc_part_info);
printf("android: reboot reason: \"%s\"\n", android_boot_mode_str(mode));
// todo (rammuthiah) fastboot isn't suported on cuttlefish yet.
// once it is, these lines can be removed.
if (mode == android_boot_mode_bootloader) {
mode = android_boot_mode_normal;
}
bool normal_boot = (mode == android_boot_mode_normal);
switch (mode) {
case android_boot_mode_normal: // 正常启动
#ifdef config_android_system_as_root
/* in normal mode, we load the kernel from "boot" but append
* "skip_initramfs" to the cmdline to make it ignore the
* recovery initramfs in the boot partition.
*/
mode_cmdline = "skip_initramfs"; // system-as-root时跳过boot分区中的initramfs
#endif
break;
case android_boot_mode_recovery: // 进入recovery
#if defined(config_android_system_as_root) || defined(config_android_uses_recovery_as_boot)
/* in recovery mode we still boot the kernel from "boot" but
* don't skip the initramfs so it boots to recovery.
* if on android device using recovery as boot, there is no
* recovery partition.
*/
// system-as-root时使用boot分区中的initramfs,recovery-as-root时没有recovery分区
#else
boot_partition = android_partition_recovery;
#endif
break;
case android_boot_mode_bootloader: // 进入bootloader·
/* bootloader mode enters fastboot. if this operation fails we
* simply return since we can't recover from this situation by
* switching to another slot.
*/
return android_bootloader_boot_bootloader(); // 启动进入bootloader
}
......
/* load the kernel from the desired "boot" partition. */
// 获取boot分区信息,用于加载kernel
boot_part_num =
android_part_get_info_by_name_suffix(dev_desc, boot_partition,
slot_suffix, &boot_part_info);
/* load the vendor boot partition if there is one. */
// 获取vendor boot分区信息。当使用gki时,boot分区存储gki kernel,vendor boot供应商客制化的boot代码
vendor_boot_part_num =
android_part_get_info_by_name_suffix(dev_desc, vendor_boot_partition,
slot_suffix,
&vendor_boot_part_info);
struct disk_partition *bootconfig_part_info_ptr = null;
......
// 加载boot镜像
struct andr_boot_info* boot_info = android_image_load(dev_desc, &boot_part_info,
vendor_boot_part_info_ptr,
kernel_address, slot_suffix, normal_boot, avb_bootconfig,
persistant_dev_desc, bootconfig_part_info_ptr,
verified_boot_img, verified_vendor_boot_img);
......
/* assemble the command line */
// 整合boot信息到command line中,传递给kernel
command_line = android_assemble_cmdline(slot_suffix, mode_cmdline, normal_boot,
android_image_get_kernel_cmdline(boot_info),
android_image_is_bootconfig_used(boot_info),
avb_cmdline);
env_set("bootargs", command_line);
debug("android: bootargs: \"%s\"\n", command_line);
android_bootloader_boot_kernel(boot_info); // 启动进入kernel
......
}bootloader 的启动流程也比较清晰,先解析启动需要的信息,然后加载镜像进行启动。启动信息是通过 misc 分区读取的,misc 分区存储的正是 android 系统关机过程中需要更新的 bcb。
bcb(bootloader control block)是 android 系统中定义的一个启动控制区域,以 raw 格式进行存储,用于在 android 用户空间和 android 兼容的 bootloader 之间交换交换信息。在 bootloader 中,bcb 的读写代码如下,
/u-boot/common/android_bootloader.c
static int android_bootloader_message_load(
struct blk_desc *dev_desc,
const struct disk_partition *part_info,
struct bootloader_message *message)
{
ulong message_blocks = sizeof(struct bootloader_message) /
part_info->blksz;
if (message_blocks > part_info->size) {
printf("misc partition too small.\n");
return -1;
}
if (blk_dread(dev_desc, part_info->start, message_blocks, message) !=
message_blocks) {
printf("could not read from misc partition\n");
return -1;
}
debug("android: loaded bcb, %lu blocks.\n", message_blocks);
return 0;
}
static int android_bootloader_message_write(
struct blk_desc *dev_desc,
const struct disk_partition *part_info,
struct bootloader_message *message)
{
ulong message_blocks = sizeof(struct bootloader_message) /
part_info->blksz;
if (message_blocks > part_info->size) {
printf("misc partition too small.\n");
return -1;
}
if (blk_dwrite(dev_desc, part_info->start, message_blocks, message) !=
message_blocks) {
printf("could not write to misc partition\n");
return -1;
}
debug("android: wrote new bcb, %lu blocks.\n", message_blocks);
return 0;
}
......
static enum android_boot_mode android_bootloader_load_and_clear_mode(
struct blk_desc *dev_desc,
const struct disk_partition *misc_part_info)
{
struct bootloader_message bcb;
#ifdef config_fastboot
char *bootloader_str;
/* check for message from bootloader stored in ram from a previous boot.
*/
bootloader_str = (char *)config_fastboot_buf_addr; // fastboot模式先先检查ram中的boot信息
if (!strcmp("reboot-bootloader", bootloader_str)) {
bootloader_str[0] = '\0';
return android_boot_mode_bootloader;
}
#endif
/* check and update the bcb message if needed. */
// 从misc分区中加载bcb信息
if (android_bootloader_message_load(dev_desc, misc_part_info, &bcb) <
0) {
printf("warning: unable to load the bcb.\n");
return android_boot_mode_normal;
}
// bootonce-bootloader意味着要启动计入bootloader,此时擦除bcb内容。
if (!strcmp("bootonce-bootloader", bcb.command)) {
/* erase the message in the bcb since this value should be used
* only once.
*/
memset(bcb.command, 0, sizeof(bcb.command));
android_bootloader_message_write(dev_desc, misc_part_info,
&bcb);
return android_boot_mode_bootloader;
}
if (!strcmp("boot-recovery", bcb.command))
return android_boot_mode_recovery;
return android_boot_mode_normal;
}bcb在 android bootloader 中定义为一个结构体数据,在 flash 中以 raw 格式存储。其结构定义为,
/u-boot/include/android_bootloader_message.h
// spaces used by misc partition are as below:
// 0 - 2k for bootloader_message
// 2k - 16k used by vendor's bootloader (the 2k - 4k range may be optionally used
// as bootloader_message_ab struct)
// 16k - 64k used by uncrypt and recovery to store wipe_package for a/b devices
// note that these offsets are admitted by bootloader,recovery and uncrypt, so they
// are not configurable without changing all of them.
static const size_t bootloader_message_offset_in_misc = 0;
static const size_t wipe_package_offset_in_misc = 16 * 1024;
/* bootloader message (2-kib)
*
* this structure describes the content of a block in flash
* that is used for recovery and the bootloader to talk to
* each other.
*
* the command field is updated by linux when it wants to
* reboot into recovery or to update radio or bootloader firmware.
* it is also updated by the bootloader when firmware update
* is complete (to boot into recovery for any final cleanup)
*
* the status field was used by the bootloader after the completion
* of an "update-radio" or "update-hboot" command, which has been
* deprecated since froyo.
*
* the recovery field is only written by linux and used
* for the system to send a message to recovery or the
* other way around.
*
* the stage field is written by packages which restart themselves
* multiple times, so that the ui can reflect which invocation of the
* package it is. if the value is of the format "#/#" (eg, "1/3"),
* the ui will add a simple indicator of that status.
*
* we used to have slot_suffix field for a/b boot control metadata in
* this struct, which gets unintentionally cleared by recovery or
* uncrypt. move it into struct bootloader_message_ab to avoid the
* issue.
*/
struct bootloader_message {
char command[32];
char status[32];
char recovery[768];
// the 'recovery' field used to be 1024 bytes. it has only ever
// been used to store the recovery command line, so 768 bytes
// should be plenty. we carve off the last 256 bytes to store the
// stage string (for multistage packages) and possible future
// expansion.
char stage[32];
// the 'reserved' field used to be 224 bytes when it was initially
// carved off from the 1024-byte recovery field. bump it up to
// 1184-byte so that the entire bootloader_message struct rounds up
// to 2048-byte.
char reserved[1184];
};bcb主要的功能如下
- 实现 android 特定的 bootloader 流程。
- 在用户空间和 bootloader 之间传递
boot reason,并控制对应的行为。 - 传递 recovery 系统需要的 commands。
android 用户空间(normal / recovery) 也是读写bcb来控制启动行为,如上文中 init 的 reboot 过程中就会更新bcb。bcb的读写函数如下,
/bootable/recovery/bootloader_message/bootloader_message.cpp
bool read_bootloader_message_from(bootloader_message* boot, const std::string& misc_blk_device,
std::string* err) {
return read_misc_partition(boot, sizeof(*boot), misc_blk_device,
bootloader_message_offset_in_misc, err);
}
// 从misc分区读取bcb
bool read_bootloader_message(bootloader_message* boot, std::string* err) {
std::string misc_blk_device = get_misc_blk_device(err);
if (misc_blk_device.empty()) {
return false;
}
return read_bootloader_message_from(boot, misc_blk_device, err);
}
bool write_bootloader_message_to(const bootloader_message& boot, const std::string& misc_blk_device,
std::string* err) {
return write_misc_partition(&boot, sizeof(boot), misc_blk_device,
bootloader_message_offset_in_misc, err);
}
// 写bcb到misc分区
bool write_bootloader_message(const bootloader_message& boot, std::string* err) {
std::string misc_blk_device = get_misc_blk_device(err);
if (misc_blk_device.empty()) {
return false;
}
return write_bootloader_message_to(boot, misc_blk_device, err);
}
// 清空bsc
bool clear_bootloader_message(std::string* err) {
bootloader_message boot = {};
return write_bootloader_message(boot, err);
}
// 写recovery commands到bcb
bool write_bootloader_message(const std::vector<std::string>& options, std::string* err) {
bootloader_message boot = {};
update_bootloader_message_in_struct(&boot, options);
return write_bootloader_message(boot, err);
}
bool write_bootloader_message_to(const std::vector<std::string>& options,
const std::string& misc_blk_device, std::string* err) {
bootloader_message boot = {};
update_bootloader_message_in_struct(&boot, options);
return write_bootloader_message_to(boot, misc_blk_device, err);
}
// 更新recovery commands
bool update_bootloader_message(const std::vector<std::string>& options, std::string* err) {
bootloader_message boot;
if (!read_bootloader_message(&boot, err)) {
return false;
}
update_bootloader_message_in_struct(&boot, options);
return write_bootloader_message(boot, err);
}
bool update_bootloader_message_in_struct(bootloader_message* boot,
const std::vector<std::string>& options) {
if (!boot) return false;
// replace the command & recovery fields.
memset(boot->command, 0, sizeof(boot->command));
memset(boot->recovery, 0, sizeof(boot->recovery));
strlcpy(boot->command, "boot-recovery", sizeof(boot->command));
std::string recovery = "recovery\n";
for (const auto& s : options) {
recovery += s;
if (s.back() != '\n') {
recovery += '\n';
}
}
strlcpy(boot->recovery, recovery.c_str(), sizeof(boot->recovery));
return true;
}
// 将重启到bootloader的命令写入到bcb,这里是bootonce-bootloader
bool write_reboot_bootloader(std::string* err) {
bootloader_message boot;
if (!read_bootloader_message(&boot, err)) {
return false;
}
if (boot.command[0] != '\0') {
*err = "bootloader command pending.";
return false;
}
strlcpy(boot.command, "bootonce-bootloader", sizeof(boot.command));
return write_bootloader_message(boot, err);
}以上就是android系统中底层reboot流程的详细内容,更多关于android系统中底层reboot流程的资料请关注代码网其它相关文章!





发表评论