代码示例:
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
import pytesseract
from pil import image
img = cv.imread('test.jpg')
rows, cols, _ = img.shape
img = cv.resize(img, (int(cols/2), int(rows/2)))
img = cv.cvtcolor(img, cv.color_bgr2gray)
nrows, ncols = img.shape
print(cols, ncols, rows, nrows)
gray_blurred = cv.gaussianblur(img, (5, 5), 0)
flag = 200
lines = []
while len(lines) != 4:
# 使用canny边缘检测
edges = cv.canny(gray_blurred, 50, 150, aperturesize=3)
lines = cv.houghlines(edges, 1, np.pi / 180, flag)
if lines is none:
lines = []
if flag < 80:
raise exception('未找到合适的边缘处理参数')
flag -= 5
print(flag)
nlines = []
# 如果找到了直线,使用它们来计算仿射变换矩阵
if lines is not none:
for rho, theta in lines[:, 0]:
a = np.cos(theta)
b = np.sin(theta)
x0 = a * rho
y0 = b * rho
x1 = int(x0 + 1000 * (-b))
y1 = int(y0 + 1000 * (a))
x2 = int(x0 - 1000 * (-b))
y2 = int(y0 - 1000 * (a))
cv.line(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 0, 255), 2)
nlines.append([(x1, y1), (x2, y2)])
points = []
for i in range(len(nlines) - 1):
for j in range(i + 1, len(nlines)):
line = nlines[i]
x1, y1 = line[0]
x2, y2 = line[1]
line1 = nlines[j]
x3, y3 = line1[0]
x4, y4 = line1[1]
try:
u = ((x4-x3)*(y1-y3) - (y4-y3)*(x1-x3)) / ((y4-y3)*(x2-x1) - (x4-x3)*(y2-y1))
except exception as e:
continue
x = x1 + u * (x2 - x1)
y = y1 + u * (y2 - y1)
if x > 0 and y > 0 and x < ncols and y < nrows:
points.append((x, y))
pytesseract.pytesseract.tesseract_cmd = r'd:\program files\tesseract-ocr\tesseract.exe'
center = (int(ncols/2), int(nrows/2))
pstmap = {}
for point in points:
x, y = point
cx, cy = center
if x < cx and y < cy:
pstmap['lt'] = point
elif x > cx and y < cy:
pstmap['rt'] = point
elif x > cx and y > cy:
pstmap['rb'] = point
else:
pstmap['lb'] = point
pst1 = np.float32([pstmap['lt'], pstmap['rt'], pstmap['rb'], pstmap['lb']])
pst2 = np.float32([[0, 0], [ncols, 0], [ncols, nrows], [0, nrows]])
m = cv.getperspectivetransform(pst1, pst2)
dst = cv.warpperspective(img, m, (ncols, nrows))
x1, y1 = 0, 0
def mouse_callback(event, x, y, flags, param):
global x1, y1
if event == cv.event_lbuttondown:
x1, y1 = x, y
elif event == cv.event_lbuttonup:
x2, y2 = x, y
wimg = dst[y1:y2, x1:x2]
_, wimg = cv.threshold(wimg, 80, 255, cv.thresh_binary)
wimg = cv.bitwise_not(wimg)
cv.imwrite('test_dst.jpg', wimg)
image = image.open('test_dst.jpg')
# 打印选定区域的坐标
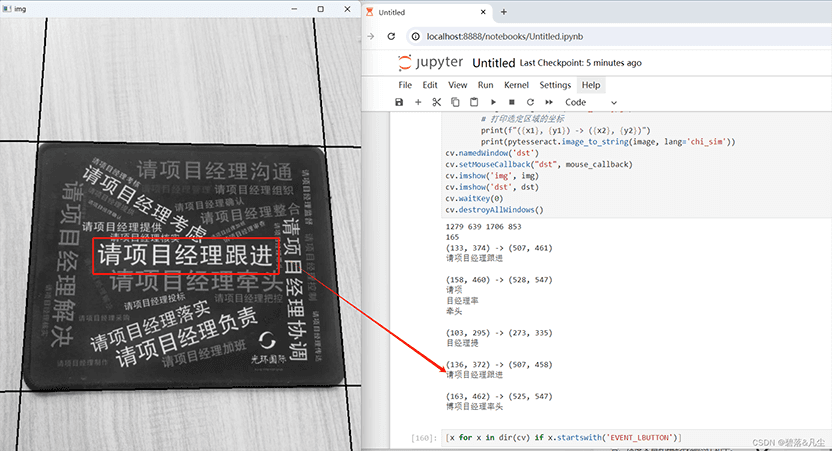
print(f"({x1}, {y1}) -> ({x2}, {y2})")
print(pytesseract.image_to_string(image, lang='chi_sim'))
cv.namedwindow('dst')
cv.setmousecallback("dst", mouse_callback)
cv.imshow('img', img)
cv.imshow('dst', dst)
print(dst[2])
cv.waitkey(0)
cv.destroyallwindows()方法:
1. 首先读取图片, 因为我手机拍摄图片尺寸太大, 所以进行了缩放
2. 对图片进行高斯模糊, 方便进行边缘处理
3. 从高到低适配不同的阈值检测图片内容边缘
4. 通过反向霍夫变换获取确定边缘直线的四个点
5. 通过直线两两相交确定四个定点
6. 进行透视变换
7. 添加鼠标事件, 监测鼠标选定区域
8. 鼠标选定区域后, 裁剪图片, 对图片进行二值化处理, 我这里做了文字黑白反转
9. 利用pytesseract对裁剪后的图片进行文字识别
注意事项:
1. 选择的文字区域会影响识别成功率, 如果文字区域紧贴文字, 可能会失败, 盲猜影响了特征提取
2. 图片尺寸大小会影响边缘检测, 不缩放图片时, 阈值调整不当的话, 很容易生成n条边缘直线, 阈值怎么选定请了解霍夫变换的原理。
识别效果(加了二值化处理的准确度会很好):
补充:几个常用的opencv二值化代码示例
1. 全局阈值二值化:
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('image.jpg', 0)
_, thresh = cv2.threshold(img, 127, 255, cv2.thresh_binary)
cv2.imshow('image', img)
cv2.imshow('threshold', thresh)
cv2.waitkey(0)
cv2.destroyallwindows()
2. 自适应阈值二值化:
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('image.jpg', 0)
thresh = cv2.adaptivethreshold(img, 255, cv2.adaptive_thresh_mean_c, cv2.thresh_binary, 11, 2)
cv2.imshow('image', img)
cv2.imshow('adaptive threshold', thresh)
cv2.waitkey(0)
cv2.destroyallwindows()
3. otsu二值化:
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('image.jpg', 0)
_, thresh = cv2.threshold(img, 0, 255, cv2.thresh_binary + cv2.thresh_otsu)
cv2.imshow('image', img)
cv2.imshow('otsu threshold', thresh)
cv2.waitkey(0)
cv2.destroyallwindows()
这些示例代码可以根据需要进行修改和调整,以适应不同的图像处理任务。
总结
到此这篇关于如何利用opencv对拍摄图片进行文字识别的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关opencv对图片文字识别内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论