两级缓存简介
一级缓存 localcache
效果
一级缓存是 session 或者说事务级别的,只在同一事务内有效,在以相同的参数执行多次同一个查询方法时,实际只会在第一次时进行数据库 select 查询,后续会直接从缓存中返回。如下:
@getmapping("/test1")
@transactional(rollbackfor = exception.class)
public string test1() {
log.info("---------------------------------------------------------------------------");
teacher teacher1 = teachermapper.selectbyprimarykey("01");
log.info("teacher1: {}, hashcode: {} \n", teacher1, system.identityhashcode(teacher1));
teacher teacher2 = teachermapper.selectbyprimarykey("01");
log.info("teacher2: {}, hashcode: {} \n", teacher2, system.identityhashcode(teacher2));
student student1 = studentmapper.selectbyprimarykey("01");
log.info("student1: {}, hashcode: {} \n", student1, system.identityhashcode(student1));
student student2 = studentmapper.selectbyprimarykey("01");
log.info("student2: {}, hashcode: {} \n", student2, system.identityhashcode(student2));
return "test1";
}
下图中是调用了两次的输出,从第一次输出中可以看出查询 teacher、student 的 sql 都只打印了一遍,说明分别只执行了一次数据库查询。且两个 teacher、student 的 hashcode 分别是一样的,说明是同一个对象。第二次调用的输出和第一次的相似,都重新执行了一次数据库查询,说明一级缓存只在同一事务内有效,不能跨事务。
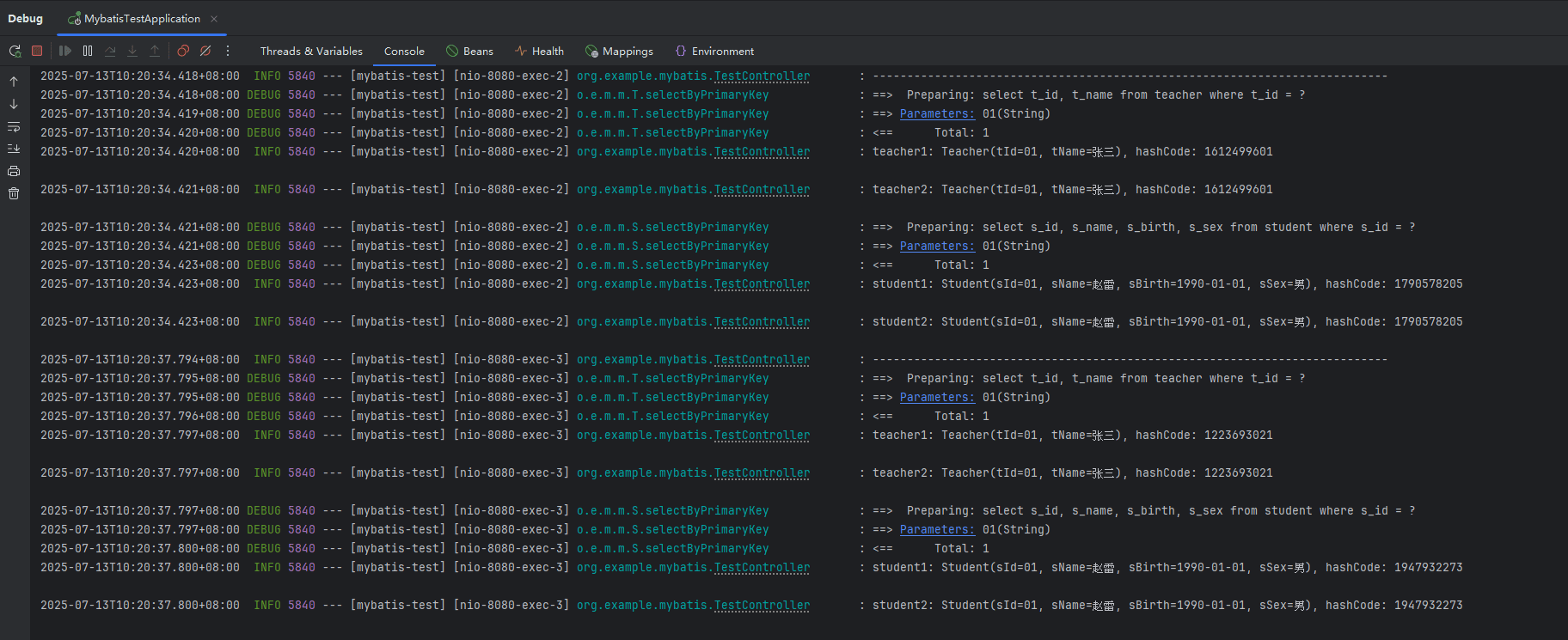
如果事务中有 dml 语句的话,会清空所有的缓存。不管 dml 语句中的表是否与缓存中的表相同,都会无条件的清空所有缓存。
@getmapping("/test2")
@transactional(rollbackfor = exception.class)
public string test2() {
log.info("---------------------------------------------------------------------------");
teacher teacher1 = teachermapper.selectbyprimarykey("01");
log.info("teacher1: {}, hashcode: {} \n", teacher1, system.identityhashcode(teacher1));
teacher teacher2 = teachermapper.selectbyprimarykey("01");
log.info("teacher2: {}, hashcode: {} \n", teacher2, system.identityhashcode(teacher2));
student student1 = studentmapper.selectbyprimarykey("01");
log.info("student1: {}, hashcode: {} \n", student1, system.identityhashcode(student1));
student student2 = studentmapper.selectbyprimarykey("01");
log.info("student2: {}, hashcode: {} \n", student2, system.identityhashcode(student2));
insertscore();
log.info("insertscore\n");
teacher teacher3 = teachermapper.selectbyprimarykey("01");
log.info("teacher3: {}, hashcode: {} \n", teacher3, system.identityhashcode(teacher3));
student student3 = studentmapper.selectbyprimarykey("01");
log.info("student3: {}, hashcode: {} \n", student3, system.identityhashcode(student3));
return "test2";
}
private void insertscore() {
score score = new score();
score.setsid("08");
score.setcid("01");
score.setsscore(100);
scoremapper.insert(score);
}
前半部分的输出与 test1 相同,当插入 score 后再次查询 teacher、student 时,打印了 sql,且与上半部分的 hashcode 不相同,说明执行 insertscore 时缓存被全部清空了。
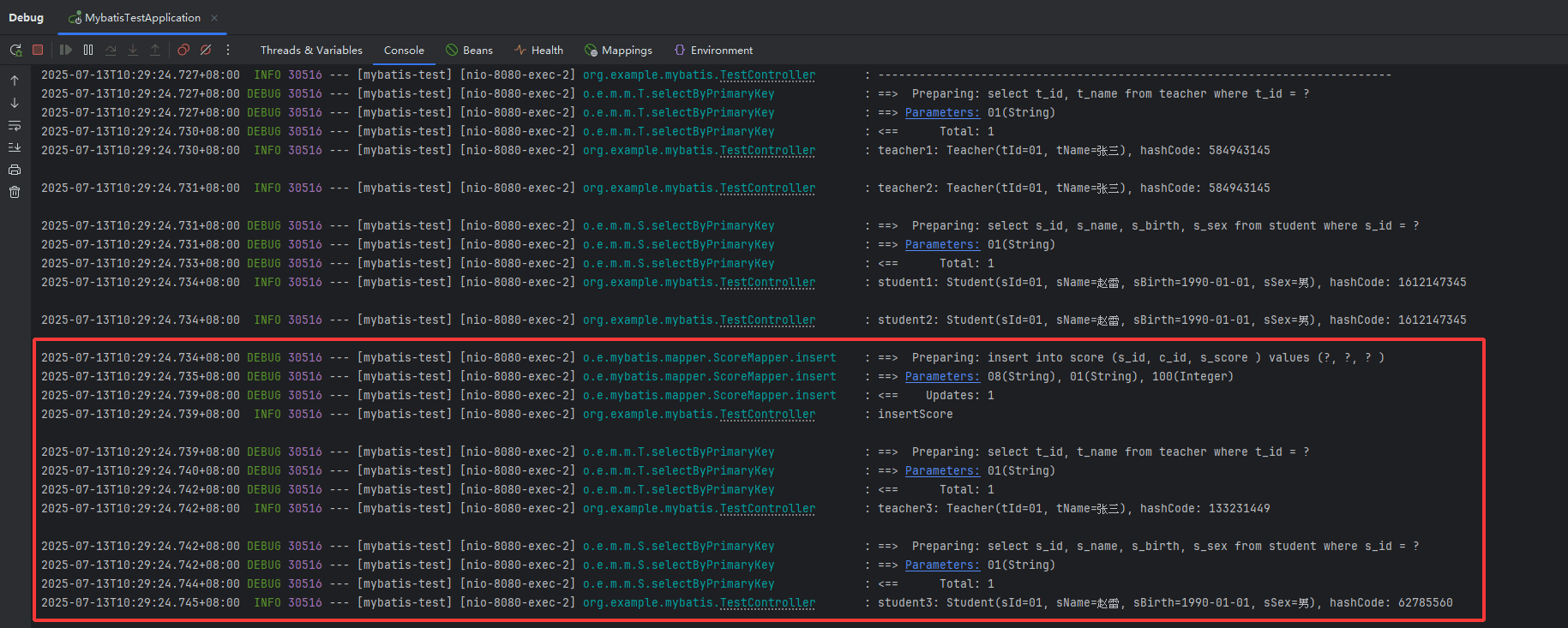
开关
一级缓存在 mybatis 源码中被称为 localcache,springboot 可使用 mybatis.configuration.local-cache-scope 来控制其行为,默认值是 session,也就是事务级别的缓存。可将其配置为 statement 以关闭 localcache 功能。
下面是将 mybatis.configuration.local-cache-scope 配置为 statement 后再执行 test1 的输出,每次都打印了 sql,且 hashcode 都不一样,说明缓存没有起作用。
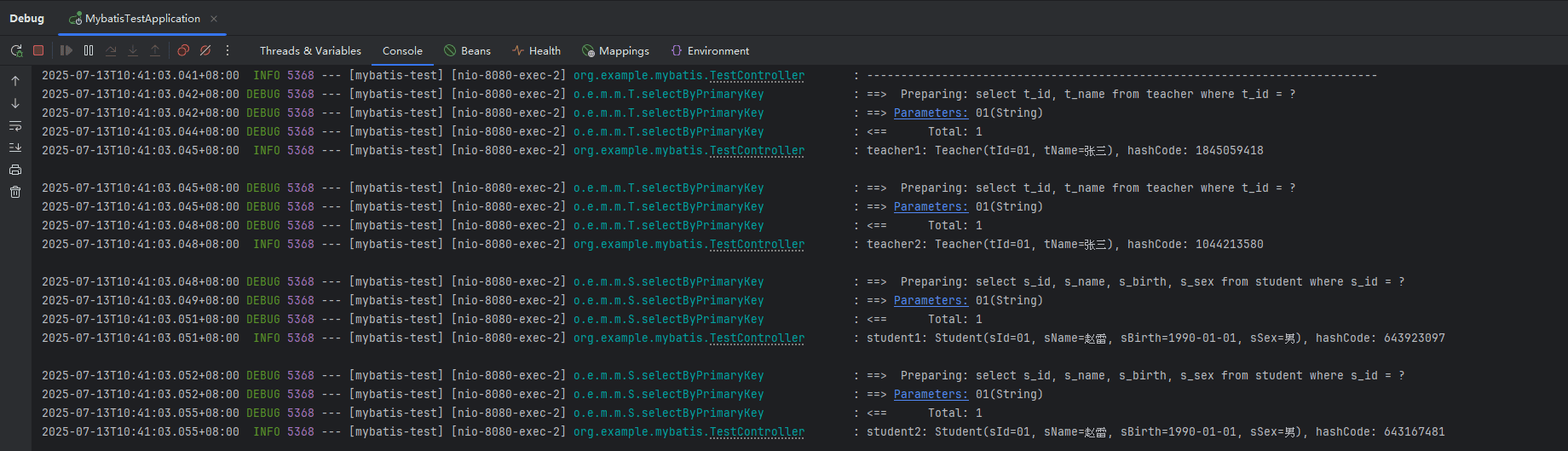
二级缓存
二级缓存是 namespace 级别的(或者说是 mapper 级别的,如下 xml),与一级缓存类似,在以相同的参数执行多次同一个查询方法时,实际只会在第一次时进行数据库 select 查询,后续会直接从缓存中返回。如果执行同一个 namespace 中的 dml 语句(比如 delete、insert、update)的话,会清空 namespace 相关的所有 select 的缓存。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!doctype mapper public "-//mybatis.org//dtd mapper 3.0//en" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="org.example.mybatis.mapper.studentmapper">
<select>
...
</select>
<delete>
...
</delete>
<insert>
...
</insert>
...
</mapper>
二级缓存由 mybatis.configuration.cache-enabled 控制,默认为 true。除此之外还需要在要开启二级缓存的 mapper.xml 中添加 <cache/> 表情才能开启对应 mapper 的二级缓存。
下面是在关闭一级缓存,且只开启 studentmapper.xml 二级缓存的情况下的测试:
application.properties
... mybatis.configuration.local-cache-scope=statement mybatis.configuration.cache-enabled=true
studentmapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!doctype mapper public "-//mybatis.org//dtd mapper 3.0//en" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="org.example.mybatis.mapper.studentmapper">
<resultmap id="baseresultmap" type="org.example.mybatis.entity.student">
<!--@mbg.generated-->
<!--@table student-->
<id column="s_id" jdbctype="varchar" property="sid" />
<result column="s_name" jdbctype="varchar" property="sname" />
<result column="s_birth" jdbctype="varchar" property="sbirth" />
<result column="s_sex" jdbctype="varchar" property="ssex" />
</resultmap>
<cache readonly="true"/>
...
</mapper>
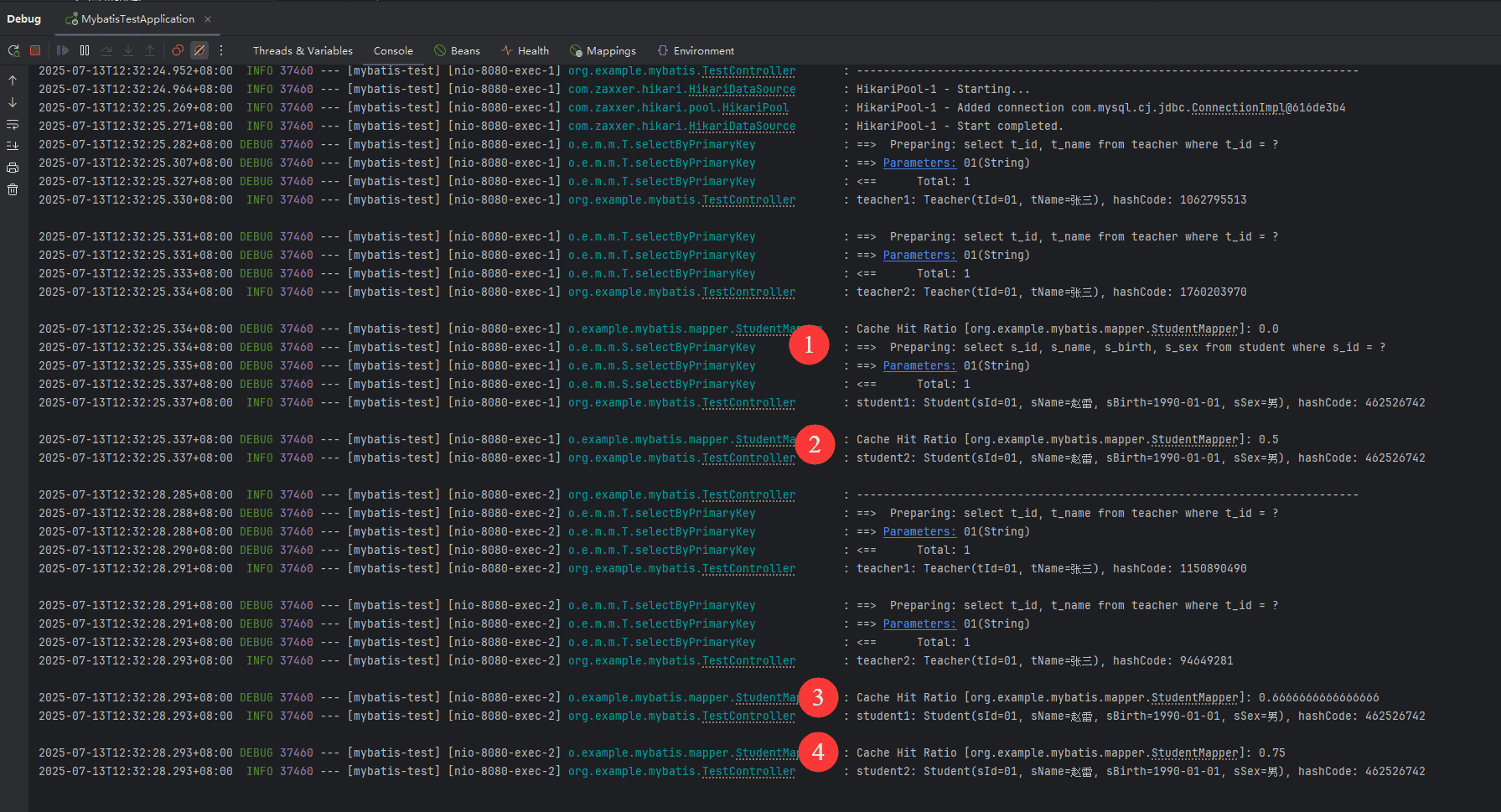
这是执行了两次 test1 的输出:
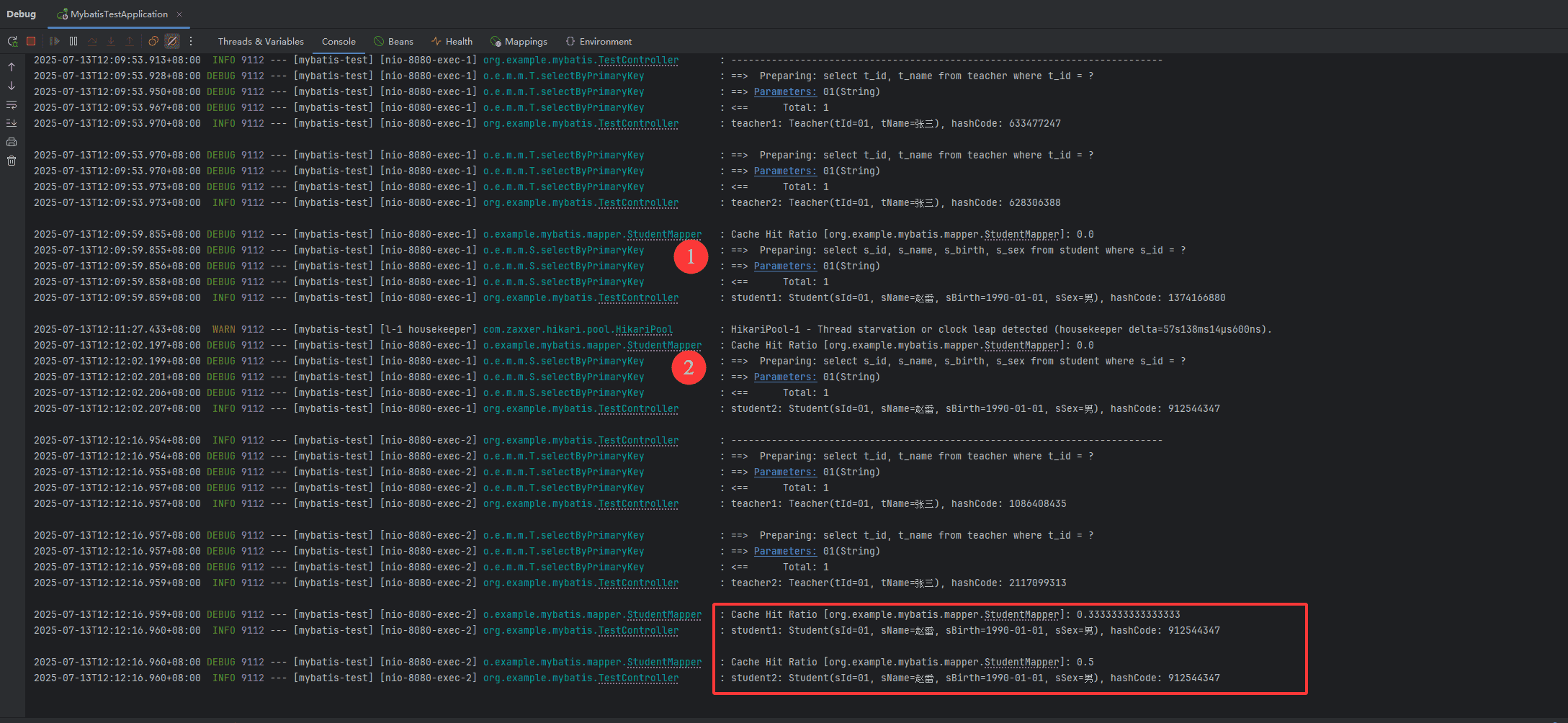
由于没有开启 teachermapper.xml 的二级缓存,所以每次查询 teacher 都打印了 sql,且 hashcode 不相同,说明 teacher 的缓存没起作用。
第 ① 次查询 student 打印了 sql,直接查询了数据库,这是正常的,因为此时缓存中没有数据。但第 ② 次查询 student 也没有走缓存,也直接查询了数据库,这是为啥?是因为二级缓存不是在执行完 select 后立即填充的,是要等到事务提交之后才会填充缓存。
从最后几行的输出能看出最后两次查询 student 确实走了缓存,并且还打印了缓存命中率。这是因为第一次调用 test1 结束后事务提交了,数据被填充到了缓存里。
测试无事务时的效果
test3 是在 test1 的基础上删除了 @transactional 注解
@getmapping("/test3")
public string test3() {
log.info("---------------------------------------------------------------------------");
teacher teacher1 = teachermapper.selectbyprimarykey("01");
log.info("teacher1: {}, hashcode: {} \n", teacher1, system.identityhashcode(teacher1));
teacher teacher2 = teachermapper.selectbyprimarykey("01");
log.info("teacher2: {}, hashcode: {} \n", teacher2, system.identityhashcode(teacher2));
student student1 = studentmapper.selectbyprimarykey("01");
log.info("student1: {}, hashcode: {} \n", student1, system.identityhashcode(student1));
student student2 = studentmapper.selectbyprimarykey("01");
log.info("student2: {}, hashcode: {} \n", student2, system.identityhashcode(student2));
return "test3";
}
teacher 的缓存还是没起作用。
只有第一次查询 student 时直接查询了数据库,其他三次都命中了缓存。
两级缓存可能导致的问题
分布式环境下查询到过期数据
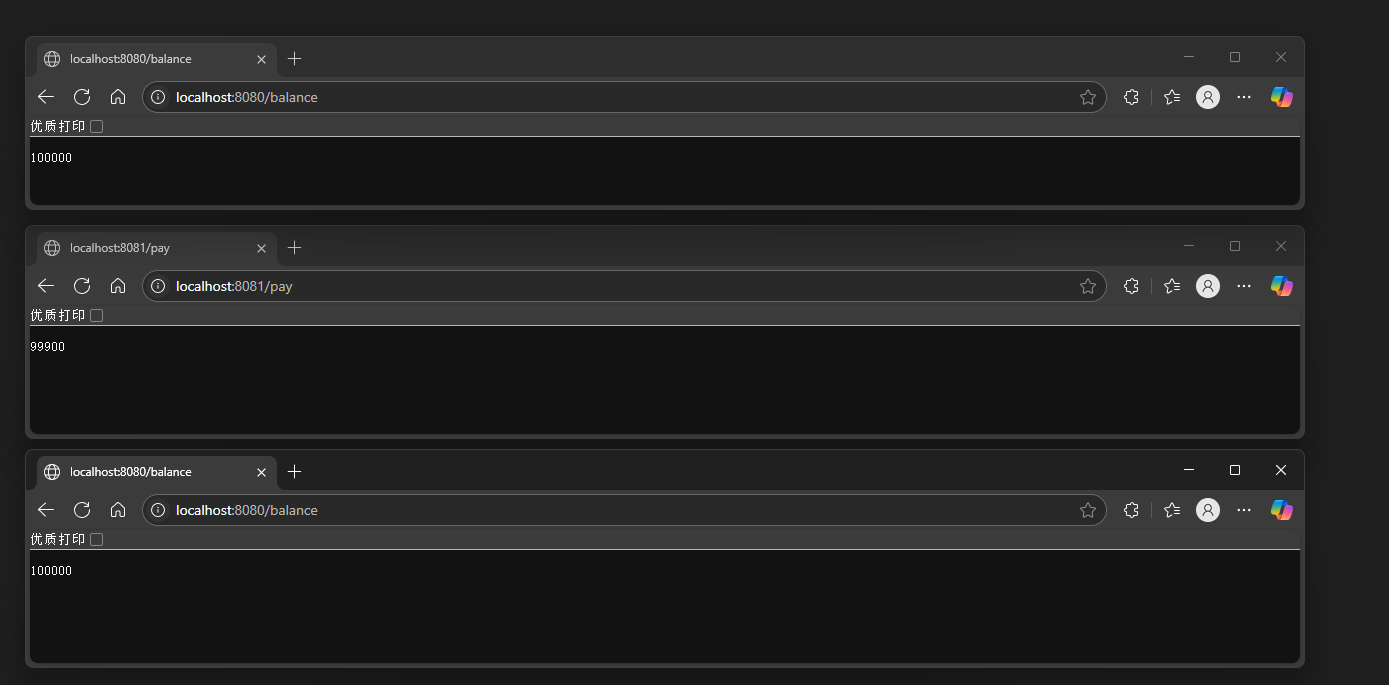
假设支付服务 a 有两个实例 a1、a2,负载均衡采用轮训策略,第一次查询余额访问 a1 返回 100000,第二次消费 100 访问 a2 返回余额 99900,第三次查询余额访问 a1 返回的还是 100000。如下的模拟
application.properties
... mybatis.configuration.local-cache-scope=statement mybatis.configuration.cache-enabled=true
accountmapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!doctype mapper public "-//mybatis.org//dtd mapper 3.0//en" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="org.example.mybatis.mapper.accountmapper">
...
<cache readonly="true"/>
<update id="pay">
update account
set balance = balance - #{amount}
where id = #{id}
</update>
</mapper>
@getmapping("/balance")
public long querybalance() {
return accountmapper.selectbyprimarykey(1).getbalance();
}
@getmapping("/pay")
public long pay() {
accountmapper.pay(1, 100);
return accountmapper.selectbyprimarykey(1).getbalance();
}
分别在 8080、8081 启动两个实例,如下输出:
要解决这个问题很简单,就是不使用缓存,比如 mybatis.configuration.cache-enabled=false 或者将 accountmapper.xml 中的 <cache/> 标签删除。
事务隔离级别失效
读已提交失效
在开发中经常有这种场景:先判断是否存在,如果不存在再插入。这种判断再插入的操作不是原子的,多线程会有问题,所以需要加锁保证操作的安全性。在读多写少的场景中,会使用 double check 来尽可能的减少用锁的使用,伪代码如下:
def doublecheck(id) {
o = select(id);
if (o == null) {
lock.lock();
try {
o = select(id);
if (o == null) {
o = create(id);
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
return o;
}
创建 account 的测试
application.properties
还原成默认值,且删除 accountmapper.xml 中的 <cache/> 标签,用以关闭 accountmapper 的二级缓存。
... mybatis.configuration.local-cache-scope=session mybatis.configuration.cache-enabled=true
注意这里使用的隔离级别为读已提交
@putmapping("/accounts/{id}")
// double check 需要使用读已提交隔离级别才能读到最新数据
@transactional(rollbackfor = exception.class, isolation = isolation.read_committed)
public account createaccount(@pathvariable("id") integer id) throws interruptedexception {
account account = accountmapper.selectbyprimarykey(id);
// 等待多个请求到达
timeunit.seconds.sleep(5);
// 如果账户不存在,需要加分布式锁后进行 double check,防止并发问题
if (account == null) {
rlock lock = redissonclient.getlock("lock:account:create:" + id);
boolean locked = lock.trylock(10, timeunit.seconds);
if (locked) {
try {
account = accountmapper.selectbyprimarykey(id);
if (account == null) {
// 创建账户
account = createaccount0(id);
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
return account;
}
public account createaccount0(integer id) {
account account = new account();
account.setid(id);
account.setbalance(0l);
accountmapper.insertselective(account);
// 操作其他表
return account;
}
同时发起两个 put 请求 http://localhost:8080/accounts/2。一个正常返回,另一个在 insert 时报错 duplicate entry ‘2’ for key ‘account.primary’,说明读已提交的隔离级别没起作用,第二个请求没有读到最新的数据。
一级缓存实际起到了类似可重复读的效果。
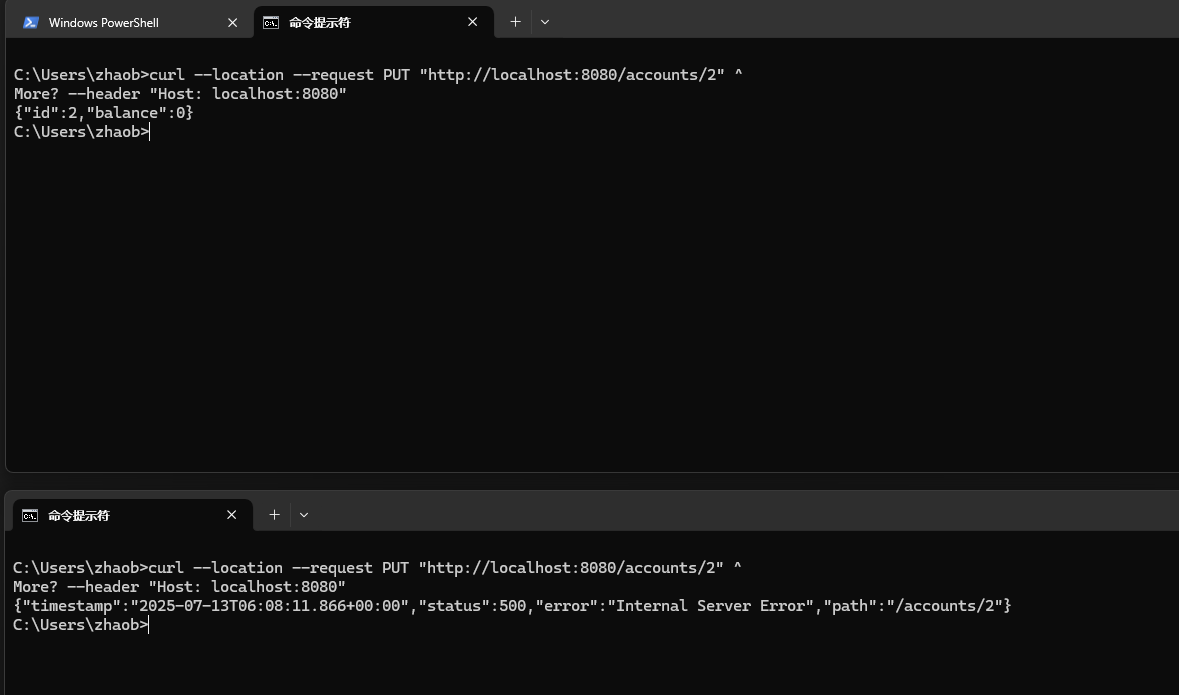
两个请求(线程分别为 nio-8080-exec-3、nio-8080-exec-4)执行了 3 次(第一个请求 1 次,第二个请求 2 次) accountmapper.selectbyprimarykey(id),但每个线程都只打印了 1 次 sql,说明第二个请求的第 2 次查询走了缓存,导致没有查询到第一个请求插入的最新数据,才导致的后来的报错。

解决办法
最简单办法就是修改
mybatis.configuration.local-cache-scope=statement,直接关闭一级缓存。直接去掉@transactional注解肯定能解决问题,但如果createaccount0方法中操作多张表的话,如果部分失败事务将无法回滚。不能直接去掉
@transactional注解,但可以缩小事务的范围,将两次查询放到事务外,只将createaccount0方法放到事务内。@lazy @autowired private testcontroller self; @putmapping("/accounts/{id}") public account createaccount(@pathvariable("id") integer id) throws interruptedexception { account account = accountmapper.selectbyprimarykey(id); // 等待多个请求到达 timeunit.seconds.sleep(5); // 如果账户不存在,需要加分布式锁后进行 double check,防止并发问题 if (account == null) { rlock lock = redissonclient.getlock("lock:account:create:" + id); boolean locked = lock.trylock(10, timeunit.seconds); if (locked) { try { account = accountmapper.selectbyprimarykey(id); if (account == null) { // 创建账户 account = self.createaccount0(id); } } finally { lock.unlock(); } } } return account; } @transactional(rollbackfor = exception.class) public account createaccount0(integer id) { account account = new account(); account.setid(id); account.setbalance(0l); accountmapper.insertselective(account); // 操作其他表 return account; }如果外层有其他事务的话,由于一级缓存只有在同一个事务中才会生效,所以可以将两个
accountmapper.selectbyprimarykey(id)拆分到不同的事务中,propagation必须是propagation.requires_new。@lazy @autowired private testcontroller self; @putmapping("/accounts/{id}") public account createaccount(@pathvariable("id") integer id) throws interruptedexception { account account = self.getaccount0(id); // 等待多个请求到达 timeunit.seconds.sleep(5); // 如果账户不存在,需要加分布式锁后进行 double check,防止并发问题 if (account == null) { rlock lock = redissonclient.getlock("lock:account:create:" + id); boolean locked = lock.trylock(10, timeunit.seconds); if (locked) { try { account = self.getaccount0(id); if (account == null) { // 创建账户 // account = self.createaccount0(id); } } finally { lock.unlock(); } } } return account; } // 读已提交 requires_new @transactional(rollbackfor = exception.class, isolation = isolation.read_committed, propagation = propagation.requires_new) public account getaccount0(integer id) { return accountmapper.selectbyprimarykey(id); }
读未提交失效
同样的由于一级缓存的存在,读未提交也读不到最新的未提交数据。
读未提交 查询 account 的测试
application.properties
还原成默认值,且删除 accountmapper.xml 中的 <cache/> 标签,用以关闭 accountmapper 的二级缓存。
... mybatis.configuration.local-cache-scope=session mybatis.configuration.cache-enabled=true
@getmapping("/accounts/{id}")
// 读未提交
@transactional(rollbackfor = exception.class, isolation = isolation.read_uncommitted)
public account getaccount(@pathvariable("id") integer id) throws interruptedexception {
account account = accountmapper.selectbyprimarykey(id);
log.info("account1: {}\n", account);
// 若不存在,则等待几秒再查
if (account == null) {
timeunit.seconds.sleep(10);
}
account = accountmapper.selectbyprimarykey(id);
log.info("account2: {}\n", account);
return account;
}
@putmapping("/accounts/{id}")
@transactional(rollbackfor = exception.class)
public account createaccount(@pathvariable("id") integer id) throws interruptedexception {
account account = new account();
account.setid(id);
account.setbalance(0l);
accountmapper.insertselective(account);
log.info("insert account: {}\n", account);
// 延迟提交事务
timeunit.seconds.sleep(15);
// 操作其他表
return account;
}
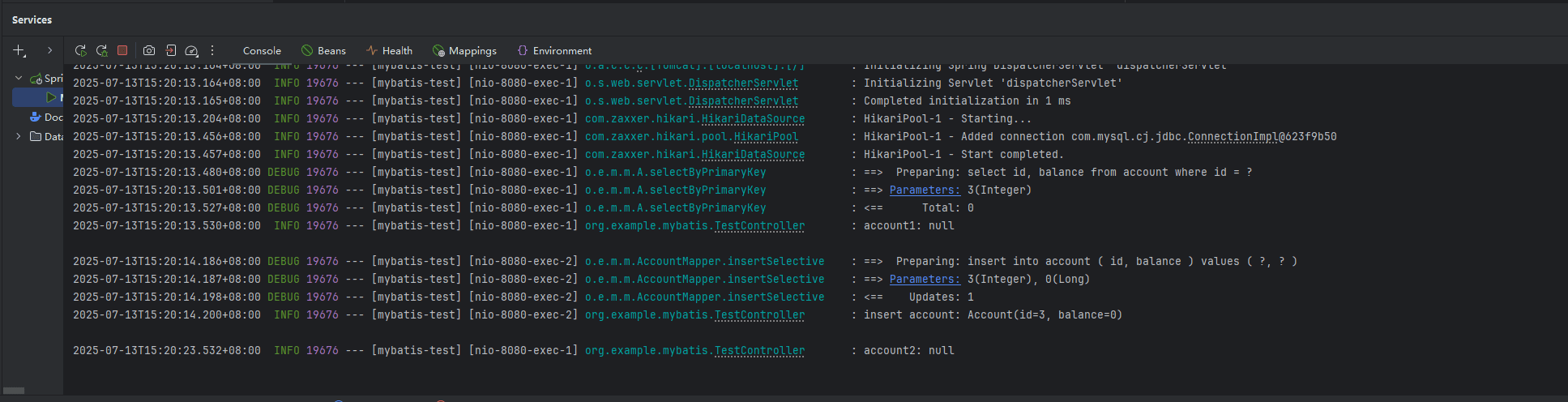
先请求 getaccount 再请求 createaccount,从输出中可以看出,在使用读未提交的情况下,account2 依旧为 null,走了缓存,导致读未提交失效。
解决办法
最简单办法就是修改
mybatis.configuration.local-cache-scope=statement,直接关闭一级缓存。由于一级缓存只有在同一个事务中才会生效,所以可以将两个
accountmapper.selectbyprimarykey(id)拆分到不同的事务中,propagation必须是propagation.requires_new。@lazy @autowired private testcontroller self; @getmapping("/accounts/{id}") public account getaccount(@pathvariable("id") integer id) throws interruptedexception { account account = self.getaccount0(id); log.info("account1: {}\n", account); // 若不存在,则等待几秒再查 if (account == null) { timeunit.seconds.sleep(10); } account = self.getaccount0(id); log.info("account2: {}\n", account); return account; } // 读未提交 requires_new @transactional(rollbackfor = exception.class, isolation = isolation.read_uncommitted, propagation = propagation.requires_new) public account getaccount0(integer id) { return accountmapper.selectbyprimarykey(id); }
总结
一级缓存是事务级别的,实际起到了类似可重复读的效果,而且比可重复读的性能更好,因为多次查询的话不会请求数据库了。在事务隔离级别是可重复读时使用一级缓存能提高性能。但就因为其类似可重复读的效果会导致其他的隔离级别失效。要解决失效的问题,最简单方式就是关闭一级缓存,但这样会损失性能。另一个解决办法是将需要使用其他隔离级别的方法使用 propagation = propagation.requires_new 拆分到新的事务中。如果是读已提交的话可通过缩小事务范围的方式解决。
一级缓存是事务级别的,缓存的生命周期较短,但二级缓存是 namespace (mapper)级别的,生命周期可能很长,在分布式、多实例环境中很容易查询到过期的数据,导致其他问题。我个人建议在分布式、多实例环境中应该设置 mybatis.configuration.cache-enabled=false 来关闭二级缓存,从根源上杜绝这种问题。
到此这篇关于mybatis两级缓存可能导致问题的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关mybatis两级缓存问题内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!




