一、基础逻辑运算符
python 包含三个核心逻辑运算符:
| 运算符 | 描述 | 示例 | 结果 |
|---|---|---|---|
and | 逻辑与 | true and true | true |
or | 逻辑或 | false or true | true |
not | 逻辑非 | not false | true |
二、真值表与运算规则
1. and 运算符
| 左操作数 | 右操作数 | 结果 |
|---|---|---|
| true | true | true |
| true | false | false |
| false | true | false |
| false | false | false |
2. or 运算符
| 左操作数 | 右操作数 | 结果 |
|---|---|---|
| true | true | true |
| true | false | true |
| false | true | true |
| false | false | false |
3. not 运算符
| 操作数 | 结果 |
|---|---|
| true | false |
| false | true |
三、短路求值特性
1. and 的短路行为
def check():
print("执行检查")
return true
print(false and check()) # 输出 false,不执行check()
2. or 的短路行为
def load_data():
print("加载数据")
return []
print(true or load_data()) # 输出 true,不执行load_data()
3. 实际应用:避免除零错误
x = 0
if x != 0 and (10 / x > 2): # 安全判断
print("条件成立")
else:
print("跳过危险计算")
四、运算符优先级
优先级顺序(从高到低)
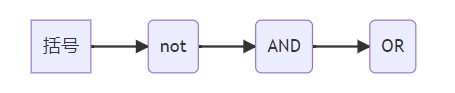
示例解析
result = not false or true and false # 等效于 (not false) or (true and false) → true or false → true
五、非布尔类型的处理
python 将以下值视为 false:
nonefalse0(各种数值类型的零)- 空序列/集合:
"",[],{},set() - 其他值视为
true
返回值规则: 通常备用来赋值,省略 if 判断
| 运算符 | 返回规则 |
|---|---|
| and | 返回第一个假值或最后一个真值 |
| or | 返回第一个真值或最后一个假值 |
| not | 始终返回布尔值 |
示例
# and
## 如果 a 为真,b 为真,输出 b
c = 1 and 2
print('c =', c) # c = 2
## 如果 a 为假,b 为假,输出 a
c = [] and 0
print('c =', c) # c = []
## 如果 a 为假,b 为真,输出 a
c = [] and 1
print('c =', c) # c = []
## 如果 a 为 真,b 为假,输出 b
c = 1 and 0
print('c =', c) # c = 0
# 总结:a 为假,输出a;a为真,输出b
# or
# 如果 a 为真,b 为真,输出 a
c = 1 or 2
print('c =', c) # c = 1
# 如果 a 为假,b 为假,输出 b
c = [] or 0
print('c =', c) # c = 0
# 如果 a 为假,b 为真,输出 b
c = [] or 1
print('c =', c) # c = 1
# 如果 a 为 真,b 为假,输出 a
c = 1 or 0
print('c =', c) # c = 1
# 总结:a 为假,输出b;a为真,输出a
结合短路逻辑理解即可
六、实际应用案例
1. 设置默认值
username = input("用户名: ") or "guest"
print(f"欢迎, {username}")
2. 条件验证链
def validate(email, password):
return "@" in email and len(password) >= 83. 链式比较
x = 5 print(0 < x < 10) # 等效于 (0 < x) and (x < 10)
七、常见错误与注意事项
1. 混淆逻辑与按位运算符
# 错误用法(应使用 and/or)
if (a > 5) & (b < 10): # 正确应使用 and
pass
2. 忽略运算符优先级
# 错误写法 if not x > 5 or y < 3: # 实际是 (not x) > 5 or y < 3 # 正确写法 if not (x > 5) or y < 3: # 或 x <= 5 or y < 3
- 副作用操作
# 危险写法(依赖短路特性修改状态)
def update():
global counter
counter += 1
return true
flag = false and update() # update() 不会执行
总结
- 使用 and/or 时注意短路特性优化性能
- 复杂表达式使用括号明确优先级
- 理解非布尔值的真假判断逻辑
- 避免在逻辑表达式中引入副作用
通过掌握这些要点,可以编写更高效、安全的 python 条件判断逻辑。
到此这篇关于python逻辑运算符详解与实际应用指南的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python逻辑运算符内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!







发表评论