python爬虫用到的两个主要的库是:bs4和request,request用于发起请求,而bs4用于网页元素解析。
以阮一峰老师的博客为例,每周最喜欢的是科学爱好者周刊中的“言论”不分,以 科技爱好者周刊(第 253 期)为例,让我们来看看能不能将言论部分提取出来。
import requests
from bs4 import beautifulsoup
url = "http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2023/05/weekly-issue-253.html"
response = requests.get(url)
soup = beautifulsoup(response.content, "html.parser")
first_tag = soup.find("h2", string="言论")
next_sibling = first_tag.find_next_sibling()
content1 = ""
while next_sibling.name != "h2":
content1 += str(next_sibling.get_text())
# content1 += str(next_sibling)
content1 += "\n\n"
next_sibling = next_sibling.find_next_sibling()
print(content1)
执行结果:
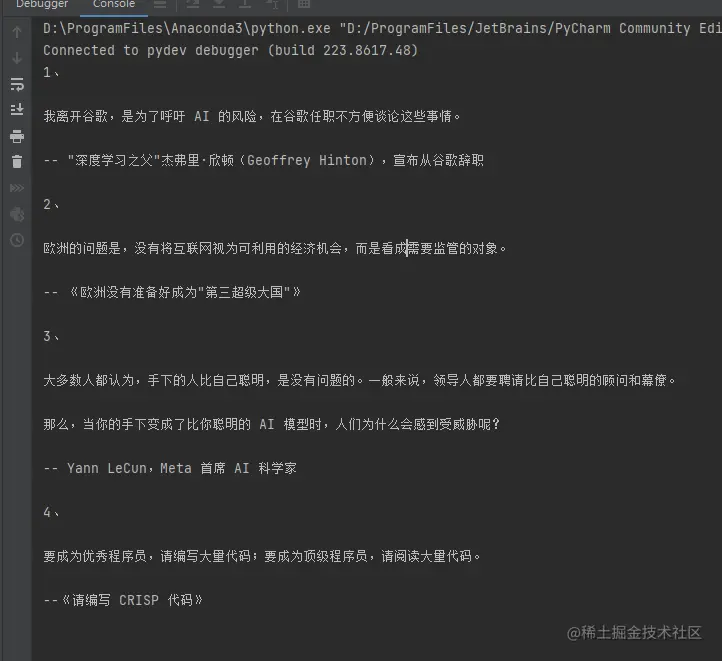
用到的重要函数是查找某个tag,获取某个tag的下一个tag函数:
find与find_all
函数定义如下:
def find(self, name=none, attrs={}, recursive=true, text=none,
**kwargs):
"""look in the children of this pageelement and find the first
pageelement that matches the given criteria.
all find_* methods take a common set of arguments. see the online documentation for detailed explanations.
:param name: a filter on tag name. :param attrs: a dictionary of filters on attribute values. :param recursive: if this is true, find() will perform a recursive search of this pageelement's children. otherwise, only the direct children will be considered. :param limit: stop looking after finding this many results. :kwargs: a dictionary of filters on attribute values. :return: a pageelement.
:rtype: bs4.element.pageelement
"""
r = none
l = self.find_all(name, attrs, recursive, text, 1, **kwargs)
if l:
r = l[0]
return r
def find_all(self, name=none, attrs={}, recursive=true, text=none,
limit=none, **kwargs):
"""look in the children of this pageelement and find all
pageelements that match the given criteria.
all find_* methods take a common set of arguments. see the online documentation for detailed explanations.
:param name: a filter on tag name. :param attrs: a dictionary of filters on attribute values. :param recursive: if this is true, find_all() will perform a recursive search of this pageelement's children. otherwise, only the direct children will be considered. :param limit: stop looking after finding this many results. :kwargs: a dictionary of filters on attribute values. :return: a resultset of pageelements.
:rtype: bs4.element.resultset
"""
generator = self.descendants
if not recursive:
generator = self.children
return self._find_all(name, attrs, text, limit, generator, **kwargs)
find 返回的是一个元素,find_all返回的是一个列表,举例说明比较清晰。
允许传入的参数包括:
1.字符串:tag的名称,如h2, p, b, a等等分别表示查找<h2>, <p>, <b>, <a>等标签。 如:
soup.find_all('b')
# [<b>这里加粗</b>]
2.正则表达式
# 导入包
import re
for tag in soup.find_all(re.compile("^b")):
print(tag.name)
# 结果会找出 body, b等b开头的标签
.3列表:与列表中任一元素匹配的内容返回
soup.find_all(["a", "b"]) # 输出: [<b>加粗</b>, # <a class="ddd" href="http://xxx" rel="external nofollow" >xxx</a> ]
4.true: 返回所有非字符串节点。
5.方法:传入的方法接受唯一参数:元素,并返回true或者false,若元素计算的值为true,则返回。
# 判断一个tag有class属性,但是没有id属性
def has_class_but_no_id(tag):
return tag.has_attr('class') and not tag.has_attr('id')
# 使用方式
soup.find_all(has_class_but_no_id)
6.对元素指定判断函数:
# 查找所有href标签不是https的a标签
def not_https(href):
return href and not re.compile("https").search(href)
soup.find_all(href=not_https)
通过上述第5种和第6种方法,可以构造很复杂的tag过滤函数,从而实现过滤目的。
其他相关搜索函数如下:
find_next_sibling 返回后面的第一个同级tag节点 find_previous_sibling 返回前面的第一个同级tag节点 find_next 后面第一个tag节点 find_previous 前面第一个tag节点
更多内容可以在bs4官方文档中查看。
到此这篇关于python实现获取网页信息并解析的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python获取网页信息内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!







发表评论